
COMPONENT BASED INFORMATION SYSTEM
RE-ENGINEERING APPROACH
Abdelaziz Khadraoui, Michel Léonard
MATIS Geneva Team - Database Laboratory, CUI - University of Geneva
Uni-Dufour, rue du Général Dufour 24, CH-1211 Genève 4, Switzerland
Key
words: Information System, Component, Renovation, Inva
riant Concepts, Re-Engineering.
Abstract: This paper presents a concept called Component based Information Systems Re-Engineering (CISRE),
which lays down the foundation of a new re-engineering approach. CISRE covers all the facets of
Information Systems (IS) at three levels: system, collaboration and organization. This approach contains
two main phases respectively: the comprehension phase and the renovation phase, which are not disjointed.
The main goal of this approach is to converge into a new IS, within a rapid evolving environment. Thus, the
new IS will be achieved on stable concepts based on invariants.
1 INTRODUCTION
Information Systems (IS) are recognized as a
strategic asset of most mediums and large
enterprises, and of public organizations. These IS
could be found in many economic sectors and social
activities. Most of the time, these organizations have
a very important legacy and strategic applications
those are essential to deal with their main business
activities. Some of them are relatively new while the
others are older. This inheritance is often built
gradually and based on the heterogeneous
technologies, it is also developed for specific needs,
at different periods and by different teams.
Consequently, it leads to IS with their components
and architectural layers. Those components and
layers are not always able to communicate with
others. In most of cases, these systems became non-
adaptive to new requirements after many evolutions.
In other words, these organizations should
constantly undertake changes in their human and
technical environments according to the functional
needs.
Facing this increasing evolution, a lot of
o
r
ganizations are brought to rebuild the pre-existing
IS and take into account the data-processing support
o
f
the new activities related to the various changes.
In fact, the interests to IS rebuilding are mainly
expl
ai
ned regarding to their complexity, because of
the following particular factors: (i) the defective
character of the design and the development of the
applications, particularly at the analysis phase of
user's needs; (ii) the inability of the systems to
evolve; and (iii) the insufficiency in documentation.
In this paper, we present a new approach of IS Re-
engi
neeri
ng focused on the concept of Information
System Component (ISC). The goal is to develop
information systems that can support future
improvements in an easy way.
2 OUR APPROACH OF
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
RE-ENGINEERING
As illustrated in figure 1, our approach of IS Re-
engineering composes of two main phases. The first
phase consists of comprehension of the legacy
information system (LIS). This step aims to produce
the basis for the renovation. The second phase
consists of defining the process of renovation of LIS.
The activities of comprehension and renovation are
related.
625
Khadraoui A. and Léonard M. (2004).
COMPONENT BASED INFORMATION SYSTEM RE-ENGINEERING APPROACH.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 625-628
DOI: 10.5220/0002657306250628
Copyright
c
SciTePress
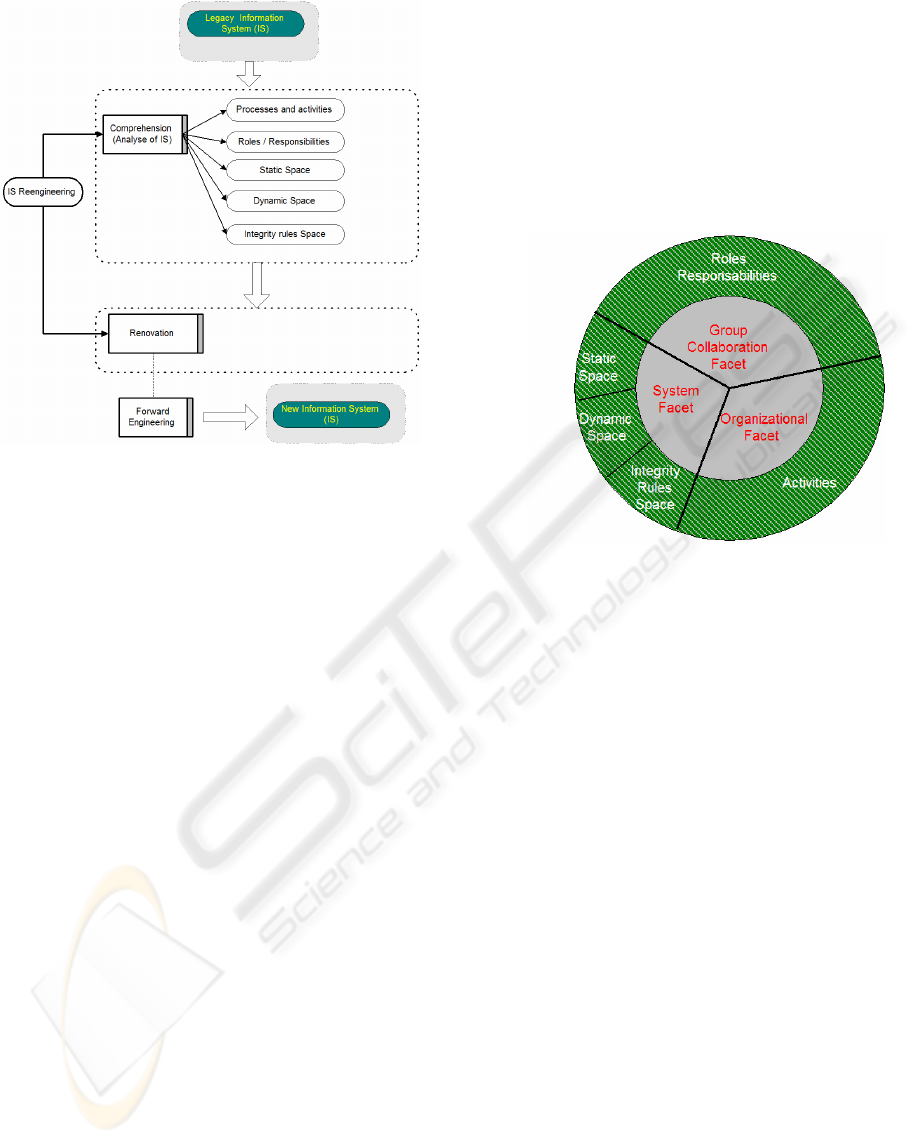
In the schema of figure 1, the forward engineering
concerns to the classical process of developing
system. It starts from the specifications of the pre-
existed information systems and moves down
towards implementation and deployment (Bisbal,
and al, 1999).
2.1 The process of comprehension
The process of comprehension basically involves in
the analysis of the IS. The purpose of the IS analysis
is to identify: (i) activities of the organizations; (ii)
roles and responsibilities; and (iii) the static space,
the dynamic space, and the integrity rules space of
LIS.
As mentioned below, several sources of information
are needed to carry out this analysis. In fact, the
analysis of the pre-existed IS (figure 2) involves in
the three following facets of an IS (De Michelis, and
al., 1998):
1. The organizational facet that is concerned
with work management from a formal
organizational perspective. This facet
addresses global organizational concerns,
including organizational objectives and
business goals, policies, regulations, as well
as resulting workflow or project plans.
2. The group collaboration facet that
is
concerned with the actors (people) dealing
with a common process. These are related
to organizational roles or responsibilities
working on common business processes;
3. The systems facet
that is concerned with
computerized systems that support business
activities.
Figure 1: our approach of IS Re-engineering
Figure 2: IS analysis
The results of comprehension process are mainly
summarized as following:
To extract the most stable part of LIS;
To capture the knowledge of the data
semantics. This process is useful: (i) if we
want to use our current database to supply
data to other IS; and (ii) if we want to
replace the current IS, we need to acquire a
deep knowledge of the data. Their potential
migration requires a deep understanding of
the meaning of the data, their format and
structure, as well as how they are stored in
the database.
On the other hand, the process of comprehension
LIS also deals with the strategy to be adopted to
extract the static space, the dynamic space, and the
integrity rules space of LIS.
To capture the knowledge of the data semantics,
databases must be reverse engineered but we need to
rely the possible information sources, such as:
program sources, data, data dictionaries, reports,
screens and documentations.
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
626

The analysis of the data description language (DDL)
code of the database for instance gives precise
information, which is easy to analyze. The procedure
source code analysis gives also precise information
but in contrary, it is quite difficult in terms of
analysis cost. Documentation, if up-to-date and
carefully written, can be useful and easy enough to
analyze. When the documentation is obsolete and /or
not structured, its analysis can take time end, even
worse, lead to false assumptions (Henrard, 2003).
The extraction of the dynamic and integrity rules
spaces is the most difficult process because most of
the implicit structure and constraints are buried into
the source code of programs that is often the most
reliable place where such constraints can be found
(Henrard, 2003). Analyzing source codes of
programs requires sophisticated techniques
pertaining to the program-understanding domain.
Therefore, these techniques that seem to be adequate
for small systems become useless for medium or
large one. For these reasons, in order to extract the
three spaces as mentioned above, we need to analyze
other sources of information. The process of
extraction, applied in the case of an institutional IS,
is then facilitated by the development of a cognitive
space.
2.2 The process of Renovation
At the level of renovation, the issue is to know how
models, tools, analysis and design methods could
help to create new Information Systems supporting
evolution. The renovation implies that the IS
development has focused on the concept of ISC that
focuses on the interaction with the organizational
environment and the overlaps among IS
components.
Figure 3 shows the renovation process:
ISC (Information System Component) describes a
generic situation in the IS development. In (Léonard,
2003; Le Dinh and Léonard, 2002; Turki, and al.,
2003), ISC are defined as a particular IS.
All fundamental aspects of an Information System
such as the static, the dynamic and the integrity rules
constitute the content of an ISC as described in the
following:
Static space: where the data structure of
the ISC is defined using the concept of
hyperclass with its set of classes and
hypermethods,
Dynamic space: where the behavior of the
different elements of the ISC is expressed.
The bipartite nets are implemented to
specify the dynamic space including the
object life cycles of the hyperclass classes
(Khadraoui, 2002),
Integrity rules space: where rules
governing the behavior of the elements of
the ISC are specified. Integrity rules (IRs)
of an IS represent most often the business
rules of an organization. An IR is a logical
condition defined over classes, which could
be formally described and verified by
transactions or methods.
Another level in our approach of Re-engineering,
applied in the case of an institutional IS, consists in
the development of a cognitive space extracted from
the legal texts underlying the activities of an
organization (Visentin, 2003; Léonard, 2003b). The
legal texts describe in a precise way the field, the
rules and procedures of the organization activities.
The laws represent a knowledge source of a part of
the domain that we want to model. The concepts
related to the laws are in general stable, and
therefore, do not evolve so much. The result of this
level is to identify the most significant concepts
called the invariant concepts, which form the core
of the new IS. The cognitive space allows to clarify
the links between laws and IS, and in particular
between amendments of laws and evolution of IS.
3 CONCLUSION
In this paper we presented, in short, our approach
dedicated to IS re-engineering. This approach aims
to accompany the evolution of the IS and to
capitalize the existing regarding the business,
informational and processing point of views.
Figure 3: the renovation process
COMPONENT BASED INFORMATION SYSTEM RE-ENGINEERING APPROACH
627

Additionally to this, it concerns the ability to take
into account the new evolution situations. The
originality of the presented approach is the fact that
it is based on the IS component concepts and IS
components recovering. These components have to
be expressed regarding to an efficient and unique
semantic for a group of actors within the
organization. In the other side, we introduced the use
of the cognitive space, applied in the case of an
institutional IS, which allows the expression of the
links between the "legal texts" and the IS. Finally,
the exploitation of such space allows the
identification invariants concepts that constitute the
core of the new IS.
REFERENCES
Akoka, J., and Comyn_wattiau, I., (2001). Réingénierie
des Données et des Documents sur le Web . ISI-NIS,
Paris, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 9-59.
Albee, K., and Shekleton, J., (1992). Business Re-
Engineering and Information Systems: An opportunity
for Business Partnership. Case Outlook Vol.6, No. 4,
pp 25-34.
Bisbal, J., Lawless, D., Bing, W., and Grimson, J., (1999).
Legacy Information Systems: Issues and Directions. In
IEEE Software, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 103-111.
Delcroix, C., Thiran, P., and Hainault, J-L. (2001).
Approche Transformationnelle de la Réingénierie des
Données. ISI-NIS, Hermes Sciences Publications,
Vol. 6, No.1, pp. 61-98.
De Michelis, G., Dubois, E., Jarke, M., Matthes, F.,
Mylopoulos, J.,Papazoglou, P., Pohl, K., Schmidt,
J.W., Woo, C., and Yu, E., (1998). Cooperative
information systems: A manifesto. Cooperative
Information Systems Trends & Directions. M.
Papazoglou and G. Schlageter, Eds. Academic-Press,
pp. 315–363.
Henrard J., (2003). Program Understanding in Database
Reverse Engineering, Phd Thesis, FUNDP, Institut
d’informatique, Belgium.
Khadraoui, A., (2002). Construction de la structure
Nœuds-Etoiles d’une hyperclasse et d’un cycle de vie
d’objet. Matis report, CUI, University of Geneva.
Kullbach B:, Winter A.,(1999). Quering as an Enabling
Technology in Software Reengineering, Conference
on Software Maintenance and Reengineering
(CSMR’99).
Léonard, M., (2003a). IS Engineering Getting out of
Classical System Engineering. 5th International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, École
Supérieure d'Électronique de l'Ouest, Angers, France,
pp. 35-45.
Le Dinh, T., and Léonard, M., (2002). Defining
Information System Components. Proceeding of
Confederated International Conferences CoopIS,
DOA, ODBASE, Springer, California, pp. 1359.
Léonard, M., (2003b). La farandole des objets
imaginés, conçus et façonnées dans le monde des
Systèmes d’Information, International Workshop On
utility, usability and complexity of Emergent IS,
Namur, Belgium.
Turki, S. and Léonard, M., (2002). IS Components with
Hyperclasses. Conference of the OOIS 2002
Workshops, Advances in Object-Oriented Information
Systems, Montpellier, France, LNCS 2426, Springer.
Turki, S., Léonard, M. and Arni-Bloch, N., (2003). From
hyperclasses to components for IS development, ISPE,
Madeira.
Visentin C., (2003). Conceptualisation des lois pour le
développement d’une cyberadministration, Matis
report, CUI, University of Geneva.
ICEIS 2004 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
628
