
PRECISE DEAD-RECKONING FOR MOBILE ROBOTS USING
MULTIPLE OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS
Daisuke SEKIMORI
Akashi National College of Technology
Akashi, Hyogo 674-8501, Japan
Fumio MIYAZAKI
Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University
Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531, Japan
Keywords:
dead-reckoning, mobile robot, optical mouse sensor.
Abstract:
In this paper, in order to develop an accurate localization for mobile robots, we propose a dead-reckoning
system based on increments of the robot movements read directly from the floor using optical mouse sensors.
The movements of two axes are measurable with an optical mouse sensor. Therefore, in order to calculate a
robot’s deviation of position and orientation, it is necessary to attach two optical mouse sensors in the robot.
However, it is also assumed that a sensor cannot read the movements correctly due to the condition of the
floor, the shaking of the robot, etc. To solve this problem, we arrange multiple optical mouse sensors around
the robot and compare sensor values. By selecting reliable sensor values, accurate dead-reckoning is realized.
Finally, we verify the effectiveness of this algorithm through several experiments with an actual robot.
1 INTRODUCTION
For a mobile robot to move around autonomously, it
is necessary for it to possess the ability to estimate
its position and orientation. The localization of mo-
bile robots is roughly divided into those using internal
sensors and those using external sensors. The method
using internal sensors is known as dead-reckoning,
mainly, and estimates position by measuring and ac-
cumulating the rotation of the wheel with the rotary
encoder, etc. Dead-reckoning is a convenient estimat-
ing method using only internal sensors. However, the
accuracy of estimation decreases as the movement be-
comes longer since the errors of the transformations
and wheel slippage accumulate. On the other hand,
the method using external sensors estimates the posi-
tion by measuring positions of a landmark in the envi-
ronment with a vision sensor or a range sensor. Some
error is always caused by resolution or the noise of
the sensor; accumulated errors are not caused as such
by dead-reckoning. Therefore, because both meth-
ods have their respective merits and demerits, the two
methods are often used together (Cox, 1989) (Watan-
abe and Yuta, 1990) (Chenavier and Crowley, 1992).
In the case of the estimation method using both
dead-reckoning and an external sensor, it is advanta-
geous to improve the accuracy of dead-reckoning. As
for the reason, in general, many of the external sen-
sors are expensive, and processing is very complex.
Moreover, estimation methods using external sensors
need to have a previously installed landmark in the
environment. By improving the accuracy of dead-
reckoning and reducing the part that depends on the
method using the external sensor, the hardware and
software costs of the robot can be decreased, and the
time needed to install a landmark can be omitted.
In this paper, in order to develop an accurate
localizaion for mobile robots, we propose a dead-
reckoning system based on increments of the robot
movements read directly from the floor using optical
mouse sensors (Fujimoto et al., 2002). The move-
ments of two axes are measurable with an optical
mouse sensor. Therefore, in order to calculate a ro-
bot’s deviation of position and orientation, it is nec-
essary to attach two optical mouse sensors in the ro-
bot (Tobe et al., 2004) (Singh and Waldron, 2004)
(Cooney et al., 2004). However, it is also expected
that a sensor cannot read the movements correctly due
to the condition of the floor, the shaking of the ro-
bot, etc. To solve this problem, we arrange multiple
optical mouse sensors around the robot and compare
sensor values. By selecting reliable sensor values, ac-
curate dead-reckoning is achieved.
In section 2, we explain the optical mouse sen-
sor. In section 3, we describe the algorithm of dead-
reckoning based on optical mouse sensors. Finally, in
48
SEKIMORI D. and MIYAZAKI F. (2005).
PRECISE DEAD-RECKONING FOR MOBILE ROBOTS USING MULTIPLE OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS.
In Proceedings of the Second Inter national Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - Robotics and Automation, pages 48-54
DOI: 10.5220/0001180300480054
Copyright
c
SciTePress
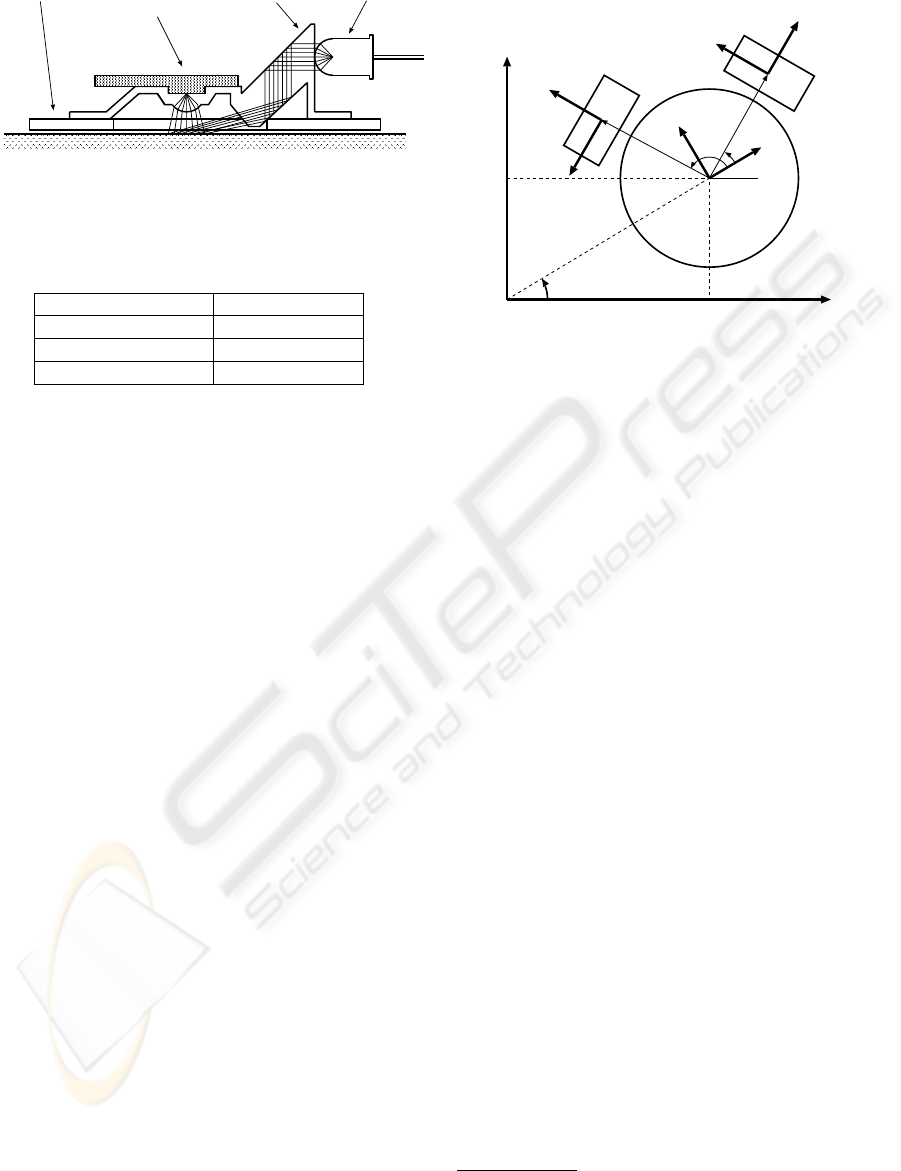
LEDlens/light pipeoptical mouse sensor
(inc. image sensor)
base plate
floor
Figure 1: Structure of optical mouse sensor
Table 1: Specifications of the optical mouse sensor (Agilent
Technologies, HDNS-2051)
resolution 800 counts/inch
max speed 14 inch/sec
scanning frequency 2300 Hz
power supply 5 volts
section 4, we verify the effectiveness of this algorithm
through several experiments with an actual robot.
2 OPTICAL MOUSE SENSOR
An optical mouse sensor is built into an optical mouse
for personal computers, and measures non-contact
movements. It is maintenance free and not influenced
by floor friction.
The principle of the optical mouse sensor is that
the installed small image sensor reads the change in
the image information on the floor and the optical
mouse sensor measures movement. The structure of
the optical mouse sensor is shown in Fig. 1. An op-
tical mouse sensor takes a floor picture irradiated by
a LED through a lens, with the image sensor located
on the sensor undersurface. Changes in the pictures
taken are processed within the sensor and transformed
into distance information. Finally the sensor outputs
a two phase pulse from the ports. The main specifica-
tions of the optical mouse sensor(Agilent Technolo-
gies, HDNS-2051) used in our research are shown in
Table 1.
3 DEAD-RECKONING BASED ON
OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS
This section describes the basic equation for dead-
reckoning based on optical mouse sensors and the
comparison method for increasing the reliability of
mouse sensor values. In this method, the mobility
range of the robot is limited to the floor whereby the
optical mouse sensor can initially measure the move-
ment.
y
x
ξ
i
η i
φ
i
ξ j
η j
dj
robot
optical mouse
sensor mi
optical mouse
sensor mj
X
Y
O
w
X
Y
Θ
φj
Oj
Oi
O
di
Figure 2: Configuration of robot and optical mouse sensors
3.1 Basic Equation
Movement of the direction of two axes is measurable
by one optical mouse sensor. Therefore, movement
(translation and rotation) of the robot which moves
through a plane is calculable by using two optical
mouse sensors.
Firstly, a robot and two optical mouse sensors
m
i
, m
j
are arranged as shown in Fig. 2. The
world coordinate system (O
w
− XY ) is placed on
the floor, the robot coordinate system (O − xy)
is placed on the robot center, and coordinate sys-
tems (O
i
− ξ
i
η
i
), (O
j
− ξ
j
η
j
) are put on the cen-
ter of two optical mouse sensors m
i
, m
j
attached
to the robot. However, axes x
m
i
, x
m
j
of each sen-
sor are located in a radial direction from the ro-
bot center
1
. The positions of each sensor in terms
of the robot coordinate system are expressed by
[d
i
cos φ
i
, d
i
sin φ
i
]
T
, [d
j
cos φ
j
, d
j
sin φ
j
]
T
. The re-
lation movement [∆ξ
i
, ∆η
i
]
T
, [∆ξ
j
, ∆η
j
]
T
measured
by each sensor and movement [∆x, ∆y, ∆θ]
T
of the
robot center is expressed as follows:
Cφ
i
−Sφ
i
Sφ
i
Cφ
i
∆ξ
i
∆η
i
=
∆x
∆y
+ ∆θ
−d
i
Sφ
i
d
i
Cφ
i
(1)
Cφ
j
−Sφ
j
Sφ
j
Cφ
j
∆ξ
j
∆η
j
=
∆x
∆y
+ ∆θ
−d
j
Sφ
j
d
j
Cφ
j
(2)
1
It is our goal to decrease the number of parameters used
for this method, and the basic equation can be derived re-
gardless of ξ
i
, ξ
j
axial direction of each sensor.
PRECISE DEAD-RECKONING FOR MOBILE ROBOTS USING MULTIPLE OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS
49

Here, Sφ
∗
and Cφ
∗
mean sin φ
∗
and cos φ
∗
respec-
tively, and use this notation as follows. Moreover, up-
per formulas are arranged as follows:
Au = a (3)
u = [∆x, ∆y, ∆θ]
T
,
A =
1 0 −d
i
Sφ
i
0 1 d
i
Cφ
i
1 0 −d
j
Sφ
j
0 1 d
j
Cφ
j
,
a =
∆ξ
i
Cφ
i
− ∆η
i
Sφ
i
∆ξ
i
Sφ
i
+ ∆η
i
Cφ
i
∆ξ
j
Cφ
j
− ∆η
j
Sφ
j
∆ξ
j
Sφ
j
+ ∆η
j
Cφ
j
Here, elements of matrix A and vector a are replaced
with A
pq
and a
p
(p = 1, 2, 3, 4; q = 1, 2, 3) respec-
tively. Furthermore, the squared error E
ij
of move-
ments is defined as follows:
E
ij
=
4
X
p=1
(A
p1
∆x + A
p2
∆y + A
p3
∆θ − a
p
)
2
(4)
The movement u = [∆x, ∆y, ∆θ]
T
that has the min-
imum square error E
ij
is determined by using the fol-
lowing equation.
u = A
−
a (5)
Here, matrix A
−
means a pseudo-inverse matrix of
A.
After movement u of the robot can be deter-
mined, dead-reckoning is computed using the follow-
ing equation and robot position [X
t
, Y
t
, Θ
t
]
T
in terms
of the world coordinate system is determined. In ad-
dition, [X
t−1
, Y
t−1
, Θ
t−1
]
T
expresses the position at
a pre-measurement point.
"
X
t
Y
t
Θ
t
#
=
"
X
t−1
+ ∆x CΘ
t−1
− ∆y SΘ
t−1
Y
t−1
+ ∆x SΘ
t−1
+ ∆y CΘ
t−1
Θ
t−1
+ ∆θ
#
(6)
3.2 Comparison of Values of Optical
Mouse Sensors
Robot movements may be incorrectly measured by
the optical mouse sensor due to robot speed, robot
shaking, the condition of the floor, etc. When errors
arise in only one optical mouse sensor between two
optical mouse sensors (since the squared error E
ij
in
(4) will be large), error is detectable by supervising
the value of E
ij
. However, when an error arises in
both of two mouse sensors, there is no corroboration
to which the value of E
ij
becomes large. That is, er-
ror is undetectable when only supervising the value
of E
ij
. Thus, we proposed a method of computing
robot movements by comparison of the optical mouse
sensor values and by selecting reliable sensor values.
The number of optical mouse sensors is N , the
squared errors E
ij
(i = 1 · · · N, j = 1 · · · N(i 6=
j)) of all optical mouse sensor values are calculated.
Then, threshold E
th
of E
ij
is decided, and accuracy
of a measurement value is evaluated by the following
equation.
r
i
=
N
X
j=1
j6=i
δ
ij
, δ
ij
=
1 (E
ij
≤ E
th
)
0 (E
ij
> E
th
)
(7)
Here, r
i
expresses the reliability of optical mouse sen-
sor m
i
. This reliability is computed to each optical
mouse sensor, and optical mouse sensors m
α
, m
β
, · · ·
with high reliability are elected using threshold r
th
.
And the following equation is derived using those val-
ues.
Bu = b (8)
B =
1 0 −d
α
Sφ
α
0 1 d
α
Cφ
α
1 0 −d
β
Sφ
β
0 1 d
β
Cφ
β
: : :
: : :
,
b =
∆ξ
α
Cφ
α
− ∆η
α
Sφ
α
∆ξ
α
Sφ
α
+ ∆η
α
Cφ
α
∆ξ
β
Cφ
β
− ∆η
β
Sφ
β
∆ξ
β
Sφ
β
+ ∆η
β
Cφ
β
:
:
A movement u of the robot is calculated by using the
following equation.
u = B
−
b (9)
In addition, when two or more sets of optical mouse
sensor values with high reliability do not exist, move-
ment of the robot is computed based on wheel rota-
tion.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In order to evaluate our methods, experiments were
executed using our robot. Firstly, we explain the sys-
tem configuration of the robot. After that, we show
the results of self-localization using dead-reckoning
based on optical mouse sensors. Finally, we make one
evaluation of our method by reporting on the results of
the integration of the global camera information and
the dead-reckoning value using the Kalman Filter.
ICINCO 2005 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
50
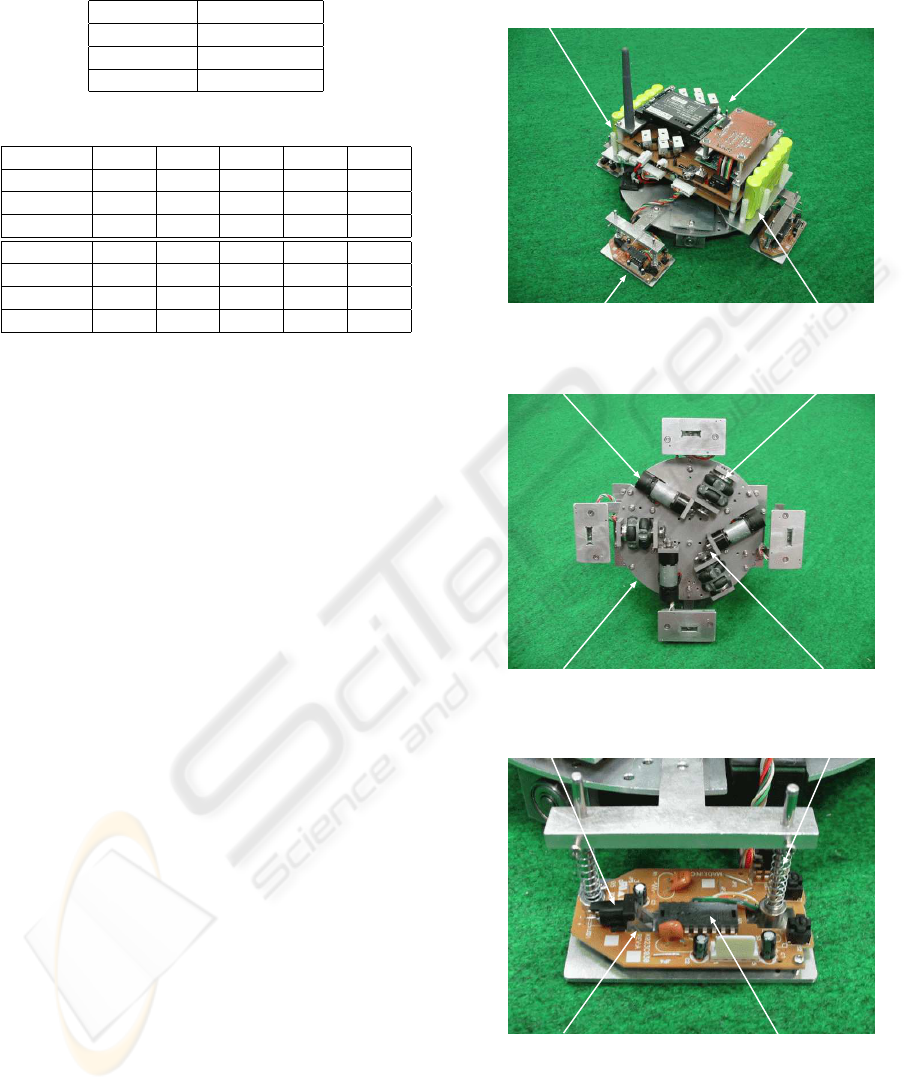
Table 2: Specifications of the mobile robot
height 120 [mm]
width 262 [mm]
weight 2 [kg]
max speed 1000 [mm/s]
Table 3: Planned path cartesian coordinates
1 2 3 4 5
X [mm] 0 500 500 500 500
Y [mm] 0 0 0 500 500
Θ [rad] 0 0 π/2 π/2 0
6 7 8 9 10
X [mm] 1000 1000 1000 1000 1500
Y [mm] 500 500 1000 1000 1000
Θ [rad] 0 π/2 π/2 0 0
4.1 System Configuration
The robot we have been developing is shown in Fig. 3,
and its control flow is shown in Fig. 4. The ro-
bot has an omni-directional mobile mechanism driven
by three omni-directional wheels .Four optical mouse
sensors are attached around the robot. And in or-
der that an optical mouse sensor may stably scan
a floor, the sensor unit is forced onto the floor by
springs. Moreover, the CPU board and control board
are mounted onto the robot. And they control driving
motors and count the pulse from optical mouse sen-
sors. The main specifications of the robot are shown
in Table 2.
4.2 Dead-Reckoning Based on
Optical Mouse Sensors
We used two robot speeds: (a) v=300[mm/s],
ω=1.82[rad/s] and (b) v=500[mm/s], ω=3.03[rad/s] in
the experiments. Speed (a) is slower than the max-
imum measurement speed of the optical mouse sen-
sor(see Table 1), and speed (b) is faster. We deter-
mined speed (b) to be the general maximum speed of
an indoor mobile robot. The motion path of the robot
is shown in Table 3. The floor is covered with the felt
mat used in the RoboCup small size league competi-
tions . Moreover, in order to measure a robot’s real
trajectory, a camera is installed on the ceiling.
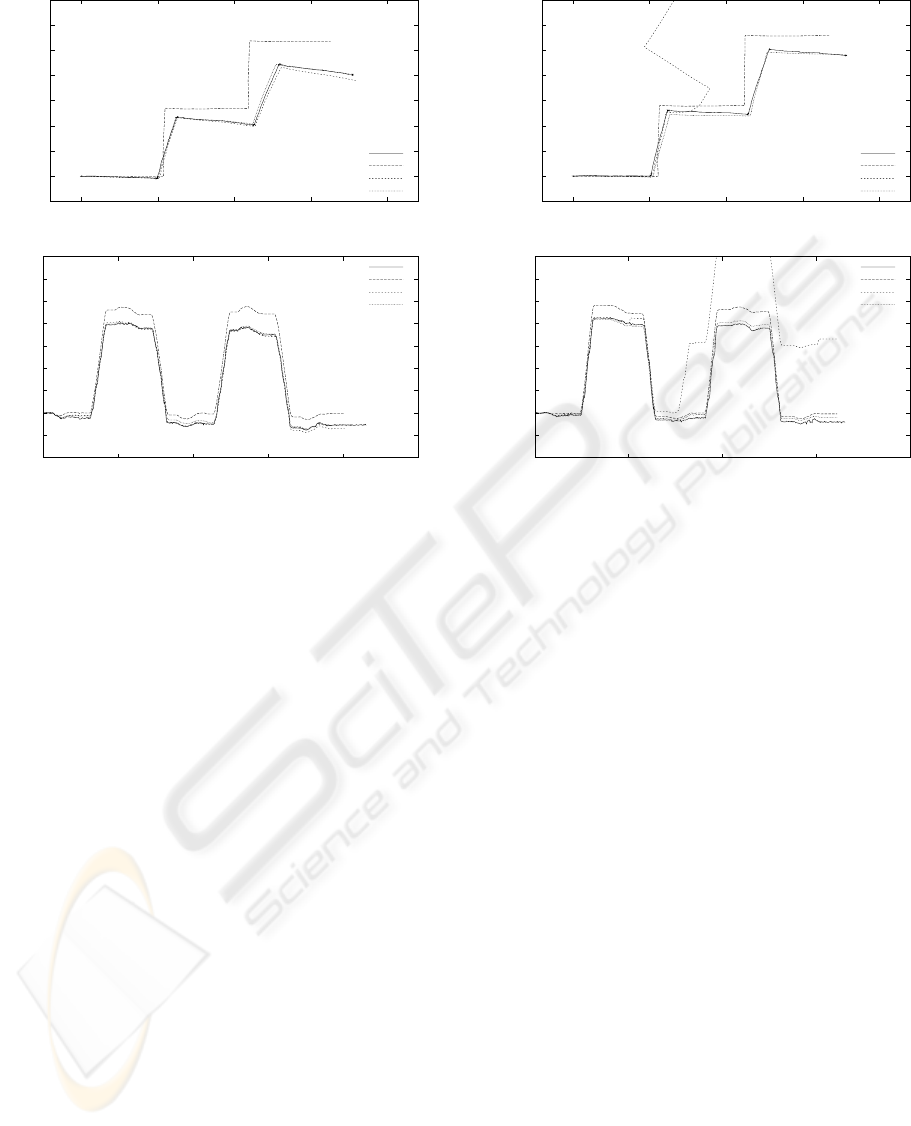
The comparison result of the real trajectory and
dead-reckoning values based on wheels, two optical
mouse sensors, and four optical mouse sensors are
shown in Fig. 5. As a result, when a robot speed is
(a), even if the dead-reckoning value based on the
wheels greatly differs from the real trajectory, two
dead-reckoning values based on the optical mouse
sensors are mostly in agreement with the real trajec-
CPU board
batteryoptical mouse sensor
control board
(a) Overall view of mobile robot
motor and encoder omni-wheel
chassis bevel gear
(b) Bottom view of mobile robot
LED spring
lens/light pipe optical mouse sensor
(c) Sensor unit
Figure 3: Robot equipped with omni-directional mecha-
nism and optical mouse sensors
PRECISE DEAD-RECKONING FOR MOBILE ROBOTS USING MULTIPLE OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS
51
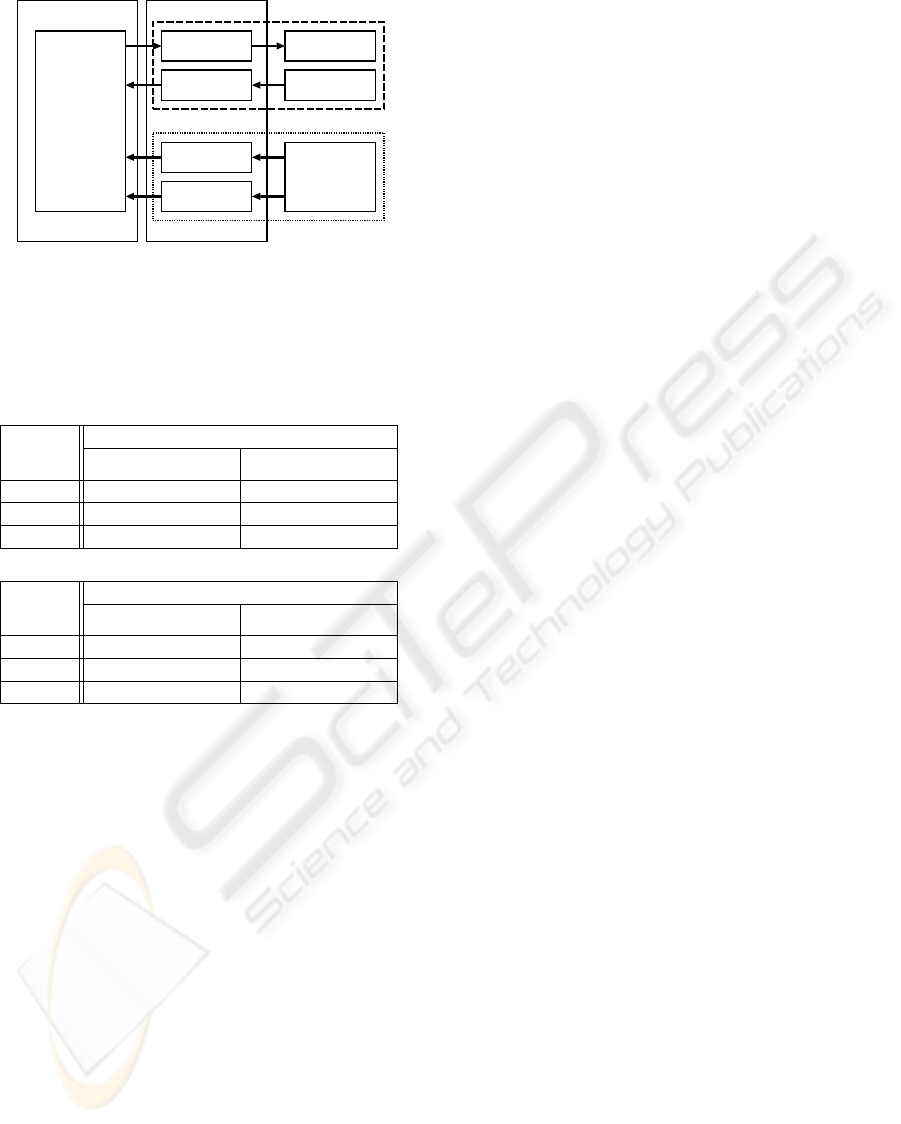
CPU
(Toshiba, TA8440H)
counter
(Nec, uPD4701)
DC motor
(Maxon, A-max)
encoder
(Maxon, 110520)
optical mouse
sensor
(Agilent Tech.,
HDNS-2051)
counter
(Nec, uPD4701)
counter
(Nec, uPD4701)
Y
X
X 3
X 4
motor driver
motor unit
sensor unit
control board
(Hitachi,H8/3054F)
CPU board
Figure 4: Control flows of the robot
Table 4: Errors in 10 dead-reckonings
(a) v = 300 [mm/s], ω = 1.82 [rad/s]
average of the maximum error
type
translation [mm] orientation [deg]
wheels 191.499 14.970
2 mice 44.516 4.918
4 mice 38.011 4.607
(b) v = 500 [mm/s], ω = 3.03 [rad/s]
average of the maximum error
type
translation [mm] orientation [deg]
wheels 239.397 19.264
2 mice 627.237 40.638
4 mice 61.593 8.588
tory. On the other hand, when robot speed is (b),
the dead-reckoning value based on the wheels dif-
fers greatly from the real trajectory as well as in the
case of speed (a). The method based on two op-
tical mouse sensors caused erroneous measurements
during movement, and a large error has arisen in the
dead-reckoning value. On the other hand, the method
based on four optical mouse sensors has carried out
position estimation with a small error, since a compar-
ison between optical mouse sensors was performed
correctly.
Moreover, we verified the dead-reckoning mea-
surements ten times under the same condition. The
average of the maximum error of the estimated value
and the measured value in the movement is shown in
Table 4. As a result, in the ten dead-reckoning mea-
surements, results similar to the above-mentioned are
obtained, and the stability of our method can be con-
firmed.
4.3 Integration of Global Camera
Information and
Dead-Reckoning Value
Using another evaluation method, we report on the
results of integration of the robot position via global
camera and dead-reckoning value using the Kalman
Filter. The handy-cam installed in the upper part of
the room is used as the global camera (A separate
camera is used for measuring). The global camera
measures only the robot position information (orien-
tation information is not included) for the sake of con-
venience. Though the extended Kalman Filter is used
for integrating the two values, its details are omitted.
We used v=500[mm/s] and ω=3.03[rad/s] as the robot
speed in the experiments.
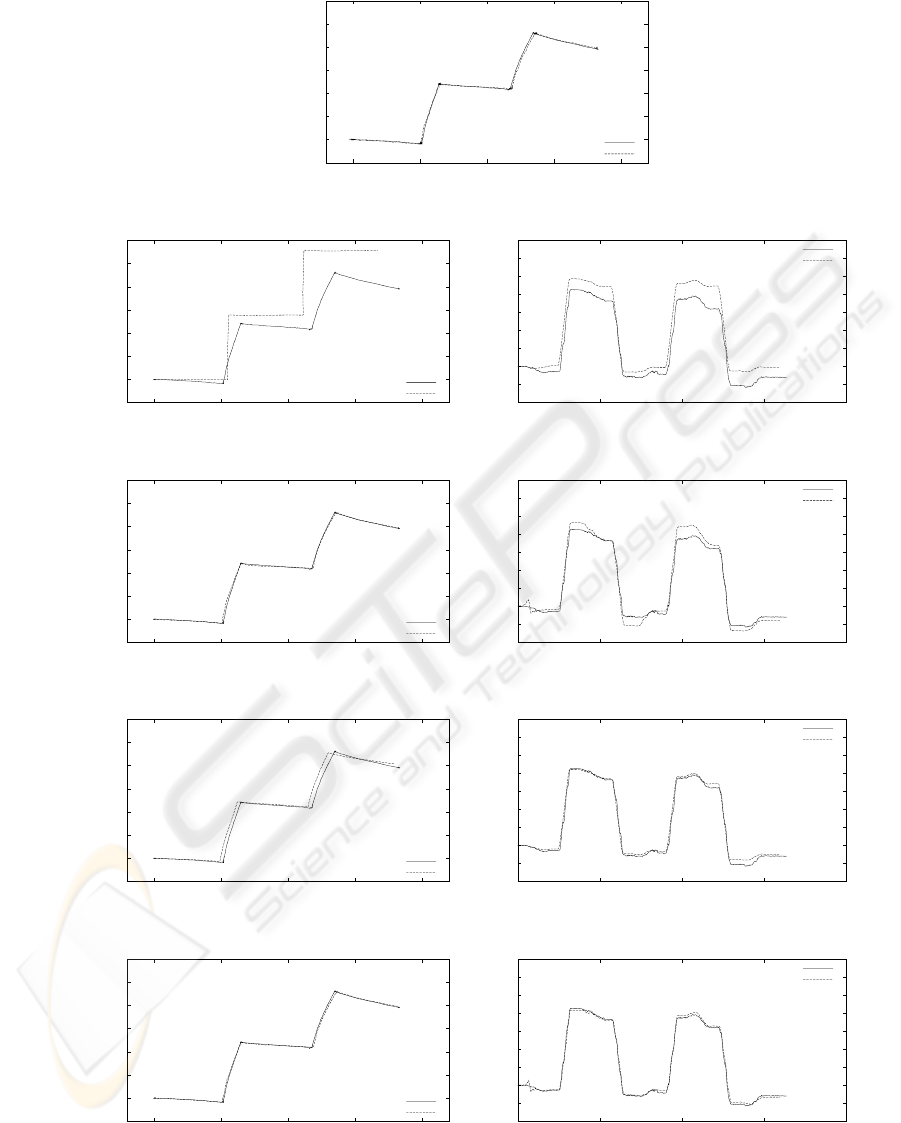
Fig. 6 shows the results of (a) measurement value
using the handy-cam, (b) dead-reckoning value using
wheel rotation, (c) estimates based on (a) and (b), (d)
dead-reckoning value using optical mouse sensors,
and (e) estimates based on (a) and (c). As a result,
in the case of (c), even if estimates of the position are
mostly in agreement with the real trajectory, a large
error has arisen in the estimates of orientation. On
the other hand, in the case of (e), estimates of both
position and orientation are mostly in agreement with
the real trajectory. In this experiment, since the ori-
entation is not included in the information from the
global camera, the accuracy of the estimates of orien-
tation tends to worsen compared with the estimates of
position. However, by using optical mouse sensors,
accurate dead-reckoning can be realized, and conse-
quently, not only a position but also an orientation is
realizable with sufficient accuracy.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed the method of accurate
dead-reckoning by measuring the movement of a ro-
bot directly from the floor with optical mouse sensors.
By comparing and selecting sensor values from the
multiple optical sensors, reliable dead-reckoning was
realized. Through several verification checks with the
actual robot, we confirmed that our dead-reckoning
can be realized accurately and with stability compared
with the method based on wheel rotation. In addi-
tion, we showed that the accuracy of estimation was
greatly improved by using only simple global camera
information.
This method of measuring the movement of the ro-
bot with optical mouse sensors is limited to the in-
door environment. Though the system becomes large
scale in an outdoor environment, it is also possible to
measure the movement of the robot by taking images
of the ground surface with multiple CCD cameras as
ICINCO 2005 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
52
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
wheels
2 mice
4 mice
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20 25
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
wheels
2 mice
4 mice
(a) v=300[mm/s], ω=1.82[rad/s]
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
wheels
2 mice
4 mice
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
wheels
2 mice
4 mice
(b) v=500[mm/s], ω=3.03[rad/s]
Figure 5: Self-localization based on dead-reckoning
well as optical mouse sensors. When CCD cameras
are used for the measurement, our method can be in-
troduced without the big alterations.
In future work, we will develop one sensor unit in-
cluding multiple optical sensors, and install this sen-
sor unit in various robots.
REFERENCES
Acroname Inc. Omni-directional poly roller wheel.
http://www.acroname.com/index.html.
Agilent Technologies Inc. ADNS-2051
optical mouse sensor data sheet.
http://www.agilent.com/semiconductors.
Chenavier, F. and Crowley, J. L. (1992). Position estimation
for a mobile robot using vision and odometry. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Ro-
botics and Automation (ICRA’92), pages 2588–2593.
Cooney, J. A., Xu, W. L., and Bright, G. (2004). Vi-
sual dead-reckoning for motion control of a mecanum-
wheeled mobile robot mecanum-wheeled mobile ro-
bot. Mechatronics, 14:623–637.
Cox, I. J. (1989). Blanche: position estimation for an
autonomous robot vehicle. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/RSJ International workshop on Robots and Sys-
tems (IROS’89), pages 432–439.
Fujimoto, R., Enomoto, M., Sekimori, D., Masutani, Y.,
and Miyazaki, F. (2002). Dead reckoning for mobile
robots using optical mouse sensor (in Japanese). In
Proceedings of the JSME Conference on Robotics and
Mechatronics (ROBOMEC’02), pages 1A1–G01.
RoboCup official web site. http://www.robocup.org/.
Singh, S. P. N. and Waldron, K. J. (2004). Design and
evaluation of an integrated planar localization method
for desktop robotics. In Proceedings of the IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA’04), pages 1109–1114.
Tobe, N., Fuchiwaki, O., Misaki, D., Usuda, T., and
Aoyama, H. (2004). Precise navigation for piezo
based versatile miniature robot with self-gauging de-
tector. In Proceedings of the 1st International Confer-
ence on Positioning Technology (ICPT’04).
Watanabe, Y. and Yuta, S. (1990). Position estimation of
mobile robots with internal and external sensors us-
ing uncertainty evolution technique. In Proceedings
of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and
Automation (ICRA’90), pages 2011–2016.
PRECISE DEAD-RECKONING FOR MOBILE ROBOTS USING MULTIPLE OPTICAL MOUSE SENSORS
53
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
handy-cam
(a) measurement value using the handy-cam
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
d.r.(wheels)
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
d.r.(wheels)
(b) dead-reckoning value using wheel rotation
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
estimation
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
estimation
(c) estimates based on (a) and (b)
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
d.r.(4mice)
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
d.r.(4mice)
(d) dead-reckoning value using optical mouse sensors
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Y [mm]
X [mm]
real trajectory
estimation
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 15 20
Θ [deg]
t [sec]
real trajectory
estimation
(e) estimates based on (a) and (d)
Figure 6: Self-localization based on Integration of global camera information and dead-reckoning value( v=500[mm/s],
ω=3.03[rad/s] )
ICINCO 2005 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
54
