
Pruning Update Log Files in Intermittently Connected
Databases
Liton Chakraborty, Ajit Singh, and Kshirasagar Naik
Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
University of Waterloo, ON, Canada, N2L3G1
Abstract. Modern databases allow mobile clients that subscribe to replicated
data, to process the replica without requiring continuous connectivity, and to re-
ceive the updateswhile connectedto the server. In suchan environment—usually
known as the Intermittently Connected Database (ICDB) system—the server
should maintain the updates to the database in the log file(s). These update log
files should be pruned to reduce update retrieval time. In this paper we propose
two pruning algorithms, based on the periodic connectivity of the clients, that
consider two scenarios: uniform client connectivity patterns and widely varying
client connectivity patterns. In the former case, the complete pruning algorithm
is effective in keeping the log file size within a bound, hence reducing both disk
I/O during update propagation, and disk storage space; whereas, in case of the
latter, the partial pruning algorithm achieves significant further reduction in disk
I/O while retrieving the updates. Any reduction in CPU or I/O time in turn re-
duces wireless connection time for each client resulting in significant savings in
time and costs. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of these algo-
rithms.
1 Introduction
With the proliferation of small low-powered palm-top devices in the mobile wireless
computing environments, there arises the issue of supporting database access for these
devices. Intermittently Connected Database (ICDB) systems allow the clients to main-
tain a replica of some subsets of the global database schema in their local databases for-
going continuous connectivity;hence, this system improves performance and availabil-
ity, and reduces cost. For example, consider mobile sales-persons equipped with small
devices having relevant data. While in the field, where maintaining a continuous con-
nection with the database server (using wireless channel) is costly, they can serve their
clients accessing or modifying the local data. A salesperson can connect to the server
periodically, and re-integrate its updates with the server database. While connected, the
salesperson receives the updates made (by co-workers) in the server database.
Therefore, in an ICDB, updates to the local database are logged and propagated
to the server upon resumption of the connection which is intermittent in nature. The
server keeps track of the updates in the primary copy of the global database and dis-
seminates the updates relevant to a client based on the knowledge of his subscription.
In propagating the updates, a client-centric approach—that maintains a customized log
Chakraborty L., Singh A. and Naik K. (2004).
Pruning Update Log Files in Intermittently Connected Databases.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Wireless Information Systems, pages 63-72
DOI: 10.5220/0002666100630072
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 Chakraborty et. al.
file for each client—is very expensive in terms of server processing, as the server load
is proportionalto the number of clients. In coping withthis scalability issue in an ICDB
environment, a dat a-centric approach [1] has been proposed that, based on the client
subscriptions, organizes the updates into a limited and controllable number of groups
shared by the clients, and allows the server to manage update processing, irrespective
of the number of clients, only for those groups. The server maintains a log file only for
each of these data-groups, and each of the log files is relevant to a number of clients.
While re-integrating a client replica with the server database, the client receives updates
only from the relevant log files.
An important aspect of an ICDB system is that, whatever may be the update propa-
gation approach (i.e., the client-centric or the data-centric), size of the log file(s) (main-
tained at the server) increases linearly with time as new updates are stored during the
operation of the DBMS. Due to this continual increase in a log file size, a client expe-
riences more and more delay during re-integration, as the retrieval time of the relevant
log file(s) goes higher—a phenomenon that increases server processing overhead, disk-
storage overhead, and wireless channel access time. However, considering the periodic
connectivity of the clients, it is possible to eliminate the “no-longer-necessary” update
tuples from the log files. This pruning operation reduces the log file size, which in turn
reduces the disk-access time and wireless connection time.
In this paper, we propose two algorithms to prune the update log files in an ICDB
environment based on the periodicinitiationof connectionby the clientswith the server.
An earlier version of this paper appeared in [2]. While pruning a log file, we consider
two scenarios: clients with equal Mean Connection Interval (MCI)—average delay be-
tween successive connections; and clients with widely varying MCIs. In the former
case, we execute the pruning exercise when all the clients subscribing to a log file have
connected to the server. We term it as the complete pruning. In case of the latter, we
modify the complete pruning algorithm. In this case, pruning is carried out whenever a
predefined fraction
—termed as the threshold fraction— of the clients subscribing to
the log file have connected to the server.We term this algorithm as the partial pruning
algorithm,and show that the partial pruning algorithm is more suitable in this scenario.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the related works
in the area. Section 3 outlines the system and the connection model. Section 4 and
section 5 present the complete pruning algorithm and the partial pruning algorithm,
respectively. Section 6 presents the experimental results demonstrating the effectiveness
of the pruning algorithms. Section 7 compares the present research work with similar
research works. Finally, section 8 describes some potential future directions for this
research and provides concluding remarks.
2 Previous W ork
An ICDB is an instance of a distributed computing system where clients are mobile
and commonly suffer long periods of disconnection with the server. Due to the mobility
and disconnected operation, traditionalconcurrency controlprotocolsare not applicable
in this system. To help ensure the ACID properties of transactions [3], traditional dis-
tributed database systems use the two-phase-commit protocol which is communication
64

Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3
intensive and requires all the participants to be simultaneously connected; therefore,
this protocol is impractical in a disconnected environment.
To start addressing the problemof dis-connectivity, researchers have proposed repli-
cating data among the clients and allowing independent operations on the replicas [4].
The scalability issue of replicated data is addressed in [5]. Analyzing the various alter-
natives, it proposes a two-tier replication model that allows the mobile, disconnected
applicationsto process tentative update transactions using the local replica that are later
applied to the master copy. This model, though relaxes the ACID properties, provides
high availability, reduces the possibility of deadlocks, reduces the need for continu-
ous communication with the server, and allows mobility despite some network outages.
In this model, when contacted by a mobile client, the server propagates the replica up-
dates to the client, receives a list of tentative transactions (locally executed in the mobile
client), and reprocesses these transactions as base transactions. For further detail, the
reader should refer to [5]. In [6], the authors propose a method of merging the two
transaction histories—tentative and base—instead of reprocessing to save substantial
work of the tentative transactions. Thus, this approach reduces the server processing
overhead in the two-tier replication model. On the other hand, the issue of efficient up-
date propagation has also been addressed by the researchers. Organizing updates into
the groups shared by clients is proposed in [7]. Built on this work, in [1], the authors
propose an update propagation algorithm to make the server workload in update propa-
gation independent of the client population.
The architecture and goal of the CODA file system [8] is similar to those of an
ICDB: it allows the clients to form replicas while disconnected, and re-integrate the
updates when a client connects to the server. However, contrary to an ICDB system,
latency in this re-integration is not considered to be a significant factor in CODA.
3 System and Connection Model
In thissection, we briefly describe an ICDB system, and present a model for the connec-
tion initiation process. The ICDB architecture consists of a database server, a network
and several clients. The global database is stored in the database server. Closely tied
with the DBMS is the update manager [9]. This Update Manager stores updates in
the database, keeps track of the client subscriptions, and propagates the updates to the
clients when they connect to the server via a network. The client is composed of a client
update agent, and a local DBMS. The update agent receives updates from the server and
applies these updates to the replica stored in the local DBMS.
We consider an environment where
number of clients intermittently connect to
the server. For the sake of simplicity, we assume only one log file in the system which
all the clients subscribe to. The case of multiple log files can be extended from this
scenario by tracking subscriptions to the individual log files, and applying the pruning
algorithm to each of these log files independently. Furthermore, we assume that con-
nection initiation,by each client, is a Poisson process [10] with
being the MCI of the
client. So, for each client, connection initiationis a Poisson process having rate
We divide the time into slots of length , and assume that connection time of a
client coincides with the end of a slot. Therefore, a client connecting to the server in a
65

4 Chakraborty et. al.
slot receives the updates generated within that slot. We use the slot number as the con-
nection time-stamp of a client. For this Poisson process, the probability of connection
initiation (within a slot) by a client can be given by the following equation [2]:
Connection arrival (1)
We use this equation in making decision about the connectivity of the clients within
each slot.
4 Complet e Pruning
In this section, we describe the algorithm to prune the update log files in an ICDB envi-
ronment based on the periodicinitiationofconnection bythe clients withthe server. The
algorithm works by keeping track of the connection time-stamps of the clients. When
all the clients connect to the server, the client(s) with the minimum recent connection
time-stamp since the last pruning is determined. Then, the log file is pruned using this
time-stamp. We describe the specific details of the algorithm in the subsequent part of
this section.
The pruning algorithm maintains the recent connection time-stamp of every client,
and works in two phases: the startup phase and the operating phase. The startup phase
finishesas soonas all the clientssubscribingto the database have connected to the server
at least once. In the operating phase, the log fileis pruned periodicallyusing the smallest
connection time-stamp among all the clients. We denote the clients having the lowest
recent connection time-stamp as the critical clients, as eventual reconnection of these
clients determines the subsequent pruning of the log file. Whenever these critical clients
connect to the server, new critical clients (clients having the lowest recent connection
time-stamp) are selected again, and the log file is pruned. This concept is illustrated in
the Figure 1.
A
B C D
t
a
(b)
(a)
A C D B AB
t
a
t
cd
Fig.1. (a) At a certain time, client A, B, C and D are connected to the server in the slots as shown.
Here,A is the client havingminimum connectiontime-stamp
. So, A is the critical client, and
pruning is done using time
. (b) Connection time-stamps of the clients after a certain interval
are shown. Here, pruning is possible due to the reconnection of
. In this case, C and D are the
critical clients, and the log file is pruned using time
.
Having outlinedthe concept, we, now, present thepruningalgorithm. The procedure
complete-prune-logfile(
, ), as given inFigure 2, is invoked whenever any client con-
66

Lecture Notes in Computer Science 5
nects to the server; here, represents the set of clients connected within a certain time
slot
. is the global variable that stores the set of clients that connect to the server
in the current startup phase;
is the total clients subscribed to the system. The startup
phase (line 1–7) finishes as soon as the size of the list
becomes equal to .Inthe
operating phase (line 8–20), the connection time-stamp of each newly connected client
is adjusted; connected clients that are also critical are deleted from
. The log file
is pruned whenever
becomes empty. At the very beginning of the server activity
both
and are set to empty. Due to this empty list of critical clients ( ),
pruning operation is invoked when the operating phase is entered for the first time.
Procedure complete-prune-logfile( , )
begin
1: if
is less than then
2: for each client
do
3: if
didn’t connect earlier then
4: add
in the list ;
5: endif
6: endfor
7: endif
8: if
is equal to then
9: for each client
do
10: set connection time-stamp of
to
11: if then
12: delete
from ;
13: endif
14: endfor
15: if
is empty then
16: determine pruning time
from the recent
17: connection time-stamps of the clients in
18: reset with critical clients selected from
19: prune the log file using time ;
20: endif
endif
end
Fig. 2. Pruning the log file (complete pruning)
5 Partial Pruning
The complete pruning algorithm, presented in the previous section, fares poorly in an
environment where MCIs for the clients show significant variations. The following ex-
ample illustrates this scenario. Consider two clients
and with MCIs and ,
respectively. Assume that
is very large compared to , and that the log file is
67

6 Chakraborty et. al.
pruned using the complete pruning algorithm. In this case, the frequency of pruning
operation, and hence the size of the log file, is solely determined by the connectivity of
client
. The re-integration time for client will suffer severely as it has to retrieve
a large log file each time it connects to the server. In a typical environment, where the
population of clients with large MCIs is very less compared to that with low MCIs, the
degradation in average re-integration time becomes very significant.
To cope with this increment in average re-integration time, we propose the partial
pruning algorithm that considers varying probability of connection initiation among
clients. This algorithm, instead of deleting a portion of the log file (that we term as the
primary log file to distinguish it from the rest) when all the clients connect to the server,
splits the primary log file, using the pruning time-stamp, when a certain fraction
—
denoted as the threshold fraction— of the clients connect to the server. This pruning
time-stamp, like the previous algorithm, denotes the minimum recent connection time-
stamp selected from the pool of connected clients. After splitting the primary log file,
using this time-stamp, we obtain one extra log file denoted as the spawned log file.
At the time of this pruning, this spawned log file is relevant to the clients that haven’t
connected (to the server) on or after the pruning time-stamp. Here, we note that at the
time of each pruning activity the primary log file is split, whereas a spawned log file is
removed when all the clients to which the spawned log file is relevant connect to the
server. So, for the primary log file (
), there remain in the system a set of log files,
where is the number of spawned log files . For each
spawned log file
we maintain a set of clients ,termedastheR-set
of the corresponding log file, who are yet to receive the updates of that log file—the
spawned log file is relevant to the clients in its R-set.
Having described the main features of the algorithm, we now present the partial
pruning algorithm. The procedure partial-prune-logfile(
, ),asgiveninFigure3,is
invoked whenever any non-zero number of clients connect to the server during a slot
; here, represents the set of clients connected within a certain slot . Here,
represents the set of clients connected to the server since the last pruning time-stamp,
and
represents the total clients subscribed to the system. The primary log file is split
(line 10–16) when the “threshold fraction”
of the total clients connect to the server.
6 Simulations
This section presents the simulation studies of the pruning algorithms. The purpose of
the simulation is to investigate the efficacy of the pruning algorithms in an ICDB envi-
ronment. We measure the effectiveness of the complete pruning algorithm by observing
the size of the log file during the period of server activity. To describe the log file size
at any point in time, we use the term pruning rat i o. The pruning ratio reflects the frac-
tion of total update volume pruned during server activity. To realize the effectiveness
of the partial pruning algorithm we measure the average retrieval time for the clients.
By average retrieval time we refer to the average delay, for each client, in accessing the
update logs at the time of each connection with the server. To measure this delay we
use the disk parameters and per-client update arrival rate (Table 1), where update arrival
rate is used to realize the size of a log file. In case of clients on wireless devices, update
68

Lecture Notes in Computer Science 7
Procedure partial-prune-logfile( , )
begin
1: for each client
do
2: if
is not in then
3: add
in the list
4: endif
5: set connection time-stamp of
to
6: delete from the R-set of the relevant spawned log files
8: endfor
9: delete the spawned log files with empty R-set
10: if
then
11: Find the critical clients and the pruning time
using the
12: recent connection time-stamps of the clients in
13: Split the primary log file using time-stamp
14: initialize R-set of the spawned file with the clients not in .
15: delete the critical clients from
16: endif
end
Fig.3. Pruning the log file (partial pruning)
retrieval time gives a measure of wireless connection time (or wireless channel access
period) required by the clients to retrieve their updates.
Parameter Description Values (control values in )
Clients
MCI, (min)
Slot Length, (sec)
, (update/min/client)
Server Disk Latency (ms)
Seek time (ms)
Disk bandwidth (mbps)
Table 1. Parameter values for experiments with the pruning algorithm
We begin with a subsection providing the experimental results for the scenario with
uniformMCIs among the clients,where complete pruning is effective in eliminating the
unnecessary updates. In the subsequent part of this section we present the experimental
results, based on varying MCIs for the clients, showing the effectiveness of the partial
pruning algorithm in such a scenario. The experimental parameters are provided in
Table 1. For each setting of the experimental parameters we run the simulation for 24
simulation hours, and collect the data averaging over upto 200 runs to smooth out the
statistical variations.
69

8 Chakraborty et. al.
6.1 Clients with Uniform MCI
In this subsection, we present the results on the efficacy of the complete pruning algo-
rithm in an ICDB environment where all the clients have uniform MCIs. To evaluate
the effectiveness of this pruning algorithm, we measure the pruning ratio, based on the
measurement of total pruned interval within the period of server activity, by varying the
MCI and client population parameters.
Figure 4(a) shows the effect of varying the MCI on the pruning ratio. Here, as ex-
pected, the pruning ratio decreases with the increase in the MCI. However, significant
portion of the update volume is pruned (e.g. more than 50%) provided the MCI remains
considerably low (e.g. around 2 hours) compared to the period of server activity which
is taken as 24 hours in the simulation.
An increase in client population results in an uniform decrease of the pruning ra-
tio (Figure 4(b)). But, significant pruning ratio is achieved even for considerably large
client population.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
15 30 60 120 180
Mean Connection Interval (min)
Pruning ratio
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
2 10 20 50 100 200 400 800
Client population
Pruning ratio
(a) (b)
Fig.4. (a) Pruning ratio with varying mean connection interval (MCI) of the clients. (b) Pruning
ratio with varying client population
6.2 Clients with Widely Varying MCIs
Here, we consider the clients with varying MCIs. We consider a set of widely varying
MCIs (shown in the Table 1), and assume that the number of clients with a particular
MCI value is inversely proportional to that MCI (i.e., zipf’s law [11].) To show the
effectiveness of the partial pruning algorithm we measure the average retrieval time for
varying threshold fraction and clients population.
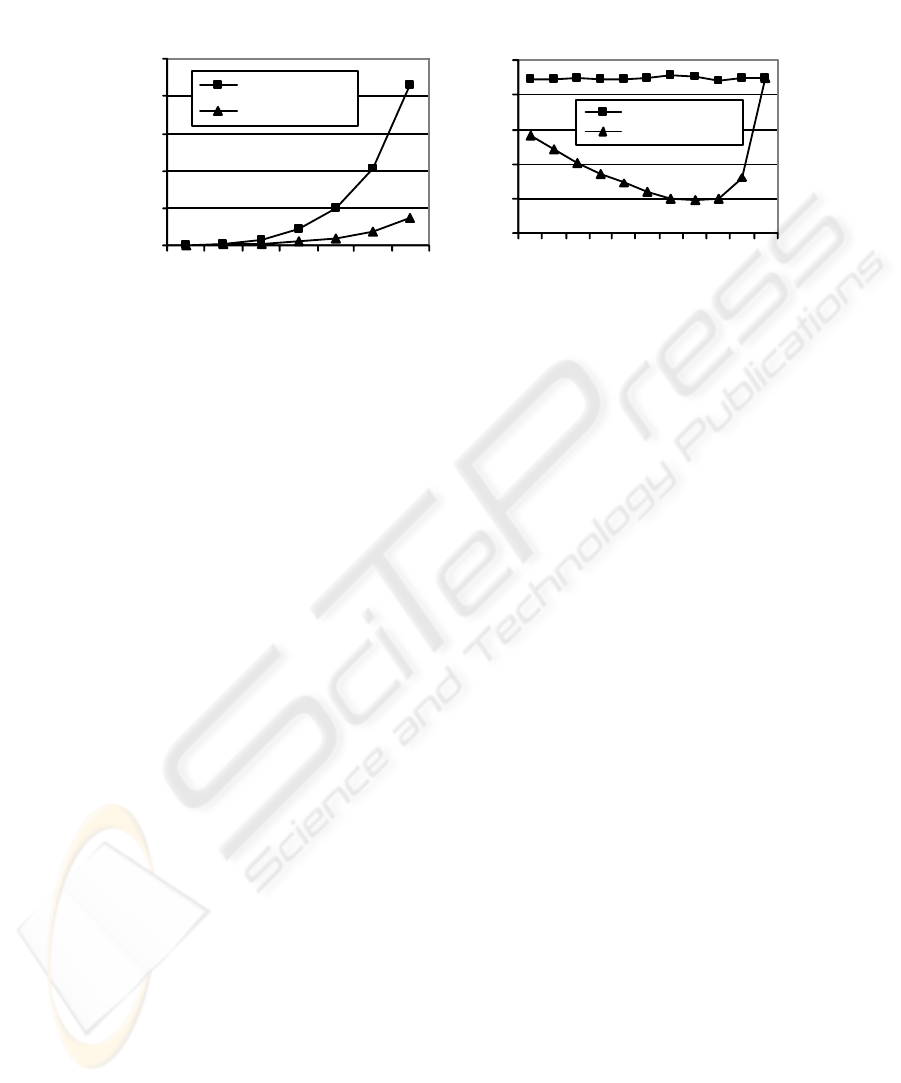
Figure 5(a) shows the effectiveness of partial pruning in such a scenario. Here, as
the client population increases, average retrieval delay with the partial pruning is sig-
nificantly reduced compared to that with the complete pruning. The reason behind this
improvement is that clients with low MCI may only have to access the primary log file;
70
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 9
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
10 20 50 100 200 400 800
Client population
Average retrieval time (ms)
complete pruning
partial pruning
0
200
400
600
800
1000
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Threshold fraction, r
Average retrieval time (ms)
complete pruning
partial pruning
(a) (b)
Fig.5. (a) Average retrieval time with varying client population. (b) Effect of varying threshold
fraction on average retrieval time
only the lazy clients are penalized as they are forced to access multiple log files (hence,
multiple disk accesses: once for each of the relevant log files). The value of threshold
fraction is set to 0.85 for this experiment.
Figure 5(b) shows the variation of average retrieval time with varying threshold
fraction.Here, theaverage retrieval timeinitiallydecreases even if thethresholdfraction
is increased. However, above a certain threshold fraction the average retrieval time starts
increasing, and eventually unifies with that with the complete pruning. This is in line
with our expectations because as the threshold fraction approaches one, the situation
essentially degenerates to complete pruning where the pruning process needs to wait
for all clients to connect.
7 Comparison with Related Research Works
Given the rising popularity of wireless data applications, the issues around the transac-
tion models for ICDB systems are gaining increasing level of attention from database
researchers [5], [4], [7], [6], [1]. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the
first research work that investigates the issue of pruning of update logs that need to be
transmitted to themobile clients in such environments. Obviously,the issue of log man-
agement has been studied in the context of traditional centralized as well as distributed
database systems [12]. However, the presence of frequently disconnected and mobile
database nodes, and also the costs associated with wireless channel access times signif-
icantly change the complexion of the problem in an ICDB environment. The research
works on scalability of update propagation in ICDB systems may be the closest to the
topic of this paper [7], [1], [9]. However, the previous work on update propagation has
mainly focused around the issue of whether the database server should organize the up-
dates as a single file for all clients, or as a separate file for each client, or as files for a
set of datagroups formed based on clients’ subscription to data. Our work on pruning
of update logs should be applicable in each case.
71

10 Chakraborty et. al.
8 Future Directions and Conclusion
In this paper we show the effectiveness of pruning operation in an ICDB environment.
Without any pruning operation, the log file size increases in an unbounded manner with
time: a phenomenon that severely affects the update retrieval time. We present two
pruning algorithms considering clients with both uniform and widely varying MCIs. In
case of uniform MCIs, we show that the complete pruning algorithm curbs the linear
growth of the log file, and keeps this size within a bound. For varying MCIs among
clients, we show the effectiveness of the partial pruning algorithm in reducing the av-
erage update retrieval time for the clients. In this paper we consider only one log file.
However, in case of multiple update log files (i.e., one for each datagroup), these al-
gorithms can obviously be applied independently to each of the log files. There are a
few issues that need further investigation. First, a cost benefit analysis is necessary to
ascertain the period after which the update log files relevant to some lazy clients may be
deleted. Second, in the case of partial pruning, merging spawned files to further reduce
the latency needs to be studied.
References
1. Yee, W.G., Donahoo, M.J., Omiecinski, E., Navathe, S.: Scaling replica maintenance in
intermittently synchronous mobile databases. Proceedingsof CIKM (2001) 450–457
2. Chakraborty, L., Singh, A., Naik, S.: Managing update log files in mobile, wireless en-
vironments. Technical Report 03-05, Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering,
University of Waterloo (2003)
3. Bernstein, P.A., Hadzilacos, V., Goodman, N.: Concurrency Control and Recovery in Dis-
tributed Database Systems. Addison Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts (1987)
4. Breitbart, Y., Korth, H.F.: Replication and consistency: Being lazy helps sometimes. Pro-
ceedings of ACM SIGMOD (1997)
5. Gray, J., Holland, P., O’Neil, P., Shasha, D.: The dangers of replication and a solution.
Proceedings of ACM SIGMOD (1996) 173–182
6. Liu, P., Amman, P., Jajodia, S.: Incorporating transaction semantics to reduce reprocess-
ing overhead in replicated mobile data applications. Proceedings of the 19th International
Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (1999) 414–423
7. Mahajan, S., Donahoo,M., Navathe, S., Ammar, M.: Grouping techniques for update propa-
gation in termittently connected databases. Proceedings of Fourteenth International Confer-
ence on Data Engineering (1998) 45–53
8. Satyanarayanan, M., Kistler, J.J., Mummert, L.B., Ebling, M.R., Kumar, P., Liu, Q.: Ex-
perience with disconnected operation in a mobile environment. Proceedings of the 1993
USENIX Symposium on Mobile and Location-Independent Computing (1993)
9. Chakraborty, L., Singh, A., Naik, S.: Maintenance of partially replicated database in dis-
connected mobile environment. Report, Network Programming Lab, Dept. of Electrical &
Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo (2002)
10. Ross, S.M.: Introduction to Probability Models. Academic Press (1997)
11. Breslau, L., Cao, P., Phillips, G., Shenker, S.: On the implications of zipf’s law for web
caching. Proceedings of INFOCOM (1998)
12. Silberschatz, A., Korth, H., Sudarshan, S.: Database System Concepts. McGraw Hill Book
Co. (2001)
72
