
TeleCARE: Collaborative virtual elderly support
communities
L. M. Camarinha-Matos
1
and H. Afsarmanesh
2
1
New University of Lisbon / Uninova,
Quinta da Torre, 2829-516 Monte Caparica, Portugal
2
University of Amsterdam,
Kruislaan 403, 1098 SJ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Abstract. The growing percentage of elderly population imposes an urgent
need to develop new approaches to care provision. Integration of a number of
technologies such as multi-agent systems, federated information management,
safe communications, hypermedia interfaces, rich sensorial environments, and
increased intelligence in home appliances represents an important enabling
factor for the design and development of virtual elderly support community
environments. In this paper, a platform based on mobile agents combined with
federated information management mechanisms is introduced as a flexible
infrastructure on top of which specialized care services are built.
1 Introduction
One of the key challenges faced by modern societies derives from the fact that with
increasing speed our average population is getting older [11]. During the last three
decades, the number of people aged 60 years or more has risen by about 50% in
Europe. By 2020, it is estimated that for every person below the age of retirement,
there will be 4 elderly people requiring support and care from their community. The
impact on costs to the community will become considerably high. To deal with this
challenge, new ways of providing elderly assistance and care, namely resorting to
technological support, must be found.
New technological infrastructures, although not the solution for all problems, can
be part of a new concept of integrated care system. An integrated elderly care system
consists of a number of organizations such as care centers / day centers, health care
institutions, social security institutions involving the cooperation of a number of
human actors e.g. social care assistants, health care professionals, elderly people, and
their relatives. When based on computer networks and adequate supporting tools, the
collaboration among the care institutions may evolve towards operating as a long-
term virtual organization and the various involved actors become part of a virtual
community (VC).
In recent years various research projects have been engaged in developing
technological solutions to increase the care services and reduce their costs. For
M. Camarinha-Matos L. and Afsarmanesh H. (2004).
TeleCARE: Collaborative virtual elderly support communities.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Tele-Care and Collaborative Virtual Communities in Elderly Care, pages 1-12
DOI: 10.5220/0002677300010012
Copyright
c
SciTePress

instance, various initiatives have established “social alarm” systems [13], namely in
the case of people living in remote and hard to access areas. Such systems comprise a
portable alarm trigger and an alarm telephone that dials a social alarm control center
when there is an emergency situation. More recent works are focused on mobile
social alarm systems and online monitoring systems based on a diversity of sensors
and other devices. Other projects are focused on the development of smart home
appliances or specialized user interfaces [7, 8]. Advances in computer networks and
ubiquitous computing suggest the opportunity for more advanced care approaches
including comprehensive status monitoring, other forms of assistance such as agenda
reminders, but also the creation of the opportunity for the elderly becoming involved
in the community, and thus reducing their feeling of loneliness.
In order to let elderly stay at home, and keep, to certain extent, their typical life
style, new support services are necessary to address, among others, the following
problems:
Loneliness is one of the most serious problems affecting the elderly population.
Development of applications to enrich the elderly’s social life and avoid problems
of loneliness is of great importance. Fieldwork data [10] show that today the
elderly hardly participate in activities relating with others, and 16% of them
express dissatisfaction with their social lives. According to family members, 28%
of the elderly have little or no contact with other people.
Interconnection between the homes of the elderly and the homes or
workplaces of the family members caring for an elderly person is important to
provide access to loved ones. According to a survey carried out with relatives
caring for an elderly person, 31% of them stated the need to be in contact with the
elderly person (currently done either by phone or personal visits) at times when
they are alone.
Widening the interconnection to also include entities dedicated to providing
different services for the elderly, such as the residential centers, social centers,
and social services, will bring potential benefits to the elderly. These
interconnection systems, based on using new technologies, would reduce the
loneliness problems of the elderly, would avoid the need for care workers to travel
each time a person who needs some sorts of assistance or a company, and would
permit continuous contact with the elderly person without the need for being
physically present.
A crucial issue when developing a system to provide care and assistance, whilst
preserving the elderly person’s independence, is the privacy assurance, and special
care must be invested in mechanisms that will protect the elderly person’s privacy.
In this context, the IST TeleCARE project [3, 4, 5] aimed at the design and
development of a configurable framework focused on virtual communities for elderly
support. The proposed solution has to be seen as complementary to other initiatives
for the integration of elderly in the society and reduction of their isolation. With
different organizations developing different products and services, in a variety of
different areas, there is a need for a common platform into which all these
developments may be plugged so that interoperability is possible. The TeleCARE
project proposes such a common and extendable platform as a common infrastructure.
2
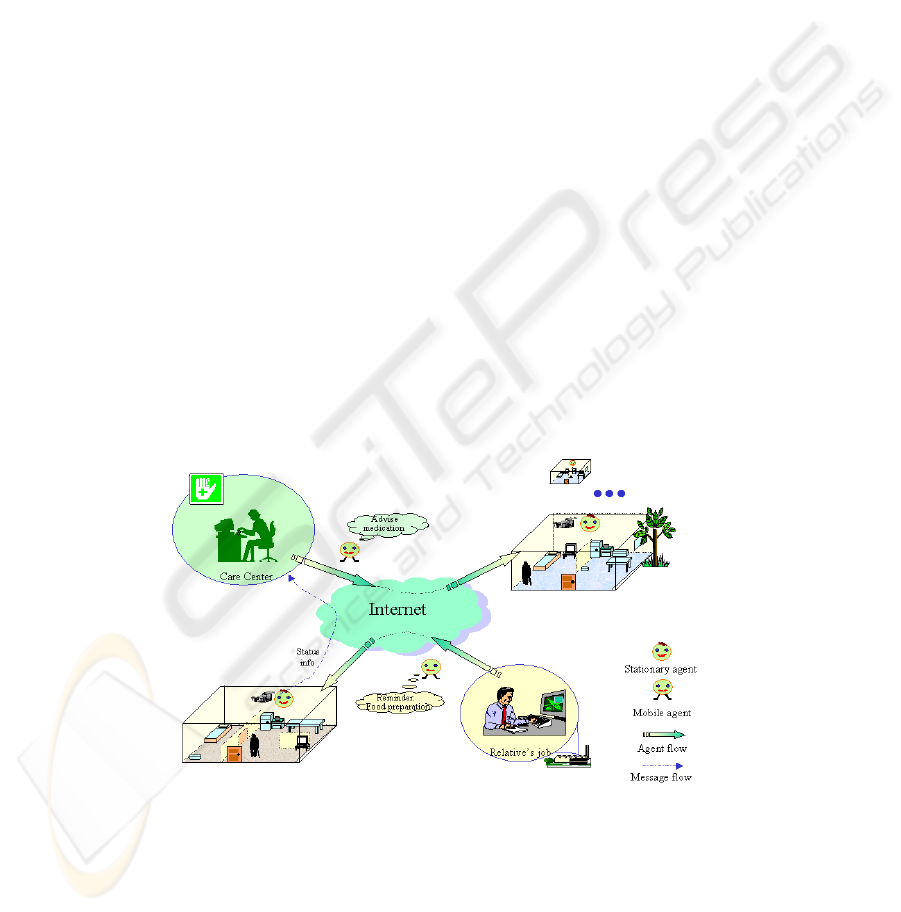
2 TeleCARE platform
The TeleCARE approach for aiming at a technological infrastructure to enhance the
collaborative virtual elderly support communities resorts at the base to the Internet
and mobile-agent technologies (Fig. 1). Internet, although appealing as a base
infrastructure, itself raises some difficulties, such as:
i) In application domains such as elderly care, high levels of heterogeneity are
expected in the sensorial and equipment richness of the remote places (homes),
which demands appropriate solutions to guarantee the necessary levels of
flexibility and scalability;
ii) The Internet is characterized by long and variable time-delays and, very often,
suffers from low levels of availability, raising new challenges in what concerns
the reliability of the implemented system and its dependence on the
characteristics of the network;
iii) The emergence of mobile and ubiquitous computing raises the importance of
wireless connections where the actual connection to the network has to be
reduced to short periods;
iv) The execution environments, involving legacy components, are potentially
unstructured and uncertain, which means that it is difficult to cope with these
environments by resorting to deterministically programmed systems.
The mobile agents paradigm offers interesting characteristics that in fact directly
addresses the above issues [6]:
i) Moving the code to the place where actions are required enables real-time
response, autonomy and continuity of service provision with reduced
dependency on network availability and delays;
ii) Since new mobile agents can be built and sent for remote execution whenever
needed, higher levels of flexibility and scalability are achieved.
Fig. 1 – The TeleCARE approach
Fig. 2 shows a block diagram of the TeleCARE infrastructure to support collaboration
in the elderly care virtual organization [2, 5]. The Basic Platform is intended to be
installed at each node of the TeleCARE network. The Specialized Components
3
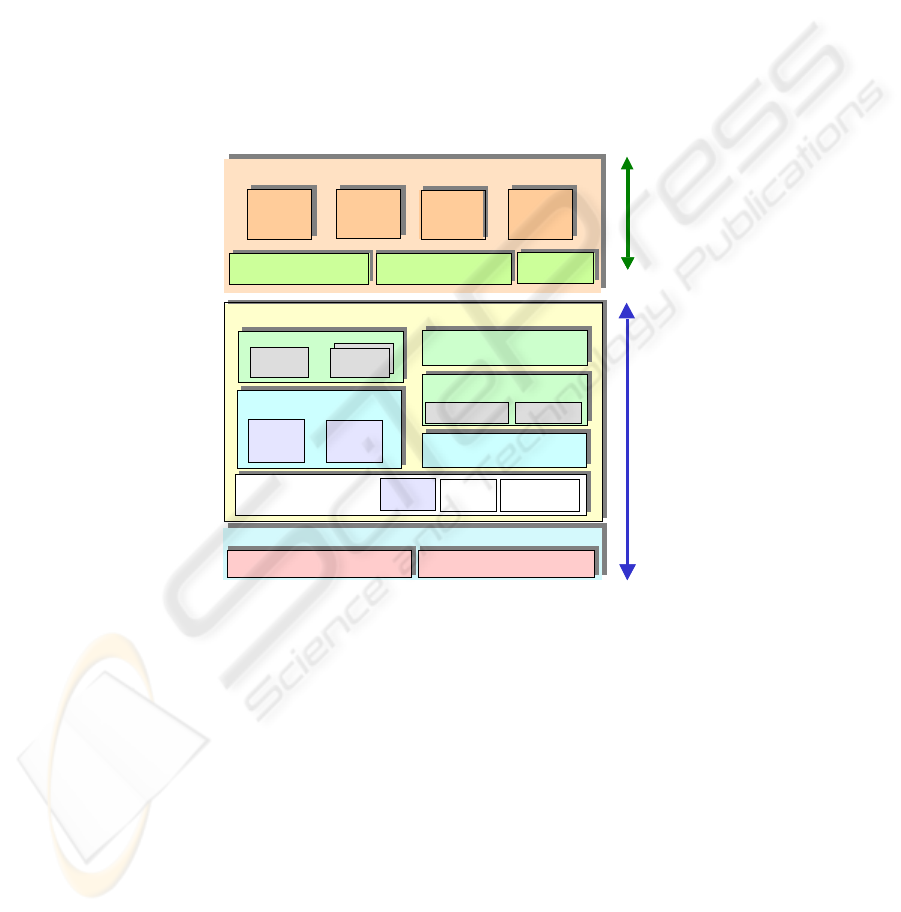
(vertical services) have a distributed implementation over the TeleCARE network.
The three-level infrastructure comprises:
• External Enabler Level: Supports the communication over the network and
interfacing to the external (local) devices. In specific it includes:
a) Safe communications infrastructure, that provides safe communications –
supporting both agent mobility and inter-agent message passing. A virtual private
network (VPN) approach is adopted; in critical cases where communications
reliability is mandatory redundant channels, in addition to Internet, may be
supported and hidden by this layer.
b) Device abstraction layer, interfaces to the sensors and monitoring devices and
other hardware (home appliances, environment controllers, etc.). These interfaces
represent the bridge to any “intelligent home” or “local domotics network”, hiding
aspects such as low-level protocols, wire-based or wireless communications, etc.
UPnP [12] is one of the approaches adopted to interface devices.
Core MAS Platform Level
Inter
-
platform
Mobility
Enter-
tainment
service
Safe Communications
infrastructure
Devices abstraction layer
TeleCARE Basic Platform
Specialized
Components
Inference
engine
Basic Multi
-
Agent Platform
Ontology
Managem.
Inter-agent communication
External Enabler Level
Vertical Services Level
Virtual Community
Support
Status
Monitoring
service
Time
Bank
service
Specialized interfaces
for elderly
Agent
Reception &
Registration
Agent
Exit
Control
Persistence
Support
Module
Agenda
service
Federated Information
Management
Agent
Factory
Resources
Managers
Platform Manager
Resource Catalog
Management System
FIMA
Dynamic
Schema generator
Web services
access
Fig. 2 - The TeleCARE platform architecture
• Core Multi-Agent System (MAS) Platform Level: It is the main component of the
basic platform. It supports the creation, launching, reception (authentication and some
rights verification), and execution of stationary and mobile agents as well as their
interactions. It supports the storage and manipulation of data and information to be
handled within TeleCARE. It provides a catalog of all devices and services supported
in TeleCARE. As intelligent agents are envisaged, an inference engine is included.
Main modules in this layer are:
a) Basic multi-agent system (MAS) platform (based on AGLETS).
b) Inference engine (based on a Prolog interpreter).
c) Ontology support (based on Protégé). A facility is developed providing the basic
mechanisms for dynamic schema description by TeleCARE service developers.
4

d) Persistence support – Extension to the MAS platform, providing some basic
recovery mechanisms in case one node goes down.
e) Inter-platform mobility – Extension to the basic MAS platform to support
generalized mobility of agents, including security mechanisms. This module
includes the Agent Reception & Registration component (for incoming mobile
agents) and the Agent Exit Control component (for outgoing mobile agents).
f) Inter-agent communication – Extension to the basic MAS platform to support
communication between / coordination of agents independently of their current
location, via FIPA ACL messages.
g) Platform manager – To specify and configure the operating conditions of the
platform in each site, recover from errors, monitor operation status, etc. It
includes:
• Agent factory – A module that supports the creation / specification and
launching of new agents.
• Resource manager agents – To provide a common and abstract way of dealing
with devices and appliances in TeleCARE.
h) Federated information management – To support the necessary management of
information while preserving the information privacy and careful control of access
rights to local data for external users. This module, installed in each site, is the
local component of the Federated Information Management Architecture (FIMA),
which includes:
• Federated query processing – providing the possibility to retrieve information
from a number of TeleCARE nodes.
• Federated access control – querying and providing access to the stored
information.
• Automatic ontology-based schema generation – generating database schemas
from the ontology definitions provided by TeleCARE software developers.
i) Resource catalog management – To manage the catalogue of resources including
support for their specification, discovery, and access proxies of all devices and
services available at each site.
• Services Level: This is the application level and consists of two sets of specialized
services:
a) Base horizontal services
– A set of specialized base services that provide specific
functionality for the other (vertical) services, including the following:
Specialized interfaces for elderly – In the case of home sites, specialized
interfaces are required for elderly that are not familiar with the use of
computers. The ultimate goal is therefore to make the usage of the system
pleasant and easy, and thus to make the TeleCARE infrastructure "invisible" to
the elderly.
Virtual Community Support – To support and facilitate the creation and
operation of community-based services designed for the elderly. For this
purpose, specific virtual community management functionalities are supported
within the service development environment of TeleCARE.
Web service access – To allow remote access to some services via a web
browser. This functionality is particularly useful to allow relatives of elderly to
have access to the TeleCARE network from their working places.
5

b) Vertical Services
– A set of specialized vertical services can be implemented on
top of the horizontal TeleCARE infrastructure defined in the previous levels to
support different interactions with the system. Taking into account the priorities
identified through an extensive fieldwork, the following initial services have been
developed by the TeleCARE consortium:
Living status monitoring. This service represents an advance regarding the
more traditional “social alarm” systems, as it allows not only bi-lateral
interactions and some semi-automatic supervision functionalities, but also the
collection of additional information when help is needed or requested. The
tranquility and assistance given 24 hours a day increase in a significant manner
the elderly’s quality of life and relative’s peace of mind.
Agenda reminder. The daily activities related to the welfare of the elderly can
be easily scheduled in order to improve their quality of life and well being.
This service, implemented through a number of agents, is able to remind the
elderly of a number of activities, ranging from medication to exercise guidance
or appointments made with the care center.
Time bank. This service provides a mechanism for collaborative community
building / re-enforcement, i.e. a way for people to come together and help each
other. At the same time it represents one of the mechanisms to support the
“active aging” concept.
Entertainment. The Entertainment Services are designed to ease the sense of
isolation elderly feel and provide light entertaining applications to improve
their sense of well being, contributing to the maintenance of a social life and
also an active aging. As a first demonstration a combination of games, music
and education programs are offered.
3 TeleCARE platform implementation
A TeleCARE prototype platform is developed in Java that integrates and resorts to
various open source or freeware supporting technologies, e.g. AGLETS mobile agents
platform [1], Protégé ontology manager, SAP DB management system, and
CASTOR.
6

Fig. 3 – TeleCARE interface for the care center
In order to support the requirements of this application domain, a number of
innovative technical features and components are developed as the middleware on top
of the base development environment. Following is a list of these features and
components, with some details about their implemented capabilities:
Inclusion of agents’ persistence support. Persistency is a mechanism that allows
storing information about the running activities of the agents and, whenever a
system crashes to allow them to be resumed when the system is restarted.
AGLETS provides a method called
snapshot, which saves a snapshot of an
agent into a secondary / non-volatile storage. For persistency purposes, every
TeleCARE agent can invoke the
tcSave method, which does a call to snapshot,
for storing information about its execution status when necessary. If there is a
system failure, the last snapshot of the agent is restored and its execution can be
resumed with the information stored in that snapshot. In the current version,
automatic support for persistency is provided on three events: (i) at the creation of
the agent, (ii) just after the agent arrives to a new location, and (iii) when the agent
is activated. It is up to the developer to decide where he/she wants to make
additional snapshots of his/her agent, calling the
tcSave method.
High-level agent identification and localization. A TeleCARE Logical Agent
Identification (TLAID) structure was introduced, which is used to validate an agent
at any platform, and to locate an agent (using human understandable data) as well.
With the information provided by the TLAID, the developers can identify any
TeleCARE agent, given its name, type, role or user ID, and/or domain node of the
TeleCARE Virtual Organization that the origin host (or platform) of the agent
belongs to. TLAID is composed of two substructures:
– TLAD – The TeleCARE Agent Data that contains specific human readable
identification of the agent, and
– TLUD – The TeleCARE User Data that contains human readable
identification of the user who created the agent;
Please note that the native AGLETS AgletID, which is a string of 16 hexadecimal
characters, is not a user-friendly identifier. Furthermore, it might change if a clone
replaces the original agent as a result of the persistency support mechanisms.
7
TLAID is, therefore, a high-level user-friendly identifier. If only part of TLAID
information is given, the result of the method
tcGetAgentTAL can be a set of
agents. This happens when a TLAID object is used to get the TAL or passport of an
agent. In many cases the result of the query is a set of agents.
Given the inter-platform mobility and the need to keep track of mobile agents, the
following agents are introduced:
Agent Registry – Keeps a record of all agents that are living in the platform.
The registration consists in a copy of the passport of each agent..
Agent Reception Control – Responsible for the reception of the incoming
mobile agents. Depending on their passports these agents can be accepted or
refused. Whether an arriving agent is accepted in the local platform or not, the
Agent Exit Control of the sender platform is notified..
Agent Exit Control – Controls the outgoing of mobile agents. Every time an
agent is to leave the platform, its passport is first checked to see if the agent
has permission to travel, and if the destination of the agent is available and/or
is a valid TeleCARE platform.
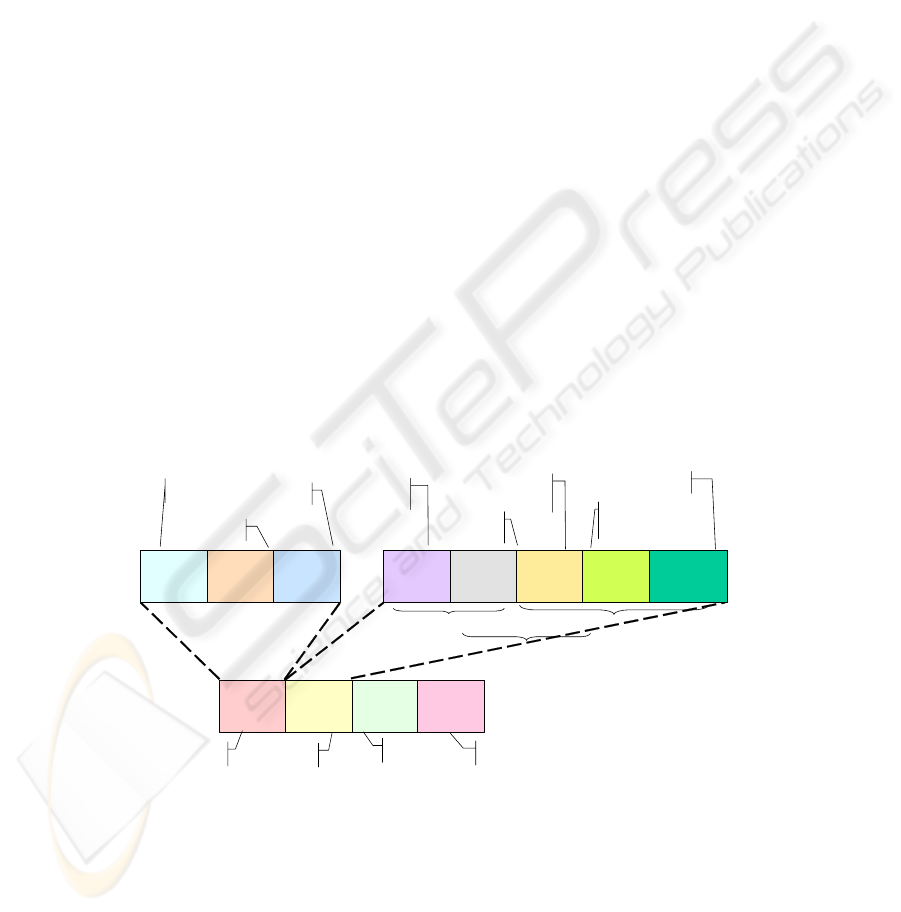
New security mechanisms for agents and messages. Both in case of mobile agents,
when an agent arrives at one node, or remote (inter-node) agent communication, it
is important to know who the agent is / who it represents. For this purpose, the
concept of passport is introduced and associated to each agent (Fig. 4). It is the
official “travel document” recognized by any TeleCARE site of the community.
Any mobile agent that intends to migrate to another platform must have a valid
passport.
The passport includes two fields used for agent identification: TAL and TLAID.
TAL is the TeleCARE Agent Locator, which is a system identifier used to locate an
agent; with the information provided by TAL, the system can find the proxy of any
agent, no matter where it is (for instance, to send it a message).
TAL
Passport
The Aglets
identification
Platform where the
Agent was created
TAL
TLAID
TLAID Validity Itinerary
AgletID hostOrigin hostCurrent agentName agentType userRole userID
Platform where the
Agent is currently living
in
Logical name of
the Agent, given
by the Developer
The category of the
Agent: System,
Resource, etc.
Category of the user who
created the Agent: Doctor,
Nurse, Relative, Elderly, etc.
The identification of the
user who created the
Agent: Mary, Joseph,
etc.
Duration time
of the Passport
List of the last
visited sites
domainNode
TLAD
TLUD
Domain node of the
TeleCARE VO to which
hostOrigin belongs to
TeleCARE
Agent Locator
TeleCARE
Logical Agent
Identifier
Fig. 4 - TeleCARE agent passport
Generalized communication mechanisms. The AGLETS system provides a simple
mechanism for inter-agent communication. However this mechanism is not
sufficient for reliable communication for highly mobile agents [9] or when
8

persistence mechanisms based on cloning are implemented, namely due to the
changes in the AgletID. Therefore, the platform implements additional
communication services:
Extended message exchange mechanisms, which allow reliable inter-agent
communication.
Handling FIPA ACL messages.
Integration and management of resources in TeleCARE. Two kinds of resources
are considered in TeleCARE including the hardware devices and the software
services. The Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) specification is an architecture for
pervasive peer-to-peer network connectivity of intelligent appliances, wireless
devices, and PCs. Home appliances and sensors are connected to the TeleCARE
platform following UPnP. The Web Services Definition Language (WSDL)
provides the framework for definition of service specifications and their
interfaces. The horizontal and vertical services of TeleCARE are defined and
provided through the TeleCARE platform using the WSDL.
The Resource Catalog Management (RCAM) component supports the
organization, storage, and access to the UPNP (for devices) and WSDL (for
services) definitions of the TeleCARE resources.
Furthermore, in order to facilitate the access to & invocation of TeleCARE
resources an Abstract Resource Manager Agent (ARMA) template is provided.
ARMA is instantiated and customized for each resource, becoming its actual
Resource Manager. Application services can access a resource’s functions through
its corresponding Resource Manager that also checks and enforces the access
rights of the requesting agents on the requested resource.
Integration of federated information management and mobile agents. The
Federated Information MAnagement (FIMA) is a key component of the 'Core
Multi-Agent System Platform Level'. FIMA enables applications to distribute data
transparently across multiple machines within the TeleCARE network. The design
of FIMA is based on the federated databases approach, in order to support
cooperation and information sharing, while reinforcing the required level of
autonomy and heterogeneity among individual data sources (e.g. elderly home,
care center, leisure center, etc.) within a TeleCARE network. The federated query
processing is implemented by MIRA - Mobile Information Retrieval Agent in
such a way that applications can request to execute queries in:
• parallel mode, e.g. accessing data from several remote sources simultaneously.
• serial mode, e.g. accessing data from different nodes, one after the other, etc.
• sequential mode, e.g. similar to the serial one but in which the process can be
stopped once the client is satisfied with the result, providing a high user
interactivity to control information processing overhead.
Ontology-based database schema generator. The Dynamic Ontology-based
Schema Generation (DOSG) component of the core platform of TeleCARE
supports and assists service developers with their direct definition of database
schemas for the data that needs to be stored and processed by their code, and thus
it can eliminate the need for database experts to define and modify these schemas.
Namely, DOSG provides facilities for dynamic and automatic definition of the
9

database schemas (relational and XML schemas) and the (Java source) code for
the structures defined by users, so that they can be automatically stored into
database and processed by application programs. As such, the service developers
of TeleCARE, can use the ontology system “Protégé” as interface for their
structure definitions, and do not need to have database expertise to define these
database schemas.
Integration of web services. In order to provide access to TeleCARE services for
relatives having access to Internet through a web browser, a mechanism is
implemented to provide a bridge between the multi-agent platform and a web
browser following a philosophy of web services.
Integration of biometric security. A finger print identification device is integrated
with the platform providing a mechanism to implement safer user identification.
This is particularly useful in the care centers where different users (e.g. nurses,
doctors, care workers), with different information access rights, can have access to
the system. A taxonomy of users and roles is therefore associated to the biometric-
based login process.
Variety of user interfaces. Considering the diversity of computer skills of the
various actors in the elderly care virtual community, access to the TeleCARE
platform and services needs to be made accessible through a variety of user
interfaces, namely for users with computer skills (e.g. care center workers having
direct access to the platform, relatives having access through a web browser from
their work locations, or elderly without computer skills interacting with the system
through a TV set).
4 TeleCARE services implementation
In the TeleCARE environment each vertical service can be implemented in different
ways as a set of distributed stationary and / or mobile agents. For instance, a
monitoring service might involve a stationary agent in the care center (interacting
with the care worker), a number of stationary agents in the elderly home (agents in
charge of monitoring local sensors, e.g. temperature sensor, presence sensor), and
some mobile agents sent from the care center to the elderly home (Fig.s 5, 6). The
mobile agents might carry a mission, for instance MIRAs sent to collect information
from different sensors and to report back to the care center.
The stationary agents in one platform can also communicate, via ACL messages,
with other mobile or stationary agents residing at another platform. Since a
TeleCARE message includes the extended agent identification (see passport section),
the receiver of a message can check the identity and rights of the sender, no matter at
which location it is running at the moment.
10
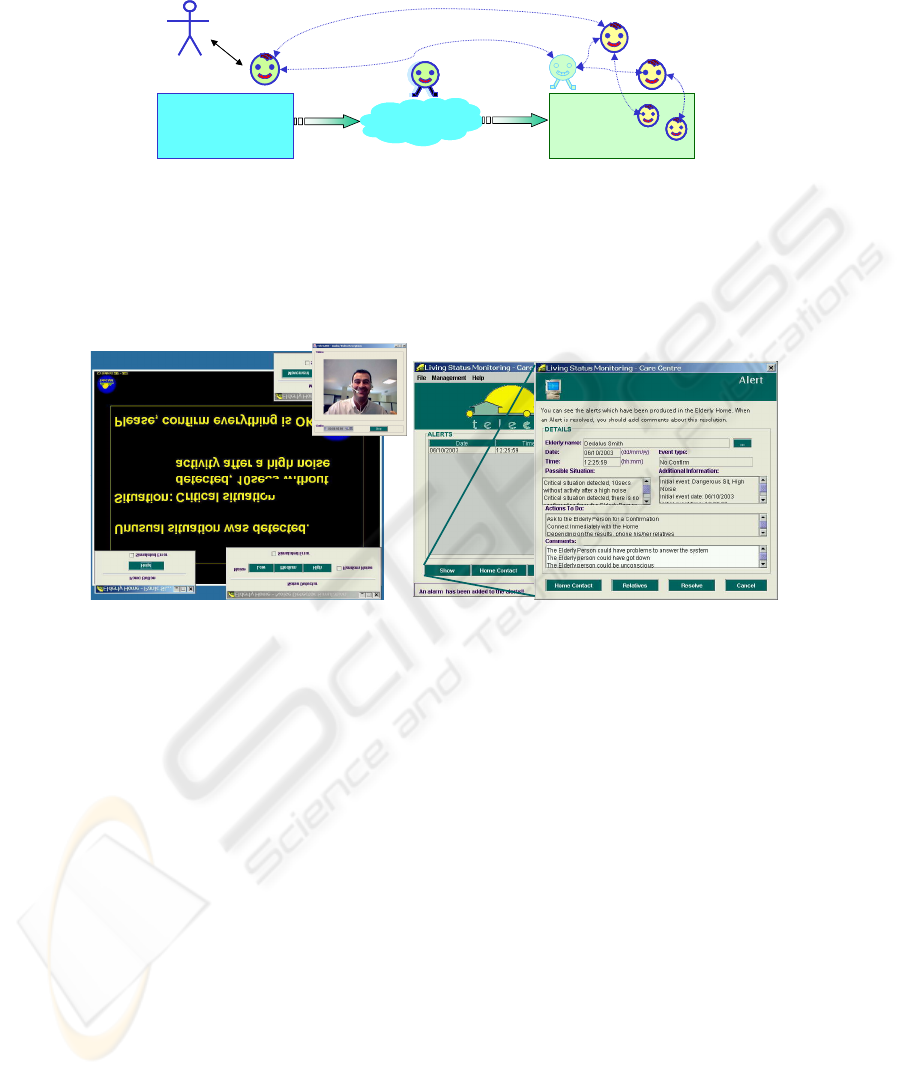
Care Center
Elderly Home
Internet
Monitoring
Application agent
Care worker
Specific
Monitor
agents
Mobile agent
with monitoring mission
TeleCARE Platform
TeleCARE
Platform
ACL
Fig. 5 - Example of service implementation
The use of mobile agents facilitates the remote deployment of the service
functionalities according to the services subscribed by each elderly. As different
elderly have different needs, such flexibility is required. With this mechanism it is
also easier to install updated versions of the services.
CARE4U
Fig. 6 - Example of monitoring service interfaces at elderly home and care center
An integrated prototype system including the TeleCARE platform and a set of
demonstration services was developed, showing the feasibility of the suggested
approach. This integrated system was partially validated through a field assessment
phase that took place in South of Spain, and involving four classes of potential users:
(i) Elderly and relatives, (ii) Care providers / care workers, (iii) Decision makers (on
social policies), and (iv) Software developers. The TeleCARE concept and its
provided functionalities were well accepted by these potential users, although it is
clear that the system is at a research prototype stage and substantial engineering work
is still necessary in order to make it a robust product.
5 Conclusions
The growing numbers of elderly population impose an urgent need to develop new
approaches to care provision. Recent developments in a number of technologies such
as multi-agent systems, federated information management, safe communications,
hypermedia interfaces, rich sensorial environments, and increased intelligence of
loud
11
home appliances represent an important enabling factor for the design and
development of virtual elderly support community environments. In particular, a
platform based on mobile agents combined with federated information management
mechanisms provides a flexible infrastructure on top of which specialized care
services can be built. Nevertheless, the specific characteristics of the elderly
population, not very open to deal with new technologies, require a careful integration
of the infrastructure with traditional home appliances and TV sets. Furthermore, the
tuning and eventual acceptance of the technology can only be determined when
reliable prototypes are tested in field with real users. This field trial constitutes the
next phase in the TeleCARE project.
Acknowledgements.
This work was funded in part by the IST program of the
European Commission. The authors thank the contribution of the TeleCARE
consortium members (Uninova, University of Amsterdam, SKILL, RoundRose
Associates, Camera de Comercio de Navarra, and Synkronix).
References
1. Aglets API Documentation, v. 2.0.2; Java Aglet Community, http://aglets.sourceforge.net/.
2. Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Afsarmanesh, H. - A multi-agent based infrastructure to support
virtual communities in elderly care, to appear in International Journal of Networking and
Virtual Organisations, 2004.
3. Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Afsarmanesh, H. - Design of a virtual community infrastructure
for elderly care, Proceedings of PRO-VE 2002 – 3
rd
IFIP Working Conference on
Infrastructures for Virtual Enterprises, Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 1-4020-7020-
9, Sesimbra, Portugal, 1-3 May 2002.
4. Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Afsarmanesh, H. - Virtual communities and elderly support,
MIV’01 in “Advances in Automation, Multimedia and Video Systems, and Modern
Compuuter Science”, (V.V. Kluev, C.E. D’Attellis, N. E. Mastorakis ed.s), WSES, ISBN
960-8052-44-0, Sept 2001.
5. Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Castolo, O.; Rosas, J. – A multi-agent based platform for virtual
communities in elderly care, Proceedings of ETFA’03- 9
th
Int. Conf. On Emerging
Technologies and Factory Automation, Lisboa, Portugal, 16-19 Sept 2003.
6. Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Vieira, W. - Intelligent mobile agents in elderly care, Journal of
Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol. 27, N. 1-2, April 1999, ISSN 0921-8890.
7. Dutta-Roy, A. – Networks for homes, IEEE Spectrum, Vol. 36, N. 12, Dec 1999.
8. Hampicke, M. – Smart home: Speech based user interfaces for smart home applications, in
COST 219 Seminar on Speech and Hearing Technology, Cottbus, Germany, 22 Nov 2002.
9. Murphy, A.; Picco G. P. – Reliable communication for highly mobile agents, Autonomous
Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (Kluwer Academic Publishers), N. 5, 2002.
10. Pascual, A. – TeleCARE Final Report on Users Requirements, TeleCARE Deliverable
D1.3, Aug 2002.
11. Saranummi, N.; Kivisaari, S.; Sarkikoski, T.; Graafmans, J. – Ageing & Technology –
State of the art, Report for the European Commission, Institute for Prospective Studies,
Seville, Spain, Nov. 1996.
12. Universal Plug and Play Device Architecture; Universal Plug and Play Forum,
http://www.upnp.org/
.
13. Vlaskamp, F. – Social alarms go mobile: emergency assistance for mobile users, 1999,
www.fernuni-hagen.de/FTB/aaate99/paper/99_67.htm
.
12
