
DURATIVE EVENTS IN ACTIVE DATABASES
Rodolfo G
´
omez
∗
Computing Laboratory
University of Kent at Canterbury
CT2 7NF, Canterbury, Kent, United Kingdom
Juan Carlos Augusto
School of Computing and Mathematics
University of Ulster at Jordanstown
BT37 0QB Newtownabbey, United Kingdom
Keywords:
Active databases, event specification language, durative events, composition operators, composition semantics.
Abstract:
Active databases are DBMS which are able to detect certain events in the environment and trigger actions in
consequence. Event detection has been subject of much research, and a number of different event specification
languages is extant. However, this is far from being a trivial or accomplished task. Most of these languages
handle just instantaneous events, but it has been noticed that a number of situations arise where it would be
interesting or even necessary to handle durative events. We elaborate on a given specification language which
combines instantaneous and durative events, revealing some issues which must be taken into account when the
semantics of event composition is defined.
1 INTRODUCTION
Active Databases (Paton and Diaz, 1999) are database
management systems (DBMS) which are able to per-
form actions in response to the detection of particular
events. The active behavior of these systems is usu-
ally defined through E-C-A rules (Event - Condition -
Action) (Berndtsson and Lings, 1995). Research has
been devoted to both models and languages for events
(see e.g., (Gehani et al., 1992b; Gehani et al., 1992a;
Chakravarthy and Mishra, 1993; Gatziu and Dittrich,
1994; Galton, 1995; Roncancio, 1999; Galton, 2000;
G
´
omez et al., 2000; G
´
omez et al., 2001; Galton and
Augusto, 2002)). Generally, events are classified as
primitive if they can be detected directly, e.g., deleting
a tuple; or as composite if they are higher level con-
structs expressing some relationship between more
primitive events, e.g., deleting a sequence of tuples.
Events defined in database contexts are useful for an-
alyzing the history of a given operation or querying
database states. From (Galton and Augusto, 2002)
we learnt that research considering events in the con-
text of active databases is far from being either a triv-
ial or an accomplished task. Most of the models and
prototypes proposed so far have considered instanta-
neous events only, and little attention has been given
to the consideration of durative events. Nevertheless,
∗
The author is supported by the ORS Award Scheme,
UK Universities
it has been recognized that duration provides a bet-
ter semantics for event composition (Galton, 2000).
Also, certain database operations are more naturally
modelled by durative events (Roncancio, 1999). The
work in (Roncancio, 1999) is one of the few attempts
made so far to combine both instantaneous and du-
rative events in the same language. As it is usual
in event languages, a set of primitive events can be
composed into more complex structures by using a
number of composition operators. We have found,
however, that some issues concerning the definition
and detection of composite events have not been sat-
isfactorily identified, leading to a number of problems
which may arise in the use of some of the composi-
tion operators. We show how these operators can be
modified in such a way that consistency is preserved
through the operator set. We also discuss the effect of
different composition semantics for durative events.
We believe this discussion is another necessary step
in the direction suggested in (Galton and Augusto,
2002) to clarify some fundamental notions which un-
derly the use of events in active databases. It is im-
portant to stress that the language proposed in (Ron-
cancio, 1999) is considered as the reference language
for durative events in the technical literature of active
databases.
Section 2 will provide the main concepts behind
the event language proposed in (Roncancio, 1999). In
section 3 problems arising in the use of some compo-
306
Gómez R. and Carlos Augusto J. (2004).
DURATIVE EVENTS IN ACTIVE DATABASES.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems , pages 306-311
DOI: 10.5220/0002647703060311
Copyright
c
SciTePress
sition operators, their causes and undesired effects are
identified. Section 3.1 shows how these operators can
be redefined to avoid the problems previously men-
tioned. In section 3.2 we discuss some different se-
mantics which can be assigned to composition opera-
tors. Conclusions are given in section 4. More com-
prehensive discussions and other problems are given
in the full version of this article (G
´
omez and Augusto,
2003).
2 A DURATIVE EVENT
SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE
Roncancio (Roncancio, 1999) proposes to extend
the instantaneous event model of NAOS (Collet and
Coupaye, 1996), an event detector module which is
part of the object-oriented DBMS O2 (Bancilhon
et al., 1992). We will refer to the proposal made in
(Roncancio, 1999) as E-NAOS (for Extended NAOS)
from now on. ECA rules take the general form:
on <event expression>
if <condition>
do <action>
A durative event identifies a “happening of interest”
which occurs over an interval of time. A durative
event can be seen as an abstraction constructed over
two instantaneous events which bound its occurrence
period. Durative events can, for example, be related
to database operations like updating a tuple stored
in the database, which can be more naturally mod-
elled as having a related duration (instead of han-
dling such start-end instantaneous events (Roncancio,
1999)). Also, durative events provide convenient se-
mantics to handle composite events (Galton, 2000).
An event type describes a set of instances with the
same behavior, e.g., tuple insertion. An event instance
carries some information related to its occurrence.
Some information depends on the event type, e.g., the
values of every field in a tuple insertion, but other in-
formation is common to all types. Our main concern
will be the time of occurrence and the time of detec-
tion. For instantaneous events these two times usually
meet. For durative events, however, the time of oc-
currence (called occurrence period) denotes the span
which bounds the event instance while the time of de-
tection (called notification time) is an instant equal or
greater than the last instant of the occurrence period.
This model consider that instantaneous events are du-
rative events with a minimum duration (a chronon, see
(Jensen et al., 1992)), so they also have an occurrence
period (although minimal).
Events are classified as primitive or composite.
Primitive events are related, amongst other things, to
read-write operations on objects, method calls and
transaction executions.
Composite events are defined by composing prim-
itive events or by composing other composite events,
using a set of operators. Operators are based on
the classic Allen’s interval relations (Allen, 1983),
and on some instantaneous operators defined in
(Chakravarthy et al., 1994). Composition results in
a new durative event with its own occurrence period.
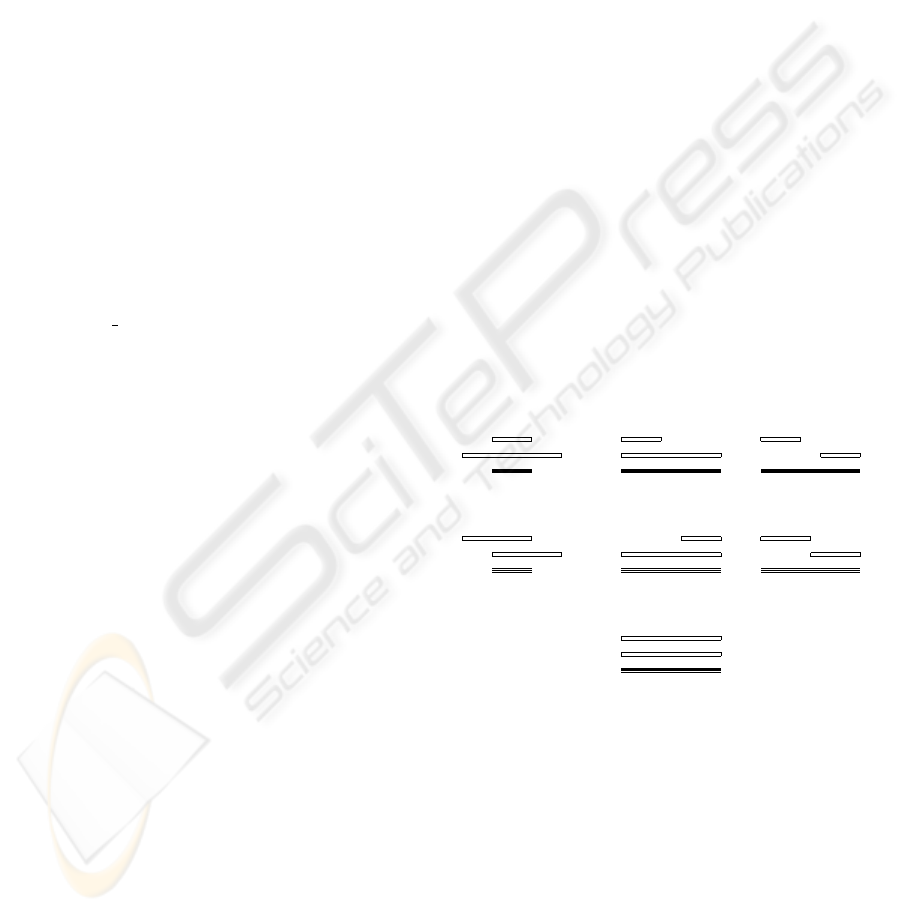
Operators are described below (Table 1 and Fig. 1),
but first, a description of the notation is in order. A,
B, etc. denote events. OP and N T stand for occur-
rence period and notification time, respectively. Func-
tions max and min return the greatest and least instant
of a pair, respectively. E
−
, E
+
stand for the bounds
of the occurrence period of E (i.e. OP =[E
−
,E
+
]).
Finally, note that we have assumed that the disjunc-
tion operator (or) is exclusive. This is not clear from
(Roncancio, 1999), but it seems to be the proper se-
mantics given the context. Also, the N T given for
overlaps corresponds to the first occurrence con-
dition (the N T is symmetric if the other condition
occurs). In any case, these do not affect the results
shown in this paper.
Fig. 1 shows (in boldface) the occurrence periods for
the relational operators.
A during B
B
A
A overlaps B
B
A
A starts B
B
A
A ends B
B
A
A precedes B
B
A
A meets B
B
A
A equal B
B
A
Figure 1: Occurrence periods
Notice that the occurrence periods are not consistently
defined for all operators. In some of them (during
and overlaps) the occurrence period only com-
prises the interval of time when the two components
are simultaneously occurring, whereas in the other
operators the period covers both components. Also,
notification times are sometimes defined as the last in-
stant of the occurrence period (precedes, starts,
ends) while for others (overlaps and during) it
depends on whether the component events are primi-
tive or composite.
DURATIVE EVENTS IN ACTIVE DATABASES
307

Table 1: Composition operators in E-NAOS
Operator Definition
A precedes B: A
+
< B
−
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A during B: B
−
< A
−
< A
+
< B
+
OP: [A
−
,A
+
]
NT: A
+
if B is primitive
B
+
if B is composite
A overlaps B: A
−
< B
−
< A
+
< B
+
or
B
−
< A
−
< B
+
< A
+
OP: [max(A
−
,B
−
),min(A
+
,B
+
)]
NT: A
+
if B primitive
B
+
if B is composite
A starts B: A
−
= B
−
OP: [A
−
,max(A
+
,B
+
)]
NT: max(A
+
,B
+
)
A equal B: A
−
= B
−
∧ A
+
= B
+
OP: [A
−
,A
+
]
NT: A
+
A ends B: A
+
= B
+
OP: [min(A
−
,B
−
),A
+
]
NT: A
+
A meets B: A
+
+ 1 chronon = B
−
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A or B: either A or B occurs (but not both)
OP: OP (A) if A occurs
OP (B) if B occurs
NT: N T (A) if A occurs
N T (B) if B occurs
A and B: both A and B occur
OP: [min(A
−
,B
−
),max(A
+
,B
+
)]
NT: max(A
+
,B
+
)
3 SOME UNDESIRED EFFECTS
OF A COMPOSITION
SEMANTICS
This section presents an example which reveals some
problems with the composition operators proposed
for E-NAOS (others can be found in (G
´
omez and Au-
gusto, 2003)). We will see a number of situations
where the detection of composite events may have an
unexpected (and possibly incorrect) outcome. These
problems may not arise in the database context the
language is currently used (i.e. NAOS-O2). Nev-
ertheless, our intention is to show that some unsafe
expressions may result when composition of durative
events is not carefully defined.
Consider a laboratory of a given pharmaceuti-
cal company, testing the effects of new drugs on
cells infected with some virus. Incompatibilities be-
tween different drugs, unwanted side effects, amongst
other hazardous situations, are part of the information
which is expected from the tests. We can imagine the
use of an active DBMS in such a context. For exam-
ple, the current level of certain substances in the cells
can be detected as an indication of some situation of
interest, which in turn can be thought of as primitive,
detectable events. Different actions can be triggered,
e.g. an alarm signal or the modification of the cell’s
environment, such as temperature or moisture condi-
tions. Therefore, we can assume a number of ECA
rules in place, and importantly, that durative events
must be handled (reactions in the cell may have a re-
lated duration).
In (Roncancio, 1999), the occurrence period for op-
erators overlaps and during only comprises the
period when the two component events are simulta-
neously occurring, whereas for every other operator
the period covers both component occurrences (see
Fig. 1). This inconsistency may cause some problems,
as shown in Example 1
2
.
EXAMPLE 1 The following active rule detects a
given reaction in the cell (event R) under the effect
of two drugs (events A and B). Suppose that this re-
action is meaningless unless a) it is detected after the
first drug and before the second drug have made effect
on the cell and b) the effect of the first drug overlaps
or precedes the effect of the second drug. The rule
below appears, then, as a natural solution:
on R during
( (A overlaps B)
or (A precedes B))
do (...)
Figure 2 shows two situations in which the rule should
have been triggered. However, and because occur-
rence periods are assigned differently to overlaps
and precedes, the reaction is not detected when
the effects of both drugs overlap, even when it hap-
pens before the effect of the second drug (B) is gone
(case 1).
Other kind of problem arises because notification
times are not uniformly defined. In (Roncancio,
1999), composite events during and overlaps
are notified to the system before all component
occurrences have been detected. For example,
A during B is notified when A finishes if B is
primitive, but instead it is notified when B finishes if
B is composite. Example 2 shows a possible conse-
quence of this definition.
2
As we are focussed on the event specification language,
our examples will show rules where the condition and ac-
tion sections will be missing or vaguely specified.
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
308
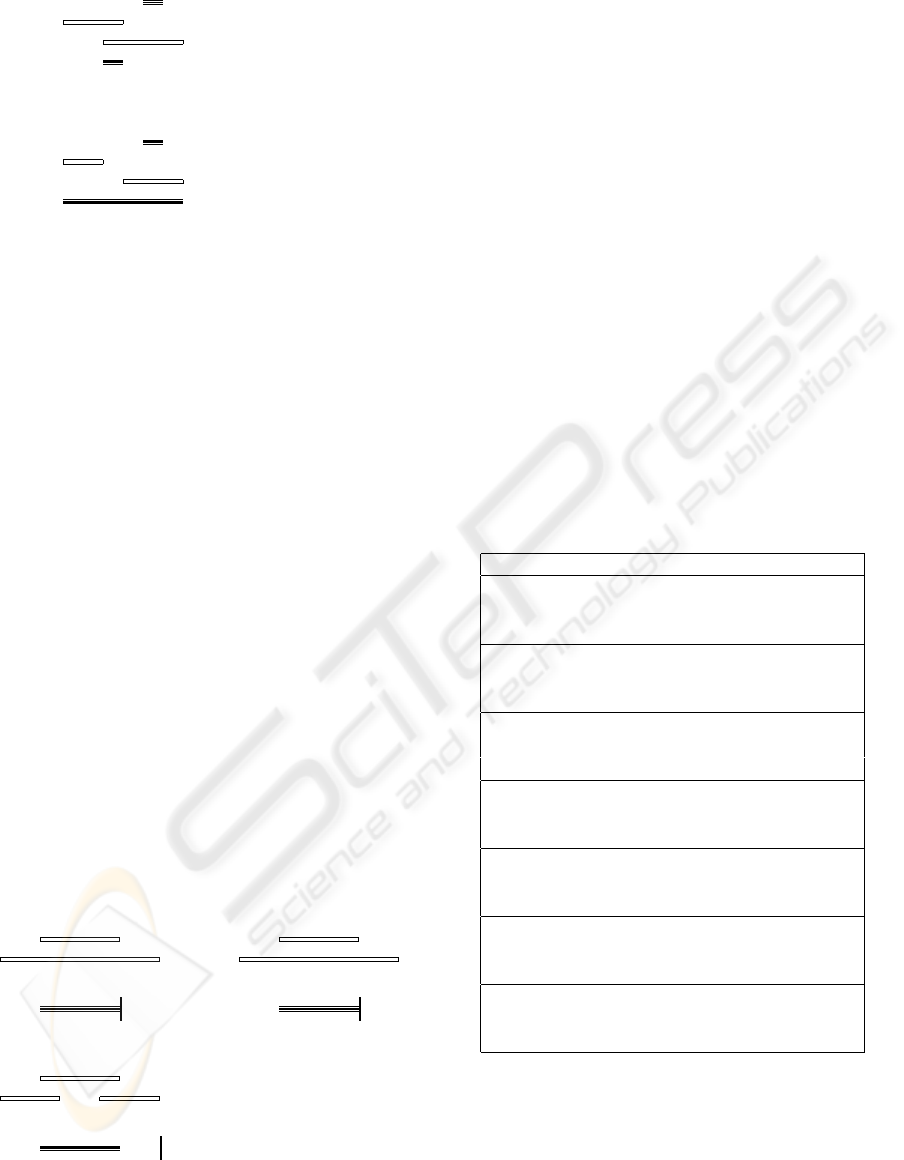
R
EA
B
A overlaps B
case 1: rule not triggered!
R
A
B
A precedes B
case 2: rule triggered
Figure 2: Missing detections (E-NAOS ops.)
EXAMPLE 2 The following rule detects a reaction
(R) in a cell under the effects of two drugs (A and
B). Different tests include the administration of a sin-
gle drug or both drugs together, and the reaction is
considered meaningless unless the effects of drugs are
completely detected (even though they can be consid-
ered as primitive events, complete detection cannot
always be ensured). Such a rule, then, could be writ-
ten as follows:
on R during
(A or B or (A and B))
do (...)
Fig. 3 shows three different situations; when the reac-
tion is detected with respect to either A or B, the rule
is triggered immediately afterwards. This is not safe
as A or B have not been completely detected at that
moment, and so it can be the case that the reaction
is meaningless if such occurrences fail to happen. On
the other hand, if both drugs are administered the rule
will not be triggered unless both A and B have been
completely detected (case 3).
R
A B
R during (A and B)
case 3: deferred
R
B
R during B
case 2: immediate
R
A
R during A
case 1: immediate
Figure 3: Deferred triggering using operators proposed for
E-NAOS
3.1 Composition Operators With A
Consistent Semantics
Definitions can be modified to obtain a new set of
composition operators where a) the occurrence period
of the resulting composite event includes the com-
plete occurrences of the components, and b) no com-
posite event is notified until all components have been
notified. Moreover, the notification time of a compos-
ite event is the same whether components are primi-
tive or composite. Therefore, problems shown in ex-
amples 1 and 2 no longer arise. The modified op-
erators are shown in Table 2 and Fig. 4. Operators
have been also modified to follow the original defini-
tions of Allen’s interval relations. Pragmatically, this
is desirable since Allen’s relations have a well-known
semantics that users may naturally expect when using
operators with similar names. The full paper (G
´
omez
and Augusto, 2003) shows an example of how the se-
mantics of E-NAOS operators could be misinterpreted
and lead to unexpected behaviour.
Table 2: Modified operators
Operator Definition
A precedes’ B: A
+
< B
−
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A during’ B: B
−
< A
−
< A
+
< B
+
OP: [B
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A overlaps’ B: A
−
< B
−
< A
+
< B
+
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A starts’ B: A
−
= B
−
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A equal’ B: A
−
= B
−
∧ A
+
= B
+
OP: [B
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A ends’ B: A
+
= B
+
OP: [B
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
A meets’ B: A
+
+ 1 chronon = B
−
OP: [A
−
,B
+
]
NT: B
+
DURATIVE EVENTS IN ACTIVE DATABASES
309

3.2 A Discussion On Composition
Semantics
We would like to emphasize that the potential prob-
lems found in E-NAOS do not arise because of a par-
ticular set of operators was chosen (this depends on
the context) but because the set is not consistent. Op-
erators in E-NAOS have been overloaded with differ-
ent semantics, where each one of these is only ade-
quate when the operator is used in a specific context.
For example, all Allen-like operators can be used to
constrain the conjunction of two events, i.e. the occur-
rences of both components have been detected, and
these satisfy certain temporal placement. For all op-
erators but during and overlaps, though, the re-
sulting event has an occurrence period which covers
both components. On the other hand, overlaps and
during results in an event whose occurrence period
only covers the shared interval between components.
Sometimes, this may be convenient. The following
rule triggers only if event A occurs while B is occur-
ring:
on A during B do (...)
If event B was used just to constrain A, then in the ac-
tion part of rule we will probably be concerned only
with the occurrence period of A. Hence, there is no
reason for operator during to be assigned an oc-
currence period that includes both component events.
However, we have shown in Example 1 that some-
times conjunction semantics is more convenient. But
there is, a priori, no reason why the occurrence period
for during and overlaps should not cover both
components (as is the case for all other operators in
the same class).
Some composite events in E-NAOS can be detected
before all component events have been fully detected,
A during’ B
B
A
A overlaps’ B
B
A
A starts’ B
B
A
A ends’ B
B
A
A precedes’ B
B
A
A meets’ B
B
A
A equals’ B
B
A
Figure 4: Occurrence periods (modified operators)
e.g., during and overlaps. Sometimes this eager
detection may be convenient, but in other contexts a
more safe approach could be required (Example 2).
Again, consistency is more important than particular
contexts, i.e., for example, the notification time for
starts should not be different than the one assigned
to during.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We analyze in this work a well-known proposal for
representing and reasoning with durative events in
active databases. We identify a number of prob-
lems which may arise in event specification languages
when the semantics assigned to the composition of
durative events is not consistent. We illustrate such
problems using the event language presented in (Ron-
cancio, 1999) as a case study. We show how appar-
ently innocuous definitions results in operators with
undesired side effects and behaviours which are dif-
ficult to predict. This, in consequence, results in a
language where “unsafe” expressions are not easy to
discover. We also show how a simple modification of
these operators achieves consistency through the set,
thus ruling out the possibly unsafe situations. The
full paper (G
´
omez and Augusto, 2003) shows other
contexts where composition operators in E-NAOS
present an undesired behaviour; also, a more compre-
hensive discussion about possible semantics for that
kind of operators is offered.
As (Galton and Augusto, 2002) and this work have
shown, neither the proposals given in (Chakravarthy
et al., 1994) nor in (Roncancio, 1999) are free from
problems in their attempts to accommodate durative
events in different ways. In this article we gave an-
other step on raising awareness of the important re-
maining problems. Despite the importance of the
topic, there is not satisfactory proposal in the area and
much more work is still needed to clarify fundamental
notions underlying the use of events in active database
systems. We expect the problems discussed in this pa-
per will inspire new proposals towards a next genera-
tion of more reliable systems.
REFERENCES
Allen, J. F. (1983). Maintaining Knowledge about Temporal
Intervals. Communications of the ACM, 26(11):832 –
843.
Bancilhon, F., Delobel, C., and P. Kanellakis, editors
(1992). Building an Object-Oriented Database Sys-
tem - The Story of O2. Morgan Kaufmann.
Berndtsson, M. and Lings, B. (1995). Logical Events
and ECA Rules. Technical Report HS-IDA-TR-95-
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
310

004, Department of Computer Cience, University of
Sk
¨
ovde.
Chakravarthy, S., Krishnaprasad, V., Anwar, E., and Kim,
S. (1994). Composite Events for Active Databases:
Semantics, Contexts and Detection. In Proceedings
of the International Conference on Very Large Data
Bases (VLDB’94), pages 606–617, Santiago de Chile,
Chile.
Chakravarthy, S. and Mishra, D. (1993). Snoop: An
expressive Event Specification Language for Active
Databases. Technical Report UF-CIS-TR-93-007,
University of Florida, USA.
Collet, C. and Coupaye, T. (1996). Composite Events
in NAOS. In 7th International Conference and
Workshop on Database and Expert Systems Applica-
tions (DEXA’96). LNCS 1134, pages 244–253, Zurich,
Switzerland.
Galton, A. (1995). Time and Change. In Hanbook of Logic
in Artificial Intelligence and Logic Programming, vol-
ume 4 (Epistemic and Temporal Reasoning), pages
175–240. D. Gabbay and C. Hogger and J. Robinson
(eds.), Clarendon Press.
Galton, A. (2000). Eventualities. In Vila, van Beek,
Boddy, Fisher, Gabbay, Galton, and Morris, editors,
The Handbook of Time and Temporal Reasoning in
Artificial Intelligence. MIT Press. (to be published).
Galton, A. and Augusto, J. C. (2002). Two approaches to
event definition. In Hameurlain, A., Ciccheti, R. and
Traunm
¨
uller, R., editors, Proceedings of 13th Inter-
national Conference on Database and Expert Systems
Applications (DEXA 2002), Aix-en-Provence, France,
Springer-Verlag, pages 547–556.
Gatziu, S. and Dittrich, K. (1994). Detecting Compos-
ite Events in Active Databases Systems using Petri
Nets. In Proceedings of the 4th International Work-
shop on Research Issues in Data Engineering: Active
Database Systems, pages 2–9, Houston, USA. IEEE.
Gehani, N., Jagadish, H. V., and Shmueli, O. (1992a).
Composite Event Specification in Active Databases:
Model & Implementation. In Proceedings of the 18th
International Conference on Very Large Data Bases
(VLDB’92), pages 327–338.
Gehani, N., Jagadish, H. V., and Shmueli, O. (1992b). Event
Specification in an Active Object-Oriented Database.
In Proceedings of the 1992 ACM SIGMOD Interna-
tional Conference on Management of Data, pages 81–
99, San Diego, California, USA.
G
´
omez, R. and Augusto, J. (2003). Durative Event
Composition in Active Databases. Techni-
cal report, University of Ulster at Jordanstown.
(http://www.infj.ulst.ac.uk/˜jcaug/
gomezaug.pdf).
G
´
omez, R., Augusto, J. C., and Galton, A. (2000).
Implementation and Testing for a Set of Event
Detection Operators. Technical Report 398,
School of Engineering and Computer Sci-
ence, University of Exeter, United Kingdom.
(http://www.infj.ulst.ac.uk/˜jcaug/
/rr398.pdf).
G
´
omez, R., Augusto, J. C., and Galton, A. (2001). Test-
ing an Event Specification Language. In Proceedings
of the 13th. International Conference of Software En-
gineering and Knowledge Engineering (SEKE 2001),
pages 341–346, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Jensen, C., Clifford, J., Gadia, S., Segev, A., and Snod-
grass, R. (1992). A Consensus Glossary of Temporal
Database Concepts. SIGMOD Record, 21, num. 3.
Paton, N. and Diaz, O. (1999). Active Database Systems.
ACM Computing Surveys, 31(1):63–103.
Roncancio, C. L. (1999). Toward Duration-Based, Con-
strained and Dynamic Event Types. In Proceedings of
the Second International Workshop on Active, Real-
Time and Temporal Database Systems (ARTDB’97),
Como, Italy, September 8-9, 1997, number 1553 in
LNCS, pages 176–194. Sten F. Andler and J
¨
orgen
Hansson (eds.), Springer.
DURATIVE EVENTS IN ACTIVE DATABASES
311
