COMPOSITION OF WEB SERVICES IN THE ICS
ARCHITECTURE
C. Roberto Baluz, S. Labidi, R. F. Tomaz, B. Wanghon and Nathália R. S. Oliveira
Eletrical Engineering Department, Federal University of Maranhão, Campus of Bacanga, São Luís-MA, Brazil
Keywords: Web Services, Semantic Web Services, Web Service Composition, Semantic Web, Ontologies.
Abstract: This paper proposes the use of the Web Services Composition to enhance the matchmaking process
acctually in use within the ICS (Intelligent Commerce System), a Business-to-Business e-commerce system.
The actual matchmaking process used in the ICS considers only single services and may return a high
number of false-negative results. The new approach aims to reduce the number of false-negative results
through the composition of existing single services to obtain new functionality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Web Services are transforming the web from a
collection of static pages to a web of dynamic
service providers that automatically discover
information that we seek, negotiate on our behalf for
goods we intend to purchase, gather information
from different sources, and fuse it into coherent
forms. Nowadays, Web Services are discovered and
invoked manually by human users (hard code
approuch), limiting their ability to take advantage of
opportunities that may exist. This investigation
represents an effort to overcome these limitations.
In this paper, we show the Web Services
composition process in the ICS context as an
alternative to reduce the number of negative results,
returned by the Matchmaker agent, responsible for
the matching of negotiating agents in the ICS.
Actually the Matchmaker agent ignores the
possibility of the salers agents combine theirs
capacities to attend a solicitation from a purchaser.
As a result of this limitation, even if there is the
possibility of attending the service by the agents
present in the negotiation environment, the
Matchmaker agent returns a denial of service (false
negative) to the requesting user.
The main contribution of our work is to improve
the matching process of agents within the ICS,
increasing the number of matching results returned
by the Matchmaker agent.
In the next section, we present an overview of
the ICS architecture. Section 3 describes three
motivating scenarios for our work. Section 4 shows
the actual matchmaking procedure used in the ICS
and emphasizes our contribution to enrich the
matchmaking process. Finally, section 5 presents our
conclusion.
2 OVERVIEW OF THE ICS
ARCHITECTURE
Aiming to describe the context of our work, we
present a brief high level vision of the ICS project.
The ICS is a Agent-Oriented implementation of
a Business-to-Business e-commerce system, where
the trading agents, representing purchasers and
salers, work in an open environment as the Internet,
moving through the network to meet at common
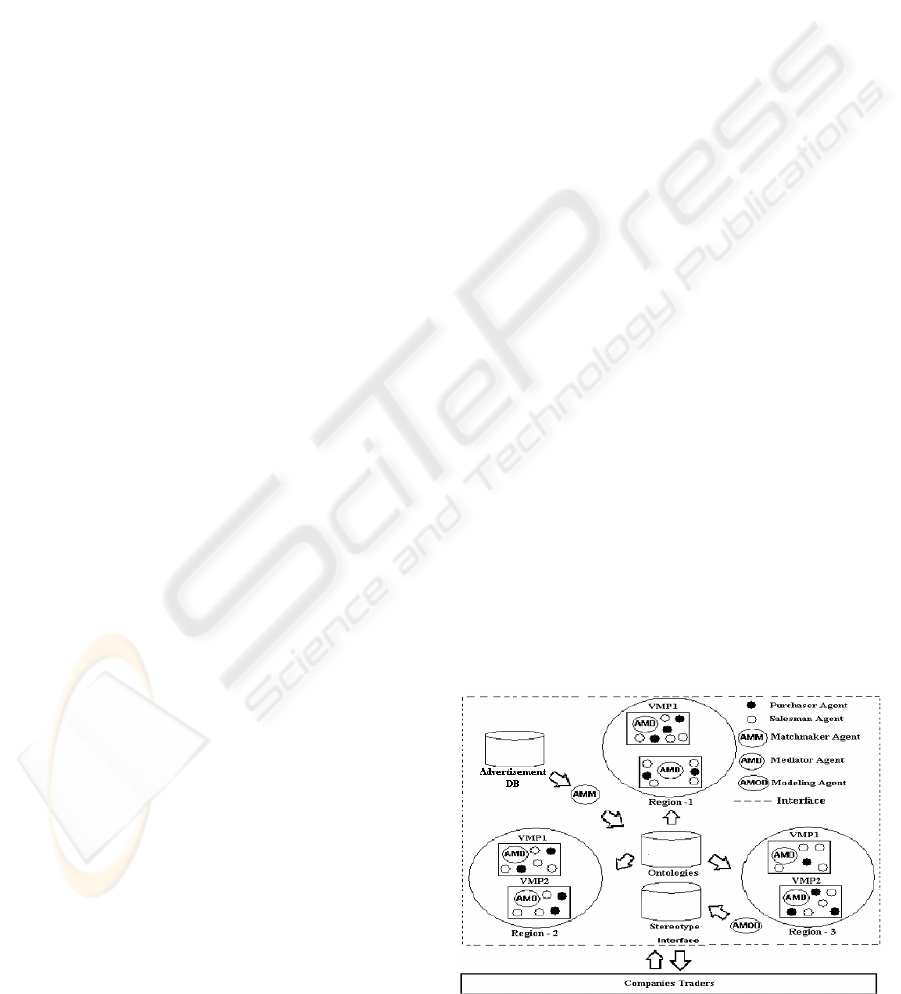
Figure 1: The ICS Enviroment
435
Roberto Baluz C., Labidi S., F. Tomaz R., Wanghon B. and R. S. Oliveira N. (2004).
COMPOSITION OF WEB SERVICES IN THE ICS ARCHITECTURE.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 435-438
DOI: 10.5220/0002645004350438
Copyright
c
SciTePress

negotiation areas. (Labidi et al., 2003)(Tomaz, 2003)
The main ICS components are: Virtual
Marketplaces (VMP), Regions, Matchmaker Agent,
Mediator Agent, Modeling Agent, Ontologies
Repository and Stereotype and Advertisement
databases as it showed figure 1.
The Virtual Marketplace (VMP) is the place
where the agents carry through the negotiation and
the closing of the contract. A Region is an
abstraction of higher level than the VMP that
provides a vision of grouping of virtual markets that
are operating on the same domain ontology, that is,
acting in the same area of business (vehicles,
remedies, books etc).
An Ontologies Repository is a semi-structured
database that allows the storing of the domain’s
ontologies. The ICS is not limited to operate in a
specific business domain. The stereotype database is
a semi-structured database that allows the storing of
the users profile. It is used by the traders agents to
deliberate on the preferences of the companies they
are representing. The advertisement database is a
semi-structured database that allows the storing of
the salers’ advertisements.
The Matchmaker Agent objectives to approach
trader agents with complementary objectives, that is,
it is the responsible for the composition of the VMP.
The Mediator Agent operates as an arbitrator
inside of a VMP, it follows each carried through
transaction and intervenes when necessary trying to
decide problems of negotiation, formation and
execution of contracts. For each Virtual Market
there is an instance of the Mediator Agent.
A Traders Agents can be a purchaser or a
salesman. These agents are triggered for the using
companies of the ICS from its WEB interface.
The Modeling Agent objectives to inform the
Mediator Agent of the preferences of each Trader
Agent so that the Mediator Agent can interact in a
particular way with each Trader Agent.
This section presented a high level vision of the
ICS architecture. In the next section we present two
motivating scenarios for the development of our
work.
3 MOTIVATING SCENARIOS
With the objective to give a better understanding of
our investigation, we present here two scenarios that
show how the composition of services can enrich the
actual matchmaking procedure used in ICS.
Suppose three services represented by Web
Services: (i) an airplane tickets agency; (ii) a hotel
chain and (iii) a transportation firm, all operating
globally. Consider that all the services are descripted
in a services description language like DAML-S
(DAML-S,2003) and published in a UDDI directory
service (Daum, 2002), as (Paolucci, 2002) proposes.
If a client wishes to buy a full travel package, a
matching service that doesn’t use the services
composition techniques will return that there isn’t a
service that satisfies the client’s request. However, a
matching engine that is capable to use the services
composition will promote the sum of the individual
capacities of each service to satisfy the client’s
needs.
Another example of Web Services composition
is presented by (Sirin, 2003). The example deals
with the composition of the capacities of an on-line
language translator and a dictionary service. The
language translation service translates texts between
various pairs of languages, the dictionary, however,
returns the meaning of words in english. If the user
needs the service of a french dictionary, neither of
the services alone will satisfy this demand. But
together the services are capable to attend the
request – the french text is passed as input to the
language translation service, who returns as output
the text in english. This output is passed as input to
the english dictionary service to obtain synonyms
and then translated back to french.
To provide the semantic concepts as “language”,
“english”, “french”, etc. we can use ontologies,
(Guarino,1998) now used in the construction of the
Semantic Web.
In the next section, we’ll give a brief description
of the matching procedure actually used in ICS,
concentrating on how the Web Services composition
could enrich it.
4 ENHACED MATCHMAKING
PROCESS
The Matchmaker agent in the ICS restricts itself to
compute the degree of similarity (distance) among
purchasers’ requests and salers’ advertisements. As
result, it returns a binary match-pairs list (or record-
match list), which contains the possible matching
among customers and suppliers (a set of clusters).
When the Matchmaker agent is asked to make a
search for a purchaser agent, this will be done inside
an advertisements database. The matchmaker looks
for possible single saler agents that satisfy the
searches requests and returns the possible partners
salers agents.
An important requirement for the Matchmaker
agent is the search flexibility. The search for
partners should not be restricted to the syntax aspect
only. This is because equivalent terms incorporated
in more generic concepts (subsumption), as well as
ICEIS 2004 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
436

terms having some relationships (such as
aggregation, synonymy, antinomy, etc.), must be
considered in the matchmaking process. The figure 2
displays the ICS Matchmaking process.
Purchasers and salers use DAML-S to express
requests and advertisements respectively. The
DAML-S parser extracts inputs, outputs and pre-
conditions from DAML-S requests and
Advertisements.
The Matchmaker Agent, made by the semantic
matching engine and DAML-S Parser, classifies and
crosses the requests inputs, outputs and pre-
conditions to the advertisements inputs, outputs and
pre-conditions. The ICS reasoning server,
implemented by a Description Logic reasoner
(Tomaz,2003), supports the classification of
taxonomy of the terms found in the inputs, outputs
and pre-conditions based on the application domain
ontology.
To maintain compatibility with the
advertisements repository structure, and the parser
capabitlity, a composed service must also use
DAML-S. In fact, a composed service entry is
exactly the same as the entry of a single service. The
composition plan – a description of wich ones and in
what order the single services will be grouped to
form the composed service - is stored in other
repository, the Composition Repository. With this
compatibility, no alteration is needed in this part of
the matchmaking process to make it use composed
services also.
When a composed service is chosen by the
Matchmaker Agent is that the first difference in the
actual process appear, but now under the control of
other agent, the Composer Agent. Instead of the
salers agent that form the composed service, it is the
Composer Agent that is warned when a composed
service is found adequate. The Composer Agent then
warns the salers agents, as the Matchmaker Agent
does, and then passes the composition plan to the
Mediator Agent, wich will be responsible for
realizing the business.
Figure 2: The ICS Architecture (Tomaz, 2003)
There are several approaches for the
development of the matchmaking algorithms.
Nevertheless, DAML-OIL is greatly influenced by
the description logics languages. That’s why, we
proposed, in our work, the use of algorithms based
on description logics (DL) languages.
A limitation of the actual matching procedure
used in ICS is that the matchmaker agent, which is
responsible to gather the negotiating agents, ignores
the possibility to compose the capacities of the salers
agents to satisfy the requests of the buyers that are
passed as parameters to it. The matchmaker simply
compares the buy requests of each one of the
advertisements published in the advertisements
repository, so that if none of them presents some
degree of similarity with the buying parameters, the
matchmaker returns an empty list (a void binary
match-pairs list).
Fi
g
ure 3: Web Com
p
osition on the ICS matchin
g
p
rocess.
Figure 4. Composition Plan
COMPOSITION OF WEB SERVICES IN THE ICS ARCHITECTURE
437

We propose the use of the Temporal Workflow
technology (Labidi et al., 2000) to model a semi-
automatic service composition tool within ICS. This
tool has a GUI (Graphical User Interface) that
allows the user to compose a new service from the
available services in the advertisement repository.
To illustrate this, let’s take the second example
presented in section 3 – Motivating scenarios.
The advantage of the use of the ICS Composer is
that, from a restrict set of services published in the
advertisement repository, a user can create a vast
number of new services that enriches the
environment and increases the possibility of
satisfaction of the requisites given by the buyers,
what increases also the number of accomplished
business in the ICS. As it is shown in figure 4, to
make the service composition it is necessary that
there is communication between them. We propose
the use of the SOAP protocol to allow each service
to pass its output as an input parameter to other
services.
After the composition of the new service from
the previously stored services of the advertisement
repository, the user must also describe its capacities.
We propose the use of the DAML-S as the
description language of the services capacities. Each
new service represents a new entry in the
advertisement repository and also a new entry in the
composition plans repository. When a composed
service satisfy the requisites of a buyer, the
Composer Agent consults the composition plan in
the composition plans repository and executes it,
receiving and sending the parameters of each one of
the simple services that constitutes the composed
service until it fulfills its objective described in the
capacities of the composed service. As figure 3
shows.
As we can observe, the main use of the
composer agent is to guarantee the execution of the
composition plan. It is the composer agent that
communicates with the buyer, giving him the
necessary details to fulfill the business (price,
payment form, delivery date, etc.)
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented how the technologies that
come from the development of the Semantic Web
allied to the technologies of the Web Services can
enrich the actual tools of e-commerce. The
composition of web services enhances the
negotiation possibilities inside the ICS, increasing
the number of possible traders partners.
The coupling of the composition service to the
ICS architecture will be an easy task, once it uses the
same standards and technologies used in the ICS
prototipation. Today, we are studying the tools and
standards used in the Semantic Web and soon we
will begin the prototipation work to validate our
propositions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are very grateful to the Faculdade Atenas
Maranhense (FAMA) for granting this research.
REFERENCES
DAML-S Semantic Matchmaker
http://www.ri.cmu.edu/projects/project_480.html
Last visited August 2003.
Daum, Bertold. Arquitetura de sistemas com XML:
conteúdo, processo e apresentação. Rio de Janeiro. Ed.
Campus. 2002.
Guarino, N. Formal Ontology and Information Systems.
in: N. Guarino, (Ed.) Formal Ontology in Information
Systems. pp. 3-15, IOS Press, Amsterdam,
Netherlands. 1998.
Hendler, J., Berners-Lee, T. and Miller, E. Integrating
Applications on the Semantic Web. Journal of the
Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. Vol.
122(10), p. 676-680. October, 2002.
Horrocks, I., Harmelen, F. V. Reference Description of the
DAML+OIL Ontology Markup Language. Draft
Report, 2001. Acessado em Janeiro de 2002.
Disponível na Internet por www em:
http://www.daml.org/2000/12/reference.html. 2001.
Labidi, S., Hammoudi, S. and Gannoun, L. Cooperation
and Temporal Organization in Workflow
Management. In the Proceedongs of the 2000
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IC-
AI'2000). World Scientific Engineering Society. Las
Vegas, USA. June 20-22, 2000.
Labidi, S., Fonseca, Luis C., Filho, Othon B. and
Nascimento, E. Intelligent B2B Commerce System. In
the textbook Techno-Legal Aspects of Information
Society and New Economy: an Overview, Formatex.
Spain. 2003.
Paolucci, M., Kawmura, T., Payne, T. and Sycara, K.
Semantic Matching of Web Servies Capabilities. In
Firts Int. Semantic Web Conf. 2002.
Sirin, E., Hendler, J. and Parsia, B. Interactive
Composition of Semantic Web Services. University of
Maryland, USA. 2003
Tomaz, Ricardo F., Labidi, S. and Wangon, B. A Semantic
Matching Method for Clustering Traders in B2B
Systems. To appear in 1st Latin American Web
Congress, Santiago, Chile. November 2003.
ICEIS 2004 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
438
