
METHOD FOR AUDIO/VIDEO STREAMING TESTBED
DEFINITION AND MODEL DEVELOPMENT
Xabiel G. Pañeda, Roberto García, David Melendi, Manuel Vilas, Víctor G. García
Computer Science Department, University of Oviedo
Campus Universitario de Viesques. Sede Departamental Oeste, 33204 Xixón-Gijón
, Asturies
Keywords: Video-on-demand, Evaluation, Testbed, Streaming, Workload.
Abstract: This paper presents a method to develop lab exp
eriments for audio/video services, both using testbed and
simulation models. Audio/video services in the Internet have special characteristics which make them very
difficult to configure. Our research group has designed a methodology (Pañeda, 2004) for video-on-demand
service analysis and configuration. In this methodology, the analysis phase is divided into two independent
parts, one which works on data extracted from the behaviour of the real service, and another which works
on predictions. The latter uses simulation models and testbeds to evaluate situations which may appear in a
near future. In all the cases, a method must be used to specify the experiments. This method must determine
elements such as: goals establishment, experiment generation process, the input data for the workload
definition, etc.
1 INTRODUCTION
The emergence of the World Wide Web has changed
the Internet world. This service has become a
powerful communication medium. Daily, an
important number of web accesses is produced and a
huge volume of information is delivered. The
bandwidth increase in subscribers’ access
capabilities has given rise to the appearance of a new
complementary service: the Internet audio/video.
There are two types of audio/video services on the
Internet: live-audio/video and audio/video-on-
demand. Both of them are usually based on
streaming technology. The special characteristics of
the audio/video services, such as, delivering
continuous information, allowing user interaction,
sending the information exclusively for each request,
etc make these services difficult to configure.
Achieving a good configuration is a hard task which
can only be based on a good analysis. Our research
group has designed a methodology (Pañeda, 2004)
for video-on-demand service analysis and
configuration. In this methodology, the analysis
phase is divided into two independent parts, one
which works on data extracted from the behaviour of
the real service, and another which works on
predictions. The latter uses simulation models and
testbeds to evaluate situations which may appear in a
near future (Jin, 2001). To obtain good results, these
experiments (Arias, 2002) must be developed
following a clear method adapted for this type of
services. Several questions have to be defined. It is
necessary to have accurate information about user
behaviour in order to characterize the system
workload accurately. It is important to define the
steps for the application process, determine the goals
and analyze the results.
The method presented in this paper covers all
these goals and, m
oreover, it can be integrated in the
analysis and configuration methodology designed in
the previous stage of our research.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Sect
ion 2 provides a detailed description of the
method, and, finally, conclusions are presented in
section 3.
2 METHOD DESCRIPTION
The designed method is oriented to clearly specify
all the steps necessary to perform a lab experiment
for an audio/video service. Its aim is to generate
accurate tests which provide important information
to the analysis task of the methodology presented in
(Pañeda, 2004).
197
Pañeda X., Garcia R., Melendi D., Vilas M. and Garcia V. (2005).
METHOD FOR AUDIO/VIDEO STREAMING TESTBED DEFINITION AND MODEL DEVELOPMENT.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on e-Business and Telecommunication Networks, pages 197-200
Copyright
c
SciTePress
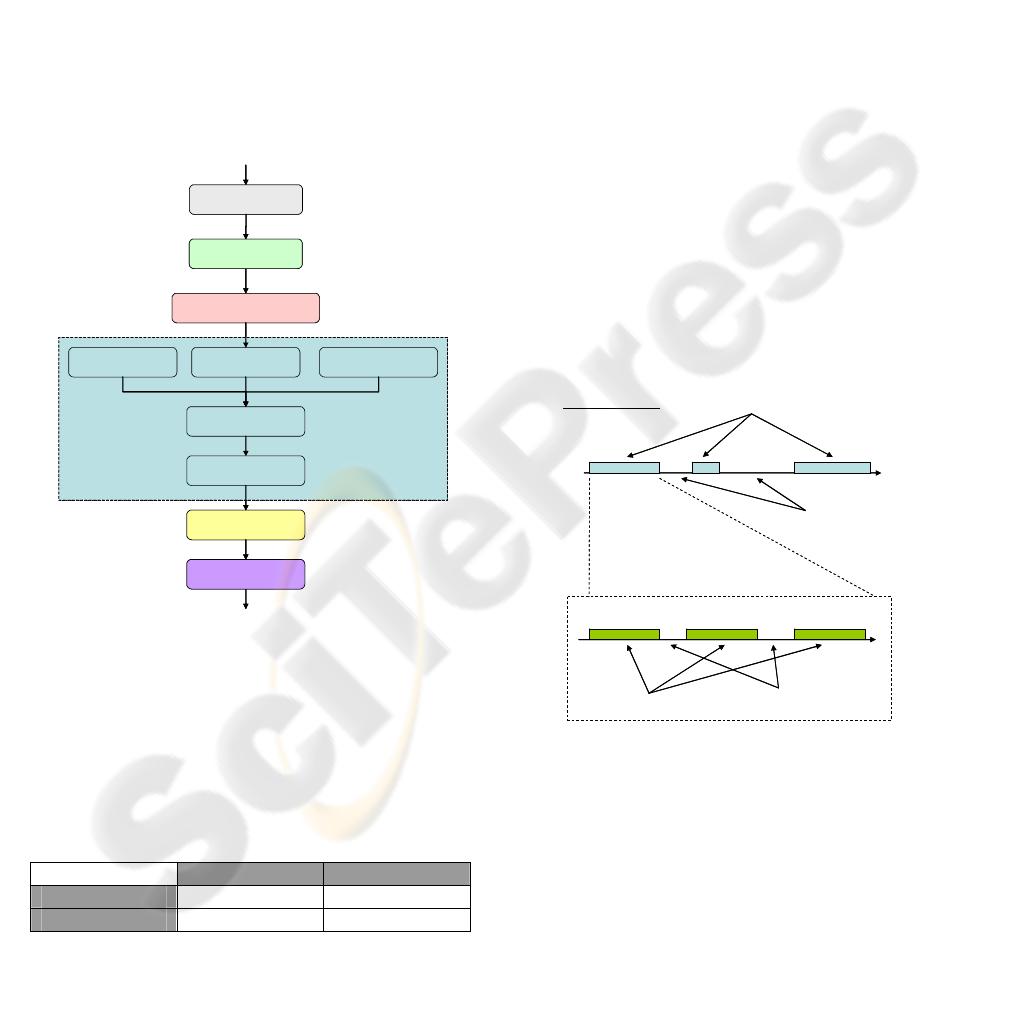
2.1 Application process
The application process, shown in figure 1, is
divided into different steps. The first one is in charge
of specifying the service. Its type and its
characteristics have to be determined. The second is
the goals definition. At this time it is necessary to
decide what kind of information the experiment has
to provide. Once the goals are clear, it is necessary
to decide which type of experiment is more
adequate: to use a simulation model or a testbed.
The following phase is the experiment definition,
which is composed of different tasks: workload
definition, resource definition, architecture
definition, parameters definition and values
definition. After that, the experiment is completely
specified and it is time to execute it. Finally, an
analysis of the results must be performed.
Service specification
Experiment type definition
Workload definition Resource definition Architecture definition
Parameters definition
Execution
Values definition
Experiment definition
Goal definition
Result analysis
Service specification
Experiment type definition
Workload definition Resource definition Architecture definition
Parameters definition
Execution
Values definition
Experiment definition
Goal definition
Result analysis
Figure 1: Application process
2.2 Service specification
There are two different types of services based on
streaming technology: audio/video on demand and
live audio/video. The first step for this method is to
define what type of service is going to be analyzed.
Depending on this type, different parameters must
be established.
Table 1 Types of service
On-demand Live
Audio Jukebox Internet radio
Audio/video Video-on-demand Internet-TV
Table 1 shows four types of services, classified
depending on the type of information and the
delivery method.
2.3 Goal definition
The second step is to answer the following
questions: what is the aim of the experiment? What
information are we interested in?
To answer these questions, the outputs of the
experiment must be defined. These outputs will be
expressed by means of the metrics defined in
(Pañeda, 2004). Elements such as bandwidth
consumed in a point of the network, throughput,
CPU utilization, etc will be considered.
2.4 Type of experiment definition
The third step in the method application process is
the definition of the type of experiment. Two types
of experiments can be performed: to use a
simulation model or a testbed.
2.5 Experiment definition
The experiment definition is composed of five tasks.
Three of them, workload, architecture and resource
definition, are oriented to define the base for the
experiment. The others, parameters and values
definition, are used to characterize the analysis
which is going to be performed.
User Session
time
reproductions
Inter-reproduction time
time
Reproduction
play pause pauseplay stopplay
receiving paused
User Session
time
reproductions
Inter-reproduction time
time
Reproduction
play pause pauseplay stopplay
receiving paused
Figure 2: User behaviour
Workload Definition
To perform a useful experiment, an accurate
workload must be defined (Cherkasova, 2004),
(Pañeda, 2005). Most of the necessary data is
extracted from real services. The rest must be
established as parameters which will be defined later
using different values to characterize the experiment.
The workload definition is divided into two
different parts: user behaviour and content
characteristics.
ICETE 2005 - MULTIMEDIA SIGNAL PROCESSING
198
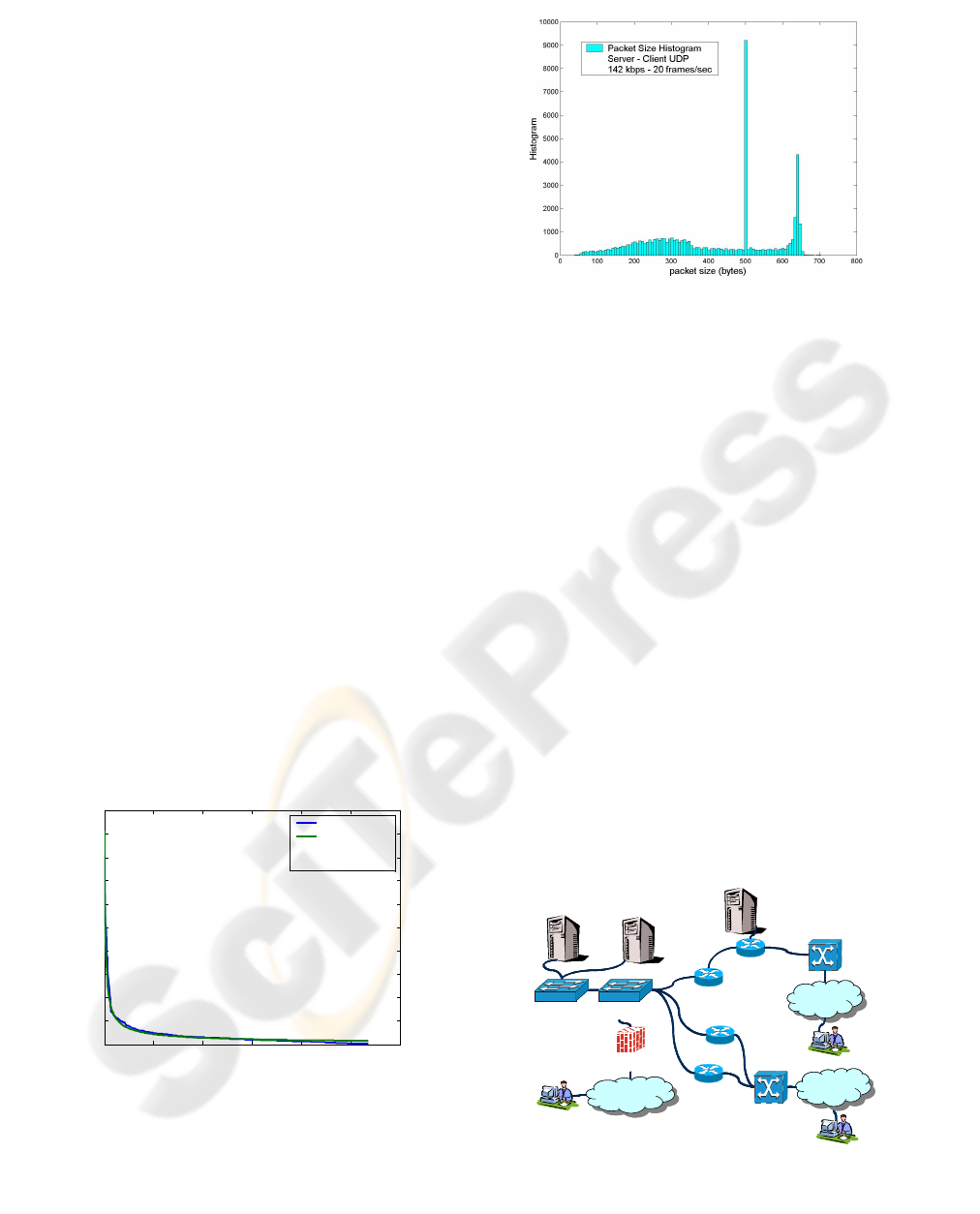
Figure 2 shows the behaviour of a user in a
service based on streaming technology. To clearly
define an experiment, all the following parameters
must be specified:
• Media delivered time: audio/video time
delivered throughout the reproduction.
• Pause number: number of pauses in a
reproduction.
• Pause time: length of a pause.
• Pause start-time: time in the audio/video when
the pause appears.
• Inter-reproduction time: time between two
reproductions of the same user.
• Reproductions per session: number of
reproductions made by a user in a given period
of time.
• Inter-session time: time between two user
sessions.
If the service is a jukebox or a video-on-demand
service, it is necessary to define:
• Length, position and number of forward
jumps.
• Length, position and number of backward
jumps.
The content characteristics have the following
elements:
• Quality of the audio and the video stream:
This parameter can either be defined using:
Frames per second and frame size, or bandwidth
consumed per second.
• Number of audio/videos: number of
audio/video files offered in the service.
• Popularity of the audio/videos: criteria used to
decide which audio/video the user selects. In
figure 3 an analysis to characterize this
parameter using a generalized Zipf-like
distribution is shown.
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
popularity
access %
Zipf Law
Real access
Estimation
θ
= 0.667
Total access
Figure 3: Popularity of the audio/videos
Figure 4: Packet size histogram
If the service is a jukebox or a video-on-demand
service it is also necessary to define:
• Length of the audio/videos.
If the type of experiment is a simulation model
the following parameters have also to be defined:
• Packet size: size of the audio and video
packets. Sometimes, there are different sizes
due to the codec used to generate the audio or
the video stream, as shown in figure 4.
• Inter-packet time: time between two packets of
the same type.
Another additional parameter can be necessary in
some types of experiments, where the main goal is
to test the service behaviour in a network where
other types of traffic compete with the service’s own
traffic:
• Background traffic: traffic which is going to
be fed into the analyzed network, not generated
by the service under study.
Architecture definition
This phase includes two different parts that must
be taken into consideration. The first is the network
architecture, and the second is the service
architecture. Figure 5 shows a typical diagram where
an experimental architecture is defined.
Producer
Server
Router
Firewall
Router
Router
Router
Internet
Internet
Switch Switch
ATM
Switch
ATM
Switch
Access
Network
Access
Network
Access
Network
Access
Network
Proxy
ProducerProducer
ServerServer
RouterRouter
FirewallFirewall
RouterRouter
Router
RouterRouter
Internet
Internet
SwitchSwitch SwitchSwitch
ATM
Switch
ATM
Switch
Access
Network
Access
Network
Access
Network
Access
Network
Proxy
Figure 5: Service Architecture example
Different questions must be determined when
dealing with service and network architectures:
METHOD FOR AUDIO/VIDEO STREAMING TESTBED DEFINITION AND MODEL DEVELOPMENT
199
• Number of servers, location in the network, and
load balancing policies.
• Number of proxies, location in the network, and
cache or splitting policies.
• Transport protocol between each service device
(TCP, UDP, etc).
• Number of clients and location in the network.
• Number of producers and location in the
network (Only in live services with online
generated information)
Resource Definition
In this step the quantity of resources, both in service
devices (servers, proxies, etc) and in the
communication network must be established.
Parameters Definition
In this phase one or more elements must be
determined as parameters. The values for these
parameters are not extracted from the real services,
instead, they will be defined arbitrarily depending on
the goal of the experiment.
Values Definition
In this phase a set of values for each parameter of
the experiment must be defined. The process is, first
to determine the maximum and minimum values and
second to establish the criteria for the intermediate
values. For instance, determining the gap between
them: Linear; Exponential; Free.
When there is more than one parameter, there are
two possibilities to combine them:
• Blind combination: generating all the
possibilities with all the parameters.
• Intelligent combination: eliminating those
combinations that are not interesting.
2.6 Results analysis
The last phase is the results analysis. The results
obtained from lab experiments are not different from
the analysis of the information gathered from the
real service. This analysis is performed using the
tests defined in (Pañeda, 2004).
3 CONCLUSIONS
Lab experiments are very important to predict the
future performance of an internet service. In the case
of audio/video this is even more true because of the
high quantity of resources necessary to provide the
contents with an acceptable quality. Defining a
method to specify the experiments is necessary to
reach accurate results and interesting conclusions.
Nowadays this method is being used to perform
lab evaluations of two real services: LNE TV, the
audio/video service of La Nueva España –which is a
video-on-demand service–, and Asturies.com
Radio, the Internet radio service of Asturies.com –a
live audio service–. Several qualities for the audio
and video contents, service architectures and
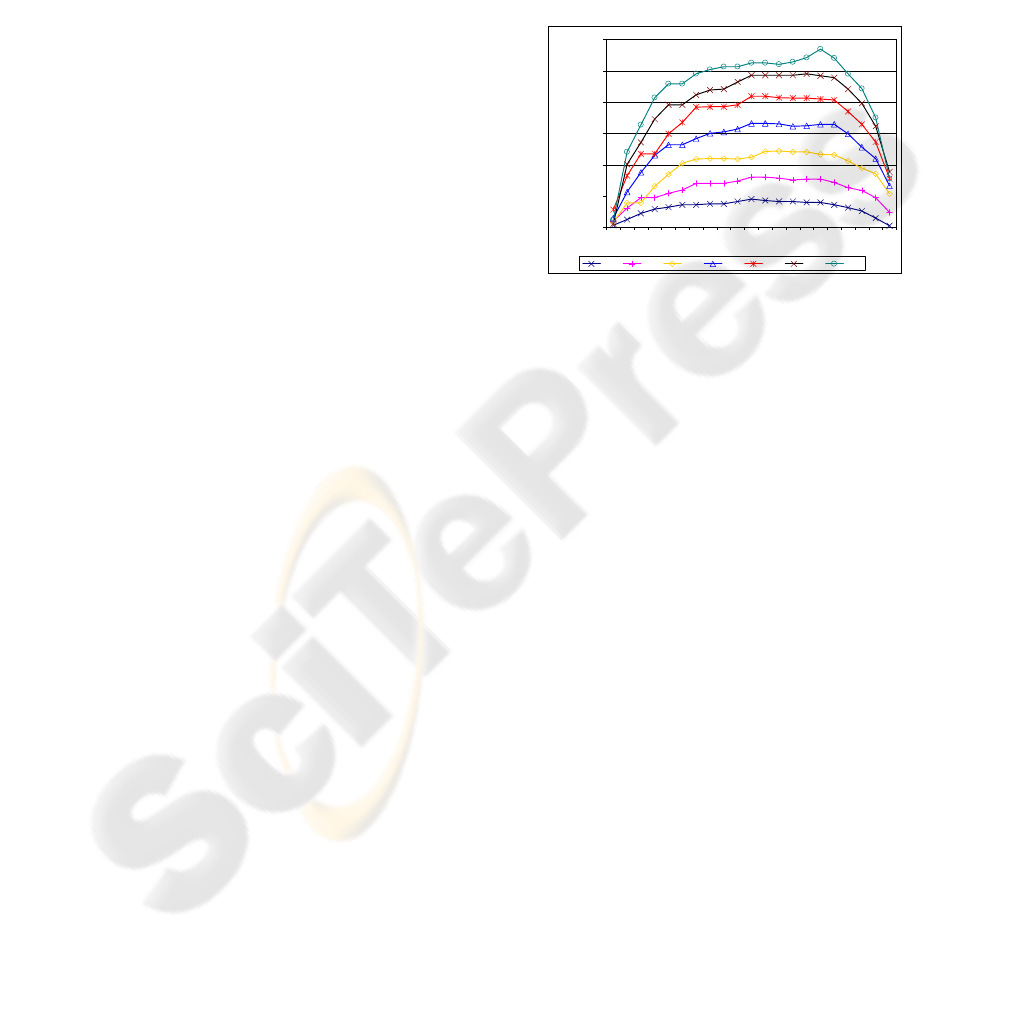
quantity of resources are being analyzed. Figure 6
shows the bitrate temporary evolution in the server
output in an experiment for the evaluation of an
Internet radio. Each line represents this evolution for
a different number of users (100 to 700).
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
123456789101112131415161718192021
Bitrate (Kbps)
100 200 300 400 500 600 700
Figure 6: Internet Radio evaluation
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research has been financed by the operator
Telecable de Asturias S.A.U. and the newspaper
La Nueva España within the Media XXI II project,
and the Spanish National Research Program
within INTEGRAMEDIA project (TSI2004-00979).
REFERENCES
Arias, J. R et al. 2002. Evaluation of Video Server
Capacity with Regard to Quality of the Service in
Interactive News-On-Demand Systems. In PROMS-
IDMS2002. LNCS 2515.
Chekasova, L. and Gupta, M. 2004. Analysis of Enterprise
Media Server Workload: Access Patterns, Locality,
Content Evolution and Rates of Change, IEEE/ACM
Transactions on Networking
Pañeda , X. G. et al. 2005. Workload analysis of a video-
on-demand service with a wide range of subjects and
length. In IASTED EUROIMSA.
Pañeda, X. G. et al. 2004. Analysis and Configuration
Methodology for Video-on-Demand Services Based
on Monitoring Information and Prediction. ICEIS.
Jin, S. and Bestavros, A. 2001. GISMO, A Generator of
Internet Streaming Objects and Workloads, ACM
SIGMETRICTS.
ICETE 2005 - MULTIMEDIA SIGNAL PROCESSING
200
