
High Level Design Quality Assessment of Object
Oriented Codes
R. A. Khan
1
, & K. Mustafa
2
1, 2
Department of Computer Science,
Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi- 110025 India
Abstract. This paper proposes an improved Object Oriented metrics, which
may be used for the high-level design quality assessment of Object Oriented
software. An integrated approach has been adopted to get a single class based
metrics that may be used for cumulative measure of all aspects of object ori-
ented design (encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism), and hence an in-
dication of quality of class in terms of complexity. These values of WCC
(Weighted Class Complexity) when averaged will enable computing the aver-
age complexity of software and also the quality. Three principle steps, identifi-
cation of product attributes, identification of quality factors and a means of
linkage, has been followed to develop such a metric. The proposed metric has
been theoretically and empirically validated. This single metric may be used in
initial stages and ensuring compliance at this stage will increase the reliability
of system as a whole, as reliability in general is a by-product of quality.
1 Introduction
Our increasing reliance on software systems and the ever-increasing domain of
software applications puts a high premium on the standard of quality these systems
offer us. This assumes all the more significance in case of critical software applica-
tions where even a minor error can prove to be devastating. Quality becomes more of
a differentiator between products and a kind of benchmark against which improve-
ment is assessed. The importance of quality software is no longer an advantage but a
necessary factor. Traditional software metrics used to evaluate the product character-
istics such as size, complexity, performance and quality is switched to rely on some
fundamentally different attributes like encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism,
which are inherent in object- orientation. This switching led to the definition of many
metrics proposed by various researchers and practitioners to measure the object ori-
ented attributes. Most of the metrics, available for object oriented software analysis,
may normally be used in later phase of system development life cycle and rely upon
information extracted on the operationalization of software. Such metrics provide the
indication of quality too late to improve the product, prior to completion of product. It
is also true that a couple of object oriented metrics altogether may be used to measure
all the aspects of object oriented Design [14]. Thus, there appeared to be need for
A. Khan R. and Mustafa K. (2004).
High Level Design Quality Assessment of Object Oriented Codes.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Verification and Validation of Enterprise Information Systems, pages 34-43
DOI: 10.5220/0002663900340043
Copyright
c
SciTePress

developing a single integrated object oriented Metric, encompassing all the object
oriented design constructs, which may be used in early stage of development to give
good indication of Software Quality. It is strongly felt to be more productive and
constructive.
Indication and anticipation of quality as early as possible in system development life
cycle is necessary because with each iteration of SDLC, cost impact of modification
and improvement will significantly increase. Rest of the paper presents the result of a
study based on assessment of quality ensuring criteria and how the high level external
attribute relates to object oriented design characteristics. These relations need to be
defined and then quantified so as to get a measurable representation of software qual-
ity. In Section 2, the Dromey’s quality model guidelines are being used to adopt the
strategies to get the measurable representation of software quality. In Section 3, a
single class based metrics, Weighted Class Complexity (WCC), is being proposed
which may be used to measure all aspects of object oriented design and hence gives
an indication of quality of a class and average complexity of Software. Section 4
describes the influences of quality factors onto the proposed Weighted Class Com-
plexity Metrics. Section 5 gives the conclusion.
2 Draomey’s Strategies for Measurable Representation
In order to better quantify quality, researchers have developed indirect models that
attempt to measure software product quality by using a set of quality attributes, char-
acteristics, and metrics. An important assumption in defining these quality models is
that internal product characteristics influences external product attributes, and by
evaluating a product’s internal characteristics some reasonable conclusions can be
drawn about the products external quality attributes. Unfortunately, earlier models
failed to include ways of accounting for the degree of influence of individual attrib-
utes [2]. A framework for building product based quality models has been devel-
oped by Dromey [5][6]. There are three principal elements to Dromey’s generic qual-
ity model: product properties that influence quality, a set of high level quality attrib-
utes, and a means of linking them [6]. From the Dromey’s Quality Model guideline,
following strategies may be adapted to workout a measurable representation:
1. Identification of product properties (Object Oriented Software) that influences
quality.
2. Selection of a set of high-level quality attributes (relevant of course to the stage
under study).
3. A means of linking of them.
Figure 1. Strategy w. r. t. Dromey’s Model
Product Property
Quality Attribute
Linking
35

2.1 Identification of Product Properties
Object Oriented Software differs from structured software in terms of its abstrac-
tion and real world modeling concepts that take the form of object oriented design
constructs. A fundamental constraint of object oriented modeling and design is the
Object, which combines both data structure and behavior in a single entity [4]. Three
fundamental characteristics required for an object oriented approach: Encapsulation,
Polymorphism and Inheritance. Polymorphism and Inheritance are two aspects unique
to object oriented approach, while encapsulation in not.
Information hiding is a way of designing such that only subsets of the module’s prop-
erties, its public interfaces, are known to users of the module. It gives rise to encapsu-
lation in object oriented language. Encapsulation means that all that is seen of an
object is its necessary interface, namely the operations we can perform on the object
[5]. Information hiding is a theoretical technique that indisputably proven its value in
practice. Large programs that use information hiding have been found to be easier to
modify by a factor of 4 than programs that don’t adhere to this technique [6], [7].
Inheritance is a form of reuse that allows a programmer to define objects incre-
mentally by reusing previously defined objects as the basis for new objects. Inheri-
tance decreases complexity by reducing the number of operations and operators, but
this abstraction of objects can made maintenance and design difficult [8].
Polymorphism is an important concept that allows building a flexible system. This
concept of polymorphism allows developer to specify what shall occur and how shall
occur. Polymorphism means having the ability to take several forms. For object ori-
ented system, polymorphism allows the implementation of a given operations to be
dependent on the object that contains the operations; and operations can be imple-
mented in different ways in different classes. There is no doubt polymorphism assists
programmer to reduce complexity [9] and improve on many desirable attributes in-
cluding reusability.
2.2 Selection of Quality attributes
Quality Model for object oriented design QMOOD [1] has specified ‘functionality,
reliability, efficiency, usability, maintainability and portability’ as the initial set of
quality attributes. After reviewing their contributions towards defining design quality,
reliability and usability were excluded from the set due to their obvious slant toward
implementation rather than design. Portability was replaced by extendibility. Effi-
ciency was replaced by effectiveness. Maintainability was replaced by understand-
ability. The goal in adopting object oriented approach for design and implementation
is to develop reliable, adaptable and flexible software system. This justified the inclu-
sion of reliability as an important attribute of object oriented design quality assess-
ment. Flexibility was also included as an important quality attribute. Hence the set
reduces to, Functionality, Effectiveness, Understandability, Extendibility, Reusability,
Flexibility.
Software Assurance Technology Center, SATC, has proposed five of quality differ-
entiators/attributes for the coding and design phase. These are, Efficiency, Complex-
36

ity, Understandability, Reusability, and Testability/ Maintainability. Hence there is no
universally agreed-upon definition for each of high-level quality attributes [9].
2.3 A Means of Linkage
In order to establish a relationship between design constructs and attributes, the in-
fluence of design constructs and quality attributes are being examined (with respect to
SATC’s attributes). It was observed that each design constructs affects certain quality
attributes. This is being depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Design constructs affecting quality attributes
Numerous software metrics related to software quality assurance have been proposed
in past and are still being proposed. Figure 3 describes the general review of metrics
suggested by various researchers/ practitioners (MOOD [10]/ MOOSE [12]/
QMOOD [1] / EMOOSE [12] etc.) and object oriented concepts evaluation by these
suggested metrics.
Figure 3.Metrics and corresponding object oriented concepts
A critical examination of existing design metrics revealed that all metrics have
relevance with respect to a class i.e. all metrics eventually conduct measures taking
Understandability
Testability/ Main-
tainability
Encapsulation
Inheritance
Coupling
Cohesion
Efficiency
Complexity
Reusability
WMC DIT
FRC NOC
COM NOR
PAP FIN
PAD
MFA
NOM etc.
CAM
CCP
CFA
CBO LCOM
DCC
En
capsu
l
a
t
i
o
n Inh
er
i
ta
n
ce
Coup
lin
g
Cohesion
37

class as a basis. This is hardly surprising as ‘class’ is the fundamental concept of
object oriented software
3 WCC- An Integrated Approach
Many of the metrics proposed by different researchers and practitioners for object
oriented software analysis relies on the information extracted from the implementa-
tion of software. Hence theses metrics may be used in later phase of software devel-
opment life cycle (SDLC). Software quality is required to be indicated as early as
possible in the SDLC since with each iteration of cycle, cost impact of modification
and improvement significantly increases. Thus, there is a need for object oriented
metrics that may be used in code and design phase and may ensure quality compli-
ances at this stage to increase the reliability of the system as a whole as reliability
itself is a byproduct of quality.
The Survey result in Figure 2 depicts that all metrics have relevance with respects
to a class [14]. This motivated effort towards developing a single class based metrics,
Weighted Class Complexity (WCC), which would give a cumulative measure of all
aspects of object oriented design and would thereby give an indication of ‘quality’ of
a class in terms of complexity. This single metrics when averaged would enable com-
puting the average complexity of software and finally the quality.
The complexity in this context has more of physiological meaning rather than com-
plexity as a quality attribute. This WCC should take into account each/ most of the
design constructs, i.e. WCC should be coupled of an encapsulation factor, an inheri-
tance factor, a coupling factor and a cohesion factor.
Better the encapsulation, better is the design and since it affects all five-quality
factors, better is the quality. This means better encapsulation measures should cause a
decrease in WCC. Again, more the number of external links (coupling), lower is the
flexibility of software and greater the complexity. So, increase in coupling factor
should cause an increase in WCC. For cohesion, we know that higher the cohesion,
better the design and therefore a measure of increasing cohesion should cause a de-
crease in WCC, or vice versa. Inheritance is a factor that has two-fold effect. While
increased use of inheritance increases reusability, it also means greater design com-
plexity and difficulty in implementation and maintenance.
After considering all these effects, an empirically and intuitively persuasive metric is
being formulated by relating measurable design characteristics together with the qual-
ity contributors as follows:
Where RFC (Response For Class) is based on the formulation for orthogonal software
given below as [13]
LCOM is the Lack of Cohesion Metrics, WMC is Weighted Method Per Class Met-
rics and CBO is the Coupling Between Objects Metrics.
WCC =
(
RFC * Level
)
+ LCOM
RFC
=
WMC
+
CBO
38

4 Influence of Quality factor to WCC
RFC is measuring the coupling in addition to encapsulation. As the deeper the
class is embedded in hierarchy, the greater would be the number of inherited methods
and hence greater the design complexity. This gives an idea to consider ‘ level’ and
find the product of RFC and level (RFC * Level), which shows the additional effort
of implementing the class with RFC calculated at the particular level. So that it gives
an indication of inheritance and coupling in addition to encapsulation. An increase in
this factor would increase the complexity measure of WCC. Addition of LCOM indi-
cates the cohesion of a class. A higher cohesion (lower LCOM) indicates a good
design. So adding LCOM implies that if cohesion is low, LCOM will be high, there-
fore WCC should be increased for low cohesion [11].
Summing up all these impacts, it is now clear that, WCC is directly proportional to
RFC * level, to LCOM and/ or inversely proportional to Cohesion. After combining
all these equations, a single class metric WCC may be defined as: WCC α (RFC*
Level) + LCOM
5 Empirical Investigation
This section applies the results obtained in the study of two commercial projects
undertaken in a software industry [15]. The outcome is validated with the results
obtained by the industry using full-scale code analysis.
The two applications used in this empirical study to validate the integrated object-
oriented metric set are industrial strength software. We labeled the applications as:
System A and System B. The industry professionals themselves have used full-scale
code analysis system for estimating the quality of these systems. They have rated the
quality of both the software systems as ‘Low’.
Table 1 and Table 2 show the values of metrics for System A and System B.
Table 1.
Metrics Values for System A
Class1
Class2
Class3
Class4
Class5
Class6
Class7
Class8
Class9
Class10
Class11
WMC
3 1 3 2 232 323 3
RFC
3 3 4 3 232 353 3
LCO
M
3 1 2 3 121 111 1
DIT
0 0 1 1 011 001 1
CBO
2 2 1 1 000 230 0
NOC
0 2 0 0 000 020 0
Level
0 0 1 1 011 001 1
WCC
3 1 6 6 153 114 4
Table 2. Metrics Values for System B
39

Class1
Class2
Class3
Class4
Class5
Class6
Class7
Class8
WMC
3132232 3
RFC
3343232 3
LCOM
3123121 1
DIT
0011011 0
CBO
2211000 2
NOC
0200000 0
Level
0011011 0
WCC
3166153 1
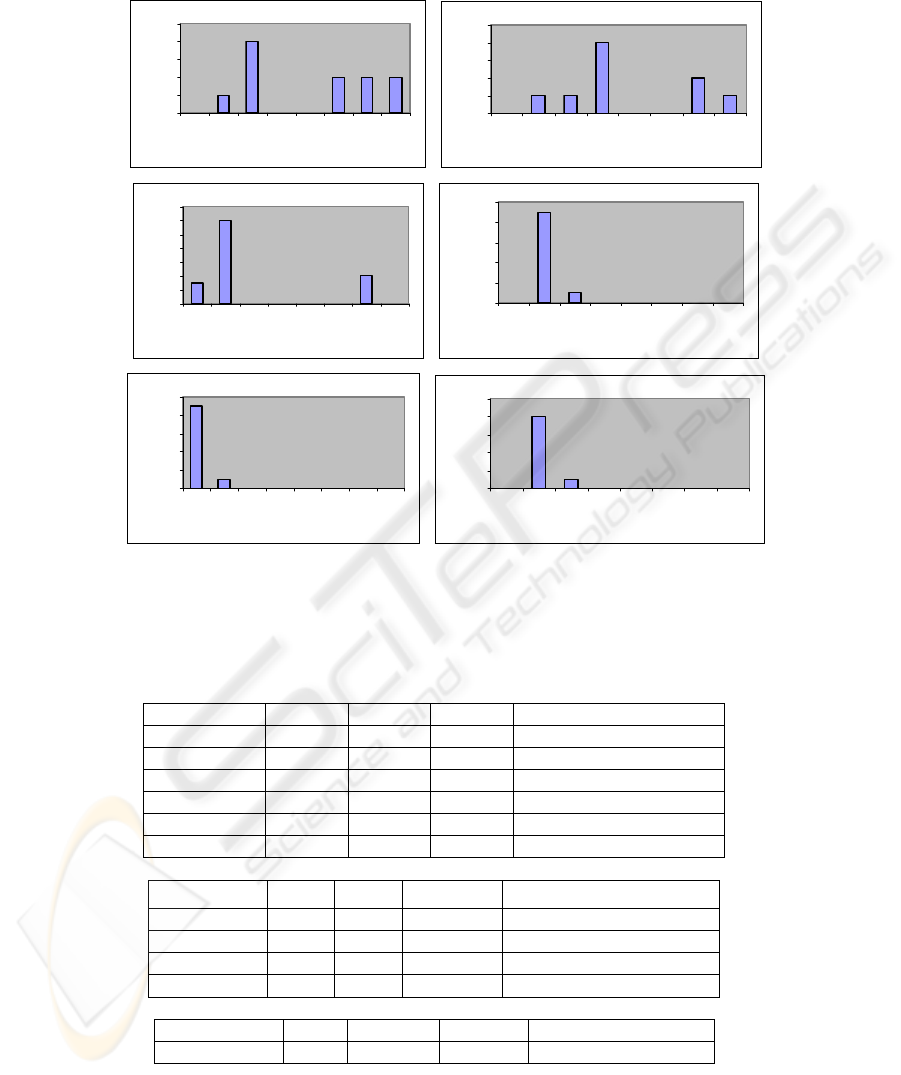
Figure 4 & 5 shows the distributions of the CK object oriented metrics suite
namely, WMC, CBO, RFC, LCOM and integrated metric WCC with level for the two
systems- System A and System B. The percentage of classes is on the X- axis and the
metrics values on the Y- axis.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0123456
WMC Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
01234567
RFC Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0123456
CBO Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0123456
LCOM Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
1234567
Level Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
0123456
WCC Count
Percent
Figure 4. Distribution of the CK Metrics Set and Integrated Metric Set for System A
40
0
10
20
30
40
50
01234567
WMC Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
01234567
RFC Count
Percent
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
01234567
CBO Count
Percent
0
20
40
60
80
100
01234567
LCOM Count
Percent
0
20
40
60
80
100
01234567
Level Count
Percent
0
20
40
60
80
100
01234567
WCC Count
Percent
Figure 5. Distribution of the CK Metrics Set and Integrated Metric Set for System B
The descriptive statistics and the correlations between the metrics for each system
are given in Table 3 -6. The values in bold are the mean value of the integrated metric
set. The descriptive statistics for System A and B are included on 11 C++ and 8 C++
classes respectively.
Table 3.
Descriptive Statistics for System A
Min. Max. Mean Std. Deviation
WCC
1 6
3.18
1.99
RFC
2 5
3
.83
Level
0 1
.55
.50
LCOM
1 3
1.55
.82
CBO
0 3 1.00 1.09
WMC
1 3 2.45 .68
Table 4. Correlation Analysis for System A
WCC
RFC
LCOM RFC*Level
WCC
1 -.009
.85 .91
RFC
1 .07 .03
LCOM
1
.31
RFC*level
1
Table 5. Descriptive Statistics for System B
Min. Max. Mean Std. Deviation
WCC
1 8
2
2.44
41
RFC
2 12
3.25
3.28
Level
0 1 .13 .35
LCOM
1 2 1.13 .35
CBO
0 6 1.50 1.85
WMC
1 7 3.75 2.25
Table 6. Correlation Analysis for System B
WCC RFC LCOM RFC*Level
WCC
1 .27
.74 .97
RFC
1 .01 .22
LCOM
1 .01
RFC*level
1
Table 7 summarizes the results of the correlation analysis for the integrated metric
set over the two software systems. The column list the correlation values for each pair
of metrics in the integrated metric set and rows list the system. In the table Metric 1 Χ
Metric 2 = correlation between Metric 1 and metric 2.
Table 7. Correlation Analysis Summary
WCCΧLCOM WCCΧ (RFC* Level) LCOMΧ (RFC* Level)
System A .60 .91 .31
System B .74 .97 .01
Examining Table 7 shows that for system A all of the metrics are highly correlated
with each other, with WCC and (FRC*Level) being the most significantly correlated.
This suggests low quality code because WCC increases due to increase in FRC not
due to increase in LCOM. Equation 2 shows that WCC= (FRC* Level) + LCOM.
The same is true for System B.
A critical examination of the results obtained leads to the following implications:
• WCC gives the same result regarding Low Quality for both the system A and B
as it was obtained by using full-scale code analyzer.
• It may be used to discover the underlying errors in the software design at the
early stage of software development life cycle leading to reduce effort on quality
assurance and avoidance of unnecessary overhead.
• It may help to evaluate the quality of software and provide the cost estimates of a
software project which facilitate the estimation and planning of new activities
• It may help to determine the effect of the object technology; especially reuse
technology applied in the software development according to some quantitative
evaluation such as productivity, quality, lead-time, maintainability, etc.
5 Conclusions
Importance of software measurement is hardly an issue of contention any longer.
It’s a well accepted fact that measurement enables designers and managers to obtain
quantitative measures of attributes in entities and also serves as a baseline for classifi-
cation, comparison and analysis of these attributes. Software measurement contrib-
utes to software quality from various aspects, such as understandability, complexity,
reliability, testability and maintainability, as well as performance and productivity of
software projects. With pervasive popularity and adaptation of Object Oriented meth-
42

odologies, software metrics tailored to Object Oriented characteristics are essential to
improve Object Oriented process and products.
All metrics available eventually conduct measures taking class as a basis. Whereas
the proposed object oriented metric is a single class based metric. It caters to all the
aspects of object oriented design, i.e. encapsulation, coupling and cohesion. The met-
ric may be used to indicate the software quality in early stage of SDLC to monitor the
cost impact of modification and improvement. Much cannot be said about the value
of this metric, before it is used on a large-scale basis and critically examined. But this
metric has a certain impact and value in terms of integral effect and reduction in ef-
fort for estimating the quality and reliability of object oriented software. This eventu-
ally leads to evaluate reusability and testability/ maintainability of software.
References
1. J. Bansiya,: A Hierarchical Model for object- oriented Design Quality Assessment, IEEE
Transaction on software engineering, Vol.28, No.1, January 2002.
2. G. R. Dromey,: A Model for Software Product Quality, IEEE Transaction on Software Engi-
neering, vol. 21, no.2, pp.146-162, Feb.1995.
3. G. R. Dromey, : Cornering the Chimera, IEEE Software, vol. 13, no.1 pp. 33-43, 1996.
4. J., Blaha, Rambaugh, M., et. al.: Object oriented Modeling and Design, Prentice hall, 1991
5. Jacobson, I., Christerson, M., Jonsson, P., and Overgaard, G.,: Object Oriented Software
Engineering: A use Case Driven Approach, Wokingham, England: Addison- Wesley, 1992.
6. Boehm, B. W.,: Improving Software Productivity, IEEE Computer, pp. 43-57, September
1987.
7. Korson, T. D. and Vaishnavi, V.K.,: An Empirical Study of Modularity on Program Modifi-
ability, Empirical Studies of Programmers, pp. 168-86, 1986
8. http://colaboration.csc.ncsu.edu/CSC325_Fall2002/lectures/Object_oriented_Metrics
9. Linda Rosenberg: Software Quality Metrics for Object Oriented System Environments, A
report of SATC’s research on OO metrics”
http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/qualazur/$swmesu2.htm
10. Abreu. F. Brito and Carpuca, Rogerio,: Candidate Metrics for Object Oriented Software
within a Taxonomy Framework, Proceeding of AQUIS’93, Venice, Italy, October 1993; se-
lected for reprint in the Journal of Systems and Software, Vol, 23(1, pp 87- 96, July 1994
11. Letha Etzkorn., Carl Davis., and Wei Li,: A Statistical Comparison of Various Definitions
of the LCOM metrics, Technical Report TR-UAH-CS-1997-02, Computer Science Dept.,
Alabama in Huntsville, 1997.
http://www.cs.uah/tech-re
ports/TR-UAH-CS-1997-02.pdf
12. Aline Lucia Baroni: Formal Definition of Object Oriented Design Metrics MS Thesis,
Vrije Universiteit Brussel- Belgium, 2002.
13. Victor Laing and Charles Coleman,: Principal Components of Orthogonal Object- Oriented
Metrics(323-08-14), White Paper Analyzing Results of NASA Object Oriented Data, May
29, 2003
14. M. Xenos, D. Stavrinoudis, K. Zikouli and D. Christodoulakis,: Object Oriented Metrics-
A survey, proceedings of the FESMA 2000, Federation of European Software Measure-
ment Associations, Madrid, Spain, 2000.
15. Telesoft India Pvt. Ltd. “Unpublished Project Documentation for System A and B”, C-
56/14, Industrial Area, Sec-62, Noida (UP), India-201304
43
