
A Context-Aware Entity Recognition Scheme for
Pervasive Computing
Rui He
1
, Jianwei Niu
1
, Jianping Hu
2
, Jian Ma
2
1
Computer School, Beijing University of Aero. & Astro. Beijing, P.R. China
2
Nokia Research Center (China)
Abstract: In the future world filled with pervasive computing, almost all entities
can be mobile, which means not only service requesters but also service providers
are always dynamic and unpredictable. This raises two security problems. For
service providers, how can they keep their security capability when they move
here and there? And for service requesters, how can they be trusted by various
service providers that may have different security requirements? Unfortunately,
available security mechanisms, including traditional authentication and
authorization approaches and exotic trust management proposals, cannot solve the
both two problems very well. In this paper, we propose a context-aware entity
recognition scheme, which enables service providers to use their current trust
infrastructures to determine whether requesters are trustworthy or not, and also
enables service requesters to be recognized through exchanging different
information with service providers according to different services they request and
different security level service providers require. We argue for the notion of
“Trust Infrastructure”, which is an abstract of all available trusted entities that can
help an entity to recognize strangers in pervasive environments and can be
dynamically built when entities move about. We also argue for an attribute-based
recognition information exchange scheme, which makes it possible for service
requesters to be checked in terms of trustworthiness in various scenarios. Finally,
we give an algorithm to compute a service requester’s trust value based on the
trust infrastructure of the service provider entity..
1 Introduction
“The most profound technologies are those that disappear. They weave themselves
into the fabric of everyday life until they are indistinguishable from it.’’[5]
Almost 10 years ago, Weiser drew for us an alluring vision of our everyday lives
with ubiquitous computing, which is also called pervasive computing today. It
envisages a world where the environment reacts automatically to one’s needs; the
technology is invisible and ‘calming’, where information is instantly available
anywhere in the world, but only information relevant to one’s immediate needs is
delivered. The technology frees people to concentrate on what is important to them
[9].
He R., Niu J., Hu J. and Ma J. (2004).
A Context-Aware Entity Recognition Scheme for Pervasive Computing.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Ubiquitous Computing, pages 147-159
DOI: 10.5220/0002662201470159
Copyright
c
SciTePress

However, it will never become true unless critical securities problems are solved
to some extent. Since in the pervasive computing world, not only service requester
entities but also service provider entities are mobile, e.g. in Ad hoc networks, how can
entities as service providers keep their security capability as strong as possible will be
a problem. As we know that mobile entities are always limited in their computation
and storage capability, so it is impossible for them to employ complete and strong
security mechanisms locally to authenticate any entities they meet. Besides, for
service providers, they may never be able to predetermine who will request services
next, so unknown users should be served if only they can meet some requirements,
e.g. they have enough electronic money. We argue that not only pervasive services
should be smart, but the security mechanism should also be smart.
Unfortunately, traditional security approaches are not adequate for such
requirements described above. Traditionally, stand-along computer and small
networks always rely on authentication and access control to achieve security. For
available traditional approaches ([11],[12],[13],etc.), there are some common features,
such as centralized management, users pre-known and security management in hands
of one or two persons, etc. Since these approaches are not suitable for pervasive
computing, new security approaches should be developed. And indeed, many efforts
([3], [8], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], etc.) have been made, and the proposed solutions
may be helpful in some cases, but they all have their own limitations, and they cannot
be deployed widely. Therefore a new question is raised, which is incompatibility.
Since different pervasive computing environments may employ different security
mechanisms, which are incompatible with one another, users cannot use various
pervasive services in these environments because they cannot be recognized or
trusted. We argue that this considerably violates the motivations of pervasive
computing.
Hence, we think it is necessary to build a new entity recognition scheme, which
enables service providers and requesters to be able to interact with each other securely
in various cases, no matter whether users are known to service providers or not, no
matter whether service providers have an authority center or not, and no matter what
security requirements service providers claim. With this scheme, we hope that, if an
entity wants to consume a service, it just needs to know what information it should
provide, and the service provider checks whether the requester entity can be trusted or
not according to the security utilities it can use at present, and then accepts or rejects
the requester entity’s request.
Therefore, we propose a context-aware entity recognition scheme in this paper.
With the term context-aware, we mean that not only service requester entities can be
recognized in different environments, but also service providers can employ different
approaches to recognize requesters.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 will describe some
scenarios that inspire us to design such scheme. Then we will introduce a key notion
of our scheme, namely Trust Infrastructure, in Section 3. And Section 4 will describe
context-aware entity recognition scheme in detail. And we will give related work on
our research in Section 5. Finally, a conclusion will be drawn in Section 6, in which
our future work will also be depicted.
148

2 MOTIVATION SCENARIOS
Since pervasive computing systems may be built by different enterprises, we may
meet some troubles because of their incompatibility. For example, when I am at
office, I use my PDA to use smart office service, which is developed by a company
and is helpful to increase my work efficiency greatly, e.g. it can prepare my
presentation document in the projector before I enter the meeting room to take my
presentation. Unfortunately, when I am off duty and go home, my PDA cannot be
recognized by my smart home system, which is another pervasive computing service
provided by another company. If I want to bring my PDA outdoors, I may also find
my PDA cannot get some public service, e.g. location tracking service, just in that I
have not registered my PDA to the third company that supplies such service. We
argue that such a world is far from a true pervasive computing world, even if so-
called pervasive computing services are everywhere.
Now let’s take a look at the life of John one day, which may be our dream for
the pervasive computing world.
z Scenario 1 - In the morning, John goes to office and his PDA gets to know
the arrival of his new emails and wants to download them (according to John’s
configuration specified before). When John’s PDA requests the emails, a valid
certificate is required by the email server. Receiving John’s certificate, the email
server consults the authority center whether it is John. With positive answer, the email
server sends the emails to John’s PDA. Then John is noticed to read the new emails
when he is seated.
z Scenario 2 - At noon, John goes to the cafe near his company to have a rest.
Since this café provides free Internet surfing service with its WLAN to its guests,
John wants to browse latest news with his PDA during enjoying coffee. Since the
café’s network access server (NAS) finds John is a guest in the shop, it permits John’s
PDA to access Internet.
z Scenario 3 - In the afternoon, John goes to a branch of his company, where
he wants to print a document. However, his PDA cannot be recognized by the printer.
Fortunately, John’s PDA finds that it can be trusted by the PDA of the manager, say
Tom. So John’s PDA asks Tom’s PDA for help. The latter then delivers a temporary
delegation to John’s PDA, and with this delegation, John’s PDA is successful to use
the printer. In this case, Tom is usually disconnected from the printer to ask for any
recommendations.
z Scenario 4 - At night, John goes to the birthday party of Mary, one of his
friends. At the party, John meets a new friend, say Alice. After exchanging each
other’s email addresses, Alice’s PDA further wants John’s home address. Before
sending out this sensitive information, John’s PDA finds it has nothing about Alice’s
trustworthiness, so it decides to consult the friends John trusts, e.g. Harry, Jerry, etc.,
and based on the answers, John’s PDA finds out Alice’s reputation is quite good and
decides to tell her John’s home address.
From the scenarios we can see that, in different pervasive computing
environments, different trust information may needed. For example, in Scenarios 1 3
4, John’s identity or credential may be needed, however, in Scenario 2, this is not
essential and some context information, e.g. location information is needed. So
recognition information is dependent upon concrete contexts. Furthermore, for entities
149

as service providers, they also cannot always rely on a certain security server. When
they move, the security server may be unavailable, so their security mechanisms
should also be context-aware.
3 Trust Infrastructure
Before we discuss the context-aware entity recognition scheme, we will describe a
novel notion, namely Trust Infrastructure. To understand Trust Infrastructure better,
we firstly introduce two concepts, Requester and Recognizer.
Requester is an entity that request services from other entities. Recognizer is an
entity that is responsible to determine Requesters’ trustworthiness, which is also the
very entity that provides services.
With the term “entity recognition”, we mean the action that Recognizer determines
Requester as a trustworthy peer or not.
In the context-aware entity recognition scheme, Trust Infrastructure is a set of
entities and trust relationships between Recognizer and these entities. Every
Recognizer has its own trust infrastructure to help it to determine a Requester’s
trustworthiness. No matter anywhere an entity moves to, it will build its own trust
infrastructure as a Recognizer.
3.1 Trust Relationships
A trust infrastructure is made up of entities that have trust relationships with
Recognizer. Trust relationships indicate how much an entity is trusted by another
entity under certain context.
A trust relationship can be denoted as follows.
),,,(
21
pctxttvaletr
e
= (1)
Which means entity e
2
is trusted by e
1
under the context of ctxt with the trust
value tval that indicates to how much degree e
2
is trusted. In formula (1), p∈ [0,1] is
privilege of this trust relationship, which is used to compute a stranger’s trust value.
With privilege value p, Recognizer can decide how trust relationships will be used to
determine a stranger’s trustworthiness. We denote the set of values of p as P.
Note that the term context here is not the same as the Context we use in the title
of this paper. The latter refers to environments of both service provider entities and
service requester entities. On the contrary, the context in trust relationships just refers
to service requester entities’ environments. Since this difference is easy to be
distinguished, we will not point it out in the rest of this paper.
Up to now, we abstract four types of trust relationships, with which we can build
the most of trust infrastructures in various pervasive environments. The four
relationships are described in detail bellow.
z Direct Trust Relationship (DTR) - If entity A trusts entity B directly and no
other entities are needed to help A to determine the trustworthiness of B, this
relationship is a direct trust relationship.
For instance, in Scenario 3, Tom has a direct trust relationship with John.
150
z Bound Trust Relationship (BTR) –If whether entity A can trust another entity
is completely dependent upon entity B’s trust knowledge in such context, we can say
entity A has a bound trust relationship to entity B. Therefore with bound trust
relationships, an entity can hand over its trust management to other entities, which
will be useful in many scenarios.
For example, in Scenario 1, the email server has a bound trust relationship with
the backend security server.
z Recommended Trust Relationship (RTR) - Supposing entity A trusts entity B,
but does not trust entity C. At the same time, B trusts C, then A can ask B for the
trustworthiness of C. Receiving the trust value of C from B, as well as the
trustworthiness of B to A, A can decide to how much degree C can be trusted. In this
case, we can say the trust relationship established from A to C is a recommended trust
relationship. As indirect trust relationships, recommended trust relationships are
useful to decide strangers’ trustworthiness
For instance, in Scenario 4, since John cannot trust Alice at first look, he will
request recommendations from other friends. With recommendations, John creates a
recommended trust relationship with Alice.
Delegated Trust Relationship (LTR) - If entity A has a trust relationship to entity
B and entity C cannot be trusted by A, then B can delegate his trustworthiness to C, so
that A can trust C as it trusts B. In such case, we can say A has a delegated trust
relationship to C. A delegated trust relationship is usually used when A is
disconnected from B at present, therefore A cannot get any recommendations from B.
Taking Scenario 3 as an example, in order to enable John to be trusted by the
printer, John has to send delegation request to Tom, and on receiving delegation from
Tom, John hands it to the printer, then the printer will establish a delegated trust
relationship with John and permit him to print files.
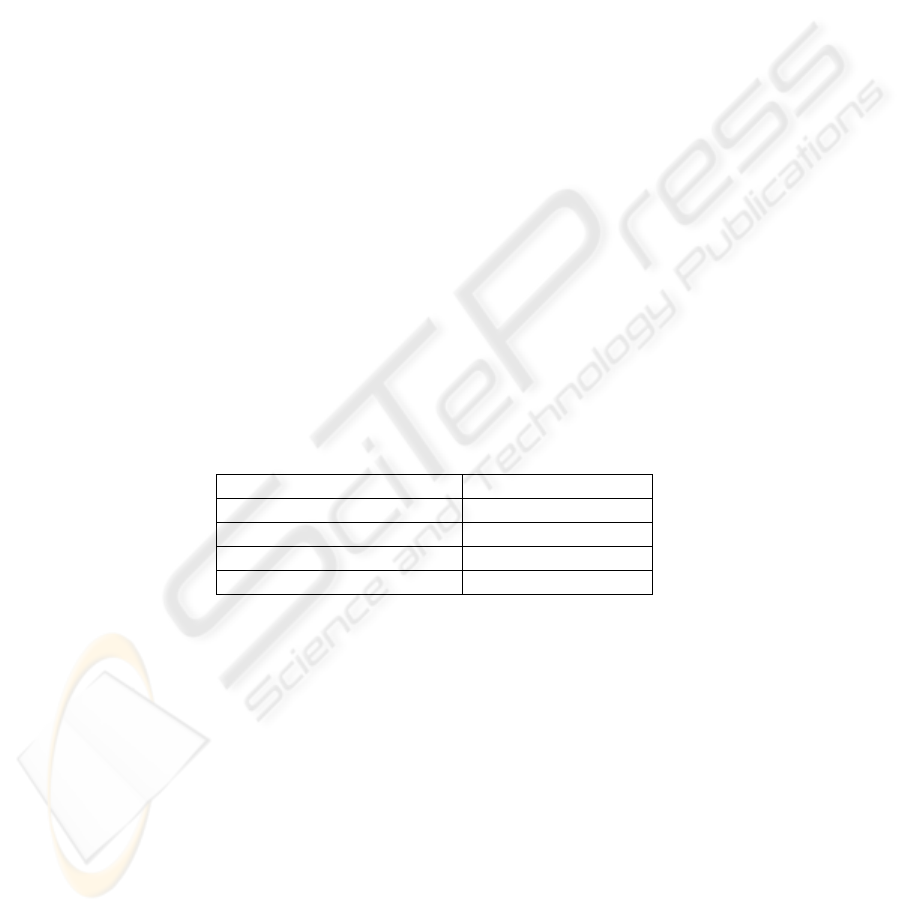
Table 1 is an example of privilege values of these four types of trust
relationships.
Table.1 an example P
Trust Relationship Type Privilege Value
BTR 1
DTR 0.5
RTR 0.3
LTR 0.1
With the privilege values in Table.2, when a stranger needs to be recognized,
Recognizer will rely on advices of trust relationships following the order
BTR>DTR>RDT>LDT.
3.2 Trust Infrastructure Definition
Since Trust Infrastructure is used by Recognizer to determine Requester’s
trustworthiness, it should provide knowledge to Recognizer that which entities can be
replied upon in a certain context. Therefore, we define Trust Infrastructure as a set of
maps from contexts to trust relationships.
Formally, we define Trust Infrastructure as
151
)}{( TRSctxtTI →= (1)
where ctxt is the context, and
)},,{( ptvaleTRS
=
, where e, tval and p are
all defined in the part A of section 3.
For example, we can describe an example trust infrastructure of Scenario 4 as
follows.
TI
John
= { (Ctxt1
→
{(Harry,1,0.5),(Jerry,0.5,0.3)}), (Ctxt2
→
{(Harry,0.5,0.3)},
(Ctxt2
→
{(Jerry,0.2,0.3)}), …… }
3.3 Building Trust Infrastructure
In the pervasive computing world, entities are mobile not only as service requesters
but also as service providers. When an entity moves to a new place, it is necessary for
it to build its trust infrastructure so as to be able to determine whether a stranger can
be trusted.
In order to build such trust infrastructure, Recognizer should maintain a trust
repository. In trust repositories, all trust relationships are recorded. Table.2 shows a
trust repository example.
Table.2 a sample trust repository
Entity Type Context Trust Value
e0 BTR Ctxt0 1
e1 DTR Ctxt1 0.3
e2 LTR Ctx1 0.7
e3 DTR Ctxt2 1
e4 RTR Ctxt3 0.4
When an entity moves to a new environment, it will refresh its trust
infrastructure based on the trust repository it maintains.
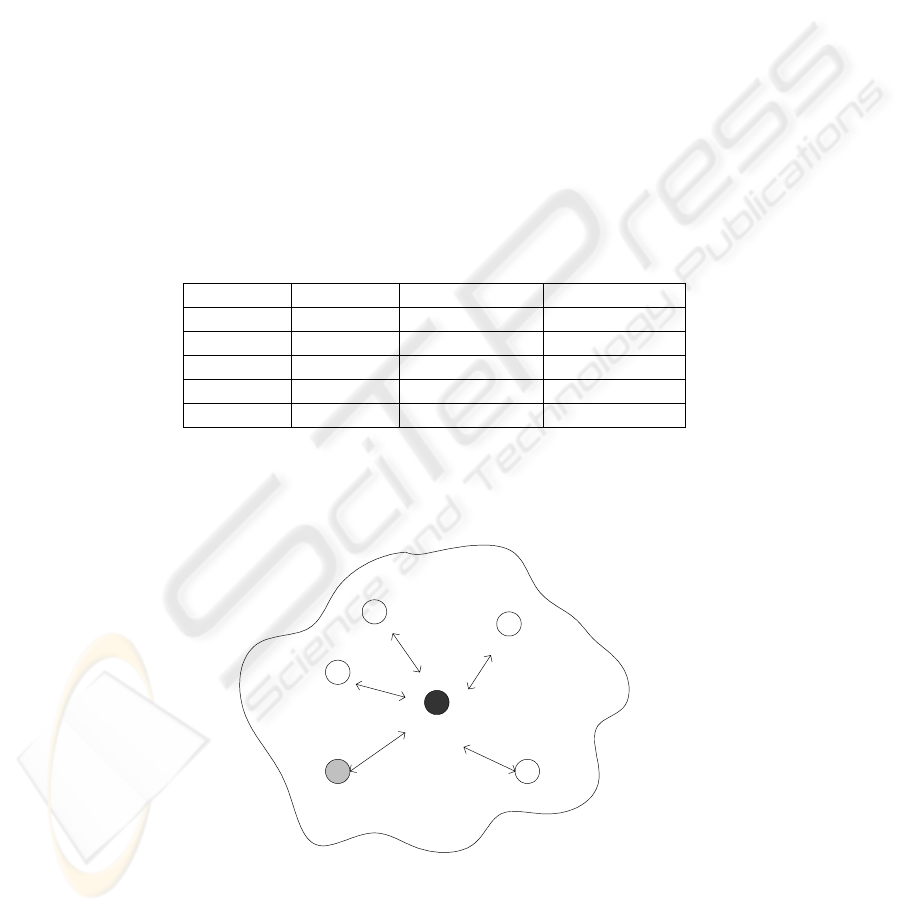
Supposing an entity, say Recognizer, has a trust repository as described in
Table.2, and it moves to a new place as described in Fig..1.
e1
Re c o g n i z e r
e2
e4e5
e0
Fig. 1. Entities Connected with Recognizer
152
In Fig..1, only e
5
is a stranger to Recognizer. Therefore, we can build the
corresponding trust infrastructure in Table.3 according to Table 1and Table.2.
Table.3 An Trust Infrastructure
Ctxt0->{(e0,1,1),
Ctxt1->{(e1,0.3,0.5),(e2,0.7,0.1)}
Ctxt3->{(e4,0.5,0.1)}
4 The Context-Aware Entity Recognition Scheme
In this section, we will describe our proposed context-aware entity recognition
scheme in detail.
4.1 Context of Pervasive Computing
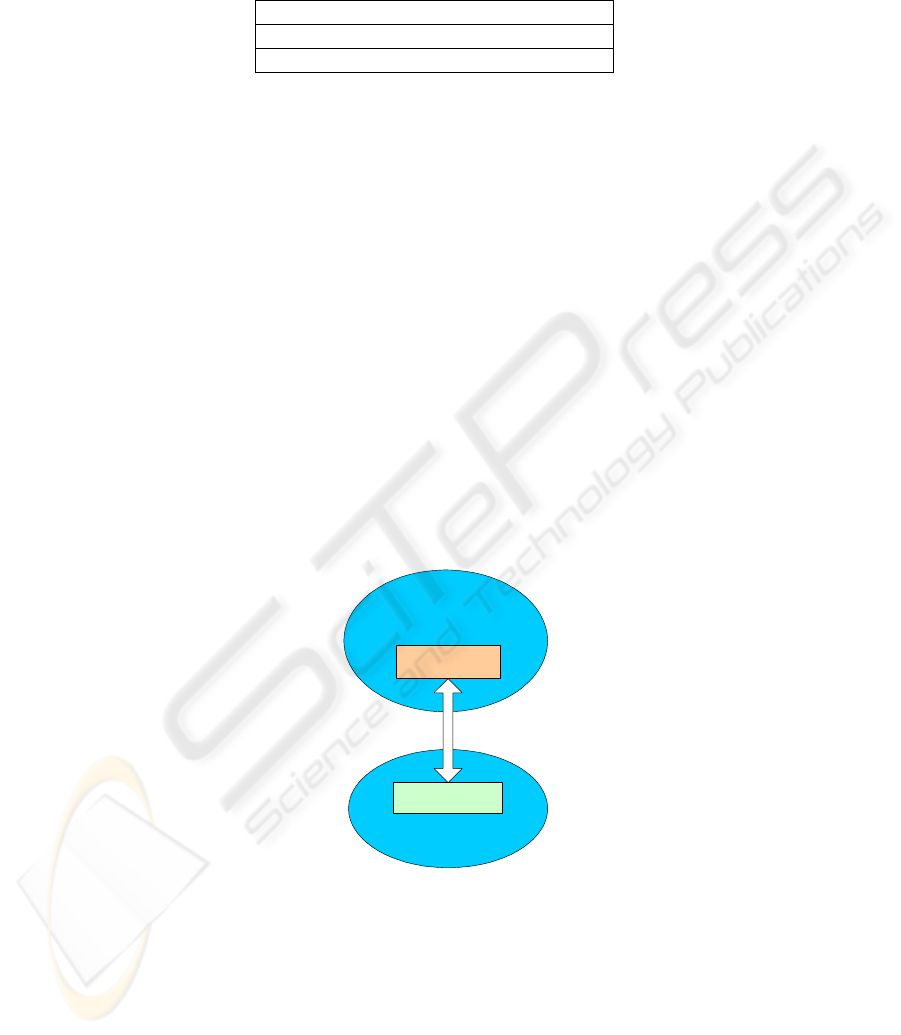
As we mentioned before, context of pervasive computing environments should play
an important role in entity recognition. In different context, provider entities will use
different recognition mechanisms to decide whether requester entities are trustworthy
or not. Although there are a lot of context factors in pervasive computing
environments, from the aspect of entity recognition, we use two context factors.
z Trust Infrastructure: this context factor is for service provider entities. With
different trust infrastructures, service provider entities will take different approaches
to recognize requester entities.
z Service Provided: With different services, different recognition information
and security level will be required by provider entities.
The context environment in pervasive computing can be illustrated in Fig..2.
Ser vi ce Pr ovi ded
Tr us t
Infrastructure
Recogni zer
Request er
Fig..2 Context of Entities in pervasive computing
So we can see that, not only context of service requester entities is considered,
but also service provider entities’ context is taken into account.
153

4.2 The Context-Aware Entity Recognition Process
Entity Recognition process can be divided into three phases.
z Initiation Phase: The service requester entity (Requester) requests service
from the service provider entity (Recognizer);
z Recognition Information Exchange Phase: Recognizer decides which
information is needed from Requester according to what service is requested and
sends the recognition information request to Requester; Requester estimates whether
it should reply the needed information, if so, it send the information back to
Recognizer;
z Trust Evaluation Phase: Recognizer evaluates Requester’s trustworthiness
and decides whether to permit its request, if so, sends permission to Requester.
4.3 Entity Recognition Initiation
An Entity recognition session is initiated by Requester with an Access Request to
Recognizer. In Access Request, Requester specifies what service it is interested in. As
for how to describe desired service, it is more relevant with research on service
discovery, which is quite out of our scope here. For more information about service
discovery, SLP[20], UpnP[21], Jini[22], RDF[25], etc. can be referred to.
In this paper, for the purpose of simpleness, we just denote Access Request as
follows,
),( ServDescServNoreq = (2)
where ServNo and ServDesc indicate the number and description of the
requested service respectively.
4.4 Recognition Information Exchange
In our proposed scheme, Entity information exchange is a negotiation process. Firstly,
Recognizer tells Requester which information is needed in order to prove its
trustworthiness, according to what trust infrastructure the Requester can reply on and
which concrete service Requester is requesting for. Then, the two entities will
continue to exchange information until Recognizer gets enough information to
evaluate Requester’s trustworthiness.
In order to describe recognition information, we use attribute vectors, which we
borrow from Shankar [23].
Therefore, we can depict recognition information specification from Recognizer
as follows.
pricn
rrrspeccie },...,,{_
21
=
(3)
where r
1
,r
2
,…,r
n
are attributes specified as needed recognition information, and
pric means encrypt attribute vector with Recognizer’s private key.
On receiving recognition information specification, Requester decrypts it with
Recognizer’s public key and gets to know which information is needed. Due to
privacy protection, Requester will not always answer Recognizer with all information
needed by it. That means Requester may reply with just part of the information
154

specified, accompanied with attributes that cannot be answered. Hence, Requester’s
answer can be denoted as follows.
prirnkkk
rrraaareplycie },...,,,,...,,{_
2121 ++
= (4)
where a
1
,a
2
,…,a
k
are information needed by Recognizer, r
k+1
, r
k+2
,…,r
n
are
attributes cannot be told to Recognizer, and prir is the private key of Requester.
When Recognizer receives Requester’s reply, it will check whether all
recognition information is answered, if so, it will begin to evaluate Requester’s
trustworthiness on the service it requests. Otherwise, Recognizer can take one of
actions described bellow, according to user’s configuration.
z To deny Requester’s request directly;
z To send alternative attributes required as recognition information to
Requester and determine Requester’s trustworthiness later;
z To accept Requester’s reply, but decrease the privilege assigned to
Requester.
If alternative attributes should be sent to Requester, Requester will also check
them in terms of privacy. So the recognition information exchange may be a multi-
trip negotiation. process
4.5 Computing Trust Value Based On Trust Infrastructure
As long as Recognizer collects all necessary attributes values, it will compute the trust
value from the collected information. This does not mean that these attributes values
are all numeric. Instead, Recognizer can find maps from these attributes values to trust
values relying on its trust infrastructure and compute Requester’s trust value based on
these trust values and structure of its infrastructure.
Trust Values
A trust value shows to how much degree an entity is trusted by another entity in a
certain context. In our scheme, a trust value is a real number and it can be denoted as:
}10|{
≤
∧
≥
∧
∈= ttRttT (5)
The bigger t is, the more an entity is trusted. When t = 0, the entity is
absolutely disbelieved. And when t = 1, the entity is absolutely believed in.
Trust Values from Trust Infrastructure
After recognitions information is exchanged, the trust infrastructure of Recognizer
will give a set of trust values about Requester. How many trust values will be returned
depends upon how many entities in the trust infrastructure that know Requester.
Supposing an entity e
i
(i=1,2,..,n) in the trust infrastructure returns trust value t
i
and the corresponding trust relationship in the trust infrastructure is (e
i
,tval
i
,p
k
), where
p
k
∈ P (k=1,2,…,4). In order to computing final trust value of Requester, we group
such involved trust relationships according to value of p
k
as follows (for simple of
brief, context is omitted).
p
1
: (e
1
, tval
1
, p
1
), (e
2
, tval
2
, p
1
),…, (e
u
,tval
u
,p
1
)
p
2
: (e
u+1
, tval
u+1
, p
1
), (e
u+2
, tval
u+2
, p
2
),…, (e
u+v
,tval
u+v
,p
2
)
155
p
3
: (e
u+v+1
, tval
u+v+1
, p
3
), (e
u+v+2
, tval
u+v+2
, p
3
),…,
(e
u+v+s
,tval
u+v+s
,p
3
)
p
4
: (e
u+v+s+1
, tval
u+v+s+1
, p
4
), (e
u+v+s+2
, tval
u+v+s+2
, p
4
),…, (e
n
, tval
n
,p
4
)
Therefore we can compute the contribute of each type of trust relationships to
finial trust value of Requester as follows.
))((
1
1
1
∑
=
×=
u
i
ii
ttval
u
p
tv
))((
1
2
2
∑
+
+=
×=
vu
ui
ii
ttval
v
p
tv
))((
1
3
3
∑
++
++=
×=
svu
vui
ii
ttval
s
p
tv
4
4
1
(())
n
ii
iuvs
p
tv tval t
nuvs
=+++
=×
−−−
∑
Then we can get the trust value of Requester according to formula (7).
)1,min(
4
1
∑
=
=
k
kfinal
tvtval
(7)
4.6 Evaluating Trustworthiness
Since trust values are not answers about yes or no, Recognizer has to translate trust
values into such decision. In our current proposed scheme, we use a simple threshold
based mechanism to make decision. Threshold values are set in a configuration file.
When a decision should be made, the following formula will be used.
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎨
⎧
<
≥
=
)(
)(
thresholdtvalno
thresholdtvalyes
permission
final
final
(8)
where tval is the trust value and threshold is the threshold value set by users.
It should be point out that we use this rule just to describe our idea. In practice,
more complex evaluation rules can be employed in the context-aware entity
recognizer scheme.
4.7 Applied to Example Scenario
In this section, we will apply our scheme to Scenario 4. Supposing the trust
infrastructure of John’s PDA is what is described in the part B of section 3, and the
service that Alice requests is Ctxt1, there are two trust relationships in its trust
infrastructure can be used, which are described as follows.
(Harry,Ctxt1,1,0.5),
(Jerry,Ctxt1, 0.5,0.3)
Supposing the trust values of Alice returned by Harry and Jerry are 0.8, 0.6
respectively, we can compute final trust value of Alice as follows according to
formula (6) and formula (7).
(6)
156

0.5 0.3
min( 1 0.8 0.5 0.6,1) 0.49
11
Alice
tval =××+××=
If the threshold value is set as 0.5, since tval
Alice
< 0.5, John will not send his
home address to Alice according to formula (8).
5. Related Work
Seigneur et al. [1] [2] put forward the notion of entity recognition and they also
proposed a pluggable entity recognition scheme to enable end-to-end trust. However,
their scheme is just a “proof-of-concept” and was described simply in terms of
cryptographics. We can say that it is not a complete entity recognition scheme.
More efforts were made on trust management. Blaze et al. [4] proposed a
disturbed trust management solution, namely PolicyMaker, which is probably one of
the first efforts on distributed trust. PolicyMaker is able to interpret policies and
answer questions about access rights. Unfortunately, it is difficult for non-programmer
to develop policies. PGP [8] is another distributed trust management scheme, but just
for sending secure emails. Shand et al. [24] proposed a trust infrastructure, as well as
a trust computation algorithm. It provides a solution to trust each other and work
collaboratively in certain scenarios. Shankar [23] tried to propose a unified model for
representing trust relationships between entities in pervasive computing
environments, but he did not provide any more details about how to employ and
implement their model. Even so, we get the idea of use an attribute sector modeling
trust evidence from Shankar’s work. Ninghui Li, et al [19] proposed a role-based
trust-management framework, namely RT, which is a family of Role-based Trust-
management languages for representing policies and credentials in distributed
authorization. RT unifies RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and trust-management
concepts; it thus differs from previous trust management systems in that it uses roles
as a central notion. These trust models may be sufficient in some cases, but none of
them is suitable to fulfill trust requirements in various pervasive computing
environments.
6. Conclusion and Future Work
In this paper, we propose a context-aware entity recognition scheme. This scheme is
aimed to enable an entity to be able to recognize other entities in various scenarios.
This has two meanings. On the one hand, an entity as the service provider can
recognize other entities securely and adaptively. We argue that its security capability
should be enhanced by or adaptive to its different environments. Therefore, we
propose a notion of “Trust Infrastructure” that helps Recognizer to be able determine
Requester’s trustworthiness. Since Recognizer may be movable, its trust infrastructure
can be built dynamically in different environments. On the other hand, an entity as
service requester may be trusted in various scenarios no matter which service it is
requesting and no matter what security level Recognizer requires. To obtain such
goal, an attribute-based recognition information exchange approach is employed,
157

which enables Requester to be able to be recognized by different service provider
entities in different cases. As an essential part of the entire entity recognition scheme,
we propose an algorithm to computer the trust value of Requester based on
Recognizer’s trust infrastructure, so that Recognizer can decide whether it can permit
Requester’s request or not according to a threshold based decision mechanism.
For future work, we will research more on trust infrastructures, especially
dynamically and securely building trust infrastructure. Besides, entities in a trust
infrastructure also have their own trust infrastructure, then how to use these indirect
trust infrastructures will also be researched. Moreover, attribute-based recognition
information exchange will also researched in detail, including designing a protocol to
support such exchange and enable Requester to protect its privacy. Finally, we hope
that entities can update their knowledge on strangers’ trustworthiness and hence their
trust infrastructures can also be refreshed based on their experiences.
References
1. J-M. Seigneur, S. Farrell, C. Jensen, E. Gray, Y. Chen:
"End-to-end trust in pervasive computing starts with recognition". In Proceedings of the
First International Conference on Security in Pervasive Computing, Boppard, Germany,
March 2003
2. J.-M. Seigneur, S. Farrell, and C. D. Jensen, "Secure Ubiquitous computing based on entity
recognition", in Ubicomp'02 Security Workshop, 2002,
3. Yarong Tang. Decentralized Trust Management.
4. M. Blaze, J. Feigenbaum, J. Ioannidis, and A. D. Keromytis. The Role of Trust
Management in Distributed Systems Security. Chapter in Secure Internet Programming:
Security Issues for Mobile and Distributed Objects, (Vitek and Jensen, eds.) Springer-
Verlag, 1999.
5. Weiser, M. The Computer for the 21st Century. Scientific American , September, 1991.
6. David Garlan, Dan Siewiorek, Asim Smailagic, and Peter Steenkist. "Project Aura: Toward
Distraction-Free Pervasive Computing", in IEE Pervasive Computing, special issue on
"Integrated Pervasive Computing Environments", Volume 21, Number 2, April-June, 2002,
pp. 22-31.
7. M. Satyanarayanan, "Pervasive computing: Vision and challenges," IEEE Personal
Communications, pp. 10--17, August 2001.
8. P. Zimmermann, PGP User’s Guide, MIT Press, Cambridge, 1994.
9. Michael Lyons. Pervasive Computing: Control and Freedom in Cyberspace. 2002
10. M. Barbeau. Mobile, Distributed, and Pervasive Computing, in: I. Stojmenovic, Chapter 27
- Handbook of Wireless Networks and Mobile Computing, John Wiley and Sons, Inc.,
February 2002 (ISBN: 0-471-41902-4)
11. J. Kohl and Clifford Neuman. The kerberos network authentication service (V5). Request
for Comments (Proposed Standard) RFC 1510, Internet Engineering Task Force, September
1993.
12. IETF: Public-Key Infrastructure (X.509).
13. IEEE Standards for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Port based Network Access
Control, IEEE Standard 802.1x-2001, June 2001.
14. M. Blaze, J. Feigenbaum, and J. Lacy. Decentralized trust management. In Proceedings
1996 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pages 164--173, May 1996
15. M. Blaze, J. Feigenbaum, and A. D. Keromytis. KeyNote: Trust management for public-
key infrastructures. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1550:59--63, 1999.
158

16. A. Abdul-Rahman and S. Hailes. A Distributed Trust Model. New Security Paradigms
Workshop 1997, ACM, 1997.
17. Seigneur, J.-M., Farrell, S., and Jensen, C. D.: Secure ubiquitous computing based on entity
recognition. In: Ubicomp'02 Security Workshop, Goteborg, (2002),
18. F. Stajano and R. Anderson. The Resurrecting Duckling: Security Issues for Ad-hoc
Wireless Networks. B. Christianson, B. Crispo, and M. Roe (Eds.), Security Protocols, 7th
International Workshop Proceedings, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1999.
19. N. Li, J. C. Mitchell, and W. H. Winsborough. Design of a role-based trust-management
framework. In “Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy”, pp.
114 – 130, 2002. IEEE Press.
20. E. Guttman, C. Perkins, J. Veizades, and M. Day "Service Location Protocol, Version 2,"
IETF RFC-2165, November 1998
21. Microsoft Corporation, "Universal Plug and Play Device Architecture", White Paper,
Version 1.0, June 6, 2000.
22. Sun Microsystems Inc.; "Jini Architecture Specification";
23. Narendar Shankar, William A. Arbaugh. On Trust for Ubiquitous Computing .
Ubicomp2002
24. Brian Shand, et al. Trust for Ubiquitous, Transparent Collaboration. IEEE Pervasive
Computing and Communication 2003.
159
