
OBJECTMINER: A NEW APPROACH FOR MINING C
OMPLEX
OBJECTS
Roxana Danger, José Ruíz-Shulcloper
Computer Science Department. University of Oriente, Santiago de Cuba (Cuba)
Institute of Cybernetics, Mathematics and Physics, La Habana (Cuba)
Rafael Berlanga
Languages and Systems Department. Jaume I University, Castellón (España)
Ke
ywords: Data-mining algorithms, Association rules, Complex objects.
Abstract: Since their introduction in 1993, association rules have been successfully applied to the description and
summarization of discovered relations between attributes in a large collection of objects. However, most of
the research works in this area have focused on mining simple objects, usually represented as a set of binary
variables. The proposed work presents a framework for mining complex objects, whose attributes can be of
any data type (single and multi-valued). The mining process is guided by the semantics associated to each
object feature, which is stated by users by providing both a comparison criterion and a similarity function
over the object subdescriptions. Experimental results show the usefulness of the proposal.
1 INTRODUCTION
The discovery of association rules (a special case of
data regularity introduced by (Agrawal et al, 1993)
is an important problem in the data mining area. In
(Agrawal, 1994) an algorithm called Apriori is
introduced to compute efficiently the frequent
itemsets. Since then, different adaptations and
optimizations have been proposed in the literature.
All of them address two key problems: how to
explore the search space, and how to determine the
actual frequency of the itemsets to be analyzed.
The inclusion of qualitative attributes has been
traditionally treated by translating them to a set of
binary variables, one for each value of the attribute.
In (Srikant and Agrawal, 1995) the problem of
mining relational data with quantitative attributes
was firstly introduced. A well-known example of
discovered associations in this context is the
following one: “10% of the married people whose
age is between 50 and 60 have at least 2 cars”. In
this work, each quantitative attribute is discretized
by partitioning into intervals the attribute domain,
and then these discrete values are translated into a
set of binary values (one for each interval). In
(Zhang et al, 1997) and (Miller and Yang, 1997)
quantitative attributes are discretized by clustering
the values according to a given similarity function.
In (Han et al, 1998) a set of abstraction funtions are
used to transform an object-oriented databases to a
multi-dimentional cube for mining proposes. The
main contribution of this work is that it deals with
any kind of data types. Alternatively, in (Gyenesei,
2000) the mining of the quantitative attribute is
treated by applying fuzzy logic. In this approach,
attribute values are mapped to the fuzzy sets
specified by the user. Then, the whole database is
translated to a fuzzy one over which the data mining
algorithm is applied. The discovered association
rules also regards the fuzziness of the items to
calculate their support and confidence.
To sum up, the inclusion of non-binary attributes
to the mining process requires in these approaches
the translation of the original database, so that each
non-binary attribute can be regarded as a discrete set
of binary variables, over which the existing data-
mining algorithms can be applied to. This approach
can be sometimes unsatisfactory due to the
42
Danger R., Ruíz-Shulcloper J. and Berlanga R. (2004).
OBJECTMINER: A NEW APPROACH FOR MINING COMPLEX OBJECTS.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 42-47
DOI: 10.5220/0002633500420047
Copyright
c
SciTePress

following reasons: the translated database can be
larger than the original one, the transformation of the
quantitative data could not correspond to the
intended semantics of the attributes.
The previous drawbacks have motivated the
present work. In our approach, we introduce a
conceptual framework for representing complex
objects, their semantics and their association rules.
In this work, complex objects are described by a set
of features, which can be of any data type. The
semantics of the objects is specified with both a set
of binary comparison criteria (one for each feature)
and a set of object similarity functions (one for each
interesting object subdescription). The comparison
criterion is used to determine whether two values of
the involved feature are equal or not. Similarly, to
compare different object subdescriptions the
similarity functions are used. The inclusion of these
functions allows users to obtain semantically richer
association rules and to express their particular view
of the mined data. In this way, different users can
exploit in different ways the same data collection,
without changing it.
Finally, we propose an algorithm that obtains the
frequent itemsets for these objects. Each itemset is
represented by a set of pairs variable-value, and its
meaning must be interpreted according to the
functions provided. In this way, an itemset is not the
specification of a set of frequent values, but a
frequent type of object subdescriptions according to
the user perspective. Thus, the generated association
rules describe the dependencies between these types
of object subdescriptions.
The paper is organized as follows: in the next
section, we introduce the necessary concepts of the
proposed framework. Then, in Section 3 we describe
a data-mining algorithm that finds frequent object
subdescriptions, and in Section 4 we describe the
preliminary experimental results. Finally, in Section
5 we give our conclusions and the future work.
2 FORMAL DEFINITIONS
In the proposed framework, a data collection
consists of a set of objects, Ω = {o
1
, o
2
, ..., o
n
},
which are described by a set of features R={R
1
,...,
R
m
}. We will denote with D
i
the domain of the i-th
feature, which can be of any data type (single and
multi-valued). Thus, each object consists of a m-
tuple (v
1
,…,v
m
), where v
i
∈ D
i
(1 ≤ i ≤ m).
In order to compare its values, each feature R
i
has
associated a comparison criterion, C
i
(x, y), which
indicates whether the pair of values,
i
Dyx ∈,
, must
be consider equal or not. This comparison criterion
can include specifications for the case of invalid and
missing values in order to deal with incomplete
information.
The simplest comparison criterion is the strict
equality, which can be applied to any domain:
⎩
⎨
⎧
≠∧≠=
=
otherwise
nullynullxyxif
yxC
0
,1
),(
Another interesting comparison criterion for
numeric features is the following one:
⎩
⎨
⎧
ε≤−
=
otherwise
yxif
yxC
0
1
),(
which expresses that two values are considered
equal if they differs from each other in at most a
given threshold ε.
Since the mining process is intended to discover
the combinations of object features and object values
that frequently co-occur, it is necessary to manage
the different object projections.
A subdescription of an object o for a subset of
features
RS ⊆
, denoted as
)(oI
S
, is the projection
of the value of o over S. As usually, we will denote
with o[r] the projection of the value of o over the
feature r.
Moreover, we assume that there exists a similarity
function between object subdescriptions, which
allows us to decide whether two objects must be
considered equal or not by the mining process. All
these similarity functions are binary, that is, they
return either 0 (not equal) or 1 (equal).
The simplest similarity function is the following
one:
[] []
⎩
⎨
⎧
=∈∀
=
.,0
1)',(,,1
))'(),((
otherwise
roroCSrif
oIoISim
SS
which expresses the strict equality by considering
the comparison criterion of each of the
subdescription features.
The following similarity function states that two
subdescriptions are considered equal if they have at
least ε features similar:
[] []
⎩
⎨
⎧
≥=∈
=
.,0
}1)',(/{,1
))'(),((
otherwise
roroCSrif
oIoISim
SS
ε
Analogously to the traditional data-mining works,
we also provide the definitions of support and
association rules, but applied to this new framework.
We define the support of a subdescription
)(oIv
S
=
, denoted with Sup(v), as the percentage
of objects in Ω that are similar to v, that is:
Ω
=Ω∈
=
}1)),'((/'{
)(
voISimo
vSup
S
OBJECTMINER: A NEW APPROACH FOR MINING COMPLEX OBJECTS
43

We say that a pair of subdescriptions
)(
1
1
oIv
R
=
and
)(
2
2
oIv
R
=
, with R
1
, R
2
⊂ R,
R
1
∩ R
2
=∅, are associated through the association
rule:
),(
21
csvv ⇒
if
svSup ≥)'(
and
c
vSup
vSup
≥
)(
)'(
1
, where
)('
21
oIv
RR ∪
=
.
The values of s and c are called support and
confidence of the rule, respectively.
The problem of computing the association rules for
complex objects consists in finding all the
association rules of the subdescriptions of Ω whose
support and confidence satisfy the user-specified
thresholds.
It must be pointed out that the previous definitions
subsume the traditional concept of association rule.
Thus, if we use the strict equality in both the
comparison criterion and the similarity function, we
obtain the classical definition of association rule.
Besides, we can include other comparison criteria
such as the interval-based partitions, for quantitative
data, and the is-a relationship of the concept
taxonomies, in order to represent other kinds of
association rules (Srikant and Agrawal, 1995)
(Zhang, 1997) (Hipp et al, 1998).
The idea that different items have different levels
of interesting for the user, as suggested in (Gyenesei,
2000), can be also incorporated in this framework by
assigning a weight to each variable in the similarity
function. Moreover, when the variables are fuzzy
data, it is perfectly admissible to use as comparison
criterion the membership of the values to the same
fuzzy set.
Figure 1: Data-mining algorithm for object subdescriptions.
FreqItemSets_ComplexObjects (Ω, CriterionComps, SimilFuncs, MinSupp, FreqSets)
Input:
Ω = {o
1
, o
2
, ..., o
n
}, a set of complex objects
CriterionComps: array of comparison’s functions.
SimilFuncs: Dictionary of similarity functions, such that the key that corresponds to the
similarity function for the subdescription S’ = {K
i
1
, ..., K
i
s
} is the own set S’.
MinSupp: Minimal support to consider a subdescription as frequent.
Output:
FreqSets: Set of dictionaries that maintain for each size and combination of features (with at
least one frequent value) the frequent subdescriptions in Ω and the index of the objects that
are similar to each one of these subdescriptions.
Method:
1. F
1
= SetFreqValues (Ω, CriterionComps)
2. k = 2
3. while
F
k-1
≠ ∅ do
4. SetCandidatesVars = {{f
i
, f
j
} / f
i
, f
j
∈ F
k-1
.keys(), ⏐f
i
∪ f
j
⎥ = k}
5. for
each pair of features {f
i
, f
j
} in SetCandidatesVars do
6. for
each O in Ω do
7. if
[]
().)(
1
keysfFOI
ik
f
i
−
∈
and
[
]
().)(
1
keysfFOI
jk
f
j
−
∈
then
8. IndexSimObjs =
[]
[
]
[
]
[
]
)()(
11
OIfFOIfF
ji
f
jk
f
ik −−
∩
9. SimObjs = {}
10. for
O
k
in Ω, k ∈ IndexSimObjs do
11. if
SimilFuncs[f
i
∪ f
j
](
)(),(
ii
kffff
OIOI
jj
∪∪
) = 1 then
12. SimObjs = SimObjs ∪ {k}
13. if
⎥ SimObjs⎥ ≥ MinSupp then
14.
[
]
[
]
=∪
∪
)(
i
i
OIffF
j
ff
jk
SimObjs
15. FreqSets = FreqSets ∪ {F
k
}
16. k = k + 1
ICEIS 2004 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
44

3 COMPUTING FREQUENT SUB-
DESCRIPTIONS
In this section we present an algorithm for
computing the frequent subdescriptions for a
collection of complex objects (see Figure 1). This
algorithm is inspired in the original algorithm of
(Agrawal, 1994). However, it also uses the strategy
of the Partition algorithm (Srinkat and Agrawal,
1995) to compute the support of the object
subdescriptions.
It is worth mentioning that in this work, an itemset
is a subdescription, and its support is the number of
objects in the database that are similar to it.
The algorithm works as follows: firstly, it
determines all the frequent values for each variable,
by using the SetFreqValues function (line 1). It is
worth mentioning that we can use list of stop values
for each attribute in order to reject those frequent
values with little meaning (e.g. false value for binary
attributes).
Afterwards, while at least two frequent
subdescriptions have been found in the previous
iteration k, they are combined two by two in order to
create candidate subdescriptions of k+1 attributes
(line 4). Then, it determines which of the candidate
subdescriptions are frequent enough (lines 5-14).
It’s important to take into account that in order to
guarantee the monotonic construction of the frequent
itemsets, it is necessary that the similarity functions
satisfy the following condition: if two objects are
different with respect to a subdescription S
1
, they are
also different with respect to any other
subdescription S
2
, such that S
1
⊂ S
2
.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In order to evaluate the proposed methodology, we
have selected two databases publicly available on
Internet. The first one is about the flags of the
world
1
, and the second one, is about general
information of a large number of world countries
2
.
Next, we present some of the most significant
results obtained for these databases. The association
rules have been represented using the approximation
symbol, ~, in order to emphasize that the relation
between a feature and its corresponding value is not
the strict equality but the comparison criterion
defined for the feature.
1
http://ftp.ics.uci.edu/pub/machine-learning-databases/flags
2
http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/
Flags of the world
Figure 2 shows the set of the most relevant features
used for this database, as well as their types and the
comparison criteria used for them. The rest of the
variables are either binary or integer, which are
compared by using the strict equality.
The similarity function employed for them is the
following one:
()
[] []
{}
p
S
roroCSr
oIoISim
SS
≥
=∈
=
1)',(,
)'(),(
The value of p was empirically fixed to 0.8.
Basically, this function considers that two objects
are similar with respect to the features of S if the
percentage of similar features in the subdescriptions
is greater than the 80%.
For this collection, the algorithm found 379
frequent subdescriptions. Some interesting
association rules with minimal size in the antecedent
are the following ones:
• {Color in the bottom-left corner ~ Green} ⇒
{Continent ~ Africa} (12%, 60%).
That is, if the bottom-left corner of a flag is green,
with a 60% of probability it belongs to a country
of Africa.
• {Continent ~ Europe} ⇒
{Color in the bottom-left corner ~ Red}( 10%, 57%).
The 57% of the Europe’s flags have red in their
bottom-left corner.
• {Religion ~ Other Christian} ⇒
{Geographic quadrant ~ NE, Colors ~ {Red, Green,
White}} (10%, 55.6%).
About the 55% of the countries that practice
Christian Religions different from the Catholic
one, use more that 4 colors in their flags and at
least two of the them are in the set {Red, Green,
White}. Besides those countries are located in the
Northeast quadrant.
• {Continent ~ Asia} ⇒ {Number of different colors ~ 3,
Predominant color ~ Red, Geographic quadrant ~ NE}
(10.3%, 51.3%).
A high amount of the flags of the Asiatic countries
have more than 2 colors, being the red
the predominant one.
OBJECTMINER: A NEW APPROACH FOR MINING COMPLEX OBJECTS
45
• {Language ~ English} ⇒ { Geographic quadrant ~ NW,
Religion ~ Other Christian} ( 11.3%, 51.2%)
When the official language of a country is
English, we can expect that it is located in the
Northwest quadrant and it is a Christian country
but no Catholic.
As it can be noticed, most of the co-occurrences
involve the colors used in the design of the flags.
Moreover, it is also possible to find associations
between the flag's colors and both the country
religion and the country’s continent.
Countries of the world
This database was mined using 30 variables, all of
them related with geographic, people and economic
features, and a number of 177 countries. We have
applied to this collection the same similarity
function than for the Flag World.
Some interesting association rules with minimal
size in the antecedent are the following ones:
• {GDP - composition by sector_agriculture ~ 2%} ⇒
{Infant mortality rate ~ 6.7, Population below poverty
line ~ 13} (24.3%, 88%).
This rule expresses that in the 88% of the
countries where the gross domestic product is
about 2%, both the infant mortality rate and the
number of people below poverty line are relatively
low.
• {Map references ~ Africa} ⇒
{Area total ~ 622984.0 km
2
, Area land ~ 622984.0 km
2
,
Infant mortality rate ~ 103.81} (22.6%, 85%).
This corroborates that in Africa a lot of countries
are continental (do not have any area with water)
and the Infant mortality rate is very high.
• {Industries ~ {phosphate rock mining and processing,
food processing, leather goods, textiles, construction,
tourism}} ⇒
{Area_total ~ 446550.0, Area_land ~ 446300.0,
Percent of land use_permanent crops ~ 2.05 ,
Population ~ 31167783, Debt external ~ 19000.0}
(23.3%, 59.46%)
{Industries ~ {phosphate rock mining and processing,
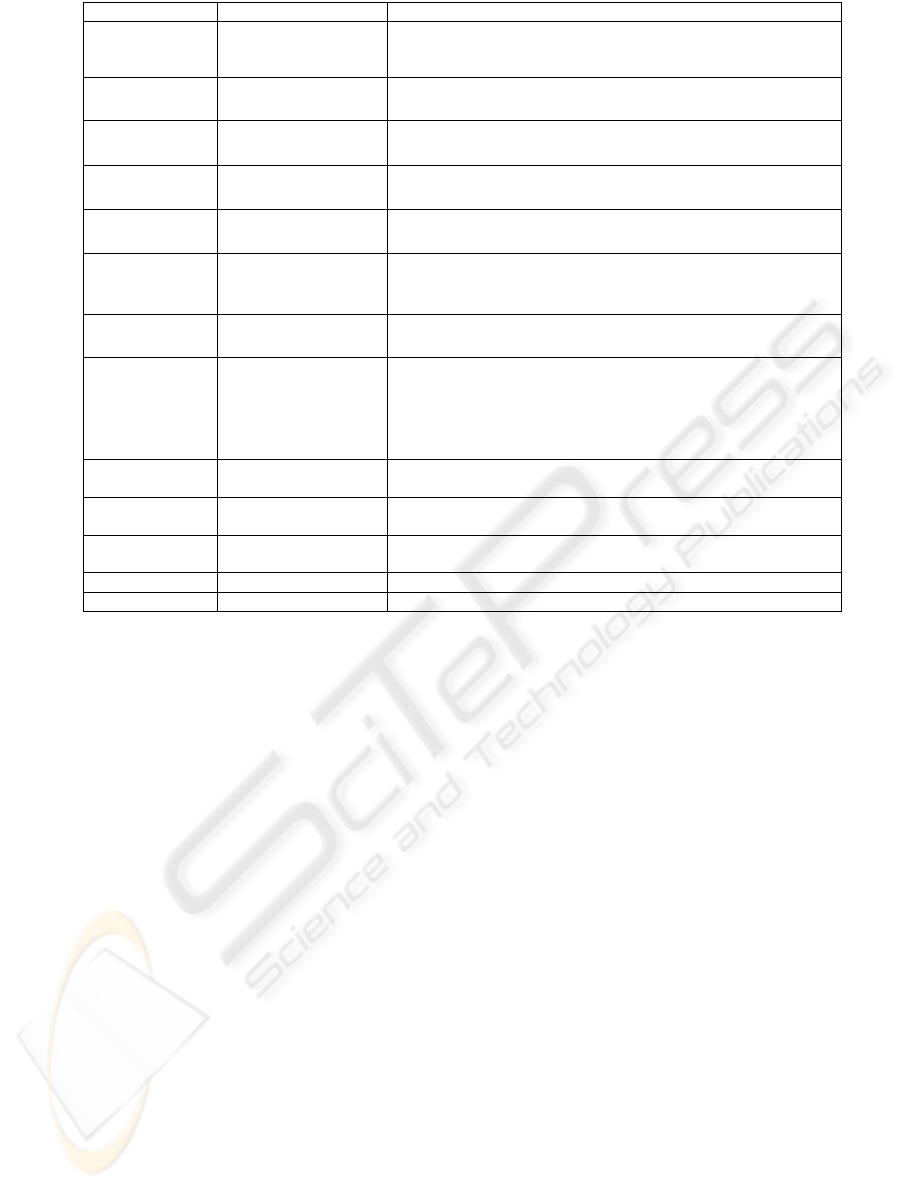
Figure 2: Flags of the World Database
Feature Domain Comparison Criterion
Continent {North America, South
America, Europe,
Africa, Asia, Oceania}
⎩
⎨
⎧
∈=
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
America}South America,{North yor x,y xif ,1
),(
Colors Set of colors (*)
⎩
⎨
⎧
=∩
=
otherwise
yx
yxC
,0
1|| if ,1
),(
Number of
vertical bars
Integer
⎩
⎨
⎧
>∈∈∧=
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
4yor x, {3,4}y or x, 0,1,2}){xy(x if,1
),(
Number of
horizontal stripes
Integer
⎩
⎨
⎧
>∈∈∧=
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
4yor x, {3,4}y or x, 0,1,2}){xy(x if ,1
),(
Number of
different colors
Integer
⎩
⎨
⎧
≠=∧=
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
2 y or x, 2 xy(x if ,1
),(
Number of sun or
star symbols
Integer
[] [] [] [ ]
[
)
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎨
⎧
∈
∈∈∈∈
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
11,y x,
or 5,10y or x, 4,2y or x, 1,1 yor x, 0,0y, xif ,1
),(
Number of circles Integer
⎩
⎨
⎧
≥∈=∧=
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
4yor x, {1,2,3}y or x, 0xy(x if ,1
),(
Predominant color *
⎪
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎧
∈
∈∈∈
∈∈∈
=
otherwise
yxC
,0
{black}y or x,
{white}yor x, orange} {brown, y or x, {blue} y x,
or {green}y or x, {red} yor x,gold}, {yellow,y, xif ,1
),(
(1)
Color in the top-
left corner
* (1)
Color in the
bottom-left corner
* (1)
Geographic
quadrant
{NE, SE, SW, NW} Strict Equality
Language *1 Strict Equality
Religion *2 Strict Equality
* {yellow, gold, red, green, blue, brown, orange, white, black}
*1 {English, Spanish, France, German, Slavic, Other Indo-European, Chinese, Arabic,
Japanese/Turkish/Finnish/Magyar, Others}
*2 {Catholic, Other Christian, Muslim, Buddhist, Hindu, Ethnic, Marxist, Others}
ICEIS 2004 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
46

food processing, leather goods, textiles, construction,
tourism }} ⇒
{Area_total ~ 446550.0, Area_land ~ 446300.0,
Population ~ 31167783, Debt external ~ 19000.0}
(25%, 72%)
These two rules states that countries with few
types of industries, which include the 5 ones
mentioned in the rules, use to have a large area,
being it mainly land, a high population, a very
high external debt, as well as a low proportion of
cultivated area.
• {Natural resources ~ {gold, copper, silver, natural gas,
timber, oil, fisheries}} ⇒ {Area_total ~ 462840.0,
Area_land ~ 452860.0, Population ~ 5172033,
Population below poverty line ~ 37%} (23.3%, 41.83%)
This rule indicates that many countries with
considerable natural resources have a high percent
of people living below poverty line.
• {Map references ~ Central America and the Caribbean}
⇒ {Infant mortality rate ~ 24.2, Life expectancy at birth
female ~ 71.25} ( 23.3%, 93.02%)
The majority of the countries of the Central
America and the Caribbean have a medium infant
mortality rate, whereas the life expectancy of the
female population is relative high. It is worth
mentioning that the algorithm has not found any
association between these countries and the life
expectancy of the male population.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents a general framework for mining
complex objects that can include either single and
multi-valued attributes of any type. The mining
process is guided by the semantics associated to
each object attribute, which are stated by selecting
the appropriate representation model. Preliminary
experimental results show the usefulness of the
proposal.
In future works, we will analyze how to measure
the relevance of the co-occurrences and the
association rules by using background knowledge
that minimizes the number of associations presented
to the user.
Moreover, there are many subdescriptions that are
similar to each other according to the user-defined
similarity function. Consequently, they are presented
to the user as different cases. Hence, it is necessary
to group similar subdescriptions and to represent
each group with a representative. For this purpose,
traditional clustering algorithms could be applied.
Finally, another application under study is the
mining of XML documents, which can be seen as
complex objects with nested structures. Here, the
problem is to deal with the hierarchical nature of
objects. This has been recently treated by the authors
in the context of text mining (Danger et al, 2003).
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R.; Imielinski, T.; Swami, A., 1993. Mining
Association Rules between Sets of items in Large
DataBases. In Proceeding of ACM SIGMOD.
Agrawal, R.; Srikant, R, 1994. Fast algorithms for mining
association rules. In Proceedings of the 20th
International Conference on Very Large Databases,
pages 487-499.
Danger, R.; Berlanga, R., Ruíz-Shulcloper, J., 2003. Text
Mining using the hierarchical syntactical structure of
Documents. In Proceeding of the 10th CAEPIA, pages
139-148.
Gyenesei, A., 2000. Mining Weighted Association Rules
for Fuzzy Quantitative Items. In Proceedings of
PKDD Conference, pages 416-423.
Han, J.; Nishio, S.; Kawano, H.; Wang, W., 1998.
Generalization-based data minimg in object oriented
databases using an object Cube Model. Data and
knowledge engineering, pages 55-97.
Hipp, J: Myka A.; Wirth R.; Günttzer U., 1998. A new
Algorithm for faster mining of Generalized
Association Rules. In Principles of Data Mining and
Knowledge Discovery.
Miller, R.J. and Yang, Y., 1997. Association rules over
interval data. In Proceedings of ACM-SIGMOD,
pages 452-461.
Savasare, A.; Omiecinski, E.; Navathe, S., 1995: An
efficient Algorithm for Mining Association Rules in
Large Databases. Technical Report No. GIT-cc-95-04.
College of Computing. Georgia’ Institute of
Technology.
Srikant, R. Agrawal, R, 1995. Mining Generalized
Association Rules, In Proceedings of Very Large
Databases.
Srikant, R., Agrawal, R.:, 1996. Mining quantitative
association rules in large relational tables. In
Proceedings of ACM SIGMOD.
Zhang, Z., Lu, Y. Zhang, B., 1997:.An effective
Partitioning-Combining Algorithm for Discovering
Quantitative Association Rules. In Proceedings of the
First Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge
Discovery and Data Mining.
OBJECTMINER: A NEW APPROACH FOR MINING COMPLEX OBJECTS
47
