
P2P WEB-BASED TRAINING SYSTEM
USING MOBILE AGENT TECHNOLOGIES
Shinichi Motomura, Takao Kawamura, Ryosuke Nakatani, Kazunori Sugahara
Tottori University
4–101, Koyama-Minami, Tottori 680–8552, JAPAN
Keywords:
P2P, e-Learning, Mobile Agent, Distributed hash table.
Abstract:
In this paper, we present a novel framework for asynchronous Web-based training. The proposed system has
two distinguishing features. Firstly, it is based on P2P architecture for scalability and robustness. Secondly,
all contents in the system are not only data but also agents so that they can mark user’s answers, can tell the
correct answers, and can show some extra information without human instruction. We also present a prototype
implementation of the proposed system on Maglog. Maglog is a Prolog-based framework for building mobile
multi-agent systems we have developed. The agent migrates using HTTP as transfer protocol and XML as
encoding format itself. The user interface program of the proposed system is built on Squeak. Performance
simulations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system.
1 INTRODUCTION
The term e-Learning covers a wide set of applications
and processes, such as Web-based training (hereafter
we abbreviate as WBT), computer-based training, vir-
tual classrooms, and digital collaboration. We are
concerned with asynchronous WBT that allows the
learner to complete the WBT on his own time and
schedule, without live interaction with the instructor.
Although a large number of studies have been made
on asynchronous WBT(Helic et al., 2003; Homma
and Aoki, 2003), all of them are based on the
client/server model. The client/server systems gen-
erally lack scalability and robustness. In the recent
years, P2P research has grown exponentially. In this
paper, we present a novel framework for asynchro-
nous WBT. The proposed system has two distinguish-
ing features. Firstly, it is based on P2P architecture
and every user’s computer plays the role of a client
and a server.
Namely, while a user uses the proposed e-Learning
system, his/her computer (hereafter we refer to such a
computer as a node) is a part of the system. It receives
some number of contents from another node when it
joins the system and has responsibility to send appro-
priate contents to requesting nodes. Secondly, each
content in the system is not only data but also an agent
so that it can mark user’s answers, tell the correct an-
swers, and show some extra information without hu-
man instruction. The agent migrates using HTTP as
transfer protocol and XML as encoding format itself.
In this paper,we present a prototype of the proposed
system on Maglog that is a Prolog-based framework
for building mobile multi-agent systems we have de-
veloped.
2 PROPOSED SYSTEM
2.1 Overview
As mentioned in the previous section, we focus on
asynchronous WBT, that is to say, a user can connect
to the proposed e-Learning system anytime and any-
where he/she wants. Once connection is established,
the user can obtain exercises one after another through
specifying categories of the required exercises. User’s
answers for each exercise are marked as correct or
incorrect right away. Extra information may be pro-
vided for each answer, which can be viewed when the
correct answer is shown.
While a user uses the proposed e-Learning system,
his/her computer is a part of the system. Namely, it
receives some number of categories and exercises in
them from another node when it joins the system and
202
Motomura S., Kawamura T., Nakatani R. and Sugahara K. (2005).
P2P WEB-BASED TRAINING SYSTEM USING MOBILE AGENT TECHNOLOGIES.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 202-205
DOI: 10.5220/0001228602020205
Copyright
c
SciTePress
has responsibility to send appropriate exercises to re-
questing nodes.
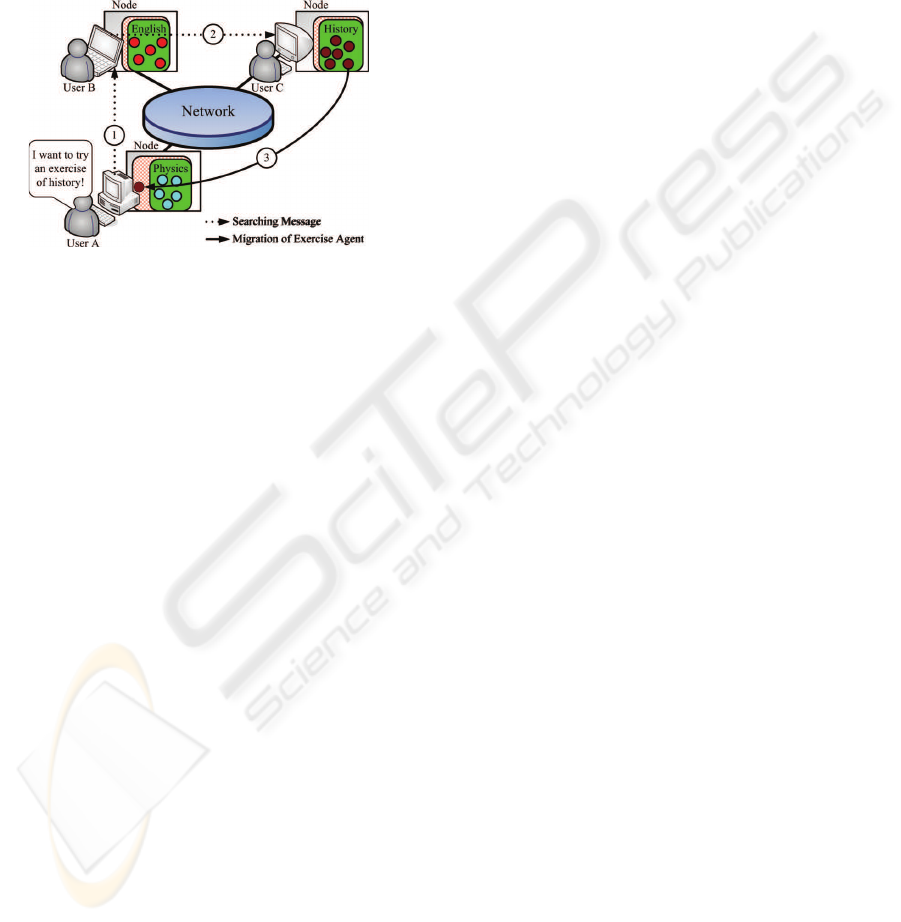
The important point to note is that the categories a
node has are independent of the categories in which
the node’s user are interested as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 illustrates that user A’s request is forwarded
at first to the neighbor node, next forwarded to the
node which has the requested category.
Figure 1: Proposed e-Learning system.
2.2 P2P Aspect
When the proposed system begins, one initial node
has all categories in the system. When another node
joins the system, it is received some number of cate-
gories from the initial node. The categories are dis-
tributed among all nodes in the system according as
nodes join the system or leave the system.
We would like to emphasize that in existing P2P-
based file sharing systems such as Napster(Napster,
1999) and Gnutella(Gnutella, 2000) each shared file
is owned by a particular node. Accordingly, files
are originally distributed among all nodes. On the
other hand, the categories in the proposed system
are originally concentrated. Consequently, when a
new node joins the system, not only location infor-
mation of a category but the category itself must be
handed to the new node. Considering that, the P2P
network of the proposed system can be constructed as
a CAN(Ratnasamy et al., 2001).
A CAN has a virtual coordinate space that is used
to store (key, value) pairs. To store a pair (K
1
, V
1
),
key K
1
is deterministically mapped onto a point P in
the coordinate space using a uniform hash function.
The corresponding (key, value) pair is then stored at
the node that owns the zone within which the point
P lies. In the proposed system, we let each category
be a key and let a set of exercises belonging to the
category be the corresponding value.
2.3 Mobile Agent Aspect
Generally, in addition to service to show an exercise, a
WBT server provides services to mark the user’s an-
swers, tell the correct answers, and show some ex-
tra information about the exercise. Therefore, for the
proposed system which can be considered a distrib-
uted WBT system, it is not enough that only exercises
are distributed among all nodes. Functions to provide
the above services also must be distributed among all
nodes. We adopt mobile agent technology to achieve
this goal. Namely, an exercise is not only data but
also an agent so that it can mark user’s answers, tell
the correct answers, and show some extra information
about the exercise.
In addition, mobile agent technology is applied to
realize the migration of categories, that is, each cate-
gory is also an agent in the proposed system.
3 DESIGN AND
IMPLEMENTATION
We have implemented a prototype of the proposed
system on Maglog that is a Prolog-based framework
for building mobile multi-agent systems we have de-
veloped(Kawamura et al., 2003).
Node Agent There is one node agent on each node.
It manages the zone information of a CAN and for-
wards messages to the category agents in the node.
Category Agent Each category agent stands for a
unit of a particular subject. It manages exercise
agents in itself and sends them to the requesting
node.
Exercise Agent Each exercise agent has a question
and functions to mark user’s answers, tell the cor-
rect answers, and show some extra information
about the exercise. These data are formatted in
HTML.
Interface Agent There is one interface agent on each
node. It is an interface between the user interface
program and other agents.
Agents communicate with other agents through
‘field’s provided by Maglog framework. A field is
kind of a preemptive queue. Roughly speaking, the
above-mentioned four kinds of agents execute a mes-
sage dispatch loop. Each message to an agent is
queued into the field owned by the agent. The user in-
terface program also communicates with the interface
agent through a field via XML-RPC(Winer, 1998).
As mentioned above, the user interface program of
the proposed system has been developed through ex-
tending Scamper which is a simple web browser runs
in Squeak(Ingalls et al., 1997).
P2P WEB-BASED TRAINING SYSTEM USING MOBILE AGENT TECHNOLOGIES
203

Figures 2 and 3 are screen-shots of the user inter-
face program. By clicking the left button of a mouse
on the category, a user can select it. After selection of
the category, a user can obtain an exercise belonging
to the category by clicking the left button of a mouse
on one of buttons in the button pane. After a while
an appropriate exercise agent comes from some node
and the user can try the question. The user can re-
quire to mark his/her answer anytime by clicking the
submit button. Figure 2 shows an example result of
marking. Figure 3 shows the correct answers and ex-
tra information about the exercise that are shown by
clicking the answer button.
Figure 2: User’s answers are marked as correct or incorrect
by clicking the submit button.
Figure 3: Correct answers and extra information are shown
by clicking the answer button on the screen shown as Figure
2.
4 PERFORMANCE SIMULATION
This section presents performance simulations ob-
tained from a prototype implementation of the pro-
posed system described in the previous section.
The experimental environment consists of 8 PCs
with Intel Pentium4 2.4GHz processor and 512MB
of RAM, and all the PCs are running on GNU/Linux
(kernel version is 2.2.26) operating system.
We measured the searching latency in the exper-
imental environment under the conditions shown in
Table 1. All nodes send searching requests at the
same time and exercises to be searched are selected
randomly. We compared distributed and concentrated
systems where these terms are defined as follows:
Distributed System Each node has one category.
Concentrated System One node has all categories
and the rest nodes have no category.
It must be noted that the distributed system represents
the proposed system in which all categories have ideal
distribution. The concentrated system is equivalent to
an ordinary WBT system.
Table 1: Experimental Conditions.
Number of Nodes 8
Number of Categories
8
Number of Exercises/Category
50
Searching Frequency [times/sec]
1
12
,
1
6
,
1
3
,
1
2
Simulations are carried out with the time interval
of 600 seconds. Each Simulation is repeated 10 times
and the average of those is reported in Figure 4. Nat-
urally, the higher searching frequency is, the larger
searching latency is. Figure 4 shows that search-
ing latency grows rapid in the concentrated system,
while it grows slowly in the distributed system. In
other words, the result suggests that the proposed e-
Learning system has higher scalability than ordinary
concentrated WBT systems have.
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Average Searching Latency [msec]
Searching Frequency [times/sec]
Concentrated System
Distributed System
Figure 4: Comparison of concentrated and distributed sys-
tems in searching latency.
5 RELATED WORKS
A great deal of effort has been made on agent-based
systems(Wong et al., 1997; Lange and Oshima, 1998;
Tarau, 1999; Satoh, 2000). However, these tech-
nologies provide support for agent collaboration and
WEBIST 2005 - INTERNET COMPUTING
204

communication but lack support for P2P technology.
Therefore, there are few agent-based P2P applica-
tions. PeerDB(Ng et al., 2003) is one of them, how-
ever agent technology is only used to assist query
processing while in the proposed e-Learning system
it is used not only for interactiveness but also for mi-
gration of the functionality of the system.
Edutella is P2P network for exchanging infor-
mation about learning objects(Nejdl et al., 2002).
Edutella is based on RDF(Resource Description
Framework), which is a framework for representing
information in the Web. Consequently, Edutella does
not intend to receive user’s response. In contrast, that
is one of main goal of the proposed system and it is
achieved through agent technology.
6 CONCLUSION
Since existing asynchronous WBT systems are based
on the client/server model, they have problems of
scalability and robustness. The proposed e-Learning
system solves these problems in decentralized man-
ner through both P2P technology and mobile agent
technology. The agent migrates using HTTP as trans-
fer protocol and XML as encoding format itself. The
user interface program of the proposed system is built
on Squeak so that it obtains much interactiveness
and flexibility. Performance simulations suggest that
the proposed e-Learning system has higher scalability
than ordinary concentrated WBT systems have. More
work needs to be done in the evaluation of the robust-
ness of the proposed system. In addition, the expan-
sion to provide popular functions of ordinary concen-
trated WBT systems for communication between the
instructor and the learners and among the learners by
means of email and BBS (Bulletin Board System), in
decentralized manner, is left for future work.
REFERENCES
Gnutella (2000). http://welcome.to/gnutella/.
Helic, D., Krottmaier, H., Maurer, H., and Scerbakov, N.
(2003). Implementing project-based learning in wbt
systems. In World Conference on E-Learning in Cor-
porate, Government, Healthcare, and Higher Educa-
tion, pages 2189–2196.
Homma, H. and Aoki, Y. (2003). Creation of wbt server
on digital signal processing. In Proceedings of 4th
International Conference on Information Technology
Based Higher Education and Training. Marrakech,
Morocco.
Ingalls, D., Kaehler, T., Maloney, J., Wallace, S., and Kay,
A. (1997). Back to the future: The story of squeak, a
practical smalltalk written in itself. In Proceedings of
ACM Conference on Object-Oriented Programming,
Systems, Languages, and Applications, pages 318–
326.
Kawamura, T., Kinoshita, S., Sugahara, K., and Kuwatani,
T. (2003). A logic-based framework for mobile multi-
agent systems. In Proceedings of International Con-
ference on Integration of Knowledge Intensive Multi-
Agent Systems, pages 754–759. Boston, Massa-
chusetts, USA.
Lange, D. B. and Oshima, M. (1998). Programming and
Deploying Java Mobile Agents with Aglets. Addison-
Wesley.
Napster (1999). http://www.napster.com/.
Nejdl, W., Wolf, B., Qu, C., Decker, S., Sintek, M., Naeve,
A., Nilsson, M., Palm
´
er, M., and Risch, T. (2002).
Edutella: A p2p networking infrastructure based on
rdf. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Con-
ference on World Wide Web, pages 604–615. ACM
Press.
Ng, W. S., Ooi, B. C., Tan, K.-L., and Zhou, A. (2003).
Peerdb: A p2p-based system for distributed data shar-
ing. In Dayal, U., Ramamritham, K., and Vijayara-
man, T. M., editors, Proceedings of the 19th Interna-
tional Conference on Data Engineering, pages 633–
644. IEEE Computer Society.
Ratnasamy, S., Francis, P., Handley, M., Karp, R., and
Shenker, S. (2001). A scalable content-addressable
network. In Proceedings of the 2001 conference on
Applications, technologies, architectures, and proto-
cols for computer communications, pages 161–172.
ACM Press.
Satoh, I. (2000). Mobilespaces: A framework for building
adaptive distributed applications using a hierarchical
mobile agent system. In Proceedings of IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Distributed Computing Systems,
pages 161–168. IEEE Press.
Tarau, P. (1999). Inference and computation mobility with
jinni. In Apt, K., Marek, V., and Truszczynski, M.,
editors, The Logic Programming Paradigm: a 25 Year
Perspective, pages 33–48. Springer.
Winer, D. (1998). Xml-rpc specification.
http://xmlrcp.com/spec.
Wong, D., Paciorek, N., Walsh, T., and Dicelie, J. (1997).
Concordia: An infrastructure for collaborating mo-
bile agents. In Proceedings of the First International
Workshop on Mobile Agents, volume 1219, pages 86–
97. Springer-Verlag.
P2P WEB-BASED TRAINING SYSTEM USING MOBILE AGENT TECHNOLOGIES
205
