
NEURAL NETWORK AND TIME SERIES AS TOOLS FOR
SALES FORECASTING
Maria Emilia Camargo, Walter Priesnitz Filho, Marcelo Mahado Barbosa Pinto
University of Caxias do Sul, CAMVA, Vacaria, RS, Brasil
Angela Isabel dos Santos
Department of Statistical, University of Santa Maria, RS, Brasil
Keywords: Neural Network, Time series
Abstract: This paper presents the use of times series AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average ARIMA(p,d,q)
model with interventions, and neural network back-propagation model in analyzing the behavior of sales in
a medium size enterprise located in Rio Grande do Sul Brazil for the period January 1984 – December 2000.
The forecasts obtained using the neural network back-propagation model were found to be more accurate
than those of ARIMA model with interventions.
1 INTRODUCTION
In various areas of research, the models obtained
using neural networks are found to be better
compared to other ways of modeling. Lapedes and
Farber (1987), published an article where they
trained the network to generate a line series using a
specific equation. They obtained agreeable results
which provided accurate forecasting. In this paper,
the sales data collected from a medium size
enterprise located in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil for
the period January 1984 – December 2000 have
been analyzed using the time series ARIMA model
with interventions and the back – propagation neural
network model.
Initially the exploratory analysis, autocorrelation
and parcial autocorrelation functions have been used
to analyze the time series sales data to verify the
existence of seasonal components, non - stationarity,
and the randomness in the data. The number of
intermediate layers for the back-propagation model
has been determined by trial and error approach.
Error analysis of the time series has been carried out
accurate forecasting. The results obtained are
presents and discussed.
2 METHODOLOGIES
2.1 AutoRegressive Integrated
Moving Average (ARIMA) Model
with Interventions
The intervention analysis is a transfer function
stochastic model from which it is possible to
interpret and incorporate its effects to time series
model (Box and Jenkins, 1970). The major effects of
intervention can be noted observing the changes in
inclination level of time series. Based on these
changes, the error variables can be altered and
components that were not present in the model can
be introduced. Let a time series for which you have
verified and estimated an ARIMA model with you
were making forecasts for certain time. At a given
instant, an independent phenomenon occurred that
originated a time series, but whose effects can be
manifested on the time series. This external event,
whose effects will influence the time series being
studied, should be incorporated in the model as an
additional. This addition is called intervention (Box
& Tiao, 1973). The intervention model can be
represented by:
476
Emilia Camargo M., Priesnitz Filho W., Mahado Barbosa Pinto M. and Isabel dos Santos A. (2004).
NEURAL NETWORK AND TIME SERIES AS TOOLS FOR SALES FORECASTING.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 476-478
DOI: 10.5220/0002648304760478
Copyright
c
SciTePress
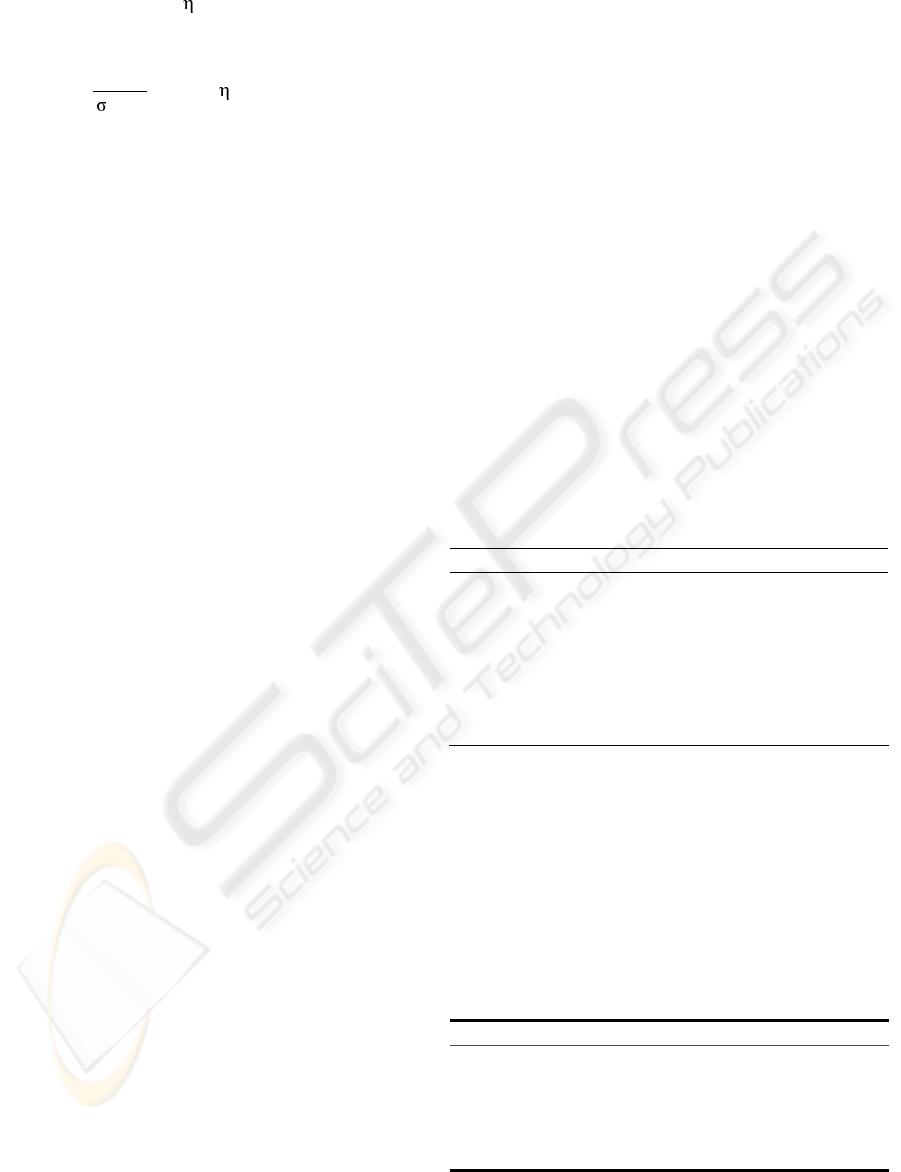
ttj
k
1j
j
(B)XVt)x,f(k, +
∑
=
=
(1)
ttj
k
1j
j
j
(B)X
(B)
(B)
t)x,f(k, +
∑
ϖ
=
=
(2)
where: X
tj
j=1.2, ........ k are exogenous variables
(interventions). Eventually.
bt
X
−
can be used where
b is the time space occurred between the input and
the output series (discrepancy between the time
series); k is a set of unknown parameters which
appears in v
j
(B) or in ω
j
(B) and σ
j
(B); where: v
j
(B)
= ω
j
(B)/σ
j
(B), j=1,2,........ k is the transfer function
of j-th exogenous variable, such that V
j
(B), ω
j
(B)
and σ
j
(B)are polynomials in B and
t
η is the noise
that can be represented by an ARIMA model with
seasonal components. Each series
tj
X is an
indicator that assumes the values 0 or 1,
representing, respectively, the absence or the
presence of j-th intervention , that is, the non-
occurrence or the occurrence of j-th event. The time
series indicators of the intervention can be
represented by three types of binary variables:
Impulse function (type 1); step function (type 2);
and impulse seasonal function (type 3).
2.2 Neural Network
The back-propagation model is a paradigm
commonly used in the areas of signal recognition,
and principally in forecasting of time series ( Beale
and Jackson, 1991). The back-propagation model
uses a topology of 3 or more layears. The
connections between the units are interlayers that are
directed from the input layer to the output layer. The
neural network adjusts itself as a time series
forecasting model in the following form:
1. The input units are made up of information
relevant to the forecasting:
2. The weights are the model parameters and be
estimated through learning by the network that takes
into account the pair of inputs to the respective
output targets (real values of the time series);
3. The hidden layers are the links between the input
and output layers. Its role is important for the
selection of better sets of weights, since the non-
linearity of the model can be located in the
activating function of the hidden units;
4. The output layer is made up of only one unit and
carries the needed information for forecasting;
5. The network is trained for estimating the model
parameters. After training, forecasting for the
periods 1,2... etc.. in the can be generated on the
output layer;
6. The hyper parameters are the values provided by
the user that in general are constants. They are: rate
of learning, momentum term, and the varying
interval size of weights.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
3.1 ARIMA Model with Intervention
The adjusted model is with interventions ARIMA
(1,1,3)x(0,1,0) The estimated parameters and
statistics of the model are prented in Table1.
Table 1: Estimated parameters and statistics “t” for the
univariate model with interventions for the time series
sales data
Parameter Estimated Value Statistic”t”
φ
1
-0.2553 -2.02
θ
3
-0.3987 -3.38
ξ
1
-0.1256 -3.78
ξ
2
-0.3765 -4.10
ξ
3
0.1857 3.97
ξ
4
0.1074 2.18
ξ
5
0.6876 1.99
The adjusted statistic and noise statistics for the
model are:
R² = 0.9647: Mean ≅ 0.0000; and
Variance = 0.00138
The identified interventions for the sales data
during the period analyzed are presented in Table 2
considering a level of significance of 5%.
Table 2: Types of detected interventions
Type of intervention Instant Period
X
1t
→ 1
99 MAR/87
X
2t
→ 1
131 NOV/89
X
3t
→ 2
123 MAR/89
X
4t
→ 3
115, 127 JUN/88
X
5t
→ 2
108 DEC/87
NEURAL NETWORK AND TIME SERIES AS TOOLS FOR SALES FORECASTING
477

The types of interventions occurred are: impulse,
step, and seasonal impulse. It observed that the
estimated coefficients of the intervention variables
ξ
i
have their expected signals. That is ξ
1
and ξ
2
have negative signals, when
ξ
3,
ξ
4
and ξ
5
have
positive signals:
1. The first interventions represents the reflections
due to Cruzado Plan that imposed freezing of prices,
which was in vigor from March to November of
1986:
2. The intervention of November 1989, is the
reflection of heterodox shock of Summer Plan.
3. The intervention occurred in March 1989 is due to
the price increase in consequence to inflationary
memory;
4. The increase in sales in June 1988 is characterized
by the seasonal effect, since every year starting from
1988 there has been increase in sales (more
emphasize in the year 1988); and a harmonic
observed with reference to the month June is highly
significant.
5. Finally X
5t
represents the intervention due to
Bresser Plan a new tentative of freezing the prices,
this time for a very short period of time, from July to
October 1987.
3.2 Neural Network
Architecture: The chosen architecture (after testing
various architectures by evaluating.
1. 14units in the input layer, in the following form: 2
past lags: X
t
and X
t-1
; 12 seasonal units.
2. two units in the hidden layer;
3. one unit in the output layer X
t-1
.
Training
: The sales series was trained 1400 times,
updating the weight for every 30 repetitions. The
learning constant was maintained at 0.12 and in the
last 300 repetitions, a memory loss term of 0.4 was
used. This term was used to provide more weight for
the most recent observations. The momentum term
used was 0.7. The varying interval size of the weight
was 4.
3.3 Comparison of forecasts
The performance of two approaches for sales we
calculate the Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE).
The two methods (ARIMA and Neural Network)
provide the following MAPE: 7.63% and 5.38%,
respectively.
The results show that the neural network model
adjust well to the sales data is the preferred model
for forecast on the basis of MAPE.
4 CONCLUSION
We presented in this paper two approaches for the
study the sales data collected from medium size
entriprise located in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil for
periodo January 1984 – December 2000.
The ARIMA model interventions presented a
residual variation of 0.0014 where as the neural
network model presented a residual variation of
0.0001. The MAPE for the neural network model
was 5.38% and for the ARIMA model with
interventions was 7.63%. The sales time series
presented a marked seasonality for which it was
necessary to use 12 binary units (0 or 1) for
determining the relative weight for weight for each
month. The results show that the neural network
model is the preferred model for forecast on the
basis of MAPE
The model obtained by the neural network was
superior to ARIMA model, in adjustment as well as
in forecasting for the data analyzed.
REFERENCES
Beale, R. and T. Jackson, T., 1991, Neural Computing –
an introduction. Adam Higler Publ.
Box, G.E.P. and Jenkins, G.M., 1970, Time Series
Analysis: Forecasting and Control. San Francisco.
Holden-Day.
Box, G.E.P. and Tiao,G.C.,1970. Intervention Analysis
with Applications to economic and Environmental
Problems. Journal of The American Statistical
Association.
Lapedes, A and Farber, R, 1987, Nonlinear Signal
Processing Using Neural Network: Prediction and
System Modeling, Proceeding of the IEEE – Los
Alamos National Laboratory report LA-UR-87-2662
.
ICEIS 2004 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
478
