
CAN AVATARS REPLACE THE TRAINER?
A case study evaluation
Ahmad Kamil Mahmood
Information Systems Research Institute, University of Salford, Salford, Greater Manchester, United Kingdom
Elaine Ferneley
Information Systems Research Institute, University of Salford, Salford, Greater Manchester, United Kingdom
Keywords:
e-Learning, avatars, learning effectiveness, interpretive case study.
Abstract: E-learning implementations have become an important agenda item for academic and business institutions
as an enabler to complement their education and training needs. However, many of the existing e-learning
systems, present several limitations such as them being static, passive and consisting of a time-consuming
set of services. This has highlighted the need for functionality, which allows more creativity, autonomy,
and flexibility on behalf of the learner. The inclusion of avatar technology in e-learning environments has
been of growing interest, aiming to encourage the learner to become more engaged and motivated whilst
augmenting the use of human trainers. However, the empirical investigations on the effect of animated
agents in teaching and learning has revealed diverse results in a continuum from avatars being helpful to
them being distracting. This research has evaluated the utility of avatars. Unusually, the research has
chosen a qualitative, interpretive approach with supporting case study data as the chosen research
methodology. The justification for this research approach will be made and the initial findings will be
presented together with a proposed conceptual framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computers and electronic media are key to today’s
learning environments and have been widely used to
support teaching and learning (Somekh 2000). E-
learning implementations have received a growing
exposure with many academic and commercial
organisations utilising them to support strategic
initiatives regarding the effective delivery of their
educational systems. E-Learning approaches have
brought in great benefits to the whole educational
domain (Sun, Williams et al. 2003). For the
academic institutions, e-learning is viewed as an
important tool to help them offer educational and
administrative support that is accessible, user-
friendly and responsive to the learners. This
flexibility is assumed to benefit both the learners and
the institutions in many ways such as learning at the
learners’ pace (Honey 2001; Picciano 2002), saving
on travelling and hotel expenses.
This paper will examine the application of
avatars,
computer representations of users, in e-
learning environments (Murch and Johnson 1999).
The research aims to provide additional insights into
the learners’ views and values of avatars in the e-
learning environment, by using a qualitative
approach, which may produce additional insight into
users' perceptions and requirements of avatars. The
underlying epistemology for this research has been
interpretivism, and the focuses has been on the
complexity of human sense making as the situation
emerges (Kaplan and Maxwell 1994). It is hoped
that the outcomes of these phenomena will be useful
to the practitioners and researchers of courseware
and avatar development. These will be in the form
of a synthesized contribution of rich insight of
phenomenal events leading to a proposed framework
or of guidelines for avatar design and
implementation in e-learning environments. In
addition, the research aims to enrich the awareness
of factors affecting e-learning effectiveness and
demonstrate the value of research using interpretive
analyses in the Information Systems (IS) field.
The paper is structured as follows. It begins with
a brief i
ntroduction of e-learning and avatars,
followed by the research method and design. An
208
Kamil Mahmood A. and Ferneley E. (2004).
CAN AVATARS REPLACE THE TRAINER? - A case study evaluation.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 208-213
DOI: 10.5220/0002639102080213
Copyright
c
SciTePress

illustrative set of research findings are then
presented using an interpretive, qualitative case
study followed by a brief discussion. The paper ends
with proposals for future research directions.
2 E-LEARNING TECHNOLOGIES
E-Learning has been defined in many different
ways, one of which learning using the internet as
well as other forms of electronic media (Rosenberg
2001; Fallon and Brown 2003). It is claimed that this
flexibility lets the courseware be delivered to the
learners in a way that is most suitable for their
learning style, time and place of preference
(Rosenberg 2001). E-learning systems are a
collection of tools for online courseware
presentation with various optional customisation
capabilities (Fallon and Brown 2003). Agent
technology – both embedded within the technology
or embodied as an avatar representation - has been
proposed to explore the possibility of releasing the
instructor’s time and assisting the learners with
specific learning needs (Jafari 2002). With avatars, it
is expected that learners will be able to interact
visually with emotional context and state, simulating
continuous instructor presence in e-learning
environments (Fabri and Moore 2002). Whilst this is
a prime intention for incorporating such technology,
to some learners, animation is annoying; for
example – flashing graphics, like Clippit™ available
in Microsoft Office, may divert attention from the
content of a page and hence hampered the learning
process (Dehn 2000; Bouras and Philopoulos 2001;
Tversky, Morrison et al. 2002). In addition, some
commented that they are lacking in pedagogical
value, for instance, there is no clear evidence that
they can enhance the flow of communication (Dehn
2000; Moundridou 2002). As such, the incorporation
of avatars in e-learning systems and their
contribution to the efficiency and effectiveness of
learning continues to be an open research agenda.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research on the effectiveness of e-learning in
general and avatars in e-learning in particular, is
relatively new, and very little is known about their
effectiveness compared to traditional classroom
education (Piccoli, Ahmad et al. 2001). The
researcher is interested in understanding the
meaning, values and views of the learners with
respect to avatars, namely how this technology
makes sense to both the learners’ learning
experiences and the lecturers’ teaching practices
which will lead to a description of patterns or themes
relevant to this study. Since this research focuses on
the use of avatars by the learners and instructors in a
single case study, the setting for this research is a
specific social interaction between them rather than
the examination of a social situation or community
over time (Miles and Huberman 1994). The
fundamental nature of this research study is
interpreting human action and perceptions, and the
researcher acknowledges the need for an
epistemological and methodological approach that is
interpretive and qualitative in order to explore and
understand the situation through a case study. This
research focuses on the complexity of human sense
making as the situation emerges and attempts to
understand phenomena through the meanings that
people assign to them (Walsham 1995). Interpretive
research can help IS researchers to understand
human thought and action in social and
organizational contexts; it has the potential to
produce deep insights into information systems
phenomena including the management of
information systems and information systems
development (Klein and Myers 1999). Empirical
studies, which collect data on stakeholder views, can
be broadly classified as ‘interpretive case studies’.
Qualitative methods of data collection, which
involved in-depth interviews and participant
observation, have been used, and the hermeneutic
mode of analysis has been applied to the data.
The research site, which took place in July-
August 2003, was at the private University
Technology PETRONAS in Malaysia, where an e-
learning facility has been established. The users
were familiar with avatar technology such as
Microsoft Assistants including Genius™, FI™ and
Clippit™ which were installed on every PC in the
campus as their personal assistant should they face
any difficulties in using the applications. In addition,
some of the interviewees were even more advance
having interacted and explored this technology by
installing avatars of their choice on their own PC or
laptop.
The data collection tasks were conducted with
appropriate preparation and strategy to ensure
efficiency and validity. In-depth interviews were the
primary data source in this study, additionally
meetings, direct observation, and documentation
were used. The guidance, as outlined by Walsham
(95) on the nature and method of conducting
interpretive case studies in IS research was a useful
reference point especially when conducting the
CAN AVATARS REPLACE THE TRAINER? A CASE STUDY EVALUATION
209
empirical work and generalizing from the
interpretive research (Walsham 1995). An interview
template was constructed as an instrument to guide
and maintain the discussion. In most cases, active
interviewing as suggested by Holstein was assumed
with the researcher furnishing precedence,
incitement, restraint and perspective as the interview
proceeded (Holstein and Gubrium 1995). The aim
was not so much to capture the representativeness of
the population but rather to continuously solicit and
analyze representative horizons of meaning centered
on the “hows” of meaning as well as the “whats” of
interviewees’ experiences. Twenty-six interviewees
were involved in twenty-one separate sessions. The
interviewees were asked to give feedback on their
comments and some of the statements from certain
interviewees were presented to other interviewees to
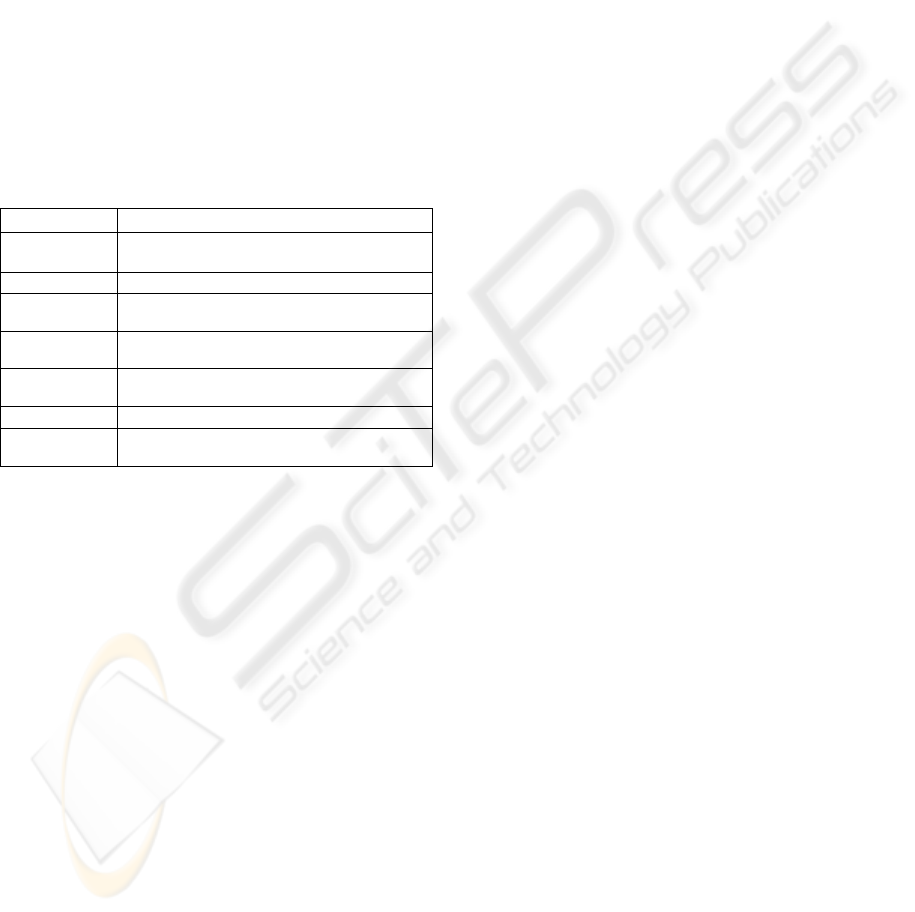
obtain their reaction. Figure 1 shows the details of
the interview activity that took place.
Number of
interviewees
26 (14 Undergraduate, 6 Post Graduate and
6 lecturers)
Length 1 – 2 hours
Number of
sessions
21 (18 single interviewee sessions, 3 multiple
interviewees sessions)
Type of
interview
Informal with mixed of and unstructured and
semi-structured interviews.
Techniques of
interview
Open ended and close-ended questions
derived from the research questions.
Location University meeting room.
Setting Audio and video facility for recording
purposes and demonstration of avatars
Figure 1: The Interview Activity
During the data analysis phase, transcriptions of
the interview data were coded by categories based
upon the researcher’s interests, the existing literature
on e-learning environments, and impressions gained
during the interviews themselves, which arose out of
the data. As highlighted by Walsham (Walsham
1995), “Interpretive researchers are not saying to
the reader that they are reporting facts but rather
they are reporting their interpretations of other
people’s interpretations” (p.109). In addition to the
guidelines by Walsham, Klein and Myers
proposition of a set of principles for conducting and
evaluating interpretive case studies in information
systems were used to guide this study (Klein and
Myers 1999).
4 CASE STUDY FINDINGS
The research presents a detailed analysis of avatars
in e-learning environments by case study, it
highlights a number of key findings but only one
aspect, namely the roles of avatars is partly
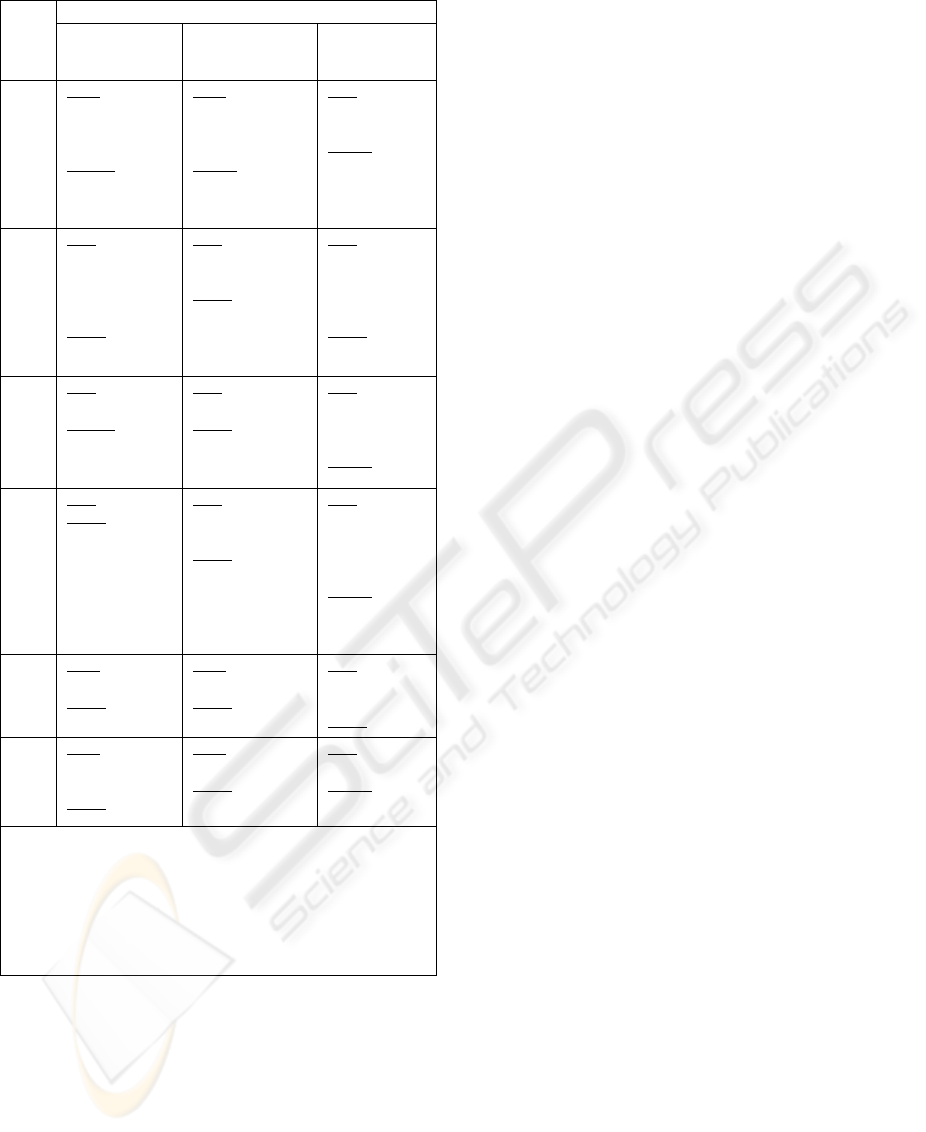
presented here. Figure 2 shows a role-ordered
matrix, which highlights the users’ view of potential
different roles that could be taken by avatars, which
may benefit them in e-learning environments.
Paraphrases, which incorporated both the positive
and negative issues, were developed.
Traversing the columns of the matrix, beginning
with the lecturers’ column, the lecturers who used
this technology suggested that they were willing to
delegate the laborious, “low risk” tasks like
searching for academic and administrative
information and replying to none crucial e-mail or
phone calls to avatars. They were of the opinion
that existing avatars could play a greater support
role in e-learning so as to allow them to spend their
time undertaking more valuable and quality
activities such as research, consultancy and
supervisory tasks. On the other hand, there were
some issues raised by the lecturers who were quite
reluctant to recognize certain potential roles of
avatars. They perceived that such avatars pose a
potential threat to their teaching career and might
affect their social lecturer-student relationships.
Others felt that this technology was troublesome,
time consuming and merely a cosmetic, which will
not simplify the already heavy workload. However,
should this technology be developed to
complement and enhance the role of the lecturers,
the avatars' roles may be considered as beneficial,
provided that their expertise was well protected and
their style and mode of teaching were within their
control.
Moving across to the postgraduate column, the
learners call for more roles to be played by avatars
namely the roles of both lecturer and advisor.
However, these roles emerged with a condition that
the avatars are able to serve them effectively and
efficiently, not merely by their being attractive,
expressive and human. One of the interviewees
commented “To me when I look at MS Clipper, it is
just like any other icon and I don’t really care how it
looks. The most important thing is whether it can
fulfil my requirement. If it can’t, no matter how good
it looks, I am not going to use it. Look is not
important – it is the practicality, speed and quality
of response that count…”
Moving on to the undergraduate column, the need
for avatars to assume additional roles such as student
counselor and lecturer was highlighted. It was
proposed that these roles would help them overcome
feelings such as shyness and inferiority, by engaging
with a more open, informal environment - one of
virtual communication with the avatar. This group
views avatars optimistically and looked forward to
more assistance and guidance through this
technology in the near future. Similarly, as with
previous groups, it is the quality of the services that
ICEIS 2004 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
210
matter to them most rather than the look. One of the
interviewees stated“To me the main thing is
efficiency, because I don’t judge a book by its cover.
If it has a good look but it does not give any learning
benefit, it is good for nothing. The first priority is the
efficiency, then come the graphics.”
Moving down the table to focus on the various
potential roles of avatars that emerged from the
interviews, as mentioned above, the interviewees are
generally more concerned with quality of service for
each role rather than the graphical look of the
avatar's representation in the e-learning
environment. The users cross-referenced quality of
service to information usefulness, details, currency
(up to date), accuracy, response time as well as the
presentation of lessons to the users. One of them
stated, “To change the representation cosmetically,
won’t help, whether the representation is in 3D or
2D, Caucasian or Asian look…it makes no different.
It’s the quality of help that is important.”
Type of Users
Avatar
Roles
Lecturer
(6)
Post Graduate
(6)
Under
Graduate (14)
Personal
Assistant (PA)
Pros: Routine
laborious tasks.
Answer the
FAQ.
Issues: Don’t
‘over ruled me’
Pros: Search
material in a
more efficient
way
Issues:
Prompt &
effectiveness.
Pros: Quite
optimistic and
look forward.
Issues:
Accurate
search engine
based on my
interest.
Tutor/
Demonstrator
(PT)
Pros: Explain in
different ways.
To complement
me in my
absence.
Issues: nil
Pros: Useful
when learning
new software
Issues: Not
impressed by
looks but service.
Pros: 24/7
service,
interactive,
guiding
assignments”
Issues: Sustain
the learner’s
interest.
Lecturer
(L)
Pros: Help new
lecturer
Issues: Will be
a threat.
Can’t beat F2F.
Pros: Able to get
quick advice.
Issues: Work for
kids, but not
adults.
Pros: one to
one. May
overcome
shyness
Issues:
Social ability.
Counselor/
Advisor (C)
Pros: nil
Issues: May
sacrifice
student-lecturer
relationship
Pros: Advice on
general research
matter
Issues:
Experience
count.
Pros: Advise
on career
opportunity &
personal
matter
Issues:
Knowledge
first then
appearance.
Peer (P)
Buddy
Pros: nil
Issues: nil
Pros: nil
Issues
: nil
Pros
:
Companion
when lonely
Issues
: nil
Enter-
tainer
(E)
Pros:
Nice when get
bored
Issues
: nil
Pros:
nil
Issues
: nil
Pros
: nil
Issues:
nil
PA = Searching for academic information, reminder, reply e-
mail.
PT = Tutoring, error identification, demonstrate, experiments.
L = Q & A, clarification, conceptual & motivational discussion
etc.
C = Give advice on the academic matters.
P = Quick confirmation/reference, social chatting/discussion.
E = Virtual entertainer during free hours – relax
When questioned further about the graphical look
of the avatar representation, the cultural influence on
look and feel was not of primary concerned, no
preference was identified Asian or Caucasian
characteristics. In addition, an avatar's presence
should add value to the learning process by
improving interaction and simplifying steps towards
understanding the subject matter faster and more
easily. When asking about the social personality of
avatars in assuming their roles, the users expressed a
desire for avatars that used a more informal, friendly
language, communicating at the intellectual level of
the user, again taking into account the user’s profile
and preference. The users, nevertheless, will not
treat avatars as humans even though they incorporate
elements of social characteristics such as the ability
to communicate through voice and emotional facial
expression. Avatars are perceived as a tool for
learning and will remain as a “machine” despite the
social features embedded within them.
5 DISCUSSION
The key findings of the interviews showed that users
prefer to have interactions with avatars and their
various supporting roles; unique user profiles were
the key to avatar acceptance; avatar service quality
is of utmost importance. The aim of this paper was
to explore the users’ views of the role of avatars in
supporting e-learning environments. The results
have shown that the interviewees’ views vary with
respect to the roles of avatars and that they were not
driven by technology sophistication. Avatar
personae whether male or female, Asians or
Westerners, 2D or 3D, human or caricature were of a
secondary importance. User requirements also
focused on the quality of service that the avatars
could offer - they would vary according to the users’
profiles.
Figure 2: Role Order Matrix
The above essentially explains why there exists
the diverse views of animated agents in teaching and
learning which is in a continuum from avatars being
helpful to distracting as found in various empirical
investigations (Dehn 2000; Bouras and Philopoulos
2001; Tversky, Morrison et al. 2002; Baylor and
Ryu 2003). Distraction and annoyance was caused
CAN AVATARS REPLACE THE TRAINER? A CASE STUDY EVALUATION
211
by the inappropriate roles and behaviour, which has
lead to the rejection of avatars by some users.
Should the role and behaviour be appropriate, taking
into account the users’ profile, the result would
probably be more conclusive as to who rejects or
accepts avatars and why. Hence, from then on detail
fittings of avatars could be incorporated according to
the users needs and preferences. This paper
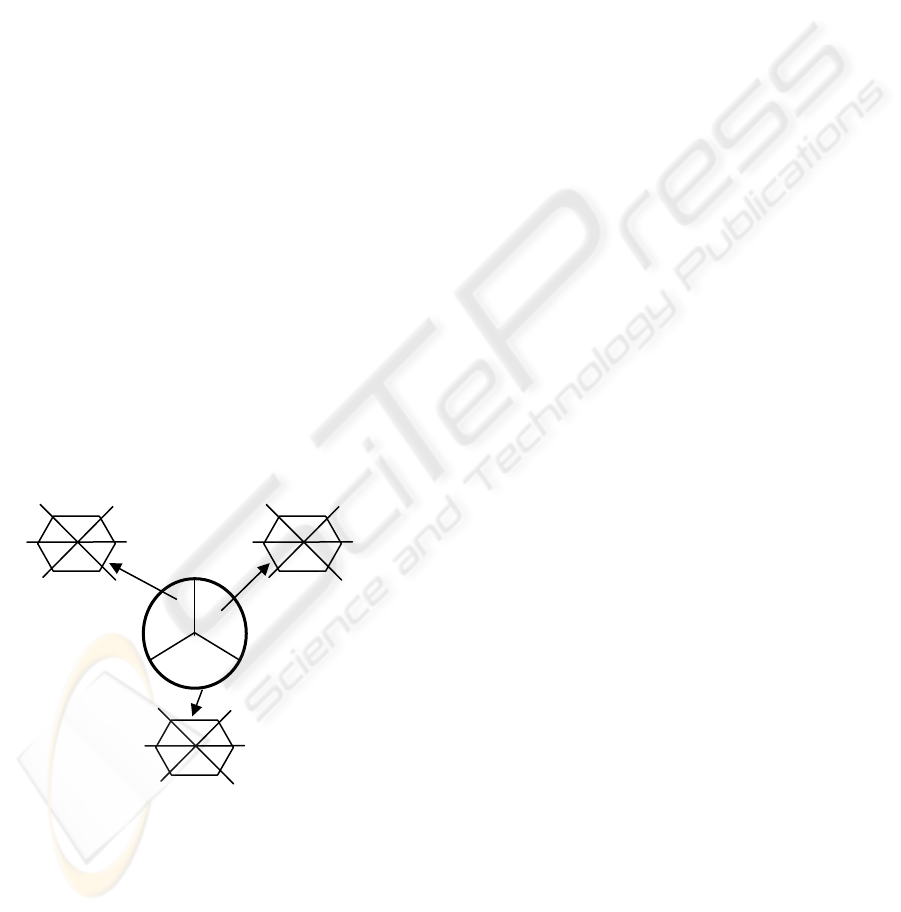
proposes a conceptual framework of avatars'
“chemistry” in e-learning environments, integrating
the three key elements that emerged from the above
findings namely the avatars’ roles, service quality
and user profiles, shown in Figure 3.
The three-axis circle in the middle depicts the
three core elements mentioned, each with its own
attributes. The first is the roles taken by avatars, as
highlighted in the previous section, which outlined
the six relevant roles of avatars in the e-learning
environment. While these roles were vital in this
case study as viewed by the interviewees, they were
by no means final and absolute as they only emerged
from this single case study. Additionally, these roles
vary in their degree of relevance and usefulness,
which very much depends on the user needs.
Nevertheless, the inclusion of these roles in the
framework will facilitate the development of
appropriate avatars that may serve the user. The
framework uses hexagons to represent the six roles
of the avatar, as the symbol allows for future
expansion without difficulty in the event that more
roles may emerge or be eliminated as the study is
undertaken.
L
Figure 3: A conceptual framework of avatars’
“Chemistry” in the e-learning
The second element, namely user profiles,
comprise of users’ interests, preferences, life
experience, learning styles and customs, all of which
are unique to an individual learner that has made his
learning experience a personal journey. Over a
period, the learners develop the ways they prefer to
receive, process and present information and ideas,
known as their learning styles (Ayre and Nafalski
2000). For instance, some people find it easier to
understand a new concept by reading a textbook,
whilst others prefer a verbal explanation. Likewise,
people may vary in how they most effectively
demonstrate their understanding whether
graphically, verbally or in writing. The matured
formation of this learning style has then become a
custom in that it influences the learner’s interest and
preferences. All these factors are usually within
contexts that need to be accounted for and have been
identified as parts of the avatars’ elements. Again,
these factors were by no means final and
comprehensive as they were only discovered from
this single case study.
The third element, which is no less important, as
identified in this case study, is the service quality of
the avatars in the e-learning environment. This
element, which appears in many research papers
(Dehn 2000; Baylor and Ryu 2003) as quantitative
measurements, has continued to be an essential
element comprising of efficiency, effectiveness,
responsiveness, friendliness, and the informal-casual
personality as well as a fulfilling service that the
avatars could offer. Even though this case study did
not measure the elements quantitatively, the learners
mentioned them in a number of instances during the
interview indicating that they continue to be
imperative. Nevertheless, it is believed that
discounting the first two elements within this
framework would not make the avatars capable of
satisfying the users’ needs.
There are a number of implications arising from
the above framework and two of them will be
highlighted here. At the individual level, recognizing
the varying needs and expectations of the learners
makes avatar development very challenging for the
future. Avatars should be designed in such a way
that they are highly adaptive, flexible and
customisable in order to suit the learners’ needs,
preferences, styles and customs. The lecturers’ needs
would have additional challenges, one of which was
to complement and to assist the lecturers inside and
outside the classroom settings. This would certainly
be a unique situation for each lecturer who would
expect different level of assistance at different times
driven by the needs of the learners. This three-way
relationship would be an interesting research
opportunity and challenging tasks lie ahead for
avatars’ design and development in this area.
Informal Lecturer
Efficient Tutor
At the organizational level, organizations that
have a vision towards embedding this technology in
their e-learning environments, should take into
consideration their overall e-learning goals and
strategies regarding how much this technology
delivers value to their business. Ultimately, the
organization may look from an IS quality
Custom
Preference
Interest
ife Experience
Learning
Style
Life Exposure
Roles
User
Profiles
Service
Quality
PA
Counsellor
Buddy
Entertainer
Friendly
Responsive
Fulfilling Effective
ICEIS 2004 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
212
perspective in order to value the worthiness of this
innovation with respect to the overall organizational
value systems so as the benefits of this innovation
can be thought-out. The notion of IS quality as
proposed by Vidgen and Wood-Harper would be
appropriate to these situations to place emphasis on
user views of quality on top of production views of
quality (Vidgen, Wood-Harper et al. 1993).
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper addresses the roles of avatars, which has
emerged from a case study investigation. The roles
of avatars have been presented as a supporting tool
to enhance e-learning services to users. Avatar
services have been explored with the aim of
evaluating the more advanced features available to
e-learning users. Exploiting the characteristics of
avatars, such as autonomy and social ability is likely
to fit well within an overall e-learning framework.
Moreover, the quality of interaction and services are
expected to be more interesting to the users which
may lead to effective and efficient learning provided
that the agents behavior or interaction are based on
user profiles. Full exploitation of avatar technology
is expected to increase user satisfaction. This paper
has also demonstrated that a qualitative, interpretive
approach utilizing in depth case study analysis as the
chosen research methodology was able to help the
researcher to explore and understand the users’
views on avatar roles, both socially and culturally in
e-learning environments. The future work is directed
towards the full implementation of avatars in e-
learning environments but many prerequisites have
to be explored as avatar interaction involves not only
technical challenges but also requires study of the
psychological, social and cultural backgrounds of
users.
REFERENCES
Ayre, M. and A. Nafalski (2000). Recognising Diverse
Learning Styles in Teaching and Assessment of Elec.
Engineering. 30th ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education
Conference, Kansas City, MO.
Baylor, A. and J. Ryu (2003). "Does the presence of image
and animation enhance pedagogical agent persona?"
Journal of Edu. Computing Research
28(4): 373-395.
Bouras, C. and A. Philopoulos (2001). "e-Learning
through distributed virtual environments." Journal of
Network and Computer Applications. 24
Dehn, D. M. (2000). "The Impact of Animated Interface
Agents: A Review of Empirical Research." Int. Journal
Human-Computer Studies 52: 1-22.
Fabri, M. and D. J. Moore (2002). Face Value: Towards
Emotionally Expressive Avatars. HCI 2002.
Fallon, C. and S. Brown (2003). e-Learning Standards: A
guide to purchasing, developing and deploying
standards - conformant e-learning. Lon, St Lucie
Press.
Holstein, J. A. and J. F. Gubrium (1995). The Active
Interview. Qualitative Research Methods SERIES 37.
London, Sage Publication.
Honey, P. (2001). Learning styles - the key to personalised
e-learning, Peter Honey Learning. Retrieved Dec 7
2002 from
http://www.peterhoney.com/article/66.
Jafari, A. (2002). "Conceptualising Intelligent Agents For
Teaching and Learning." Educause Quarterly
3.
Kaplan, B. and J. A. Maxwell (1994). Qualitative
Research Methods for Evaluating Computer
Information Systems. Evaluating Health Care
Information Systems: Methods and Applications. S. J.
Jay. Thousand Oaks, CA, Sage: 45-68.
Klein, H. K. and M. D. Myers (1999). "A Set of Principles
for Conducting and Evaluating Interpretive Field
Studies In Information Systems." MISQ
23(1): 67-94.
Miles, M. and A. Huberman (1994). Qualitative data
analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA, Sage.
Moundridou, M. (2002). "Evaluating the Persona Effect of
an Interface Agent in an Intelligent Tutoring System."
Journal of Computer Assisted Learning,
18(2).
Murch, R. and T. Johnson (1999). Intelligent Software
Agents. New Jersey, Prentice Hall PTR.
Picciano, A. G. (2002). "Beyond Students Perceptions:
Issues of Interactions, Presence, and Performance in
an Online Course." Journal of ALN
6(1).
Piccoli, G., R. Ahmad, et al. (2001). "Web-Based Virtual
Learning Environments: A Research Framework and
a Preliminary Assessment of Effectiveness in Basic IT
Skills Training." MIS Quarterly
25(4).
Rosenberg, M. J. (2001). E-Learning: Strategies for
Delivering Knowledge in the Digital Age. NY,
McGraw Hill.
Somekh, B. (2000). "New Technology and Learning:
Policy and Practice in the UK, 1980 - 2010."
Education & Information Technology
5(1): 19-37.
Sun, L., S. Williams, et al. (2003). Knowledge
Construction in E-Learning: Designing an E-Learning
Environment. Fifth Int. Conference Enterprise
Information Systems (ICEIS 2003), Angers,
FRANCE.
Tversky, B., J. B. Morrison, et al. (2002). "Animation: can
it facilitate?" International Journal of Human-
Computer Studies 57(4): 247-262.
Vidgen, R., T. Wood-Harper, et al. (1993). "A Soft
Systems Approach to Information Systems Quality."
Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems
5.
Walsham, G. (1995). "Interpretive case studies in IS
research: nature and method." European Journal of
Information System 4(2): 74-81.
CAN AVATARS REPLACE THE TRAINER? A CASE STUDY EVALUATION
213
