
PERSONALIZING DIGITAL LIBRARIES FOR EDUCATION
Floriana Esposito, Oriana Licchelli, Pasquale Lops, Giovanni Semeraro
Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Bari
Via E. Orabona, 4 – I70126, Bari
Keywords: Digital Library, e-Learning.
Abstract: E-Learning Systems enable students to work with electronic teaching materials, to join online courses, to
pass tests, and to communicate with other students or instructors. An important requirement of this systems
is the integration of external knowledge management resources into them. The digital libraries are helpful to
this purpose because materials of many digital libraries are valuable for learning. The availability of
teaching materials provided by an E-Learning Systems can be enlarged by reverting to materials existing in
several digital libraries. In this case, it is necessary to find the right document source and to supply the
suitable documents basing on the student requirements, also when the student model of the e-learning
system is still not available. In this paper, we have focused our attention on the use of user profiles,
generated by a personalization system (the Profile Extractor), to improve searching among digital libraries
or other generic information sources.
1 INTRODUCTION
Adaptive personalized e-learning systems could
accelerate the learning process by revealing the
strengths and weaknesses of each student. They
could dynamically plan lessons and personalize the
comunication technique and the didactic strategy. In
this systems, the Learning Management Systems
(LMS) consist of several components representing
different services to be used within a learning
environment. They enable students to work with
electronic teaching materials, to join online courses,
to pass tests, and to communicate with other students
or instructors. The availability of teaching materials
provided by a modern Learning Management
System (LMS) could be enlarged by reverting to
existing materials with the integration of external
knowledge management resources into LMS
(Rosenberg, 2001). It seems obvious that digital
libraries (DL) are predestinated for this purpose
because materials of many DL are valuable for
learning. For example, the contents of the DL of the
Association for Computing Machinery (ACM,
http://www.acm.org/dl) and the IEEE Computer
Society (http://www.computer.org/publications/dlib)
can be used for higher education and scientific
research. In this case, it is necessary to find the right
document source and to supply the suitable
documents basing on the student requirements, also
when the student model of the e-learning system is
still not available. Then the personalization of the
digital libraries access becames an important feature,
in fact, the personalization (Resnick and Varian,
1997; Riecken, 2000) involves techniques and
mechanisms to reduce the information overload and
facilitate the delivery of information that has been
customised for the preferences of individual users.
Machine Learning techniques have a significant role
to play in the personalized services of the Digital
Library. For example, many Machine Learning
techniques are well suited for transforming user-
activity data into useful preference rules as part of a
user profile (Jennings and Higuchi, 1993). Similarly,
case-based reasoning techniques can be used to
implement flexible similarity-based content retrieval
strategies (Balabanovic, 1997, Hammond et al.,
1996), and recently automated collaborative filtering
techniques have been used to transform raw user
preference data into sophisticated content filters
(Billsus and Pazzani, 1998; Konstan et al., 1997;
Perkowitz and Etzioni, 1997).
In this paper, we have focused our attention on a
generic LMS and the way to improve searching
among digital libraries or other generic information
sources, using the user profiles generated by our
personalization system (Profile Extractor).
The Profile Extractor system, based on Machine
Learning techniques, processes the logs of the user
279
Esposito F., Licchelli O., Lops P. and Semeraro G. (2004).
PERSONALIZING DIGITAL LIBRARIES FOR EDUCATION.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 279-284
Copyright
c
SciTePress

accessing the Digital Library and automatically
builds the user model.
2 PERSONALIZED E-LEARNING
SYSTEMS
In (Lauzon and Moore, 1989) Computer-Assisted
Learning is defined as “the delivery of educational
materials using computers as the main medium of
communication between instructor and student.” In
the decade that followed, several standards emerged
that emphasized the machine delivery of content
without an instructor. Thus, most contemporary
computer-based instruction emphasizes learner-
content interaction or learner-learner interaction.
In Intelligent Tutoring System area (Woolf,
1992), the module devoted to build the student
model is one of the major components of the
teaching system: namely, the student model module,
the pedagogical module, the domain knowledge
module, and the communication module. The
student model stores information that is specific to
each individual learner: it is “how” and “what” the
student learns or her/his errors, and the student
model plays a main role in planning the instructional
path. The pedagogical module provides a model of
the teaching process, using the student model in
order to decide the instruction method that reflects
the differing needs of each student. The domain
knowledge module contains information the tutor is
teaching, and the communication module creates the
interactions with the learner using the information
contained in the student model in order to render the
communication more effective. The information
collected during the interaction can be used to
modify the student model.
The use of student models to individualise the
interaction in hypermedia and on-line instruction
systems has been described by several authors (Bull,
1995; Bull and Smith, 1997; Smith and Jagodzinski,
1995), but the application of the techniques
suggested by ITS technology to generate the
effective presentation of instructional material has
had little practical success. According to Hartley
(Hartley, 1998), the main cause is the lack of
dialogue between researchers of the different areas,
while others think that the intrinsic complexity of
student models is at the root of the problem of their
application to configure learning for the individual
(Cummings, 1998; Ohlsson, 1993; Self, 1990).
The range of student modelling approaches
available is surveyed by Ragnemalm (Ragnemalm,
1996), who
distinguishes between models that
contain student’s actual domain knowledge and
those that contain student characteristics.
In the 1996 Vassileva (Vassileva, 1996)
describes a student model as an example of a general
user model, but where a representation of student
knowledge, held by the system, is compared with a
representation of the domain and a representation of
an expert or desired state. The aim of such systems
is to compare the student, domain and expert models
and to attempt to configure presentation of
information based in some way upon differences
between them, in order to permit to the student to
reach a desirable knowledge level (educational
goal).
In the 1996, Brusilovsky (Brusilovsky, 1996)
faces the problem to make the adaptive hypermedia
systems and states that is necessary to use some
features as goals, knowledge, background,
experience and preferences.
At present, the main engines of an e-Learning
System are the Learning Management System
(LMS) and the Learning Content Management
System (LCMS).
A Learning Management System is intended to be a
content-neutral platform that helps a learner to tailor
the delivery of instruction to individual needs. These
systems are concerned with the delivery of pre-
packaged content. They use the information in the
learner profile and learner history to select materials
from the content database. In these systems, each
instructional module and test in the content database
is tied to one or more learning objectives, material
selection and sequencing is under the control of the
instructional designers who created the original
learning modules. Most of these systems will present
a pre-test, choose material according to the test
results, present the material, then administer post-
tests and store those results as well.
The LMS integrates all aspects for managing on-
line teaching activities. From an end-user point of
view, a LMS provides an effective way to keep track
of individual skills and competencies, and provides a
means of easily locating and registering for relevant
learning activities to further improve the learner’s
skill levels.
The LCMS (Maish Nichani) offers services that
allow for the content management, creation, delivery
and reuse. Content is typically maintained in
learning objects, each of which satisfies one or more
well-defined learning objectives. A LCMS may
locate and deliver a learning object to the end-user
as an individual unit to satisfy a specific need or
may deliver the learning object as part of a larger
course, curriculum, or learning activity defined in a
LMS. Then the LMS and LCMS both monitor the
delivery of content but at different levels of
granularity. A LMS concentrates on course-level
tracking, on particularly completion status and
rolled-up scores. In contrast, an LCMS employs
ICEIS 2004 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
280
detailed tracking at the learning-object level, not
only to trace user performance and interactions at a
finer granularity, but also to provide the metrics that
help authors analyze the learning object’s clarity,
relevance, and effectiveness.
Users play a central role in both LMS and
LCMS. A typical LMS maintains all information of
each user such as organizational affiliations, job
role, preferences, competencies, skill levels,
participation in past learning activities, and so forth.
Adding to this information the capability of
monitoring and planning the educational process in
order to attain learning objectives means to have an
effective student model, with the same philosophy of
a traditional computer assisted learning system.
In an e-learning system, users typically use the
LMS to manage their current competency status, to
analyze their skill gaps, and to register for learning
activities that will help them reduce their skill gaps
against an aspired career path. An LCMS focuses on
delivering a personalized experience to the user
providing just enough content to address the
person’s individual needs, when she/he needs it. An
LCMS may also enhance this experience by
customizing the content basing on a user’s profile or
by offering rich collaborative and knowledge-
exchange capabilities about the content. The key
difference is that the LCMS takes advantage of all
the information available about the user to offer a
personalized experience when delivering a learning
object, while a LMS typically maintains the user
information and makes it available to the LCMS to
deliver the personalized experience.
The LCMS can use this information also to
deliver a customized track of the learning object to
the user automatically; it can also analyze trends by
correlating the user properties from LMS and can
use it to prescribe an appropriate track to future
users, based on their profiles. The LCMS may
behave as an intelligent system that learns, based on
real data, what worked for whom and then uses this
information to help future users.
During the learning session many references
could be cited and, if possible, reproduced. The
availability of teaching materials provided by an e-
learning system can be enlarged by reverting to
materials existing in several digital libraries. In this
case, it is necessary to find the right document
source and to supply the suitable documents basing
on the student requirements, also when the student
model of the e-learning system is still not available.
The accessibility to the digital library material must
be guaranteed and a simple student model which
discovers the preferences, needs and interests of
users accessing the Digital Library should be
sufficient. The preferred searched documents supply
an interesting information for the student model too
since suggest the user main interest to deepen
specific subjects.
3 USER MODELLING FOR
ACCESSING DOCUMENT
EXTERNAL SOURCES (DL)
In our laboratory, a system has been developed to
generate user profiles automatically: the Profile
Extractor personalization system which employs
supervised learning techniques to automatically
discover user/student model through the analysis of
past user interaction with the “web” system.
The Profile Extractor is able to analyze data
gathered from sources such as data warehouse or
interactions (between student and LMS) in order to
infer rules describing the user/student behavior.
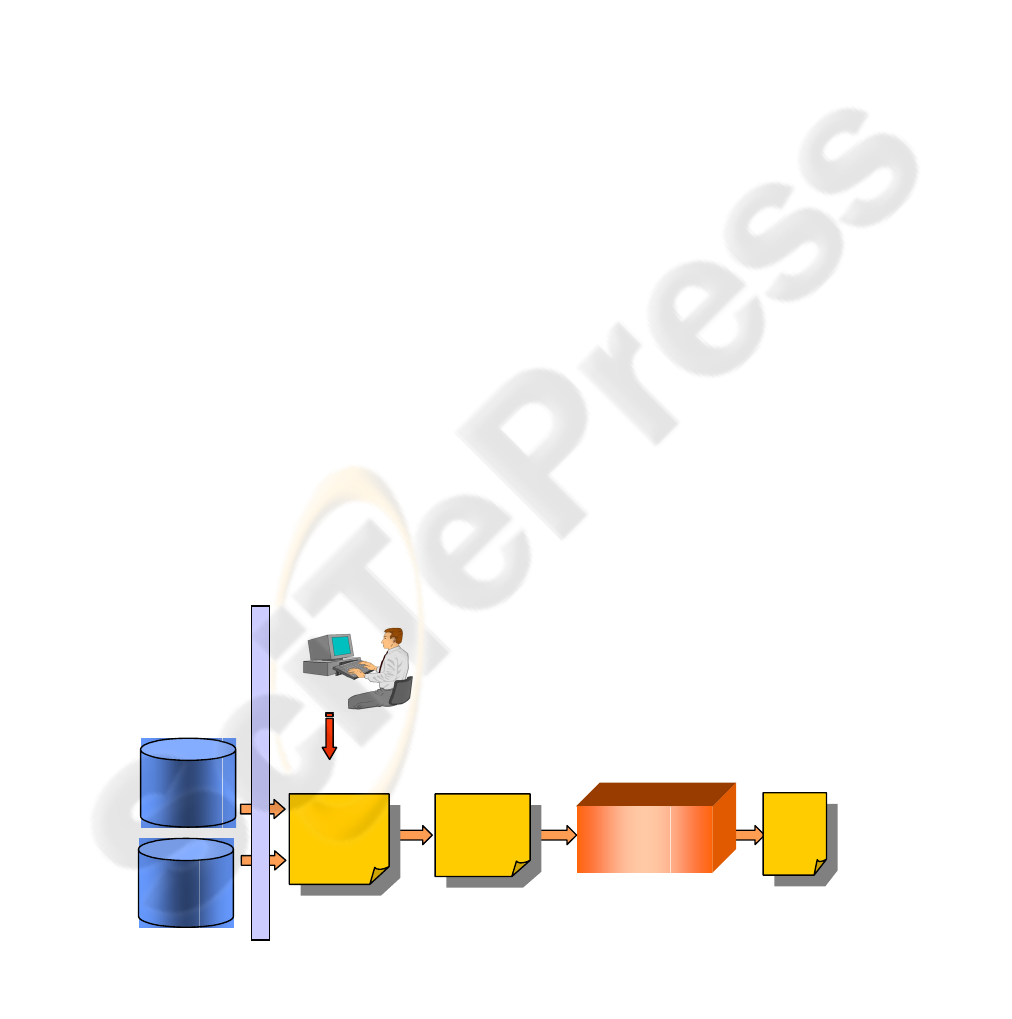
Figure 1: The learning process
E
XML-compliant
Learning
System
Rule
Sets
Training
Instances
Unclassified
Instances
Interaction
Data
Personal
Data
X
M
L
-
I
O
-
W
R
A
P
P
E
R
Figure 1: The learning process
PERSONALIZING DIGITAL LIBRARIES FOR EDUCATION
281

Rules are exploited to build profiles containing
preferences such as the material categories the
user/student is interested into.
Some preliminary work is needed to establish a
formal description of the features and attributes that
are needed to accomplish the given task; we can use
the results to define the representation language of
the entire learning framework. From our point of
view, the problem of learning user’s preferences can
be cast to the problem of inducing general concepts
from examples labelled as members (or non-
members) of the concepts. In this context, given a
finite set of categories of interest C = {c
1
, c
2
, …c
n
},
the task consists in learning the target concept T
i
“users interested in the category c
i
”. In the training
phase, each user represents a positive example of
users interested in the categories he or she likes and
a negative example of users interested in the
categories he or she dislikes. We chose an
operational description of the target concept T
i
,
using a collection of rules that match against the
features describing a user in order to decide if he or
she is a member of T
i
.
As depicted in Figure 1, the data about users (an
XML file containing personal and interaction data of
the user) are arranged into a set of unclassified
instances (each instance represents a user). The
subset of the instances chosen to train the learning
system has to be labeled by a domain expert, that
classifies each instance as member or non-member
of each category. The training instances are
processed by the Profile Extractor, which induces a
classification rule set for each category of interest.
More precisely, the architecture of the PE is made
up of several sub-modules:
− XML I/O Wrapper, which is the layer responsible
for the extraction of data required for the learning
process.
− Rules Manager, which is implemented through
one of the WEKA (Frank and Witten, 1998)
classifiers. The learning algorithm adopted in the
rule induction process is PART (Witten and
Frank, 1999), which produces rules from pruned
partial decision trees.
− Profile Manager, which classifies each user on
the ground of the users’ transactions and the set
of rules induced by the Rules Manager. The
classifications, together with the interaction
details of users, are gathered to form a user
profile.
Extensive experimentation of the system proposed
for the automatic extraction of the user profile has
been carried out in the digital libraries. In particular,
the system was tested on the frame of COVAX
Digital Library.
The purpose of COVAX (Contemporary Culture
Virtual Archives in XML) project (Bordoni, 2002)
was to analyse and draw up the technical solutions
required to provide access through the Internet to
homogeneously-encoded document descriptions of
archive, library and museum collections based in the
application of XML. The project demonstrated its
feasibility through a prototype containing a
meaningful sample of all the different types of
documents to build a global system for search and
retrieval.
In the experiment we considered the four main
collections of the COVAX Digital Library
(Bibliographic, Museum, Electronic Text, Archive).
For each of the 4 classes, the system was trained to
infer proper classification rules, on the basis of an
instances set representing different digital library
users given by an expert acting as a trainer of the
system. Figure 2 shows a classification rule set
example, that is generated for the “Bibliographic
Collection” on the ground of logs containing
interaction and user features; those rule sets are
expressed as disjunctions of conditions.
Figure 2: An example of classification rules for the class “Bibliographic Collection”
Figure 2: An example of classification rules for the class “Bibliographic Collection”
ICEIS 2004 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
282

Figure 3: An example of a user profile
Fi
g
ure 3: An exam
p
le of a user
p
rofile
Using these rule sets, the classifier (Profile
Manager) predicts, for each category, whether the
user is interested or not. All these classifications,
together with the interaction details, are gathered to
form a user profile (see Figure 3 as user profile
example).
After the training phase, once a user accesses the
COVAX Digital Library, his/her dialogue history
file is generated or updated by the system. The file is
then exploited to produce a new example that the
Profile Extractor classifies on the grounds of the
rules inferred. In this way, the system is capable of
tracking user behaviour evolution and, consequently,
the profiles are updated across multiple interactions.
The concepts underlying information retrieval
were conceived long before computers and
information systems were employed to store library
materials. In the digital library domain there is a
variety of information retrieval techniques, including
metadata searching, full-text document searching,
and content searching for several data types.
The success of information retrieval can be
measured in terms of the percentage of relevant and
extraneous information retrieved, but it is difficult to
identify quantitatively the effectiveness of the
retrieval process because only an individual user can
determine what is truly useful. There are different
techniques to improve the retrieval effectiveness by
means of the extraction of additional metadata, and
recently also by means of the creation and
maintenance of user profiles.
A possible way to improve searching in COVAX
DL or in another Digital Library is to use the
information stored in a user’s profile in order to
refine the original query issued by the user. For
example, the preferred category can be enclosed in
the query submitted to COVAX search engine for
more precise result identification.
Another possible way to improve the retrieval
process (without modifying the original user’s
request) is to rank the documents in the result set
according to the categories and their degree of
interest stored in the user’s profile.
The preferred searched documents supply an
interesting information for the student model too
since suggest the user/student main interest to
deepen specific subjects.
4 SUMMARY AND OUTLOOK
A key issue when developing personalized
applications is constructing accurate and
comprehensive customer profiles based on the
collected data. User modelling is crucial for
improving the interaction between systems and their
users. In the e-learning systems, the teaching
materials provided by Learning Management System
(LMS) could be enlarged by the integration into
LMS of external knowledge management resources
as the Digital Libraries. Indeed, documents and
materials of many DL are valuable for learning and
providing intelligent personalized user support in
accessing the digital libraries, in finding the right
document source and in supplying the suitable
documents basing on the student requirements is a
main topic.
We have presented the Profile Extractor, a
system based on Machine Learning techniques,
which processes the logs of the user accessing the
PERSONALIZING DIGITAL LIBRARIES FOR EDUCATION
283

Digital Library and automatically builds the user
model. The automatic generation and discovery of
the user profile allows to improve searching among
extremely large Web repositories, such as Digital
Libraries or other generic information sources, by
providing them with personal recommendations.
By the e-learning system perspective, this profile
con
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was partially supported by ENEA under
REFERENCES
Balabanovic, M. and Shoham, Y., 1997. Fab: Content-
Bil 8. Learning
Bru s and techniques in adaptive
Bo Culture
Bull, S., Brna, P, and Pain, H., 1995. Extending the scope
Bu student models to
Cummings, G., 1998. Artificial intelligence in education:
an exploration. Journal of Computer Assisted
Learning, 14(4) 252-259.
Experiences Lessons and
Har
, 1-25.
net News.
Lau
computer
Ma
ng, 9(4) 194-221.
onference on Artificial
Rag
action, 5, 93-116.
lized Views of Personalization.
Ros
egies for
oads of artificial intelligence and education.
Sm
earning Technology
Vas
odelling and User-Adapted
Wo
I
4.
stitutes a first student model, based on
communication preferences more then on learning
performances, useful to create a personalized
education environment. The future step is trying to
use such information in order to plan a personalized
educational path, constantly monitoring the
educational process. The student model constructed
initially can be refined and/or reviewed on the basis
of the new inputs to the system. Once again Machine
Learning techniques could be of use in the automatic
review of student models, by offering incremental
learning methods in order to update the knowledge
learned on the basis of new observations.
grant “An innovative system for the extraction of
user profiles”. The authors would like to thank
Luciana Bordoni and Fabrizio Poggi for the dataset
used in the Profile Extractor.
Based, Collaborative recommendation.
Communications of ACM, 40 (3),66-72.
lsus, D. and Pazzani, M. J., 199
Rie
Collaborative Information Filters. In Proceedings of
the International Conference on Machine Learning,
Wisconsin, USA, 46-54.
silovsky, P., 1996. Method
hypermedia. User Modelling and User-Adapted
Interaction, 6(2-3), 87-129.
rdoni, L., 2002. COVAX: A Contemporary
Virtual Archive in XML. In Proceedings of the 6th
European Conference ECDL 2002, Rome, Italy, 661-
662.
of the student model. User Modelling and User-
Adapted Interaction, 5(10), 45-65.
ll, S. and Smith, M., 1997. A pair of
encourage collaboration. In Proceedings of the 6th
International Conference on User Modeling UM97,
Italia, 339-341.
Hammond, K. J., Burke, R. and Schmitt, K., 1996. A
Case-Based Approach to Knowledge Navigation.
Case-Based Reasoning
Future Directions, MIT Press, 125-136.
tley, J.R., 1998. Ospite Editoriale: CAL and AI - a
time for rapprochement? Journal of Computer
Assisted Learning, 14(4), 249-250.
Jennings, A. and Higuchi, H., 1993. A user model neural
network for a personal news service. User Modeling
and User-Adapted Information, 3(1)
Konstan, J. A., Miller, B. N., Maltz, D., Herlochker, J. L.,
Gordan, L. R. and Riedl, J., 1997. Grouplens:
Applying Collaborative Filtering to Use
Communications of the ACM, 40(3), 77-87.
zon, A.C. and Moore, G.A.B., 1989. A fourth
generation distance education system: Integrating
computer-assisted learning and
conferencing. The American Journal of Distance
Education, 3(1), 38-49.
ish Nichani. LCMS = LMS + CMS
http://www.elearningpost.com/features/archives/00102
2.asp
Ohlsson, S., 1993. Impact of cognitive theory on the
practice of authoring. Journal of Computer Assisted
Learni
Perkowitz, M. and Etzioni, O., 1997. Adaptive Web Sites:
An AI Challenge. In Proceedings of the 15th
International Joint C
Intelligence, Nagoya, Japan. Morgan Kaufmann, 16-
23.
nemalm, E.L., 1996. Student Diagnosis in Practice;
Bridging a Gap. User Modelling and User-Adapted
Inter
Resnick, P. and Varian, H., 1997. Recommender Systems.
Communications of the ACM, 40(3), 56-58.
cken, D., 2000. Persona
Communications of the ACM, 43(8), 27-28.
enberg, M.J., 2001.
e-Learning – Strat
Delivering Knowledge in the Digital Age. McGraw-
Hill.
Self, J.A., 1990. Bypassing the intractable problem of
student modelling. Intelligent tutoring systems: at the
crossr
Frasson, C., Gauthier, G. (eds.), Ablex Publishing,
Norwood, New Jersey, 107-123.
ith, C. and Jagodzinski, P., 1995. The implementation
of a multimedia learning environment for graduate
civil engineers. Association for L
Journal, 3(1) 29-39.
sileva, J., 1996. A task-centred approach for user
modelling in a hypermedia office documentation
system. User M
Interaction, 6(2-3) 185-223.
olf, B., 1992. AI in Education. Encyclopedia of
Artificial ntelligence. Shapiro, S. ed., John Wiley &
Sons, Inc., New York, 434-44
ICEIS 2004 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
284
