
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML
DOCUMENTS
Sven Groppe, Stefan Böttcher, Georg Birkenheuer
University of Paderborn, Faculty 5, Fürstenallee 11, D-33102 Paderborn, Germany
Keywords: XSLT, XPath, query transformation, query reformulation.
Abstract: An application using XML for data representation requires the transform
ation of XML data if the
application accesses XML data of other applications, or of a global database using another XML format.
The common approach transforms entire XML documents from one format into another e.g. by using an
XSLT stylesheet. The application can then work locally on a copy of the original document transformed in
the application-specific format. Different from the common approach, we use an XSLT stylesheet in order
to transform a given XPath query such that we retrieve and transform only that part of the XML document
which is sufficient to answer the given query. Among other things, our approach avoids problems of
replication, saves processing time and in distributed scenarios, transportation costs. Experimental results of
a prototype prove that our approach is scalable and efficient.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Problem definition and
moti
vation
In database theory, the problem of query
reformulation is commonly defined as follows (e.g.
(Deutsch & Tannen, 2003)):
Given two schemas F
orig
and F
transf
and a
correspondence S between them, find a query
XP
orig
formulated in terms of schema F
orig
that is
equivalent to a given query XP
transf
formulated in
terms of schema F
transf
modulo the correspondence
S.
Query reformulation is used in database
tech
nology within different scenarios, for example
within data integration, where schema F
transf
is the
global schema and schema F
orig
is one of several
local schemas, within schema evolution, where
schema F
orig
is the old schema and schema F
transf
the new schema, or within bilateral situations, where
two applications exchange data.
Within this paper, we apply query reformulation
t
o XML, and in particular to XPath and XSLT. This
enables similar scenarios, where XML, XPath and
XSLT are continuously used, as for query
reformulation in traditional databases. Within these
scenarios, using query reformulation has several
advantages in comparison to the state-of-the-art
method of XML and XSLT, which at first
transforms the entire XML document and then
works on the copy of the original document
transformed into F
transf
: Using query reformulation
avoids replication problems, saves processing time
for the transformation and in distributed scenarios
reduces transportation costs.
In terms of XML and within this paper, the
schem
as are XML formats, the correspondence is an
XSLT stylesheet and the queries are XPath queries.
In the following, we use the notation XP
orig
(D)
for the query result of applying the query XP
orig
to
the data D, and S(D) for the transformation of the
data D (which can again be a resultant XML
fragment of a query) according to S.
Within this paper, we modify the definition of
que
ry reformulation above and call it query
transformation: The algorithmic problem of query
transformation is to determine XP
orig
according to a
given XPath query XP
transf
and an XSLT stylesheet
S such that it meets the following conditions: The
resultant XML fragment of XP
orig
(D) has to be as
small as possible but has to guarantee the
equivalence of XP
transf
(S(XP
orig
(D))) and
XP
transf
(S(D)), i.e. that
XP
transf
(S(XP
orig
(D))) returns the same result
as XP
transf
(S(D)) for every XML document D.
This allows us to build a new query
trans
formation framework for XPath and XSLT with
241
Groppe S., Böttcher S. and Birkenheuer G. (2004).
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML DOCUMENTS.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 241-250
DOI: 10.5220/0002629102410250
Copyright
c
SciTePress
the core of a new query transformation algorithm for
determining XP
orig
(see (Groppe & Böttcher,
2003a) and (Groppe & Böttcher, 2003b)).
Furthermore, we can use standard XSLT processors
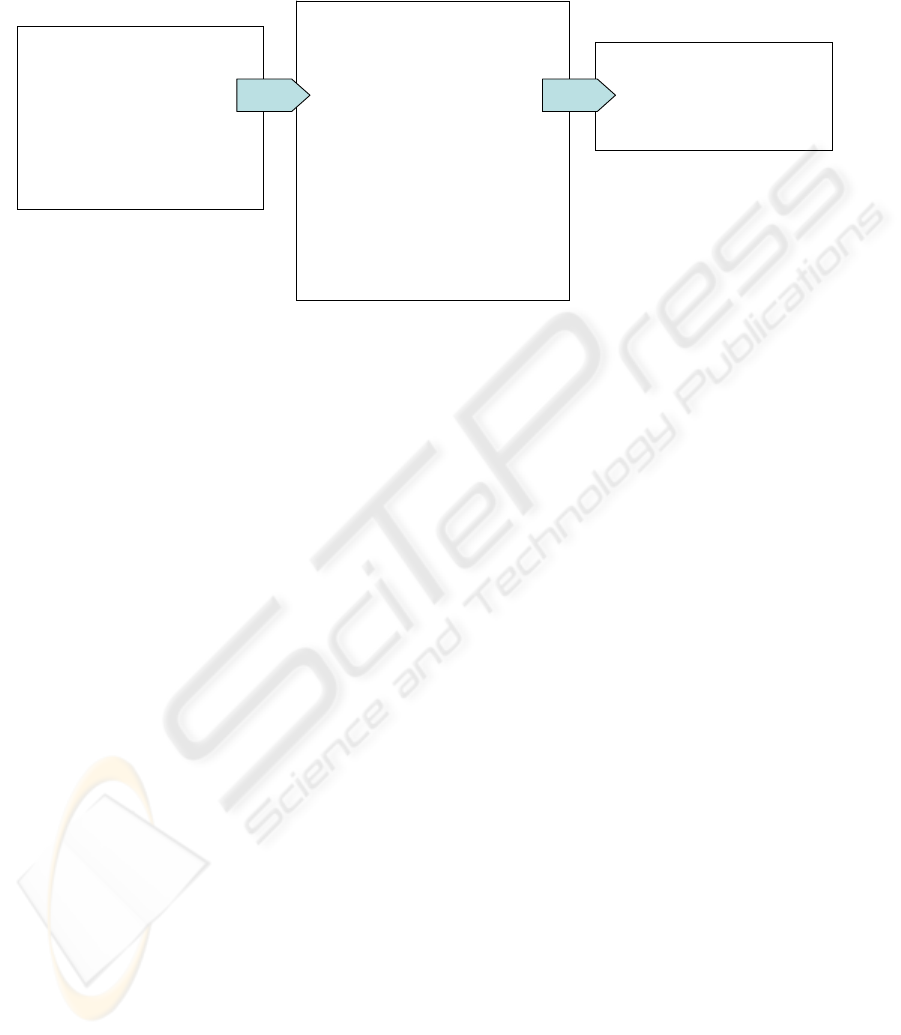
<object name="car">
<contains>
<object name="door"/>
<object name="cockpit">
<contains>
<object
name="button_heating"/>
</contains>
</object>
</contains>
</object>
<product_list>
<product label="car"/>
<product label="door"/>
<product label="cockpit"/>
<product label="button_heating"/>
</product_list>
<xsl:stylesheet >
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:element name="product_list">
<xsl:apply-templates select="object"/>
</xsl:element>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="object">
<xsl:element name="product">
<xsl:attribute name="label">
<xsl:value-of select="@name"/>
</xsl:attribute>
</xsl:element>
<xsl:apply-templates
select="contains/object"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
XML document D
XML fragment XP
orig
(D) (bold)
transformed XML document S(D)
XML fragment S(XP
orig
(D)) (bold)
XSLT stylesheet S
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
for transforming documents according to the XSLT
stylesheet S and standard XPath evaluators for
evaluating XP
transf
.
Within this paper, we present the experimental
results of a prototype of the query transformation
algorithm. The experimental results demonstrate that
our approach is scalable and efficient.
1.2 Relation to other work and our
focus
For the transformation of XML queries into queries
based upon other data storage formats, at least two
major research directions can be distinguished.
Firstly, the mapping of XML queries to object
oriented or relational databases (e.g. (Bourret et al.,
2000), (Deutsch & Tannen, 2003)), and secondly,
the transformation of XML queries or XML
documents into other XML queries or XML
documents (e.g. (Abiteboul, 1999)). We follow the
second approach; however, we focus on XSL (W3C,
2001) for the transformation of both data and XPath
(W3C, 1999) queries.
Within related contributions to schema
integration, two approaches to data and query
translation can be distinguished. While the majority
of contributions (e.g. (Cluet et al., 1998), (Abiteboul
et al., 1997)) map the data to a unique
representation, we follow (Chang and Garcia-
Molina, 2000) and map the queries to those domains
where the data resides.
The contribution in (Cluet et al., 2001) contains
query reformulation according to path-to-path
mappings. We go beyond this, as we use XSLT as a
more powerful mapping language. (Moerkotte,
2002) describes how XSL processing can be
incorporated into database engines, but focuses on
efficient XSL processing. The complexity of XPath
query evaluation on XML documents is examined in
(Gottlob et al., 2003). In comparison, we use an
evaluation based on output nodes of XSLT and
consider query transformation. Altinel and Franklin
present in (Altinel & Franklin, 2000) an algorithm to
filter XML documents according to a given query
and analyses the performance, but the algorithm
does not contain query transformation.
(Marian & Siméon, 2003) projects XML
documents to a sufficient XML fragment before
processing XQuery queries. (Marian & Siméon,
2003) contains a static path analysis of XQuery
queries, which computes a set of projection paths
formulated in XPath from an arbitrary XQuery
expression. In comparison to this approach and
among other things, we describe a path analysis
within XSLT stylesheets depending of an input
XPath query. Furthermore, we analyze paths within
recursive calls (of templates).
In contrast to all these approaches, we focus on
the transformation of XPath queries according to an
XSLT stylesheet.
Within this paper, we go beyond our previous
contributions of (Groppe & Böttcher, 2003a), as we
support a larger subset of XSLT (i.e. absolute paths
are now allowed in select attributes of XSLT nodes)
and a larger subset of XPath (i.e. predicates are now
allowed) for the XPath query transformation.
Furthermore, we show the advantages of our
algorithm presented in (Groppe & Böttcher, 2003b)
Figure 1: Example of the transformation by an XSLT stylesheet S
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
242

like scalability and efficiency by experimental
results of a prototype.
2 XPATH QUERY
TRANSFORMATION
For an example of the usage of our approach, see
Figure 1: The XSLT stylesheet S transforms the
representation of nested objects (XML document D)
into a flat model of a list of products, i.e. the
transformed XML document S(D). Assume, we
have to answer an XPath query
XP
transf
= /product_list/product
[@label=„cockpit“]/@*
on the transformed XML document S(D). It is
sufficient to transform only a resultant XML
fragment XP
orig
(D) (see bold face part of the left
box of Figure 1) for answering XP
transf
, where
XP
orig
is a query in XML format F
orig
computed by
our new query transformation algorithm.
Notice, that standard XPath evaluators only
return a query result as a node set, not as a resultant
XML fragment. This resultant XML fragment
XP
orig
(D) is defined to contain all nodes and all
their ancestors up to the root of the original XML
document D, which contribute to the successful
evaluation of the query XP
orig
given in XML format
F
orig
.
In the example, it is sufficient for answering
XP
transf
to transform the resultant XML fragment
(see the bold face part of the left box in Figure 1) of
the query
XP
orig
=/object(/contains/object)*
[@name=„cockpit“]
where A* is a short notation for an arbitrary number
of paths A. Notice, that standard XPath evaluators do
not support A*, but we can retrieve a superset by
replacing A*/ with //.
In our approach of our new query transformation
algorithm for determining XP
orig
, we search at first
for paths within the XSLT stylesheet (see Section
2.2), which generate elements, attributes and
attribute values in the correct order, i.e. as needed in
order to answer the query XP
transf
.
For each of these successfully searched paths, we
determine the input path expression of the XSLT
stylesheet (see Section 2.3), which summarizes the
XPath expressions of input nodes along the
stylesheet path. The transformed query XP
orig
is the
disjunction of the determined input path expressions
of each successfully searched path.
First of all, we describe the considered subsets of
XPath and XSLT in the next Section 2.1.
2.1 Considered subsets of XPath and
XSLT
In order to keep the presentation simple, we
currently restrict XPath queries XP
transf
, such that
they conform to the following rule for
AttributeQuery given in the Extended Backus
Naur Form (EBNF):
AttributeQuery ::= LocationPath
"/@*"|("/@" Name).
LocationPath ::= Step*.
Step ::= ("/"|"//") Name
Predicate*.
Predicate ::= "[" "@" Name "="
String "]".
This subset of XPath allows querying for an
XML fragment which can be described by
succeeding elements (in an arbitrary depth), the
attributes of which can be restricted to a constant
value.
Similarly, we restrict XSLT, i.e., we consider the
following nodes of an XSLT stylesheet:
• <xsl:stylesheet>,
• <xsl:template match=M name=N>,
• <xsl:element name=N>,
• <xsl:attribute name=N>,
• <xsl:apply-templates select=I>,
• <xsl:text>,
• <xsl:value-of select=I>,
• <xsl:for-each select=I>,
• <xsl:call-template name=N>,
• <xsl:attribute-set name=N>,
• <xsl:if test=T>,
• <xsl:choose>,
• <xsl:when test=T>,
• <xsl:otherwise>,
• <xsl:processing-instruction>,
• <xsl:comment> and
• <xsl:sort>,
where I and M contain an XPath expression without
function calls, T is a boolean expression and N is a
string constant.
Whenever attribute values are generated by the
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML DOCUMENTS
243

XSLT stylesheet, we assume that this is only done in
one XSLT node (i.e. <xsl:text> or
<xsl:value-of select=I>).
We define the following terms for later use.
Definition relative and absolute part: An XPath
expression I can be divided into a relative part
rp(I) and an absolute part ap(I) (both of which
may be empty) in such a way, that rp(I) contains a
relative path expression, ap(I) contains an
absolute path expression, and the union of ap(I)
and rp(I) is equivalent to I.
Example: The relative part of
I=(/E1|E2/E3|E4)/E5 is
rp(I)=(E2/E3|E4)/E5, the absolute part is
ap(I)=/E1/E5.
2.2 Searching for relevant output
nodes
We firstly look at the output nodes of the XSLT
stylesheet S, which generate an element E by the
XSLT node <xsl:element name=E> or
generate an attribute A by the XSLT node
<xsl:attribute name=A>.
In the example of Figure 1, all the
product_list elements in S(D) in the right part
of Figure 1 are generated by the node (3) of S (see
the middle box of Figure 1), all the product
elements in S(D) are generated by node (6). These
output nodes (3) and (6) of the XSLT stylesheet S
are reached, after a sequence of nodes of the XSLT
stylesheet S are executed. In the example,
<(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6)> is one sequence which
reaches the nodes (3) and (6), i.e. which generates
output that is relevant for an XPath query
/product_list/product.
For the purpose of using an adequate data
structure for a goal-oriented search through an
XSLT stylesheet according to a query XP
transf
, we
define a stylesheet path as a list of entries of the
form (N, XPr
transf
) where N is a node in the
XSLT stylesheet and XPr
transf
is the suffix of
XP
transf
which still has to be searched for. We call
the stylesheet path, which contains all the visited
nodes of the path from the start node to the current
node of the search in the visited order, the current
stylesheet path.
We call the stylesheet paths, which begin with
the node <xsl:stylesheet> and may generate
output that is relevant to XP
transf
, successful
element stylesheet paths. Each successful element
stylesheet path can be attached by attribute, filter
and loop stylesheet paths (see below).
We start the search at the node
<xsl:stylesheet>, which does not generate
any output. The search continues from a node S1 to
a node S2, if
a. S2 is a child node of S1 within the XSLT
stylesheet, or
b. S1 is a node with an attribute xsl:use-
attribute-sets=N and S2 is a node
<xsl:attribute-set name=N> with the
same N, or
c. S1 is a node <xsl:call-template
name=N> and S2 is a node <xsl:template
name=N> with the same N, or
d. S1 is <xsl:apply-templates select=
I/> and S2 is <xsl:template match=M>
and the template of S2 can possibly be called
from the selected node set I. This is the case if
ap(I)|//rp(I) and ap(M)|//rp(M) are
possibly not disjointed which can be checked by
a fast (but incomplete) tester (e.g. the tester
presented in (Böttcher & Türling, 2003)).
For example, for XP
transf
=/product_list/
product[@label="cockpit"]/@* and the
XSLT stylesheet of Figure 1, we search for the
output nodes which generate the product_list
elements (see node (3)) and then product (see
node (6)). The search can pass non-output nodes as
they do not generate any output, which does not fit
to XP
transf
. The search can also pass any output
nodes if we search next for an element E in arbitrary
depth, i.e. for //E.
While searching for attributes (e.g., for /@* see
nodes (7) and (8) in Figure 1), we branch off the
successful element stylesheet path. In order to allow
a sequential (but recursive) computation of the input
path expressions in Section 2.3, we store paths
resulting from a search for attributes separately in
attribute stylesheet paths.
We store the filter itself and paths resulting from
a search for filters in filter stylesheet paths (e.g., for
[@label=”cockpit”] see nodes (7) and (8) in
Figure 1). If the attribute value of the filter is
generated by an input node <xsl:value-of
select=I/>, we can transform the filter to a filter
in XML format F
orig
within XP
orig
(see Section
2.3), which restricts the node set of the input XML
document more precisely when we apply XP .
orig
If the value of the attribute of the filter is
generated by an output node
<xsl:text>const</xsl:text> within the
XSLT stylesheet, we can currently decide without
access to the XML document that a filter [@A1 =
V] will always be
• true, if V is equal to const. In order to be sure,
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
244
that the attribute @A1 and its value V will be
nevertheless generated by the XSL processor, we
store the suitable information in the set of attribute
stylesheet paths.
• false, if V is not equal to const. We abort the
search at this node.
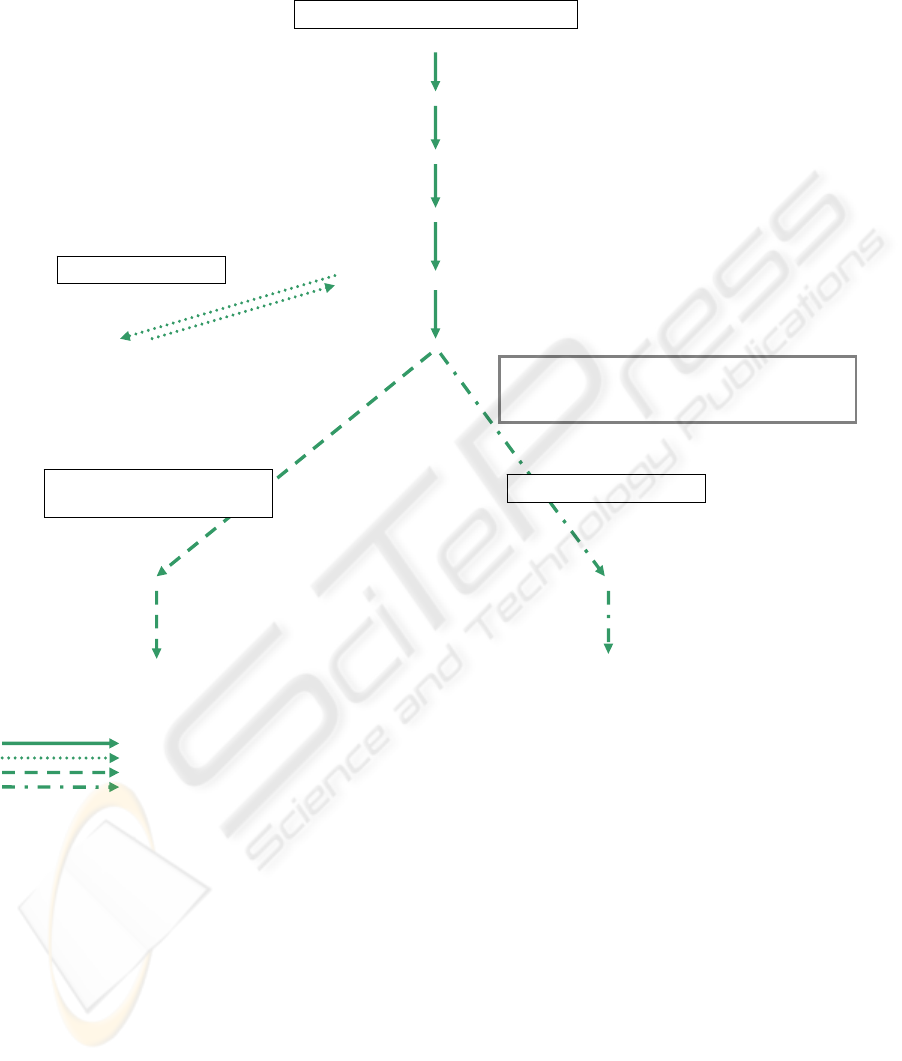
successful element stylesheet path
(9) <xsl:apply-templates
select=„contains/object“>
(6) <xsl:element name=„product“>
(3) <xsl:element name=„product_list“>
(4) <xsl:apply-templates select=„object“>
(1) <xsl:stylesheet …>
loop stylesheet path
(7) <xsl:attribute name=„@label“>
(8) <xsl:value-of select=„@name“>
filter stylesheet path of filter
[@label=“cockpit”]
attribute stylesheet path
Successful Element Stylesheet Path
Loop Stylesheet Path
Filter Stylesheet Path
Attribute Stylesheet Path
current ipe = /
completed ipe =
current ipe =
completed ipe =
current ipe = contains/object
completed ipe =
current ipe = /
completed ipe =
current ipe = /
completed ipe =
current ipe = /object
completed ipe =
current ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
completed ipe =
current ipe =
completed ipe =
current ipe =
completed ipe =
current ipe = @name
completed ipe =
current ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
[@name=“cockpit”]
completed ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
[@name=“cockpit”]/@name
current ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
[@name=“cockpit”]
completed ipe =
current ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
[@name=“cockpit”]/@name
completed ipe =
current ipe = /object (/contains/object)*
[@name=“cockpit”]
completed ipe =
Resulting Input Path Expressions
(2) <xsl:template match=“/“>
(5) <xsl:template match=„object“>
(7) <xsl:attribute name=„@label“>
(8) <xsl:value-of select=„@name“>
During the search it may occur, that we revisit a
node N of the XSLT stylesheet without any progress
in the processing of XPr
transf
. For example, we can
visit node (1), (2), (3), (4), (5), then node (9) and the
node (5) again in Figure 1. We call this a loop and
we define a loop as follows: The loop is the current
stylesheet path minus the stylesheet path of the first
visit of N. In the example of Figure 1, the loop
contains the nodes (9) and (5). For each loop in the
XSLT stylesheet, we store the loop itself, the current
node N and XPr
transf
as an entry to the set of loop
stylesheet paths, because we need to know the input
which is consumed when the XSLT processor
executes the nodes of a loop (see Section 2.3). In
order to avoid an infinite search, we do not continue
the search at the final node when the loop is
detected.
2.3 Determining the sufficient node
set of the original document
While executing the successful element stylesheet
paths (and attached attribute, filter and loop
stylesheet paths) computed in Section 2.2, the XSLT
processor also processes input nodes (e.g. node (4)
in Figure 1) each of which selects a certain node set
described by a local input path expression I of the
input XML document D. The input nodes of the
considered XSLT subset with local input path
Fi
gu
r
e
2
:
Co
m
put
in
g
In
put
P
at
h Ex
p
r
ess
i
o
n
s
o
f
t
h
e
r
u
nnin
g
e
x
a
m
p
l
e
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML DOCUMENTS
245
expression I are
• <xsl:apply-templates select=I/>,
• <xsl:value-of select=I/>,
• <xsl:for-each select=I>,
• <xsl:if test=T> and
• <xsl:when test=T>,
where T is a Boolean expression and I occurs in T.
When considering all executed input nodes of a
successful element stylesheet path (and its attached
paths), the input nodes altogether select a certain
node set of the input XML document D. If we can
determine the whole node set (described using a
query XP
orig
), which is selected on all stylesheet
paths, which generate output relevant to the query
XP
transf
and which we already computed in Section
2.2, we can then select a smaller, but sufficient part
XP
orig
(D) of the input XML document D, where
XP
transf
(S(XP
orig
(D))) is equivalent to
XP
transf
For this reason, we have to combine all the local
input path expressions of input nodes along a
successful element stylesheet path (and its attached
paths). For this purpose, we use two different
variables:
(S(D)).
The current input path expression (current
ipe) contains the whole input path expression of the
successful element stylesheet path down to (and
including) the current XSLT node. We guarantee
that the XSLT processor processes the current XSLT
node with a subset of the XML nodes of the original
XML document described by current ipe while
the XSLT processor executes the successful element
stylesheet path.
The completed input path expression
(completed ipe) contains all such input path
expressions, which are selected within the stylesheet
path before the current node, but which will not be
used further in the computation of a current
ipe.
Figure 2 shows the computation of the current
input path expressions and the completed input path
expressions of the example of Figure 1 and a given
query XP
transf
= /product_list/product
[@label=„cockpit“]/@*. The node identifiers
(1) to (8) in Figure 2 refer to the node identifiers of
the XSLT stylesheet in Figure 1.
The completed ipe is always initialized with
the empty set. For the example within Figure 2, the
current ipe is initialized with /. In general, the
XSLT processor starts executing the successful
element stylesheet path with the node set described
by the match attribute M of the first template
<xsl:template match=M> within the
successful element stylesheet path. The template can
match nodes of the node set rp(M) occurring in
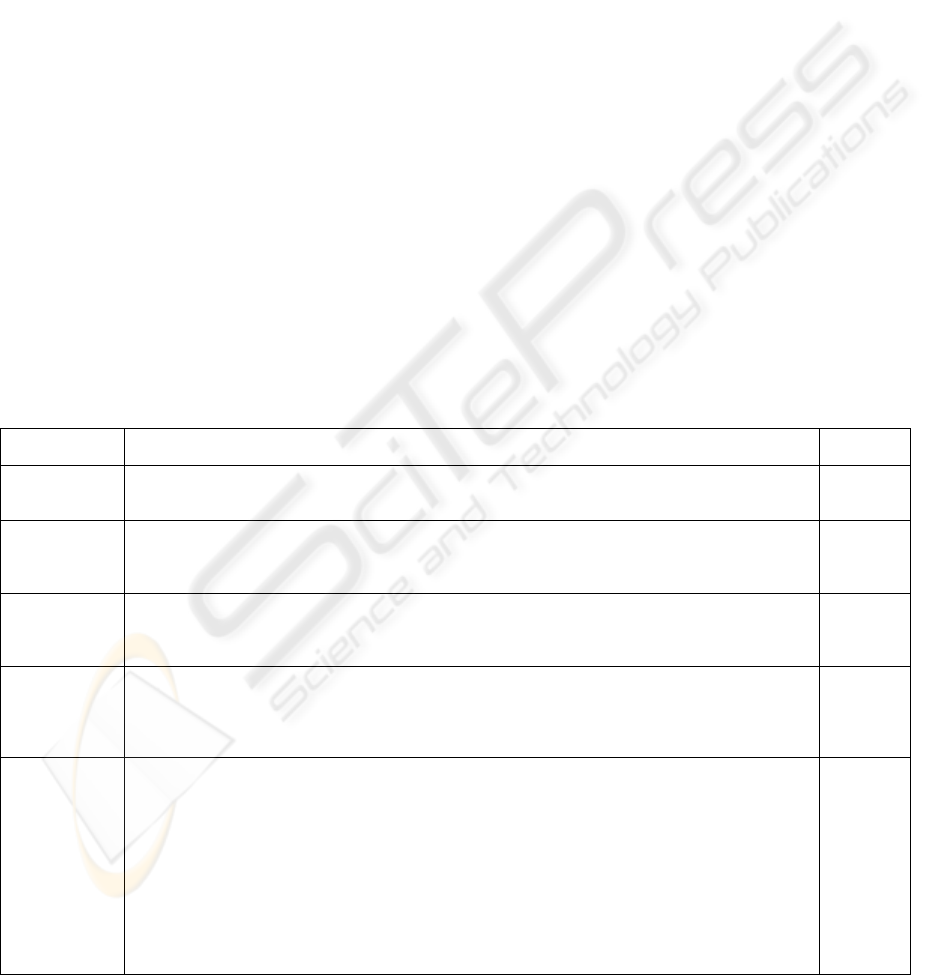
Current Node Computation of current ipe and completed ipe
Example
Nodes
Non-input
nodes without
attached paths
current ipe = current ipe
new old
completed ipe
new
= completed ipe
old
(2), (3),
(7)
Input node
current ipe
new
= if (rp(I) is empty) ap(I)
else current ipe / rp(I) | ap(I)
old
completed ipe
new
= if(ap(I) is empty) completed ipe
old
else completed ipe
old
| current ipe
old
(4), (8),
(9)
Attached
attribute
stylesheet path
current ipe
init
= current ipe
old
completed ipe
init
= completed ipe
old
current ipe
new
= current ipe
old
completed ipe
new
= current ipe
path
| completed ipe
path
(6)
Attached filter
stylesheet path
according to a
filter
[@A=const]
current ipe
init
= empty
completed ipe
init
= completed ipe
old
current ipe
new
= current ipe
old
[current ipe
path
=const]
completed ipe
new
= completed ipe
path
(6)
Attached loop
stylesheet paths
1.. n
current ipe
init
= empty
completed ipe
init
= empty
current ipe
new
= (current ipe
old
|
ap(current ipe
path1
) |…|ap(current ipe
pathn
))
(/rp(current ipe
path1
)|…|/rp(current ipe
pathn
))*
completed ipe
new
= if(rp(completed ipe
path1
) = …
= rp(completed ipe
pathn
) = empty)
(completed ipe
old
|
(ap(completed ipe
path1
)|…|ap(completed ipe
pathn
)))
else (completed ipe
old
| current ipe
new
/
(rp(completed ipe
path1
) |…| rp(completed ipe
pathn
))
|(ap(completed ipe
path1
)|…|ap(completed ipe
pathn
)))
(5)
Figure 3: Computing steps of current ipe and completed ipe
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
246
arbitrary depth of the XML document because of
built-in templates. Therefore, we initialize
current ipe with ap(M)|//rp(M).
Figure 3 lists the different computing steps for
current ipe and completed ipe (column
2). These steps depend on the type of the current
node or the type of paths attached to the current
node (column 1).
Furthermore, Figure 3 contains the identifiers of
example nodes (column 3) for each computing step
applied to these example nodes in Figure 2.
In order to compute current ipe and
completed ipe for each node along the
successful element stylesheet path and its attached
paths (as e.g. for the nodes (2) to (8) in Figure 2), we
mainly iterate through the successful element
stylesheet path. Then depending on the current node
we
• compute new path expressions of the current ipe
(current ipe
new
) and the completed ipe
(completed ipe
new
). The result is based on
the local input path expression of the current
node (I) and the old input path expressions of
the current ipe (current ipe
old
) and the
completed ipe (completed ipe
old
).
• recursively compute and combine current
ipes and completed ipes of attached
attribute stylesheet paths, filter stylesheet paths,
and loop stylesheet paths. For this purpose, at
first we initialize current ipe (current
ipe
init
) and completed ipe (completed
ipe
init
), then recursively compute along the
attached path as before and get the current
ipe (current ipe
path
) and completed
ipe (completed ipe
path
) after the last node
of the attached path. At last we compute
current ipe
new
and completed ipe
new
of
the node with the attached path.
The complete input path expression which is
used as query XP
orig
on the input XML document is
the union of all the completed ipes and the
current ipes of the last node of each of the n
successful element stylesheet paths (1..n),
XP
orig
= completed ipe
1
| current ipe
1
| … |
completed ipe
n
| current ipe
n
.
If there is no entry in the set of successful
element stylesheet paths, i.e. n=0, XP
orig
remains
empty.
In the example of Figure 2, we get
XP
orig
=/object(/contains/object)*
[@name=”cockpit”] |
/object(/contains/object)*
[@name=”cockpit”]/@name
3 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
Within this section, we show the results of the
experiments with our prototype in comparison to the
standard approach, which transforms the entire XML
document in order to answer a query.
3.1 Experimental Environment
The test system for all runtime measurements is an
Intel Pentium 4 processor 2,66 Ghz with 512
Megabyte DDR-RAM, Windows XP as operating
system and Java VM build version 1.4.2. We use
Xerces2 Java parser 2.5.0 release as XML parser and
the Xalan-Java version 2.5.1 as XSLT processor.
<xsl:stylesheet>
<xsl:template match="/root">
<xsl:element name="root">
<xsl:apply-templates select="object"/>
</xsl:element>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="object">
<xsl:element name="product">
<xsl:attribute name="id">
<xsl:value-of select="@id"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="sel1Percent">
<xsl:value-of select="@sel1Percent"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="sel25Percent">
<xsl:value-of select="@sel25Percent"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="sel50Percent">
<xsl:value-of select="@sel50Percent"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="sel75Percent">
<xsl:value-of select="@sel75Percent"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="sel100Percent">
<xsl:value-of select="@sel100Percent"/>
</xsl:attribute>
</xsl:element>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Figure 4: Used XSLT stylesheet S for the measurements
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML DOCUMENTS
247
<!ELEMENT root object*>
selectivity [%]
1 25 50 75 100
time in seconds
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Time to transform entire document
(1) Time used for the XPath transformation
(2) Time for generating the result XML fragment
(3) Time for the transformation of the result
XML fragment
Total time of our approach (1+2+3 together)
<!ELEMENT object EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST object id CDATA #REQUIRED
sel1Percent CDATA #REQUIRED
sel25Percent CDATA #REQUIRED
sel50Percent CDATA #REQUIRED
sel75Percent CDATA #REQUIRED
sel100Percent CDATA #REQUIRED
>
Figure 5: Used DTD F
orig
for the measurements
filesize in kilobyte
0 5000 10000 15000
time in seconds
0
60
120
180
240
Time to transform entire document
Time of our approach
Figure 4 contains the XSLT stylesheet, which we
used for all experiments
We have generated test XML documents of
different size according to the DTD in Figure 5. The
id attribute of the object tag contains an
unambiguous identifier for the purpose of querying
for a single entry with XP
transf
=/root/product
[@id=”1”]/@*.
The selectivity of a query is defined to be the
size of the query result divided by the size of the
original document.
The selXPercent attributes occurring within
the generated test XML documents are set to the
value ”1” with a probability of X percentage where
X is in {1, 25, 50, 75, 100}. For the
Figure 6: Querying for a single entry
filesize in kilobyte
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
time in seconds
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Time to transform entire document
Time of our approach
Figure 7: Zoom of Figure 6
Figure 8: Experiment with constant file size of 3,5
Megabyte
selectivity [%]
1 25 50 75 100
time in seconds
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Time to transform entire document
(1) Time used for the XPath transformation
(2) Time for generating the result XML fragment
(3) Time for the transformation of the result
XML fragment
Total time of our approach (1+2+3 together)
Figure 9: Experiment with constant file size of 7
Megabyte
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
248
measurements, we use the query XP
transf
=
/root/product[@selXPercent=”1”]/@*
for a query with a selectivity of X percentage.
Before the measurements start, all documents are
loaded into main memory. The prototype uses the
DOM-API for accessing the documents. The
prototype generates the resultant XML fragment of
XP
orig
(D) by cloning the relevant nodes.
3.2 Analysis of Experimental Results
3.2.1 Querying for single entries
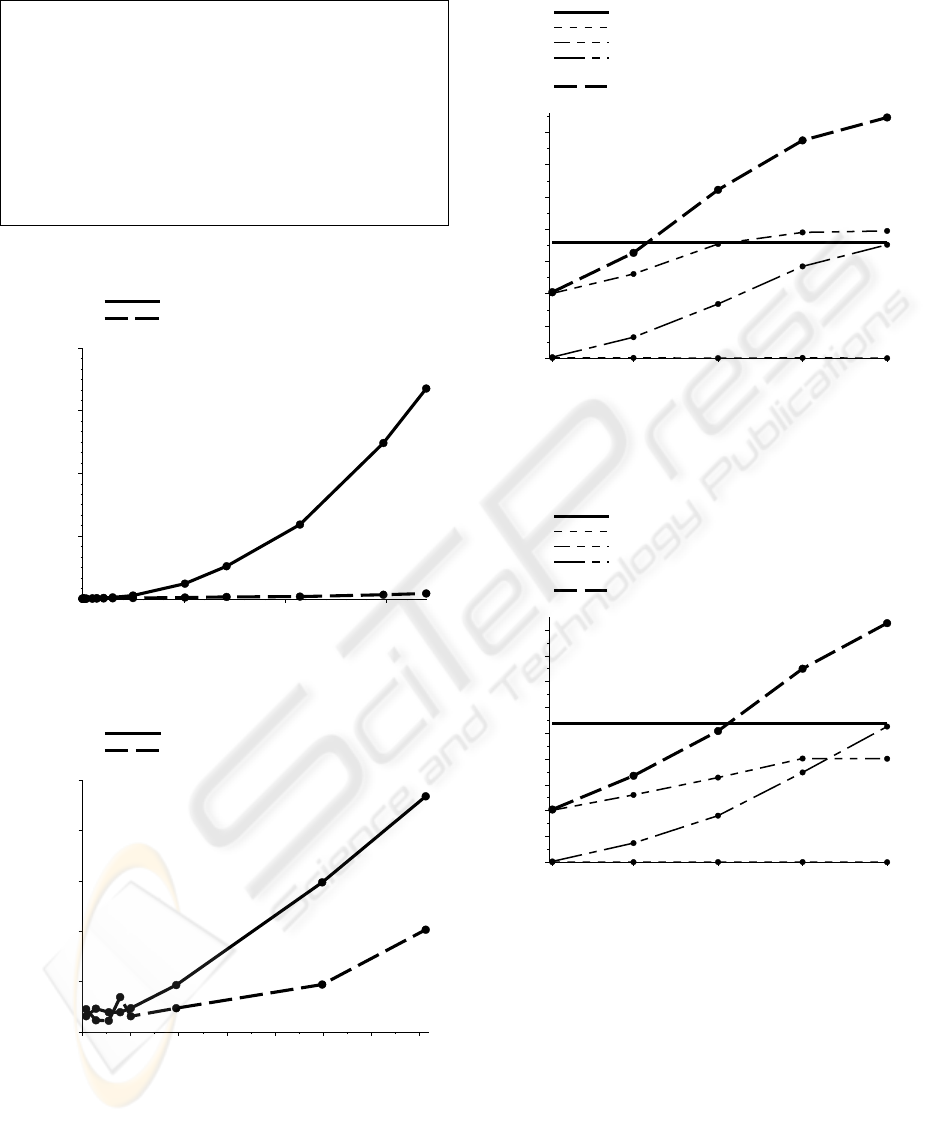
Figure 6 shows how the runtime for querying for a
single entry depends upon the size of the original
document D. As the resultant XML fragment always
has a size of 100 bytes, the reduction of the original
document grows from 98,7% for a document size of
7,5 Kilobytes to 99,9994% for a document size of 17
Megabytes. Within this experiment, our approach is
2 times faster compared to transforming the entire
document at an original document size of 200
Kilobytes, 3 times faster at 500 Kilobytes and up to
40 times faster at 17 Megabytes. At 17 Megabytes,
transforming the entire document requires 3 minutes
and 20 seconds, whereas our approach requires 5
seconds.
Figure 7 zooms in a part of Figure 6, which
shows, that our approach is faster with file sizes
larger than 100 Kilobytes.
3.2.2 Varying the selectivity whilst
maintaining constant file size
Within Figure 8, the selectivity of the transformed
query varies, but the file size 3,5 Megabytes of the
original document is fixed. Figure 8 shows that
given a document size of 3,5 Megabytes, our
approach is faster for queries with a selectivity less
than 30%. Similarly, Figure 9 shows that given a
document size of 7 Megabytes our approach is faster
for queries with a selectivity less than 53,3%.
Furthermore, Figure 8 and 9 show that the XPath
transformation requires little time (<0,016 seconds).
However, the time taken to retrieve the resultant
XML fragment and its transformation increases with
the selectivity and are the main processing costs.
Within the next section, we examine up to which
limit of selectivity depending on the file size our
approach is faster than the standard approach which
transforms the entire XML document.
3.2.3 When is our approach faster?
Figure 10 shows the biggest selectivity of
transformed queries depending on the file size of the
original query, where our approach is faster (solid
line) than the standard approach. Furthermore,
Figure 10 shows where our approach is two times
faster (dashed line). Figure 10 demonstrates that our
approach is scalable, i.e. our approach performs
increasingly better the larger the XML documents
are compared to the standard approach.
filesize in kilobyte
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 900010000
selectivity [%]
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Our approach is faster than
transforming the entire document
Our approach is 2 times faster than
transforming the entire document
4 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
Whenever XML data D given in an XML format
F
orig
can be transformed by an XSLT stylesheet S
into an XML format F
transf
, and a query expressed
in terms of format F
transf
has to be applied, our
goals are as follows: to avoid replicas, to reduce the
processing costs for document transformation by an
XSLT processor and to reduce data shipping costs in
distributed scenarios.
Within our approach, we transform a given
query XP
transf
by using a given XSLT stylesheet S
into a query XP
orig
. XP
orig
can be applied to the
input XML document D in order to retrieve a smaller
fragment XP
orig
(D) which contains all the relevant
data. XP
orig
(D) can be transformed by the XSLT
stylesheet into S(XP
orig
(D)), from which the
query XP
transf
selects the relevant data.
We proved by experimental results that our
approach to queries on transformed XML data has
considerable advantages over transforming the entire
XML document. Particularly this is the case when
using queries with low selectivity and for queries on
large XML documents. Furthermore, we showed
Figure 10: When is our approach faster?
EFFICIENT QUERYING OF TRANSFORMED XML DOCUMENTS
249

that our approach is scalable and becomes more
efficient for larger XML documents.
Within a professional environment, the use of
our approach can be switched on and off depending
on the file size of the original XML document, and
estimations of selectivity of the transformed query.
Summarizing all, our approach enables the
seamless incorporation of XSL processing into
database management systems in an efficient and
scalable manner.
In order to keep this presentation simple, we have
restricted our presentation to the given subset of
XPath and a subset of XSLT. However, the
approach is not limited to these subsets, and we
consider it to be promising to extend it to a larger
subset of XPath and XSLT.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is funded by the MEMPHIS project (IST-
2000-25045).
REFERENCES
Abiteboul, S., 1999. On views and XML. In PODS, pages
1-9.
Abiteboul, S., Cluet, S., and Milo, T., 1997.
Correspondence and translation for heterogeneous
data. In Proc. of the 6th ICDT.
Altinel, M., and Franklin, M. J., 2000. Efficient Filtering
of XML documents for Selective Dissemination of
Information, In Proceedings of 26th International
Conference on Very Large Databases, Cairo, Egypt.
Apache Software Foundation, 2003. Xalan-Java,
http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/index.html.
Apache Software Foundation, 2003. Xerces2 Java Parser
2.5.0 Release,
http://xml.apache.org/xerces2-j.
Birkenheuer, G., 2003. An XPath Query translation
Framework based on XSLT Stylesheets. BSc
Computing Science project report, University of
Paderborn.
Böttcher, S., and Türling, A., 2003. Checking XPath
Expressions for Synchronization, Access Control and
Reuse of Query Results on Mobile Clients. Workshop:
Database Mechanisms for Mobile Applications,
Karlsruhe, Germany.
Bourret, R., Bornhövd, C., and Buchmann, A. P., 2000. A
Generic Load/Extract Utility for Data Transfer
Between XML Documents and Relational Databases.
2nd Int. Workshop on Advanced Issues of EC and
Web-based Information Systems (WECWIS), San Jose,
California.
Chang, C.-C. K., and Garcia-Molina, H., 2000.
Approximate Query Translation Across
Heterogeneous Information Sources. VLDB 2000.
Cluet, S., Delobel, C., Simon, J., and Smaga, K., 1998.
Your mediators need data conversion! In Proc. of the
1998 ACM SIGMOD Conf..
Cluet, S., Veltri, P., and Vodislav, D., 2001. Views in a
Large Scale XML Repository. In Proceedings of the
27th VLDB Conference, Roma, Italy.
Deutsch, A., and Tannen, V., 2003. Reformulation of
XML Queries and Constraints, In ICDT 2003, LNCS
2572, pp. 225-241.
Gottlob, G., Koch, C., and Pichler, R., 2003. The
Complexity of XPath Query Evaluation, In
Proceedings of the 22th ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-
SIGART symposium of Principles of database systems
(PODS 2003), San Diego, California, USA.
Groppe, S., and Böttcher, S., 2003a. Querying transformed
XML documents: Determining a sufficient fragment
of the original document. 3. International Workshop
Web Databases (WebDB), Berlin.
Groppe, S., and Böttcher, S., 2003b. XPath Query
Transformation based on XSLT stylesheets, Fifth
International Workshop on Web Information and Data
Management (WIDM’03), New Orleans, Louisiana,
USA.
Marian, A., and Siméon, J., 2003. Projecting XML
Documents. In Proceedings of the 29
th
VLDB
Conference, Berlin, Germany.
Moerkotte, G., 2002. Incorporating XSL Processing Into
Database Engines. In Proceedings of the 28
th
VLDB
Conference, Hong Kong, China.
W3C, 2001. Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL).
http://www.w3.org/Style/XSL/.
W3C, 1999. XML Path Language (XPath) Version 1.0.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath/.
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
250
