
INVARIANT SIGNAL RECOGNITION IN NOISE ENVIROMENT
Riad Taha Al-Kasasbeh
Faculty of Engineering Technology, Al-Balqa Applied University, Amman, Jordan
Keywords: signal/noise, speech recognition, invariant signal recognition.
Abstract: Recognition of signals is considered at the presence of noise. The problem is actual for the speech signals
recognition, acoustic diagnostics of mechanisms. The model of recognized signal contains a priori unknown
parameter - the relation a signal / noise. For considered model the approach to construction of the signal
description, which is invariant to a level of the noise is offered. Efficiency of invariant signals recognition is
analyzed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The task of recognition of random noise signals with
reference to such tasks as speech recognition
(S1ozokai et al., 1998) (Schalkoff, 1992), technical
diagnostics of mechanisms on their noise, processing
of the biomedical data is considered.
In real conditions of application of recognizing
devices for such tasks it is necessary to allow the
fact, that on an input of the recognizing device the
signal is the sum of a temporary useful signal and
one or several disturbance acts. The noncorrelation
of a useful signal and disturbances among
themselves is supposed. As is known, many tasks of
recognition of random signals effectively are solved
by transition in spectral area. Therefore in the
spectral form representation of a signal, it is possible
to write
),()()(
1
ω+ω=ω
∑
=
k
i
nC
i
SSS
(1)
Where - spectrum of a signal on an input of
the classifier, - spectrum of a useful signal,
- spectrum i-th noise disturbance, k – number of
noise. Further passing to the description of a
spectrum in the vector form as countings on the
given set of frequencies
ω
1
, ω
2
, …….., ω
d
and
entering concept of the normalized vectors of the
spectral description of a signal and noise ,
expression (1) it is possible to write as
S
C
S
i
n
S
0
C
x
0
i
n
x
∑
=
λ+λ=
k
i
niC
i
xxS
1
00
0
,
(2)
Where
0
λ
and
i
λ
- the coefficients defining
accordingly power of a signal and disturbances
appropriate. Thus the ratio
0
λ
/
i
λ
is the ratio signal
/ noise for i-th noise.. In case power of a classified
signal does not carry the information on the class of
the recognized object, parameters
0
λ
and
i
λ
can be
considered as hampering parameters.
Since signal distortion parameters (in particular
the ratio signal / noise) are unknown, and distortions
can reach significant values, there is impossible a
correct recognition of signals with the help of the
classifier is trained with standard signals, or on
the signals subjected to distortions with parameters,
distinguished from what take place actually at the
moment of recognition. Various approaches to
solution of the considered task are known. The most
widespread is the method of spectral subtraction of
disturbances and its various modifications (Glunder,
1991) (Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis,
2003). A disadvantage of this approach is necessity
of knowledge of the ratio signal / noise or obtaining
of its estimation. In some cases to receive this
estimation it is not possible and accordingly the ratio
signal noise appears as hampering parameter to the
task of recognition. In such situation natural way is
initial creation of the new system of features, wich
are invariants (Ben-Arie and Wang, 2002) (Flusser
and Suk, 1993) (Glunder, 1991) concerning effect of
hampering parameters is represented. Construction
of the decision rules is made already at the following
79
Taha Al-Kasasbeh R. (2005).
INVARIANT SIGNAL RECOGNITION IN NOISE ENVIROMENT.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - Signal Processing, Systems Modeling and
Control, pages 79-83
DOI: 10.5220/0001157900790083
Copyright
c
SciTePress

stage, and the class of decision rules that can be used
for classification, beforehand to nothing is limited.
2 CREATION OF INVARIANT
DESCRIPTIONS OF A SIGNAL
AT RECOGNITION ON A
BACKGROUND OF
DISTURBANCES WITH
UNKNOWN POWER
Let's consider a case when on an input of recognition
device the signal is, combined with one (k=1)
additive disturbance. And powers of a useful signal
and disturbance are unknown, is equal as the ratio
signal / noise q is not known also. Is known sort of
the normalized spectrum of power of the noise
disturbance, described as vector
0
n
x
G
of dimension d
. Then the spectral vector of power of a recognized
signal
can be written as
x
G
x
G
=С
0
0
C
x
G
+С
1
0
n
x
G
(3)
Where
0
C
x
G
- spectral vector of normalized useful
signal, С
0
,С
1
– the unknown coefficients depending
on powers of a useful signal and disturbance.
If the signal on an input of the classifier is
exposed to normalization on power it is easy to
show, that coefficients С
0
and С
1
depend only on the
ratio signal / noise. Taking into account model of a
signal (3), we shall enter in space the initial features
X set of transformations
G= {g: g
=
x
G
0
λ
0
C
x
G
+
1
λ
0
n
x
G
}, (4)
0<
0
λ
< , - <∞ ∞
1
λ
< . ∞
Is simple enough to show that these transformations
is algebraic group of transformations, caused by two
subgroups
G
0
= {g
0
: g
0
=
x
G
0
λ
x
G
}, 0<
0
λ
< , ∞
G
1
= {g
1
: g
1
= +
x
G
x
G
1
λ
n
x
G
}, - <∞
1
λ
<
∞
.
Construction of the invariant description of a signal
in the indicated setting is reduced to finding
maximum invariant (MI) of transformations group
G (Leman, 1959). For construction MI concerning
group of transformations G the stage-by-stage
method of construction MI offered by Leman
(Leman, 1959) is used. In the beginning it is defined
MI concerning subgroup G
1
. It is shown by usage
(Geppener and Ekalo, 2002), that it is linear
transformations
y
G
= А
x
G
, (5)
Where the matrix A by dimensions (d-1) *d defines
transition in new space Y of features with,
dimension d-1 , and satisfies to a condition
А
n
x
G
=0 (6)
Geometrical interpretation of invariant
transformations (5) consists that we select a new
coordinate system, one of w ich axes coincides with
a direction of a vector
. In the further this
coordinate is discarded. Thus, is constructed the
matrix of transformations A , which rows are the
vectors of new axes of coordinates except
. For
construction of new basis the procedure of
orthonormalization by Gramm-Shmidt , in
particular, can be used.
h
n
x
G
n
x
G
Effect of a subgroup of
induces a subgroup
of the transformations in space Y defined as
0
G
*
G
}.:{
*
0
*
0
*
0
yyggG
G
G
α
== (7)
MI is relative to (7) is usual normalization and can
appear as
,
y
y
z
G
G
G
=
(8)
where
y
G
- norm of vector
y
G
, defined, in
particular, as
∑
=
d
i
i
y
1
2
.
According to the theorem of a stage-by-stage
method of construction MI (Leman, 1959), we
receive an ending expression for MI concerning
group G .
.
xA
xA
z
G
G
G
=
(9)
ICINCO 2005 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
80

3 EXPERIMENTS
For the experimental research of recognition under
the condition of disturbance three etalon
disturbances, used for the noise-protected classifier
training, were generated. During the experiment
distortion of signals was modeled by the disturbance
with the given signal to noise ratio q. In the process
of training a disturbance with fixed spectrum was
used, and for recognition a fluctuation of the
disturbance was modeled defined by factor K
f1
, that
shows the ratio of the mean square deviation of the
disturbance vector to its mean value. Modeling of
two classes of signals for identified objects was
fulfilled. Signals were presented by spectral
description vectors with dimension 50, number of
vectors for each class was equal to 250.
Fig.1 shows the averaged spectra of the generated
signals, when Fig.2 shows the etalon disturbances.
Experiments were done using the training algorithm
based on the Fisher discriminant (Lockwood and
Boudy, 1992) with the use of non-invariant features
in the form of countings of spectra for two classes of
model signals, and the invariant features for three
types of disturbances, correspondingly.
Figure 1: Averaged spectral description.
Figure 2: Spectra of etalon disturbances used of classes in
the experiment
Figures 3-5 show the dependence of the estimation
of correct identification probability P
cr
on
The signal/noise ratio q. Fig.3 shows the results of
the identification experiments with the first type of
disturbance (in all figures curve 1 corresponds to the
use of non-invariant features, while curve 2
corresponds to the identification with invariant
features. Fig.4 shows experimental results of
identification modeling, made at the same conditions
as in the previous experiments, but for the
disturbance type 2, and Fig.5 shows the
experimental results for the disturbance type 3,
correspondingly.
a:
INVARIANT SIGNAL RECOGNITION IN NOISE ENVIROMENT
81
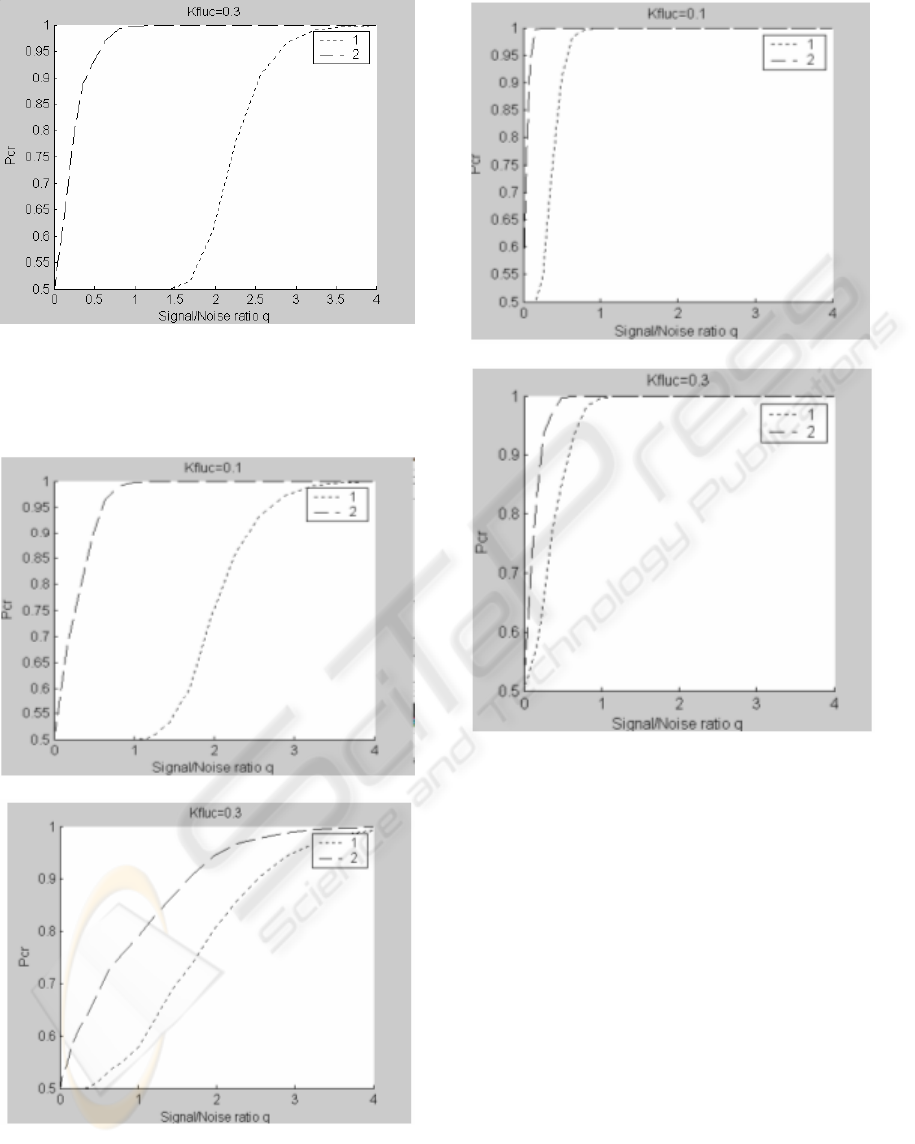
b:
Figure 3: Experiment with a model signal with a
disturbance type 1.
a) K
fl
=0.1 , b) K
fl
=0.3
а:
b:
Figure 4: Experiment on the model signal with the
disturbance type 2.
а) K
fl
=0.1 , b) K
fl
=0.3
a:
b:
Figure 5: Experiment on the model signal with the
disturbance type 3.
а) Kfl=0.1 , b) Kfl=0.3
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the experiments can be formulated as
follows.
Identification with the Fisher classifier:
-
for the given sample of signals under the
influence of the disturbance type 1,
The obvious advantage of the noise-protected
classifier based on invariant features is discovered,
together with the deteriorating quality of
identification at the increased fluctuation of the
disturbance.(Fig.3).
-
Under the influence of disturbances type 2
“noise-protected” dependence is better than non-
protected, but is worse than the dependence with the
ICINCO 2005 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
82

disturbance type 1 under the same circumstances.
(Fig.4).
-
under the influence of disturbances type 3 one
can fix the least difference between the noise-
protected dependence and the non-protected one
(Fig.5), but it should be stated that the identification
quality is sufficiently good for both cases even at
small signal/noise ratio, that is the disturbance of
that type is sufficiently “good” for identification.
In addition, similar experiments were done using
perceptron algorithm of identification. As a whole,
the identification results with invariant features for
that algorithm were slightly worse (5-10%)
compared with the Fisher classifier, but the
difference in the identification quality with the
original features was rather big.
Thus, in most cases the investigated method of
invariant identification of signals under the
influence of disturbances gives practically
acceptable results. Nevertheless one should take into
account the fact that under the influence of the
disturbances of certain types the identification
results can be unsatisfactory, so the additional
research in the field is necessary.
REFERENCES
S1ozokai M., Nakamura S., Shicado K. Robust 1998 Car
Recognition in Car Enviroment. ProcICASSP, pp.
269-272.
Ben-Arie J., Wang Z. 2002 Shape Description And
Invariant Recognition Employing Connectionist,
International Journal of Pattern Recognition and
Artificial Intelligence,v. 16, N. 1, 69-83.
Flusser J, Suk T., 1993, Pattern Recognition by Affine
Moment Invariants// Pattern Recognition, v.26, N. 1,
p.167-174.
Glunder H., 1991, Pattern Properties, Invariances, and
Classification, in Vision and Visual
Dysfunction//Pattern Recognition by Man and
Machine, MacMillan Press, p.69-82.
Leman E.L. , 1959, Testing Statistical Hypothesis. Willey
, New York.
Geppener V.V., Ekalo S.A.,2002, Invariant Signal
Recognition in the Presence of Noise //
Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 2003, Vol. 13,
No. 2,pp. 266–269
Lockwood P., Boudy J, 1992, Experiments with a
nonlinear spectral subtractor , hidden markov models
and the projection, for robust speech recognition in
cars. Speech Communication, v. 11, pp. 215-228.
R. Schalkoff. , 1992, Pattern Recognition. Statistical,
Structural, and Neural Approaches. John Wiley &
Sons, Inc.
Berouti N., Schwartz R., Makhoul J., 1979 Enhancement
of speech corrupted by acoustic noise. In Proc. Int.
Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing , p.
208-211
INVARIANT SIGNAL RECOGNITION IN NOISE ENVIROMENT
83
