
REMOTE MONITORING DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
The new generation of control systems
Víctor Ruiz Valera, Mario de la Cruz Ortiz, Rafael Herradón Díez and Florentino Jiménez Muñoz
Departamento de Ingeniería Audiovisual y Comunicaciones (DIAC), Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain
Keywords: Internet services, Distributed systems, Parameters Control, Data acquisition systems.
Abstract: Nowadays, it is increasingly necessary and interesting to measure
and control the levels of some parameters.
This research and project work has been developed with the aim of creating a data acquisition and
monitoring distributed system that allows the users to monitor and control easily, powerfully and flexibly
any parameter interesting enough to be studied for later monitoring in real time. At the same time, it is also
intended to make the system accessible to the general public and citizens, by using the most implanted and
widespread network: Internet and the TCP/IP networks. As a result we present an application offering a
“measurement transport layer” providing several services that will work with any kind of parameter.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, it is more and more necessary and
interesting to measure and control the levels of some
parameters. These measurements can be used in two
ways. On the one hand, we consider real time
measurement where the most interesting part is to
control discrete time value of the parameter. On the
other hand, we deal with the storage of all these
measurements in databases with the purpose to make
later analysis about the parameter time evolution.
Our research and projects have been developed
with the
purpose of creating a data acquisition and
monitoring distributed system that allows the users
in an easy, powerful and flexible way, to monitor
and control any parameter that may be interesting to
study for monitoring in real time and later analysis.
At the same time, it is also intended to be able to
make the system accessible to the general public and
citizens, by using the most implanted and
widespread network: Internet and the TCP/IP
networks.
Due to the growing proliferation and installation
o
f systems that work with electromagnetic
emissions, we decided to apply the system to
electromagnetic fields measurements because lately
the society is very worried about it. This concern is
owing partly to the ignorance of the consequences
that radiant systems and its emissions can have in
our health and on the other hand, to the necessities
of controlling the emissions in the electromagnetic
spectrum and their influence or interference with
other systems.
The system is a distributed application based on
sev
eral main servers providing support to the
measurement equipment located in the monitored
area, and to the users that are going to view and
request the information and data captured with the
measurement equipment. These measurement
equipments can be static or mobile travelling around
the zones that we want to monitor. The monitoring
application will allow to know in real time the
measurement of the electromagnetic field and
spectrum at a concrete instant and place. In addition,
the application will also show a series of statistics
and possible alarms when the measurement levels
overcome certain thresholds. And all these features
work on a web environment, and are accessible and
usable from a computer with TCP connectivity.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The basic idea of the system is to have distributed
measurement equipment that capture measurements
and send them to data centres continually through a
communication channel, typically Internet. The
distributed measurement equipment can be systems
specifically designed to do capturing and sending
functions, or can be commercial measurement
equipment connected to a computer containing
specific software to do control and measurement
sending tasks. Obviously there must be a channel
264
Ruiz Valera V., de la Cruz Ortiz M., Herradón Díez R. and Jiménez Muñoz F. (2005).
REMOTE MONITORING DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS - The new generation of control systems.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - Signal Processing, Systems Modeling and
Control, pages 264-269
DOI: 10.5220/0001177302640269
Copyright
c
SciTePress

from the each piece of distributed measurement
equipment and the system data centre so that they
are communicated.
The measurement equipment locations can be
static or mobile. In case the equipment is mobile,
they can have a coupled GPS system that will allow
us to know their position in each instant. So that, in
the server each measurement will be stored with the
time and position in which it was captured.
The system core is the database, which stores
and registers all the information; and the server, that
coordinates and manages the accesses to the
database, like an access point through which all the
other elements are interconnected. The server
handles the connections and requests from
measurement equipments, users and administrators.
To be able to assist all the tasks correctly, the Server
is composed of several subservers for each function
that dialogue to each other to coordinate their
actions.
The users access to the system through a web
interface in any browser. They can visualize the
available measurement equipment, their
measurements values, their position on a digital
map, to monitor certain areas, their temporal and
position evolution, statistical data, etc; and
everything in real time, thanks the web embedded
Java applications or applets, with a graphic interface
and forms.
The Administrator Users can also access to the
system to configure and manage the Server, the
measurement equipments, etc, from any place
through web interface with embedded applications
and forms.
The interconnection between each one of the
blocks (clients, servers and database) is over
TCP/IP. The rest of the elements are located on this
transport layer and they communicate to each other
and request services to the servers through different
protocols. The final purpose of the system is to
create a layer that allows us to exchange any kind of
measurement, as well as to store and consult them.
2.1 Election of technologies for
system implementation
Possibly, the most appropriate programming
language for the development of this system is Java.
Java has some important characteristics that make it
especially attractive: strongly oriented to intra and
inter network applications, multi-platform, client-
server applications, and distributed applications in
LANs and Internet, besides providing enough
reliability to the applications.
For information exchange between client and
server processes, the RMI (Remote Method
Invocation) package has been used, and for access
to the information stored in the database the JDBC
(Java DataBase Connectivity) package is used; and
finally, for user-application interaction it is needed a
tool to create user's graphic interfaces. This tool is
the SWING package, which allows GUIs
development (windows, buttons, labels, dialogs,
menus, images, etc).
2.2 System Architecture
2.2.1 Introduction
The designed system is a distributed application
based on the client-server model and implemented in
Java programming language, following distributed
objects techniques. The communication between
distributed objects is over TCP/IP protocols. In
Figure 2 you can see the global architectural view of
the system.
Fi
g
ure 1: S
y
stem Descri
p
tion.
REMOTE MONITORING DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS - The new generation of control systems
265

Figure 2: System Architecture
2.2.2 The server and the database, brains of
system
In our system, data are the most important thing,
because the main function of the system is data
collecting and data offering. So we decided to use a
relational database manager system software that
supports a huge volume of information. MySQL
provides a robust solution to users with powerful
multi-user tools, interface access to the data
normalized through (Structured Query Language)
SQL language, multi-threaded. It is a very quick,
robust and easy to use language, apart from being
open source.
As important as the database, it is the Java
Server, in charge of controlling all the interactions
with the database. The Server has been divided into
three small servers, with the purpose to give service
and assist to each one of the client applications of
each one functionality area.
• Measurements Server: it gives support to the
remote measurement equipment of the Client
Application in the Measurement Equipment
Control Area. The server subscribes the
measurement equipment in the database
(indicating all their characteristic data), stores the
measurements, alarms and configuration,
unsubscribes the equipment, indicates the state in
which the equipment is, etc. Also, if there are
errors in the connections with measurement
equipment, the server is able to re-establish the
connections automatically when the network
service will be up again.
• Users Server: gives support to the Remote
Measurement Equipment Monitoring Applet on
the web client in the User Area. The server will
monitor the geographical situation of the
equipment and the measurements that it is
capturing in real time, wherever it is. It requests
to the database to obtain a list with the current
data and measurements of each one of the
connected meters, in a periodic and constant
interval, to view the measurement in almost real
time.
• Administrators Server: gives support to
the Remote Control Applet on the web client in
the Administration Area, where an authorized
administrator can control remote equipment
connected to the Server, and manage the system.
2.2.3 Client Applications
The access to the server can be different depending
on which client application is accessing to the
server. There are three different working planes or
functional areas:
ICINCO 2005 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
266

• Measurement Equipment Control Area:
it is a Java application that allows to install and
configure a measurement equipment, and
subscribe it on the system, control the equipment,
establish measuring parameters such as time
length, capture and sending data interval,
measurement type, equipment position, etc. Also
it allows visualising the measurements captured,
and the alarms indicators. It will be connected,
through Internet, to the Measurement Servers that
you indicate, being able to be connected and to be
sending data simultaneously to several servers.
Figure 3: Served Pages Schema
• Users Area: offers consulting services to
the users, like real time monitoring applet, or
some forms to request statistical graphics of the
stored information. The first service is an applet
composed of a panel for the geographical
localization of the equipment and another panel
for the real time monitoring of the measurements
captured by the located meters. This application
is connected the Users Server with an RMI
connection to upgrade the data in almost real
time. With the consultation forms, the user can
curse petitions to the Statistical Graphic Server
about the stored information. The return result
will be html pages with the data in graphical
format, containing the measurements obtained by
the selected meter during the specified time
period.
• Administration Area: it offers
administration services to authorized
administrators users. In this area we can make
remote control of the measurement equipment
that is subscribed in the system and of other
managing tasks like the database administration,
etc. For Equipment Remote Control it offers an
applet that is connected with the Administrators
Server through a RMI connection to obtain the
list of current subscribed equipment. In this way,
the configuration parameters can be viewed and
remotely controlled, without needing anybody in
the place where the equipment is located.
2.2.4 Other elements
To give support to all the elements of the
architecture, it is necessary some other elements like
web servers, Apache in this case, dynamic pages
scripting technologies, for example PHP, and
application servers or servlet engines like it can be
Apache Tomcat.
2.3 System Capabilities
2.3.1 Measurement Equipment Access
Capabilities
In the start menu, you can add the measurement
equipment to the system and configure them
correctly. For each piece of equipment we can define
if the equipment is static or mobile, position (long,
lat, alt and location description or GPS option),
connection port, measurement parameters like
interval between samples (s), measurement period,
type of parameter (the value in the discrete instant or
the average along the interval) and the server list
where we want to connect and the measurements
that will be sent.
Fi
g
ure 4: Confi
g
and Monitor E
q
ui
p
ment Panels
For each added equipment, a panel appears with
a tab and the tools to control the equipment locally.
In the panel there are some bars with the values of
REMOTE MONITORING DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS - The new generation of control systems
267
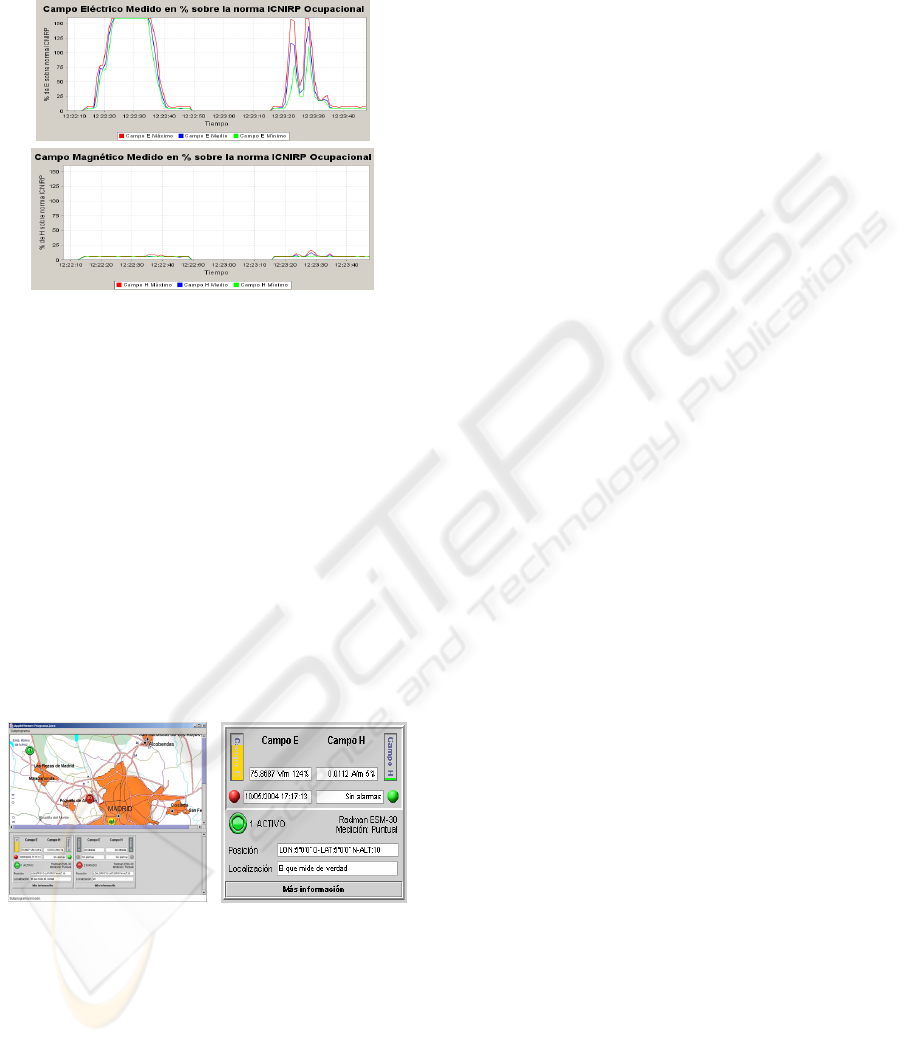
the measurements in real time (E and H), alarm
indicators (registered value, date, time), state of
connections with servers, the interval, and real time
(line) graphics with the E and H representation.
We can change and update all the explained
parameters and of course, we can delete equipment
from the system.
2.3.2 User Access Capabilities
The user access provides these capabilities:
• Real Time Monitoring: It is the embedded
application in a web page dedicated to real time
monitoring of the measurements that the
distributed equipment in different areas are
sending to the server. This applet is continuously
requesting to the Users Server the last version of
the list with the equipment and its measurements,
to be represented on the screen. At top there is a
map where the applet represented the
geographical information of the equipment, and
at bottom there are some panels with the
measurement values in real time, meters bars,
alarms indicators and other information.
• DB Information Request: using web forms, a
user can request and extract information from
database. For example, the equipments list, data
historical, alarms historical and much more.
• Statistical Graphics Generator: using web
forms we can obtain all the information but in a
statistical graphic format, with any parameter and
in the range of specified time.
2.3.3 Administrator Access Capabilities
The administrator can access to the system control
options but must be previously authenticated with
login and password:
• Remote Control: it is an embedded applet
on a web page that permits to make remote
control on any equipment from any place. This
applet is refreshing continuously the
measurement equipments list through a RMI
connection with the Administrators Server, which
obtains the information from the database.
Figure 5: Real Time E and H measurements, in
Graphical Format
• Database administration: the
administrator user has permission to manage the
database with tools like PHPMyAdmin, a web
interface database managing system.
3 CONCLUSIONS AND
POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF
SYSTEM
At first, about electromagnetic emissions theme, we
cannot affirm that are dangerous for human (when
the levels are down of limits allowed by laws)
because doesn’t exist evidences about it. But we
cannot neither say that are innocuous because there
are not enough studies about it and we don’t know
their long time effects. So it is recommended to
protect sensible zones like schools, hospitals, etc.
One of the final objects of project is to make a
“measurement transport layer” providing several
services that will work with any kind of parameter,
and can be used to create a lot of different
measurement system with the same philosophy.
Some possible cases to use this kind of systems
are:
• Investigation groups that need to work from
different places in the world, but they need
to work with the same data simultaneously.
For example, a scientist in Barcelona that
needs other opinion about some
measurements, but the other person is in
Figure 6: Real Time Monitoring Application and
panel detail
ICINCO 2005 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
268

Sidney. Both can view in their browsers the
same data at the same time.
• Creation of data repositories to make later
analysis. For example, to work with
parameters that currently we don’t know
enough, and to have a lot of data to research
later if these measurement levels are related
with others events or facts.
• The control of certain parameters that are
important to the general public and citizens,
like for example contamination parameters,
or traffic report data. For example, it is
possible to use the system with “cars
counters” and offer to the citizens a map
with traffic congestion information in real
time.
There are a lot of more possible applications for
this kind of systems, and the only limit is your
imagination.
REFERENCES
George Coulouris, Jean Dollimore and Tim Kindberg.
Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design. Ed.
Adison Wesley.
A. I. Hernández, F. Bora, G. Villegas, G. Passariello, and
G. Carrault. Real-time ECG transmission via internet
for nonclinical applications. IEEE Trans. Inform.
Technol. Biomed., vol 5, nº 3, pp. 253-257, Sept. 2001
Cay S. Horstmann / Gary Cornell. Core Java 2, Advanced
Features Vol II. Ed Prentice Hall.
Agustín Froufe. Java 2: Manual de usuario y tutorial.
Editorial Ra-Ma.
ICNIRP. 1997. Guidelines for limiting exposure to time
carrying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields
(up to 300 GHz).
BOE Num. 234. Real Decreto 1066/2001 de 28 de
Septiembre. Pages: 36217 – 36227.
BOE Num. 11. Pages: 1528 – 1536. Correction: BOE
Num. 117/2002. Orden Ministerial: ORDEN
CTE/23/2002, de 11 de Enero.
Diario Oficial de las Comunidades Europeas.
“CONSEJO: Recomendaciones del Consejo de 12 de
julio de 1999, relativa a la exposición del público en
general a campos electromagnéticos (0 Hz. a 300
GHz.). [1996/519/CE]”. L. 199/59 hasta L.199/70:
Recommendation L. 265/42: Correction.
REMOTE MONITORING DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS - The new generation of control systems
269
