
A FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATING DIFFICULTIES
IN ERP IMPLEMENTATION
Luis I. Ferrario
Facultad Regional Santa Fe, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina
Red Megatone, Information System Department, Av.Santa Fe 252, (2300) Rafaela, Argentina
Jorge M. Montagna
Facultad Regional Santa Fe, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina
INGAR, Instituto de Desarrollo y Diseño, Avellane
da 3657, (3000) Santa Fe, Argentina
Keywords: Enterprise Resource Planning; ERP implementation; ERP pro
ject
Abstract: Various sources point out very high percentages of failures to implement ERP systems. In this work, the
main difficulties for this task are analyzed and a systematic classification of fundamental reasons is
intended. By considering the reasons that lead to failure, a simple and effective mechanism is generated to
evaluate in advance complications the project might present. In this way, the tools to be used can be
adjusted to the specific characteristics of the project. Somehow, it is intended to solve the problem presented
by general methodologies, which are used for any kind of enterprise, without previously considering its
conditions and state to face this type of projects.
1 INTRODUCTION
ERP systems support most key processes of an
organization by using a common data base that
stores all the organization’s data (Abdinnour-Helm
et al., 2003). These packages expanded rapidly due
to their advantages over the rest of the legacy
systems: high integration level, operation on the
organization’s business processes, reduction of
operative costs, etc. All these advantages are not
easy to achieve. Implementing an ERP is extremely
complex and implies a great challenge for the
enterprise (Davenport, 1998).
This has led to important failure rates in
im
pl
ementations. One source of problems resides in
the difference of interests between customer
organizations who search for a unique business
solution and ERP sellers who prefer a generic
solution to be adjusted to a wide market (Hong and
Kim, 2002). In their efforts to have “their business
solution”, enterprises invest a lot of money in
customizing ERPs, which then brings about many
problems in the system updating.
This work presents a systematic classification of
so
urces
of failures to identify their origins and to
foresee solutions to overcome them. A framework is
generated to allow for a priori evaluating the main
difficulties of the project so as to focus resources
towards the appropriate direction. In general terms,
implementation methodologies tend to be general
and do not previously take into account the
difficulties they will have to face. In this case, the
complexity of the project is intended to be estimated.
2 ERP IMPLEMENTATION
In the last years, many enterprises acquired ERPs to
replace their legacy systems, attaining better
integration of their functional areas. Unlike legacy
systems, ERPs are not made to meet the
organization’s requirements but they have to be
parameterized according to the business processes of
the organization. It is not an easy task since it brings
about a great change in the organization. There are
various methodologies to implement an ERP, many
460
I. Ferrario L. and M. Montagna J. (2004).
A FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATING DIFFICULTIES IN ERP IMPLEMENTATION.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 460-465
DOI: 10.5220/0002612504600465
Copyright
c
SciTePress

of which are developed by suppliers themselves (Al-
Mashari and Zairi, 2000; Rebstock and Hildebrand,
1999; Bancroft et al., 1997). They include technical,
operative, and organizational issues.
Making the ERP system operative poses a series
of important challenges for the enterprise. In many
cases, the definition that considers when the system
is implemented is an issue to be discussed
(Gottschalk, 1999). It is also a discussion topic when
all the value the ERP system can provide for the
enterprise was reached (Davenport, 1998).
3 SOURCES OF FAILURES
We can evaluate the different sources of failures by
studying the factors that make an implementation
successful. These factors can be divided into three
big groups: human/organizational, economic and
technical factors. Within these three groups, there
are various elements that allow for identifying
possible sources of failures. This section is intended
to make a systematic classification of those elements
that are considered as source of failures in the ERP
implementation taking into account previous works
in this area (Gefen, 2002; Bajaj and Nidumolu,
1998; Hong and Kim, 2002; Jianga and Kleinb,
1999; Kuruppuarachichi et al., 2002; Krumbholz and
Maiden, 2001; Mabert et al., 2003a, 2003b; Somers
and Nelson, 2003; Mandal and Gunasekaran, 2003;
Westerveld, 2003; Soffer, 2003; Stensrud, 2001).
The following classification has been obtained:
Human/Organizational factors: They become
more important when the level of change of the
business processes is more significant. They include:
• Leadership: It arises from the sponsor group of
the project. It selects and directs functional leaders,
supports them in decision-making and provides them
capacity for deciding on the main implementation
aspects. Lack of leadership inevitably leads to
failure (Sarker and Lee, 2003).
• Communication: Everyone in the enterprise
must be informed of changes that have been already
made or are to be introduced. Communication must
be open and honest in order to minimize employees’
resistance against change.
• Organizational culture: Implementing an ERP
system implies a change in the organization’s
business processes that can be radical in most cases.
It is convenient to have a culture that enables this
kind of changes. The employees’ attitude towards a
change of this kind is vital for a project of these
characteristics to be successful.
• Implementation team: It must be balanced; i.e.
it should include people from every area of the
enterprise and it should be 100% committed to the
project.
• Organizational adjustment: The way in which
an ERP system is adjusted to the organization’s
processes is crucial and it is an important criterion to
select an ERP (Lozinsky, 1998). Suppliers strongly
recommend implementing the system following the
processes contained in the ERP, “the best practices”,
because they have been extracted from successful
examples, and reducing customization. On the other
hand, there are organizations whose business
processes cannot be adjusted to the ERP procedures.
Mainly, strategic information systems are difficult to
customize since they correspond to distinct practices
from which the enterprise gets competitive
advantages. When implementing an ERP system, its
adjustment degree to the organization must be well
defined because otherwise implementation could be
too long and expensive and could not meet the
company’s requirements.
• Company size: Organizations have different
reasons for implementing an ERP, depending on
their size. Big organizations are motivated by
strategic needs, and the smallest ones are motivated
by operative considerations. The number of
implemented modules, plans, and the expected
results are different. Big companies report great
benefits in the financial area, whereas small ones
report them in manufacture and logistics.
• Lack of experience to work on this kind of
projects: The required effort is quite big and usually
there is no experience of working with similar
previous projects. There are great risks for the
project to be out of budget and time. A careful
administration of all resources is required.
• Lack of a methodology: Most suppliers of
ERP systems have their own general implementation
methodology, which is not always compatible with
the organization it will be applied to. Many times,
people in charge of this task try to make the
organization adjust itself to the methodology
requirements, without knowing if they are the most
convenient ones according to the company’s culture.
• Satisfaction and use of the system by users: A
great effort for implementation is useless if the final
user is not satisfied by the system and does not want
to use it. It is essential to early integrate users so that
they can become involved in the project and to take
their requirements into account (Gelderman, 1998).
• Understanding of the organization strategic
objectives: To attain a successful implementation, a
clear definition of the project objectives is required.
Key managers must determine the foundations over
that the business processes have to operate to satisfy
users, company goals, employees’ needs, etc.
A FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATING DIFFICULTIES IN ERP IMPLEMENTATION
461

Economic Factors: If the needed funds are not
available, it is impossible and unfeasible for a
project to be continued. Some factors are:
• Economic plan: It is important to control costs
coming from different sources, mainly licences,
technical resources, and human resources. The last
one is the most significant one and includes
consulting, the firm staff expenses, incorporation of
specialized technical staff, etc.
• Budget adjustment: If the organization does
not respect the settled budget for the project, it will
inevitably fail. It should be taken into account that in
this kind of projects there are hidden costs that
should be considered, for example customization.
Technical Factors: the organization’s technical
capacity for implementing this type of systems must
be considered. The most important factors to be
taken into account are:
• Customization and software testing: Highly
trained staff is required to keep the ERP system
operating in future updatings. An adequate testing is
important to avoid errors at further stages.
• Staff with technical knowledge: It is necessary
to count on people that have an adequate technical
profile to manage the technological change,
minimize the impact this might cause, and reduce
implementation time.
• IT resources: The bigger the amount of
technology to be incorporated, the more expensive
and complicated the project. This technology must
be ready and available before the project starts.
4 FRAMEWORK TO ANALYZE AN
ERP IMPLEMENTATION
Frameworks are useful because they allow us to
organize and integrate the elements of a problem in a
simple and consistent way, assuring the attainment
of the pursued outcomes. In addition, they allow
holding a common work discipline. The benefits of
counting on this kind of tools exceed the reached
objectives. The framework development process and
the associated discussion among participants provide
fundamental contribution to the project (Boyer et al.,
2002; Heeks, 2003; etc.).
Before starting a project, it is convenient to bear
in mind which are the main difficulties to be
overcome and their effect over the project. For this
purpose, a framework is presented that allows
estimating the degree of difficulty and failure
probability so as to prepare suitable measures to
overcome problems. It should be taken into account
that not all projects are alike, neither should the
same methodologies be used. The tools to be used
must be adjusted to each project’s needs.
This framework is based on two states: “Where
we are now” that measures the organization’s
current reality, and “Where we want to arrive” that
estimates the desired situation when the project
ends. Failure probability or project difficulty can be
estimated through the gap existing between both
states. The greater the gap, the greater the
implementation project difficulty. It is intended to
see the enterprise’s position to face the project.
For the case of a small gap, the framework
would indicate that it is probable for the project to
be successfully finished. It also indicates that the
change level is low, which leads to questions such
as: In the face of a low level of change, is it worthy
to undertake an ERP project? Do legacy systems
with some modifications satisfy our expectancies?
Do the project objectives adequately take advantage
of ERP system capacities?
By using the previously considered factors, we
assume that an ERP implementation can be analyzed
through seven key dimensions, which we consider
necessary and enough to analyze the existing gap
between the current situation and the designed one:
• Information: It considers the information the
enterprise counts on for making decisions related to
the project.
• Technology: A very expensive technology is
needed. This dimension can be expanded to consider
hardware, data base, connectivity, etc.
• Business Processes: It deals with a quite wide
dimension. It is intended to measure the existing
distance between current and redesigned processes
to be used in the company.
• Organizational Culture: It is necessary to
count on an adequate culture, i.e. the right people
having a good predisposition to changes and creative
and optimistic personality. It also considers inner
resistance. Communication policy, previous projects
in the company, etc. must be taken into account.
• Adjustment to the ERP: Correspondence
between the organization’s redesigned business
processes with the best practices incorporated into
the ERP system must be considered. The greater the
adjustment, the easier and more economical the
implementation.
• Employees’ Skills: Training of the people
involved in the project is analyzed. It requires people
having experience in similar projects so as to make
implementation faster.
• Work with Methodologies: We analyze if the
organization is used to working with methodologies,
and if some kind of similar experience has been
developed.
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
462
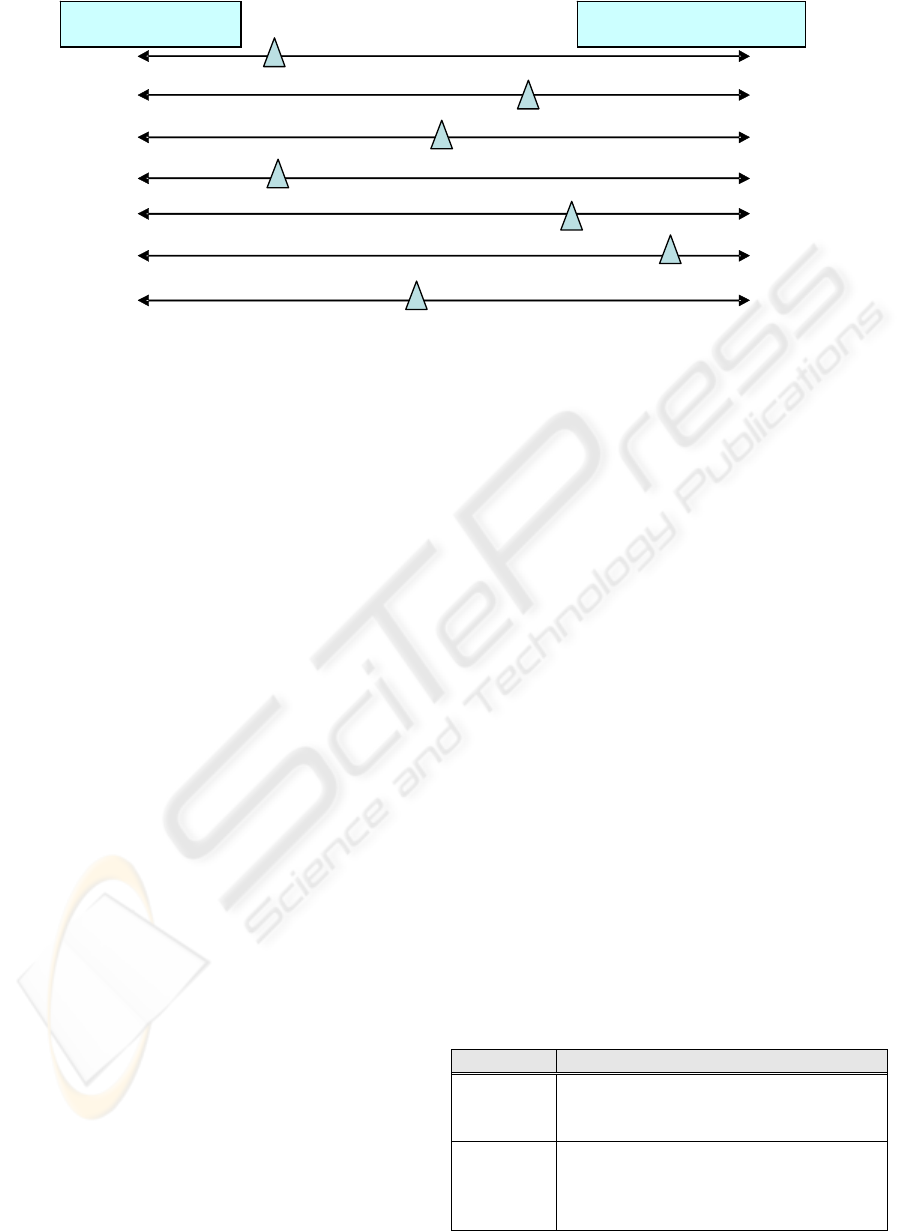
Figure 1 presents a model for evaluating an
organization as regards the specified dimensions. In
each dimension, triangles slide horizontally from
“Where we are now” to “What we want to arrive”,
determining the organization’s position to face the
project and defining the dimension’s rating. For
example, if the triangle is near “What we want to
arrive”, it means that in that dimension the
organization is near the pursued goals (the required
level of change is low). On the other hand, if the
triangle is nearer “Where we are now”, it means that
great reforms are needed in that dimension so as to
carry out the project. Particular dimensions can be
added, depending on the kind of organization.
If the gaps between reality and planning could be
reduced, we could also reduce the risk of failing in
the implementation. Anyway, it is not generally
possible to reduce these gaps since they correspond
to conditions related to the enterprise and to the
project. These gaps allow for predicting or
estimating the difficulties to be faced. In this way, it
is easier to determine and use the appropriate
resources and to foresee the project length.
5 METHODOLOGY
We present the general steps to follow for using the
presented framework.
5.1 Evaluation of gaps
For each dimension, an analysis is made to evaluate
the existing gap between the current situation of the
organization and the desired situation expected after
implementing the ERP system. Numerical values are
assigned to consider distance between both
situations. For this purpose, a 0 to 100 scale has
been taken for each dimension. For the purpose of
guidance, we provide meanings for some values, but
any value can be assigned in this range:
• 0 Value: It indicates that there is no difference
between the current and the redesigned situation.
• 50 Value: It indicates that there is a degree of
mean difference between the current and the
redesigned situation.
• 100 Value: It indicates that the current
situation is completely different from the solution
proposed with the ERP system.
A particular dimension can be divided in several
subdimensions with a weight according to their
relative importance in the main dimension. For
example, we can take Technology dimension and
subdivide it into four elements: Data Base,
Operative System, Hardware and Connectivity.
Once all proposed dimensions have been
assigned, a global indicator, or general gap, is
generated, which estimates the degree of success the
ERP implementation project may have. It is obtained
from the sum of the gaps of the proposed dimensions
in the model. Here weights for each dimension can
be considered.
The table shows how to interpret simply results
obtained for the General Gap:
General Gap Interpretation
501-700 The project is highly risky and many
precautions must be taken before starting in
order to do so successfully.
301-500 The project has a considerable risk if the
appropriate measures are not taken.
Precautions should be taken on the most
affected dimensions.
Figure 1: Model for Evaluating the Project Gap.
Information
Technology
Business Processes
Organizational culture
Adjustment to the ERP
Emplo
y
ees’ Skills
Work with methodolo
g
ies
Where we are now
Where we want to arrive
A FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATING DIFFICULTIES IN ERP IMPLEMENTATION
463
101-300 The project does not have too many risks.
There might be problems if we do not work
on dimensions with significant gaps.
0-100 The project will surely be successful,
without significant risks. Te settled goals
must be analyzed since the change and the
impact on the business are low and thus the
ERP acquisition might not be justified.
5.2 Analysis of the general gap in
relation to available resources
Available resources cannot be analyzed in the same
way that previous dimensions but the general gap
must be related to three key resources (Budget,
Availability of Human Resources, Time Assigned to
the Project) to determine the probability of the
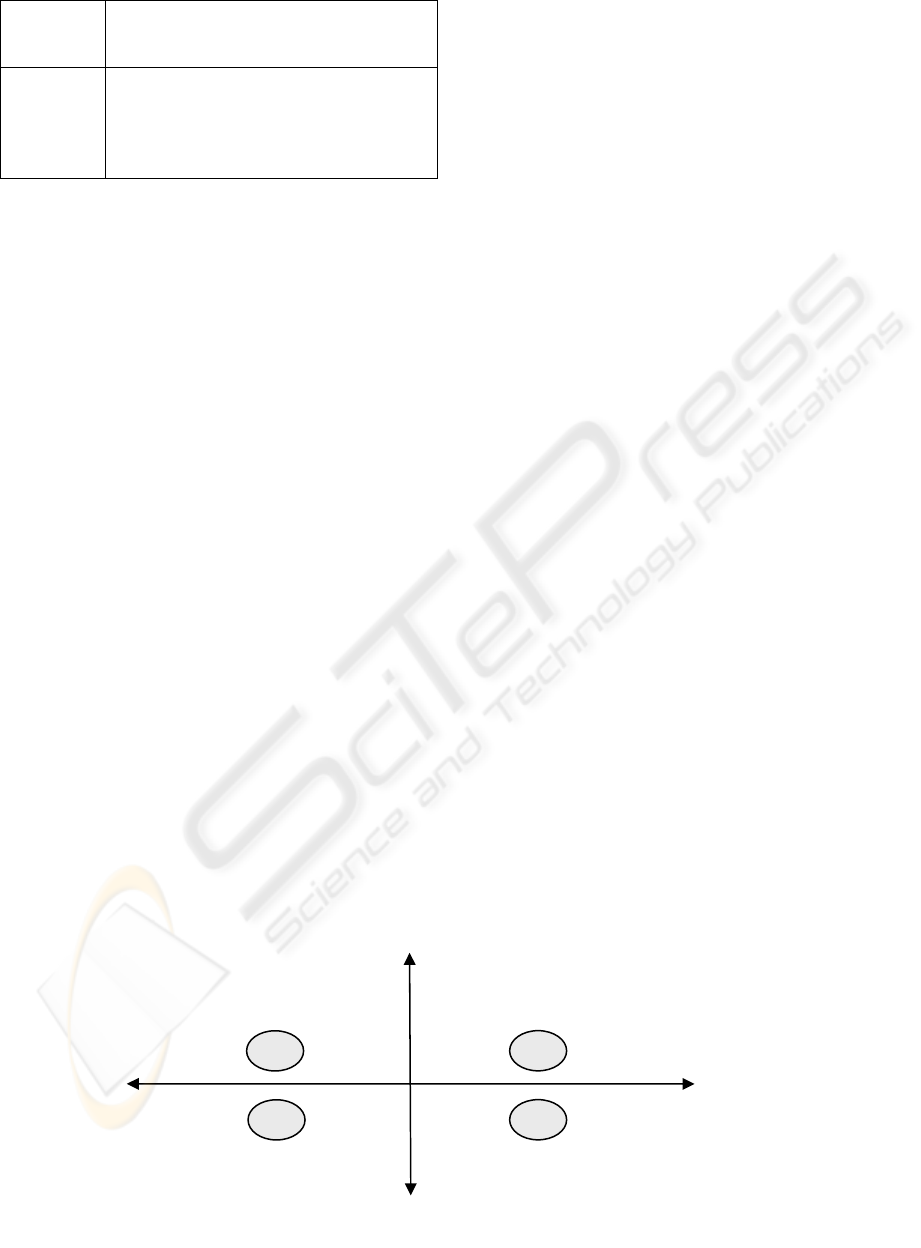
project success. Figure 2 shows four quadrants to
indicate possible locations of the organization
relating both elements, whose meanings are:
• Quadrant I: It encompasses organizations with
a low general gap that do not count on enough
resources to undertake the project. The organization
is not in optimal conditions to start implementation
but with some adjustments it can go further towards
a successful project.
• Quadrant II: The general gap is high and the
organization does not count on the resources needed
to face implementation. There are great probabilities
of failure. The effort to be made in order to achieve
a successful project is very significant and risky.
• Quadrant III: Organizations with greater
possibilities of success. They have a low general gap
and count on enough resources assigned to the
project. Taking into account the value of the general
gap, available resources should be assigned to
analyze the project goals so as to know if it is really
necessary to implement an ERP system since the
level of change is too low, or if the project
objectives have not been well planned according to
the ERP potentialities.
• Quadrant IV: Organizations that have
resources for the project but as the general gap is
high, there are many difficulties for the project. A
great effort is required. However, having available
resources may constitute an incentive to try to
overcome the existing problems and constraints
using a suitable methodology.
Appropriate scales should be defined over each
axis. The previous analysis has been made taking all
resources into consideration simultaneously. It can
be very useful to unfold the graph in Figure 2 for
each separated resource in the y-axis. Also, the
different levels of the resources and the general gap
must be considered in a detailed analysis.
5.3 Determining actions to be taken
In most cases, the studied organizations will be
located over 100 points, for which actions should be
taken so as to minimize project risks. One option is
to try to reduce gaps. In many cases this is not
feasible, because it attacks project quality and leads
to less ambitious goals. In some cases a revision of
the gaps of certain dimensions may be necessary.
For example, in Technology we can consider
questions such as: Is it necessary to buy a new data
base? In Business Processes, we can analyze
whether the redesign proposal has been too
ambitious. Therefore, in many cases the first step
consists of iterating over previous stages and
evaluating other alternatives.
The most important action is to adjust the
implementation project steps according to the
obtained results; i.e., we must set a period of
realistic time for the project, define stages, and make
a good distribution of resources. This implies
considering each of the standard stages in the
methodology and revises them according to the
available elements. In many cases, this forces the
project to have longer stages with a greater level of
detail and more sophisticated tools so as to assure
the project’s success.
Budge
Availability of human resources
Time assigned to the project
Low
Hig
h
High
Low
General Ga
p
I
I
I
I
V
I
II
Figure 2: Analysis Model (General Gap of Project vs Resources)
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
464

6 CONCLUSIONS
ERP implementation presents a low rate of success.
Usually suppliers and firms that implement them
count on general methodologies for this task. One
source of the aforementioned problems may arise
from the fact that methodologies are general and
cannot be adjusted to the project’s elements.
This adjustment between methodology and the
project must be done a priori, before starting. Going
back in the project execution, reassigning resources,
etc. are mechanisms that probably lead to failure if
they are applied during the project development.
Therefore, before starting to work, the main
problems to be solved should be clearly identified.
We present a framework that allows estimating
the difficulties of an ERP implementation project. A
series of dimensions is analyzed that are considered
as basic for the success of this kind of projects and
have been derived from a bibliographic review of
works on this area and from the authors’ personal
experiences. By analyzing the difference between
the enterprise’s current situation and the one planned
with the ERP, the difficulties in the implementation
can be estimated. Then, the values obtained for this
gap are matched to the available resources to
undertake the project.
Regardless of the obtained results, the need of
carrying out the posed steps, evaluating the
elements, and revising relationships between
detected gaps and available resources allows those
groups that face such problems to exactly measure
the constraints they will have to overcome.
REFERENCES
Al-Mashari M. and M. Zairi, 2000, The effective
application of SAP R/3: A proposed model of best
practice, Logistics Informat. Manag. 13, p. 156-166.
Abdinnour-Helm S. et al., 2003, Pre-implementation
attitudes and organizational readiness for
implementing an enterprise resource planning system,
European Journal of Operational Research 146, p.
258-273.
Bajaj A. and S. Nidumolu, 1998, A feedback model to
understand information system usage, Information &
Management 33, p. 213-224.
Bancroft N., H. Seip and A. Sprengel, 1997, Implementing
SAP R/3; Manning Publications Co.
Boyer K. et al., 2002, E-services: Operating strategy-A
case study and a method for analyzing operational
benefits, Journal of Operat. Managem. 20, p. 175-188.
Davenport T., 1998, Putting the Enterprise into the
Enterprise System, Harvard Bus. Rev. 16 (4), 121-131.
Gefen D., 2002, Nurturing client’s to encourage
engagement success during the customization of the
ERP system, Omega 30, p. 287-299.
Gelderman M., 1998, The relation between user
satisfaction, usage of information systems and
performance, Informat. & Management 34, p. 11-18.
Gottschalk P., 1999, Implementation predictors of
strategic information systems plans, Information &
Management 36, p. 77-91.
Heeks R., 2003, Most eGovernment-for-development
projects fail: how can risks be reduced?, iGovernment
Working Paper Series.
Hong K. and Y. Kim, 2002, The critical success factor for
ERP implementation: An organizational fit
perspective, Information & Management 40, p. 25-40.
Jianga J. and G. Kleinb, 1999, Risks to different aspects of
system success, Informat. & Manag. 36, p. 263-272.
Krumbholz M. and Maiden N., 2001, The implementation
of enterprise resource planning packages in different
organisational and national cultures, Information
Systems 26, p. 185-204.
Kuruppuarachichi P. et al., 2002, IT project
implementation strategies for effective changes: A
critical review, Logistics Information Management 15,
p. 126-137.
Lozinsky S., 1998, Enterprise-wide software solutions.
Integration strategies and practices; Addison-Wesley.
Mabert V. et al., 2003a, Enterprise resource planning:
managing implementation process, European Journal
of Operational Research 146, 302-314.
Mabert V. et al., 2003b, The impact of organization size
on ERP implementation in US manufacturing, Omega
31, p. 235-246.
Mandal P. and A. Gunasekaran, 2003, Issues in
implementing ERP: A case study, European Journal of
Operational Research 146, p. 274-283.
Rebstock M. and K. Hildebrand, 1999, SAP R/3
Management; Coriolis Technology Press.
Sarker S., and A. Lee, 2003, Using a case study to test the
role of three key social enablers in ERP
implementation, Information & Management
40, p.
813-829.
Soffer P. et al., 2003, ERP modeling: A comprehensive
approach, Information Systems 28, p. 673-690.
Somers T. and K. Nelson, 2003, The impact of the strategy
and integration mechanisms on enterprise system
value: empirical evidence from manufacturing firms,
Europ. Journal of Operat. Research 146, p. 315-338.
Stensrud E., 2001, Alternative approaches to effort
prediction of ERP projects, Information and Software
Technology 43, p. 413-423.
Westerveld E., 2003, The project excellence model:
linking success criteria and critical success factors,
Intern. Journal of Project Management 21, p. 411-418.
A FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATING DIFFICULTIES IN ERP IMPLEMENTATION
465
