
DERIVING BEHAVIOR FROM GOAL STRUCTURE FOR THE
INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF PHYSICAL SYSTEMS
Richard Dapoigny, Patrick Barlatier, Eric Benoit, Laurent Foulloy
LISTIC/ESIA - University of Savoie (France)
BP 806 74016 Annecy cedex
Keywords:
Knowledge-based systems, teleological model, Formal Concept Analysis, Event Calculus.
Abstract:
Given a physical system described by a structural decomposition together with additional constraints, a major
task in Artificial Intelligence concerns the automatic identification of the system behavior. We will show in
the present paper how concepts and techniques from different AI disciplines help solve this task in the case
of the intelligent control of engineering systems. Following generative approaches grounded in Qualitative
Physics, we derive behavioral specifications from structural and equational information input by the user in the
context of the intelligent control of physical systems. The behavioral specifications stem from a teleological
representation based on goal structures which are composed of three primitive concepts, i.e. physical entities,
physical roles and actions. An ontological representation of goals extracted from user inputs facilitates both
local and distributed reasoning. The causal reasoning process generates inferences of possible behaviors from
the ontological representation of intended goals. This process relies on an Event Calculus approach. An
application example focussing on the control of an irrigation channel illustrates the behavioral identification
process.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most interesting and challenging tasks of
Artificial Intelligence is to derive the behavior of a
system from its components and additional informa-
tion or constraints. Reasoning about physical systems
constitutes an important and active area of research
of Artificial Intelligence, also known as Qualitative
Reasoning (QR). In QR, most works have focussed
on the representation and composition of models to
describe physical systems either with a component-
based approach (de Kleer and Brown, 1984) or with a
process-based approach (Forbus, 1984; Falkenhainer
and Forbus, 1991). Major areas of investigation are
i) the simulation of physical systems to predict their
behavior ii) given a domain theory, a structural de-
scription of the system and a query about the system’s
behavior, the composition of a model answering the
query.
Another major domain of reasoning which involves
structural modelling and behavioral analysis is the
Software Engineering (SE). A significant part of work
in software engineering is dedicated to temporal log-
ics (McDermott, 1982; Manna and Pnueli, 1992; Ma
and Knight, 1996; Galton, 1987; Freksa, 1992) with
extensions for specifying concurrent systems (Bar-
ringer, 1986; Chen and de Giacomo, 1999). These
logics form the basis of behavior analysis relying on
concepts such as goals, actions and event structures.
In this paper, we are concerned with the control of
physical activity by means of software engineering
mechanisms. Let us consider Intelligent Systems in-
teracting with a physical system. It requires at least AI
domains such as QR, for the abstraction of physical
mechanisms and SE, for behavioral analysis of soft-
ware components. This analysis has a great impact
both on the processing of variables related to physi-
cal quantities and on their control. We introduce the
notion of Intelligent Control System (ICS) composed
of a computing unit (e.g., PC, workstation, micro-
controller card, DSP-based system, ...) and sensor(s)
and/or actuator(s) unit(s). Distributed ICS exchange
information through networks using appropriate pro-
tocols (e.g., TCP/IP/Ethernet or dedicated field buses
such as CAN, LonWorks, ...). Inside an ICS, two in-
formation flows co-exist, information from/to other
ICS via network ports and information from/to the
physical system via I/O ports. The control of phys-
ical systems with ICS requires reasoning capabilities
extracted both from QR techniques and SE concepts
11
Dapoigny R., Barlatier P., Benoit E. and Foulloy L. (2005).
DERIVING BEHAVIOR FROM GOAL STRUCTURE FOR THE INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF PHYSICAL SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 11-18
DOI: 10.5220/0001162300110018
Copyright
c
SciTePress

such as events and actions. From the outside, an ICS
can be seen as an intelligent device offering a set
of services. Each of theses services are designed to
achieve a given goal, provided that some sequence of
atomic goals is achieved. More precisely, we tackle
the following problem.
Given:
• A scenario description including a physical hier-
archical structure together with a set of physical
equations relating physical variables.
• A modelling theory (derived from the General Sys-
tem Theory) whose instantiation on the given do-
main together with a set of rules will produce a lo-
cal domain theory.
• A goal (i.e., a service) request concerning the local
domain.
Produce:
• during the design step, a goal hierarchy.
• during the design step, an action hierarchy which
traduces the way of achievement of each goal.
• at run-time, the most relevant behavior depending
upon constraints.
This problem concerns major applications such as the
control of industrial processes, automotive systems,
automatic planning for control of physical systems
and measurements, robotics, ... Notice that in the
present model, the structural description of the physi-
cal system may be replaced in unknown environments
by a learning phase based on classical techniques such
as neural networks, genetic algorithms, fuzzy logic,
etc.
2 FOUNDATIONS FOR THE
MODELLING OF CONTROL
SYSTEMS RELATED TO
ENGINEERING PROCESSES
2.1 The structural model
When designing or analyzing a system, the particular
model formalisms that are used depend on the objec-
tives of the modelling. In the engineering domain, the
formalisms commonly adopted are functional, behav-
ioral and structural (Dooley et al., 1998). The struc-
tural representation is an essential component of the
model involving physical systems. Most variables of
the control process are physical variables, that is, they
are an abstraction of the physical mechanism which
is related with each ICS. We consider the semantic
representation of control variables as a tuple includ-
ing the physical role and the physical (i.e., spatial)
entity in which the physical role is evaluated. These
tuples will be referred to as Physical Contexts in the
following. Physical variables are a subset of control
variables and their physical role is in fact the so-called
physical quantity defined in standard ontologies (Gru-
ber and Olsen, 1994). In a first step, a part-of hier-
archy of physical entities can be easily sketched. In
a second step, the physical behavior of physical en-
tities is described by expressing the way these enti-
ties interact. The physical interactions are the result
of energetic physical processes that occur in physical
entities. Whatever two entities are able to exchange
energy, they are said to be connected. Therefore, the
mereology is extended with a topology where con-
nections highlight the energy paths between physical
entities. This approach extracts in a local database,
energy paths stretching between ICS in the physical
environment.
2.2 The teleological model of
actions: the goal structure
In the teleological reasoning, the structure and be-
havior of a physical system are related to its goals.
In other words, purposes are ascribed to each com-
ponent of the system and to achieve a global goal,
one must describe how each function of the systems’
parts can be connected. Moreover, since diagno-
sis is an essential part of models describing physi-
cal processes, most works relative to functional rea-
soning in the last decade have incorporated teleolog-
ical knowledge in their model (Lind, 1994; Larsson,
1996; Chittaro et al., 1993). Finally, Qualitative Rea-
soning based on a teleological approach appears to
be a useful component for planning systems involv-
ing the physical world (de Coste, 1994). Therefore,
we adopt the teleological model where goals describe
the purposes of the system, and function(s)
1
represent
the way of achievement of an intended goal. This ap-
proach is similar to that of some authors (Kitamura
et al., 2002) which claim that base-functions repre-
sent function types from the view point of their goals’
achievement.
The concept of goal is central for behavior analysis
in the control of physical systems. For example, in
failure analysis, when a behavioral change affects one
of the system goals, it means that a failure occurred
(the effect is expressed in terms of the goals that have
not been achieved). Basically, the goal representation
must facilitate the construction of knowledge data-
bases and allows to classify goals and sub-goals rel-
atively to the designers’ intents. The goal modelling
requires i) to describe goal representation (i.e., data
structures), ii) to define how these concepts are re-
lated.
1
i.e., computing function
ICINCO 2005 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
12

A goal structure must incorporate some possible
actions (at least one) in order to fulfill the in-
tended goal (Hertzberg and Thiebaux, 1994; Lif-
schitz, 1993). Representation of intended goals as
”to do action” has been proposed by several re-
searchers (Lind, 1994; et al., 1996; Kmenta et al.,
1999) but neither proposes a formal structure on
which reasoning can be based. Therefore, we extend
that textual definition by introducing a goal structure
with information relative to the physical system. Two
types of atomic goals are defined, a goal type (uni-
versal) which relate an action verb, a physical quan-
tity
2
with its arity and an entity type, and a goal token
(particular) by particularizing the physical entity type
item of the goal type. In such a way, the goal mod-
elling defines the terms that correspond to actions ex-
pressing the intension with the terms that are objects
of the actions. As it incorporates an action verb, the
basic goal definition proposed here can be seen as a
generalization of the action concept closed to the ac-
tion (or event) types defined in (Galton and Augusto,
2000).
Unlike general framework where goals cannot be for-
malized and relationships among them cannot be se-
mantically captured, the present framework restricted
to engineering physical entities makes it possible to
describe a hierarchical structure (i.e., a mereology) of
goals where the bottom level is composed of atomic
goals. Complex goals can be expressed as a mereo-
logical fusion of atomic sub-goals. One of the major
benefits of mereological framework is that it allows
for different abstraction levels to appear in the same
model.
2.3 The behavioral model
Behavior models play a central role in systems spec-
ifications and control. In order to specify the be-
havior of a system, different approaches are possible.
From the software engineering point of view, a ref-
erence model specifying the behavior of distributed
systems (ISO, 1996) introduces a minimal set of ba-
sic modelling concepts which are behavior, action,
time constraints and states. The popular approaches
to behavioral specification languages are based on ei-
ther states or actions (Abadi and Lamport, 1993). In
the state-based approach, the behavior of a system is
viewed as a sequence of states, where each state is an
assignment of values to some set of components. Al-
ternatively, an action-based approach views a behav-
ior as a sequence of actions. Selecting behavior, goals
(i.e., extended actions) time constraints and time-
variant properties (i.e., fluents), we adopt the logical
formalism of the Event Calculus (EC). This formal-
2
we generalize this definition with ”physical role” con-
cerning sorts which are not physical
ism presents some advantages well-suited to our pur-
poses, in particular its ability to represent actions with
duration (which is required to describe compound ac-
tions) and to assimilate narrative description of events
with an adjustment of the actions’effects in a dynamic
way.
Definition 1 A behavior is defined as a collection of
extended actions occurring according to a set of con-
straints, known as pre-conditions.
Therefore, two concepts are highlighted, action types
(goals) and constraints. As the physical system in-
clude artifacts, interaction with the physical system
involves actions with these artifacts. This assertion
reinforces the choice of a goal structure relating an
action with its physical entity. As a consequence, be-
haviors are the result of teleological interpretation of
causal relations among atomic goals.
As suggested in (Barwise and Seligman, 1997), dis-
Figure 1: The local model for Intelligent control.
tribution of knowledge presupposes a system of clas-
sification. Alternatively, conception and analysis of
knowledge relies on powerful techniques such as For-
mal Concept Analysis. The unification of these two
related theories seems a promising candidate to build
the foundations of a theory of distributed conceptual
structures (Kent, 2003). As a consequence each of
the previous sub-models can be related to classifica-
tions through formal contexts as described in figure 1.
The first part produces a goal hierarchy according to
a spatial classification where types are goal types and
tokens are spatial instances of goals, i.e., goals related
to a spatial localization. Constraints on goal types
DERIVING BEHAVIOR FROM GOAL STRUCTURE FOR THE INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF PHYSICAL
SYSTEMS
13

are given through physical equations or/and control
laws relating physical roles. Then, the goal hierarchy
is mapped onto programming functions through flu-
ents constraints. These constraints correspond to the
well-known pre-conditions in STRIPS-like planning.
If several preconditions are defined, then several ways
of achievement exist for a given goal, each of them
corresponding to an event (or action) type. Therefore,
a second classification is defined with events as types
and events occurrences as tokens. This classification
is a temporal one where the constraints are given by
the Event Calculus formalism through fluents, axioms
and a set of rules. The whole design process begins
with the introduction of a set of universal goals and
produces through a refinement process, a planning for
a given control system in a given environment, i.e.
spatial and temporal instances of general information.
3 THE TARGET APPLICATION
Figure 2: The hydraulic control system with two Intelligent
control nodes.
The real-world example concerns an open-channel
hydraulic system which is controlled with (at least)
two ICS, as shown in figure 2. The control nodes are
connected with a fieldbus (CAN network). Each ac-
tive ICS
i
, in the open-channel irrigation channel is
located near a water gate and performs two pressure
measurements from a Pitot tube (resp. in SF Area
i
and DF Area
i
). In addition, it is able to react accord-
ingly and to modify the gate position with the help
of a brushless motor. Pairs of goal-program func-
tions are the basic elements on which knowledge rep-
resentation is built. While the basic functions are ex-
tracted from libraries, the goal/subgoal representation
requires a particular attention. To each subgoal, one
or several dedicated software functions can be either
extracted from libraries or defined by the user. Goals
and functioning modes are user-defined. All functions
handle variables whose semantic contents is extracted
from the structural mereology.
4 THE CONCEPTUAL GOAL
HIERARCHY
The Formal Concept Analysis produces a conceptual
hierarchy of the domain by exploring all possible for-
mal concepts for which relationships between prop-
erties and objects hold. The resulting concept lattice,
also known as Galois Lattice, can be considered as a
semantic net providing both a conceptual hierarchy of
objects and a representation of possible implications
between properties. A formal context C is described
by the triple C = (O, A, I), where O is a nonempty
finite set of objects, A is a nonempty finite set of at-
tributes and I ⊆ O × A is a binary relation which
holds between objects and attributes. A formal con-
cept (X, Y ) is a pair which belongs to the formal con-
text C if X ⊆ O, Y ⊆ A, X = Y
I
and Y = X
I
.
X and Y are respectively called the extent and the in-
tent of the formal concept (X, Y ). The ordered set
(B(C), ≤) is a complete lattice called the concept lat-
tice of the formal context (C).
Definition 2 Given R, a finite set of physical
roles and φ, the finite set of physical entities,
a Physical Context (PC) is a tuple: θ =
(r, µ(r), ϕ
1
, ϕ
2
, ...ϕ
µ(r)
), where r ∈ R, denotes its
physical role (e.g., a physical quantity), µ : R →
Nat, a function assigning to each role its arity (i.e.,
the number of physical entities related to a given role)
and {ϕ
1
, ...ϕ
µ(r)
} ⊆ φ, a set of entities describing the
spatial locations where the role has to be taken.
Definition 3 Given Φ the finite set of physical enti-
ties types, a goal type is a pair (A, Ξ), where A is an
action symbol and Ξ a non-empty set of tuples ξ =
(r, µ(r), φ
1
, φ
2
, ...φ
µ(r)
) where {φ
1
, ...φ
µ(r)
} ⊆ Φ,
a set of entities types describing the spatial locations
where the role r has to be taken.
γ
def
= (a, Ξ) (1)
Definition 4 A goal token is a pair (A, Θ), where A
is an action symbol and Θ a non-empty set of tuples
θ = (r, µ(r), ϕ
1
, ϕ
2
, ...ϕ
µ(r)
).
g
def
= (a, Θ) (2)
The hydraulic control system requires the following
list of basic goals
3
:
g
1
= (to
acquire, {(pressure, 1, SF Area1)})
g
2
= (to
acquire, {(pressure, 1, DF Area1)})
g
3
= (to
compute, {(velocity, 1, W aterArea1)})
g
4
= (to
compute, {(level, 1, W aterArea1)})
3
these goals are not concepts
ICINCO 2005 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
14

g
5
= (to send, {(velocity, 1, W aterArea1),
(level, 1, W aterArea1)})
g
6
= (to
receive, {(velocity, 1, ExtEntity),
(level, 1, ExtEntity)})
g
7
= (to
compute, {(level, 2, W aterArea1,
ExtEntity)
g
8
= (to
compute, {(of f set, 1, Gate1)})
g
9
= (to
receive, {(of f set, 1, Gate1)})
g
10
= (to
move, {(position, 1, Gate1)})
A close connection between FCA and mereology
can be established by focusing on their basic topics,
i.e., concept decomposition-aggregation and concept
relationships. FCA helps to build ontologies as a
learning technique (Cimiano et al., 2004) and we
extend this work by specifying the ontology with
a part-of hierarchy. The goal hierarchy is derived
from the subsumption hierarchy of conceptual scales
where the many-level architecture of conceptual
scales (Stumme, 1999) is extended taking into
consideration the mereological nature of the extents.
Higher level scales which relates scales on a higher
level of abstraction provide information about hier-
archy. Considering the atomic goals, the compound
goals corresponding to the user intents, the ontolog-
ical nature of the extents (i.e., the physical entities)
and some basic assumptions, one can automatically
produce the relevant instrument functional context.
This context is required to produce the final concept
lattice from which the functional mereology will be
extracted.
As suggested in (Stumme, 1999), the set of sub-goals
is extended with hierarchical conceptual scales such
as the intent includes atomic and compound goals
and the ICS scale (highest level). Higher level
scales define a partially ordered set. The formal
context is filled in a two-stages process. Then, we
derive some rules from the structural mereology S
which concerns the physical entities. To overcome
difficulties about the conceptual equivalence between
sets and mereological individuals, we make the
assumption that a mereological structure can be
reproduced within sets provided we exclude the
empty set. Therefore, a set can be seen as an abstract
individual which represents a class
4
. The part-of
relation can be described as a conceptual scale which
holds between the objects (i.e., extensions) related to
the mereological individuals. The context considers
goal achievement predicates as formal objects, goals
and compound goals as formal attributes. First, the
sub-context between basic goals is derived from
qualitative reasoning on PC tuples within each
physical (or control) equation. Then this sub-context
is extended with conceptual scales corresponding to
goal requests specified by the user. For the hydraulic
system for example, we plan three services with the
4
A class is simply one or more individuals
respective goals:
G
1
= (to
measure, {(speed, 1, W aterArea1),
(level, 1, W aterArea1)})
G
2
= (to
control, {(speed, 1, W aterArea1)})
G
3
= (to
manuallyM ove, {(position, 1, Gate1)})
Then, the concept lattice is transformed in a partial
order by some elementary rules. First, for each node
the concept is labelled with the intent of the lattice
node (Cimiano et al., 2003). In a second step, over-
laps are highlighted and the previous ordering is re-
duced based on simplification rules (Dapoigny et al.,
2005). In a third step, we reduce the labelling (Ganter
and Wille, 1999), providing that each intent is entered
once in the lattice. Finally, the bottom element is re-
moved. These rules applied on the raw lattice (fig3)
result in the goal hierarchy of fig4.
Figure 3: The goal lattice.
5 BEHAVIOR REPRESENTATION
While the EC supports deductive, inductive and ab-
ductive reasoning, the latter is of particular interest for
our purpose. Given an ontological description based
on possible causal behaviors, dynamical constraints
can be translated in EC axioms. The EC axioms pro-
vide a partial temporal order from ontologies inferred
with mereological logic from user-defined goals and
SP pairs. Moreover, the abductive implementation of
the EC is proved to be sound and complete (Russo
et al., 2001). To solve the frame problem, formulae
are derived from the circumscription of the EC repre-
sentation.
DERIVING BEHAVIOR FROM GOAL STRUCTURE FOR THE INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF PHYSICAL
SYSTEMS
15
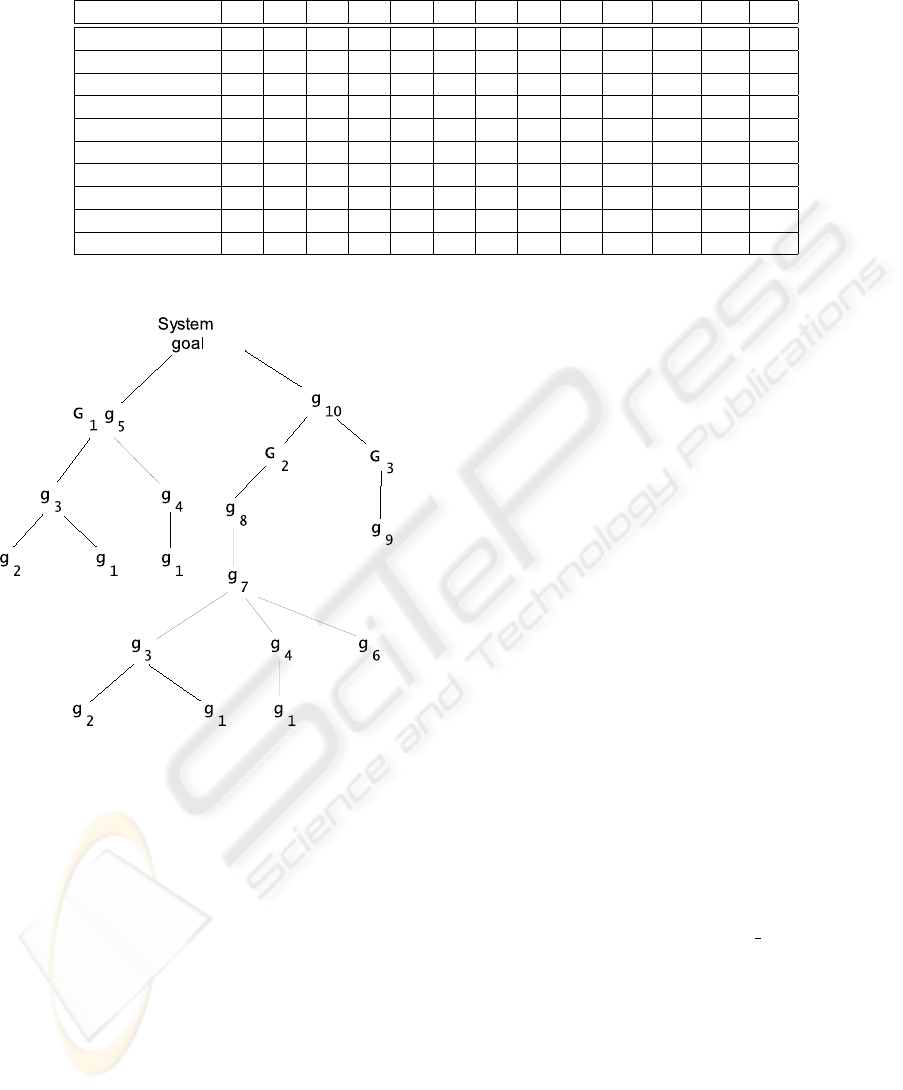
Table 1: Functional context for the open-channel irrigation canal
F g
1
g
2
g
3
g
4
g
5
g
6
g
7
g
8
g
9
g
10
G
1
G
2
G
3
Achieved(g
1
) x x x x x x x x x
Achieved(g
2
) x x x x x x x x
Achieved(g
3
) x x x x x x x
Achieved(g
4
) x x x x x x x
Achieved(g
5
) x x
Achieved(g
6
) x x x x x
Achieved(g
7
) x x x x
Achieved(g
8
) x x x
Achieved(g
9
) x x x
Achieved(g
10
) x x x
Figure 4: The goal part-of hierarchy.
Definition 5 Let G be a goal, let Σ be a domain de-
scription, let ∆
0
be an initial situation, let Ω be a
conjunction of a pair of uniqueness-of-names axioms
for the actions (goal) and fluents (Achieved(goal))
mentioned in Σ, and let Ψ be a finite conjunction of
state constraints. A plan for G is a narrative ∆ such
that,
CIRC[Σ; Initiates, T erminates, Releases] ∧
CIRC[∆
0
∧ ∆; Happens] ∧ Ψ ∧ EC ∧ Ω |= G (3)
In this work, we use the version presented in (Shana-
han, 1997) which consists in a set of time points, a
set of time-variant properties (i.e., fluents) and a set
of event types. Each event type is in fact an action
type which at least requires an action verb, therefore
we associate the extended actions (EA) to each
operational goals (i.e., the triple action verb, physical
role and physical entity). Under the assumption
where a unique computing function is related to a
single goal, domain equations are simple. For more
complex situations, several computing functions
(the actions of EC) can be related to a single goal
provided that a set of fluents (pre-conditions) selects
the relevant association in a given situation. The
circumscriptive condition is consistent if the domain
description does not allow a fluent to be both initiated
and terminated at the same time. EA in the event
calculus are considered as first class objects which
can appear as predicates arguments. The conjunction
of Initiate, T erminates and Releases formulae
describe the effects of EA and correspond to the
domain description. The finite conjunction of state
constraints Ψ expresses indirect effects of potential
actions. These constraints are available implicitly
through the goal mereology since its description is
deduced from qualitative equations where a complex
goal achievement requires physical constraints to
be satisfied. Mereological individuals from a given
level and their adjacent lower ones give rise to a
morphism between P art − of relations and state
constraints. From this assumption, state equations
expressing physical and computational causality can
be derived in event calculus (constraints on what
combinations of fluents may hold in the same time).
The uniqueness of EA names, i.e. to
Achieve(goal)
and fluents names, i.e. Achieved(goal) is a logical
consequence of the uniqueness of goal description
in the mereological model. Taking the example of
the complex goal G
2
, state equations are defined as
follows:
HoldsAt(g10, T ) ← HoldsAt(g8, T ).
HoldsAt(g8, T ) ← HoldsAt(g7, T ).
HoldsAt(g7, T ) ← HoldsAt(g3, T ),
HoldsAt(g4, T ), HoldsAt(g6, T ).
HoldsAt(g4, T ) ← HoldsAt(g1, T ).
ICINCO 2005 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
16

HoldsAt(g3, T ) ← HoldsAt(g2, T ),
HoldsAt(g1, T ).
together with domain equations:
Initiates(achieved(g8), g8, T ) ← HoldsAt(g7, T ).
Initiates(achieved(g7), g7, T ) ← HoldsAt(g3, T ),
HoldsAt(g4, T ), HoldsAt(g6, T ).
Initiates(achieved(g4), g4, T ) ← HoldsAt(g1, T )].
Initiates(achieved(g3), g3, T ) ← HoldsAt(g2, T ),
HoldsAt(g1, T )].
Initiates(achieved(g2), g2, T ).
Initiates(achieved(g1), g1, T ).
Initiates(achieved(g6), g6, T ).
Applying abductive logic for theorem proving, we
get the plan ∆:
Happens(achieved(g6), t7, t7),
Happens(achieved(g4), t6, t6),
Happens(achieved(g1), t5, t5),
Happens(achieved(g2), t4, t4),
Happens(achieved(g3), t3, t3),
Happens(achieved(g7), t2, t2),
Happens(achieved(g8), t1, t1).
before(t7, t2), bef ore(t5, t6), before(t6, t2),
before(t5, t3), bef ore(t4, t3), before(t3, t2),
before(t2, t1), bef ore(t1, t).
Figure 5: The temporal hierarchy.
This plan is sketched at figure 5. Initially an empty
plan is presented with a goal G in the form of a
HoldAt formulae. The resulting plan must respect
the causal hierarchy obtained in section 2.
6 RELATED WORK
Goal modelling is obviously investigated in require-
ments engineering. Modelling goals for engineering
processes is a complex task. In (Rolland et al., 1998)
goals are represented by verbs with parameters, each
of them playing a special role such as target entities
affected by the goal, resources needed for the goal
achievement, etc. Centered on the KAOS method,
(El-Maddah and Maibaum, 2003) used conditional
assignments based on the application’s variables in
goal-oriented process control systems design with the
B method. A tool translates the goal model into B
specifications where the behavior is state-based. In
this method no reasoning is performed at the system
level due to the lack of semantic content for variables.
For more general frameworks, (Giorgini et al., 2002)
describes a logic of goals based on their relationship
types, but goals are only represented with a label, and
the reasoning is elicited from their relations only.
7 CONCLUSION
This work is part of an ongoing attempt to develop
an automaton able to derive executable program for
the intelligent control of physical systems. From a
user-defined description of the context (i.e., the struc-
tural description of the physical system together with
the control system which operates on it) and an ini-
tial goal request, the system architecture consists of
two layered control modules to provide a response
to this request. The first layer extracts a hierarchical
functional model centered on the goal concept. This
model is mapped through fluents on the hierarchy of
action types. The second layer constructs a partial-
order temporal hierarchy relating grounded actions.
Unlike classical AND/OR goal decomposition which
does not clearly distinguish dependency types be-
tween different abstraction levels, the part-of hierar-
chy is able to extract potential relevant dependencies
(such as goal g
10
in 4). The major benefits of Arti-
ficial Intelligence in this context turns out to reduce
the design process, to generate automatic sound plan-
ning and to allow dynamic control at runtime through
a reasoning process between distributed intelligent
nodes. This last topic (under development) is cen-
tered on information flow methodology and concep-
tual structures.
REFERENCES
(1996). Open Distributed Processing - Basic Reference
model - Part 2: Foundations. ISO/IEC and ITU-T.
Abadi, M. and Lamport, L. (1993). Composing specifica-
tions. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages
and Systems, 15(1):73–132.
Barringer, H. (1986). Using temporal logic in the compo-
sitional specification of concurrent systems. Techni-
cal Report UMCS-86-10-1, Dpt of Computer Science
Univ. of Manchester.
Barwise, J. and Seligman, J. (1997). Information flow - The
logic of distributed systems, volume 44 of Cambridge
DERIVING BEHAVIOR FROM GOAL STRUCTURE FOR THE INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF PHYSICAL
SYSTEMS
17

Tracts in Theoretical Computer Science. Cambridge
University Press.
Chen, X. and de Giacomo, G. (1999). Reasoning about non-
deterministic and concurrent actions: a process alge-
bra approach. Artificial Intelligence, 107:63–98.
Chittaro, L., Guida, G., Tasso, C., and Toppano, E. (1993).
Functional and teleological knowledge in the mul-
timodelling approach for reasoning about physical
sytems: a case study in diagnosis. IEEE Transactions
on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 23(6):1718–1751.
Cimiano, P., Hotho, A., Stumme, G., and Tane, J. (2004).
Conceptual knowledge processing with formal con-
cept analysis and ontologies. In ICFCA, number 2961
in LNAI, pages 189–207. Springer.
Cimiano, P., Staab, S., and Tane, J. (2003). Deriving con-
cept hierarchies from text by smooth formal concept
analysis. In Procs. of the GI Workshop LLWA.
Dapoigny, R., Barlatier, P., Benoit, E., and Foulloy, L.
(2005). Formal goal generation for intelligent con-
trol systems. In 18th International Conference on In-
dustrial & Engineering Applications of Artificial In-
telligence & Expert Systems, number 3533 in LNCS.
Springer.
de Coste, D. (1994). Goal-directed qualitative reasoning
with partial states. Technical Report 57, Institute
for the Learning Sciences, Northwestern University
(Evanston).
de Kleer, J. and Brown, J. (1984). A qualitative physics
based on confluences. Artificial Intelligence, 24:7–83.
Dooley, K., Skilton, P., and Anderson, J. (1998). Process
knowledge bases: Facilitating reasoning through
cause and effect thinking. Human Systems Manage-
ment, 17(4):281–298.
El-Maddah, I. and Maibaum, T. (2003). Goal-oriented re-
quirements analysis for process control systems de-
sign. In Procs. of the International Conference on for-
mal methods and models for co-design, pages 45–46.
IEEE Comp. Society Press.
et al., Y. U. (1996). Supporting conceptual design based on
the function-behavior-state modeler. Artificial Intel-
ligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manu-
facturing, 10(4):275–288.
Falkenhainer, B. and Forbus, K. (1991). Compositional
modeling: finding the right model for the job. Arti-
ficial Intelligence, 51:95–143.
Forbus, K. (1984). Qualitative process theory. Artificial
Intelligence, 24:85–168.
Freksa, C. (1992). Temporal reasoning based on semi-
intervals. Artificial Intelligence, 54:199–227.
Galton, A. (1987). Temporal logics and their applications.
Academic Press.
Galton, A. and Augusto, J. (2000). Two approaches to event
definition. In Springer, number 2453 in LNCS, pages
547–556.
Ganter, B. and Wille, R. (1999). Formal concept analysis -
mathematical foundations. Springer.
Giorgini, P., Nicchiarelli, E., Mylopoulos, J., and Sebas-
tiani, R. (2002). Reasoning with goal models. In
Procs. of the int. conf. on Conceptual Modeling, num-
ber 2503 in LNCS, pages 167–181. Springer.
Gruber, G. and Olsen, G. (1994). An ontology for engi-
neering mathematics. In Doyle, J., Torasso, P., and
Sandewall, E., editors, Fourth International Confer-
ence on Principles of Knowledge Representation and
Reasoning, pages 258–269. Morgan Kaufmann.
Hertzberg, J. and Thiebaux, S. (1994). Turning an action
formalism into a planner: a case study. Journal of
Logic and Computation, 4:617–654.
Kent, R. (2003). Distributed conceptual structures. In in
Procs. of the 6th Int. Workshop on Relational Meth-
ods in Computer Science, number 2561 in LNCS.
Springer.
Kitamura, Y., Sano, T., Namba, K., and Mizoguchi, R.
(2002). A functional concept ontology and its ap-
plication to automatic identification of functional
structures. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering,
16(2):145–163.
Kmenta, S., Fitch, P., and Ishii, K. (1999). Advanced fail-
ure modes and effects anlysis of complex processes.
In Procs. of the ASME Design Engineering Technical
Conferences, Las Vegas (NE).
Larsson, J. (1996). Diagnosis based on explicit means-end
models. Artificial Intelligence, 80:29–93.
Lifschitz, V. (1993). A theory of actions. In Procs. of the
tenth International Joint Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, pages 432–437. Morgan Kaufmann.
Lind, M. (1994). Modeling goals and functions of complex
industrial plant. Journal of Applied Artificial Intelli-
gence, 8:259–283.
Ma, J. and Knight, B. (1996). A reified temporal logic. The
Computer Journal, 39(9):800–807.
Manna, Z. and Pnueli, A. (1992). The temporal logic
of reactive and concurrent systems (Specification).
Springer-Verlag.
McDermott, D. (1982). A temporal logic for reasoning
about processes and plans. Cognitive Science, 6:101–
155.
Rolland, C., Souveyet, C., and Achour, C. B. (1998). Guid-
ing goal modelling using scenarios. IEEE Transac-
tions on software engineering, pages 1055–1071.
Russo, A., Miller, R., Nuseibeh, B., and Kramer, J. (2001).
An abductive approach for analysing event-based re-
quirements specifications. Technical Report DoC-
2001/7, Dpt of Computing Imperial College, London.
Shanahan, M. (1997). Solving the frame problem: A math-
ematical investigation of the common sense law of in-
ertia. MIT Press.
Stumme, G. (1999). Hierarchies of conceptual scales.
In Procs. of the Workshop on Knowledge Acquisi-
tion, Modeling and Managenent (KAW’99), volume 2,
pages 78–95.
ICINCO 2005 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
18
