
E-BUSINESS FOR THE ELECTRICITY RETAIL MARKET
A Business to Client perspective
Victor Santos
ISCAC, Polytechnic Institute of Coimbra, Bencanta Quinta Agrícola, 3040 – 280, Coimbra, Portugal
LCT, University of Coimbra, Pólo II - Pinhal de Marrocos 3030 - 290 Coimbra, Portugal
Edmundo Monteiro
LCT, DEI, University of Coimbra
Pólo II - Pinhal de Marrocos 3030 - 290 Coimbra, Portugal
António Gomes Martins
LGE, DEEC, University of Coimbra
Pólo II - Pinhal de Marrocos 3030 - 290 Coimbra, Portugal
Keywords: Electrical retail, e-Business, B2B, B2C, real time price.
Abstract: In the new deregulated market of the electricity industry the communication and e-Business infrastructure
plays a main role for the efficiency of all the entities present in the electricity sector. From generation to the
final client there are two markets, the wholesale and the retail market. Specific characteristics of the
electricity industry make the communication support a fundamental tool to reflect the changes made by one
of the intervenients in the whole value chain. When prices change at the wholesale market it is necessary to
reflect them at the final consumers. Without a bidirectional and reliable communication systems several
problems could occur, from spikes in the electricity prices that could take retail companies to bankruptcy, to
huge blackouts that happened in Europe and in the United States. The goal of this paper is to present a
model for the electricity retail market. Several studies have been done about the electricity markets, the
grand majority focus their attention on the wholesale market. Our proposal is to analyse the e-Business
communication structure in a Business-to-Client perspective.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deregulation brought the segmentation of the
electricity industry. From generation, passing
through transmission and ending at the distribution
sector, all are separated from each other. During the
nineties several countries have adopted this
structure. Nevertheless, the traditional utility model
still exists. Generation, transmission and distribution
all belongs to the same entity which have a
monopoly or an oligopoly economic structure.
Nowadays in the developed countries customers
become the focus of energy and energy service
providers. This means that generation sells it’s
commodity in the wholesale market to retailers that
distribute to the consumers. Transmission of
electricity is usually done by state regulated entity to
clarify and avoid market influence.
The aim of this work focus on the development
of a electricity retail model that enables market
efficiency growth with the existence of the retailer
entities, and the importance of a Business-to-Client
communication infrastructure to improve better
quality of service to the final client.
There are three different types of clients,
industrial, commercial and domestic, as a
consequence different types of needs and different
types of load profiles. Without the impact of price
oscillation at the final client, it is impossible to
provide profit to the entities of the deregulated
market for new generation systems, maintenance and
to provide a new set of products besides electricity.
150
Santos V., Monteiro E. and Gomes Martins A. (2005).
E-BUSINESS FOR THE ELECTRICITY RETAIL MARKET - A Business to Client perspective.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on e-Business and Telecommunication Networks, pages 150-156
DOI: 10.5220/0001423401500156
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Studies developed in several countries, where
electricity deregulation is a fact, where conducted to
characterize the retail clients behaviour
(Cunningham,2001). The analysis of this
information is of main importance to build a retail e-
Business system that answers to clients expectations.
To model the electricity retailer reality we used a
UML representation The UML e-Business model of
the electrical retail company is presented in Fig. 2
identifying all its components, requirements and
interactions.
In this paper an e-Business model of the
electrical company is presented, and as demonstrated
will improve customer response, company
efficiency, and time-to-market response at the
wholesale market where is crucial to trade well for a
better sell.
This paper is organized as follows. In section 2 three
market models are presented and analysed. In
section 3, the UML retailer B2C model is presented.
A discussion of the model proposed is done in
section 4. Requirements for security in this kind of
markets are evaluated in section 5. The conclusions
and future developments are at the paper end in
section 6.
2 MARKET MODELS
The electricity retailer is the unified entity of the e-
Business structure that could improve benefits to
both sides, generation and final clients. The e-
Business can be supported by an e-market entity
based on a web platform. At the B2B side the
retailer acquires the electricity to sell, by bidding on
a power market or by establishing bilateral contracts
with the wholesalers. This paper is focused on the
B2C side of the e-Business retail model. Consumers
will be encouraged to renew the metering structure
of the electricity business. Smart meters with web
access are the resort of the last mille to implement,
allowing a bidirectional communication structure
that will permit the access to billing and services,
structures all based on a web platform. Considering
the web as an open space with multiple market
scenarios, what will be the best scenario, most
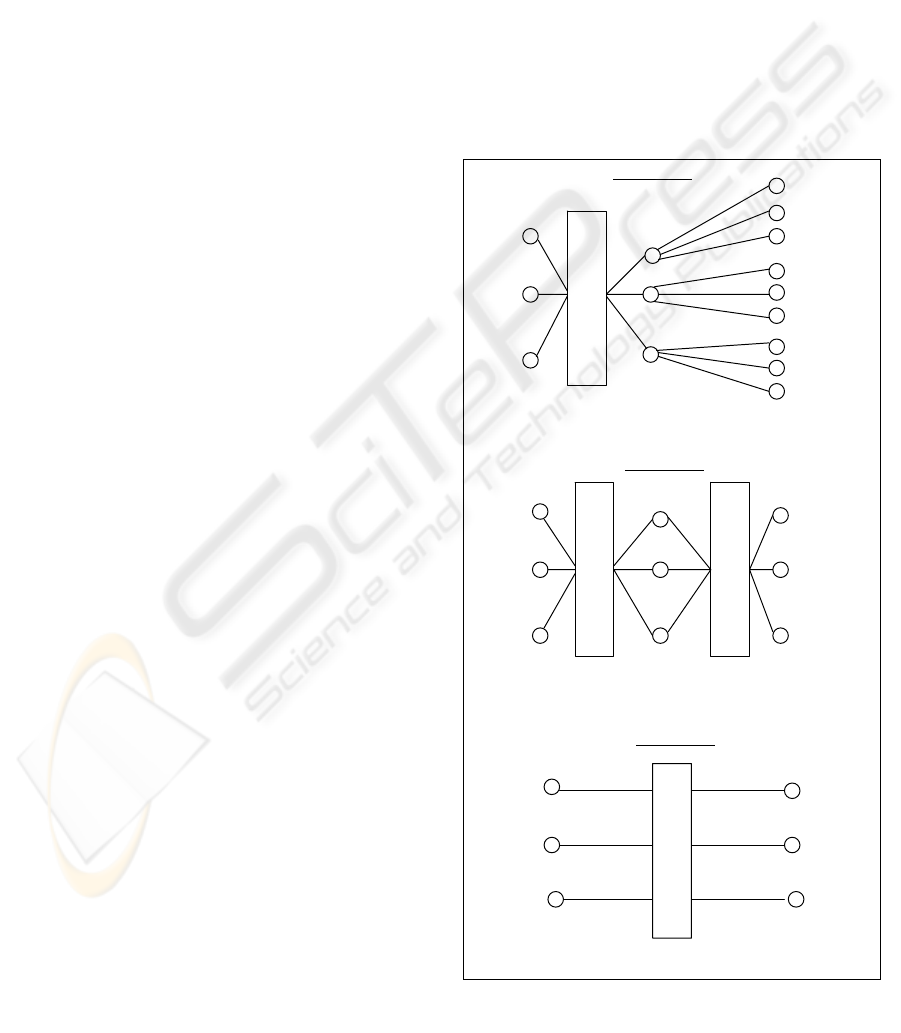
efficient, bringing win-win relations? Three different
types of markets are possible to analyse assuming
that all clients have a real time price tariff as shown
in Fig. 1.
In the first case we have a retailer for a group of
clients, where any client could choose his retailer,
this structure is used in the countries where
deregulation has arrived, it doesn’t allow a dynamic
change between suppliers.
The second model proposed, allows a dynamic
retailer multi-choice. In fact what is proposed is a
B2C web market for the electricity retailer. This web
structure have several advantages for both sides of
the business, clients could get the best price, retailers
don’t have to support the huge variation on price at
wholesale market, where prices could increase more
than 100% in one day. Nevertheless it must be
defined a time restriction for a change of retailer.
This is done to protect retailers investments and
discourage unfair clients who won’t pay theirs bills
and are always
changing from supplier, issue that is
focus below in the electricity retail market structure
security.
Retailers
Wholesalers
Clients
W
1
C
1r1
W
n
W
2
Hypothesis 1
Retailers
Wholesalers Clients
W
1
C
1
W
n
W
2
C
2
C
n
Hypothesis 2
Wholesalers Clients
W
1
C
1
W
n
W
2
C
2
C
n
Hypothesis 3
R
1
R
2
Rn
R
n
R
1
R
2
C
2r1
C
3r1
C
1r2
C
2r2
C
3r2
C
1rn
C
2rn
C
3rn
.
.
.
B2C
Market
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
B2B
Market
B2B
Market
B2B
Market
Figure 1: Hypotheses for a B2C retail market
E-BUSINESS FOR THE ELECTRICITY RETAIL MARKET-A Business to Client perspective
151

The third hypothesis is an answer to how important
is the retailer presence in this type of market, by
assuming his overtaking on the electricity
wholesaler market. Let’s suppose that the final
clients with real time price could have a direct
access to the wholesale market, what is a fact in
same traditional outlets markets (O´Sheassy, 2003).
There are some commodities where this happens but
the client is forced to acquire great amounts of the
product of his interest, in this case electricity.
Because it (electricity) is a continuous function in
time and couldn’t be stored, this must be done by a
bilateral contract, where all the parameters, like
prices, quantities, date and time periods are
previously settled. Besides that the final client could
not have the benefits of real time tariffs if he
overtakes the retailer. In addition to that fact,
electricity retailers could also have the distribution
structure to support which in that case a rent must be
established for the distribution lines if the final client
buys directly in the electricity wholesaler market.
After the choice of the market model it’s
important to deepen the electricity retail model to
understand what modules he must have for is
internal business run, and what connections he has to
establish with the wholesalers and on the other side
with their costumers. For an e-Business development
we should to distinguish two sides of the same
business, the B2Band the B2C sides. Their
interactions are of great importance not only for the
retailer but also to their clients. The good deals done
at the B2B market are reflected on the B2C services
availability.
3 B2C INFRASTRUCTURE
In this section it is presented a UML model of the
electricity retailer. The interaction between this
model and the external entities are analysed in sub-
section 3.2 e-Business transactions. Ending this
section the security requirements of the model
analysed is discussed.
3.1 Electricity retail model
Fig. 2 shows an e-Business model for the electricity
retailer and the connections with the other entities.
Besides the wholesalers and the final clients, as
could be seen there is also an Independent System
Operator – ISO which coordinates the electricity
physical structure. From country to country, this
entity can have different levels of intervention in the
market. He (the ISO) could operate only the physical
structure or also the financial market, regulating the
transactions schedule in time. Electricity can be
traded in different periods of time ranged from
fifteen minutes to several months later, before
empowering the lines. The ISO acts like a regulator
of the commodity and also of the financial systems.
Following in the UML model several modules
are presented. The energy management use case, a
crucial module in the retail business, makes the
analysis of all the impact decisions. They are made
after the evaluation of the saving measures that can
be taken to avoid new purchases and a rigorous
definition of the quantities to buy.
At the clients load management use case, the
loads are elected for automatic cut off or rearm.
The client’s consumptions are the business
beginning, read by the power meter and sent to the
automatic meter reading use case. Every service to
the final client, besides electricity distribution and
sells, are processed at the financial services use case.
On the other hand, the bids at the wholesale
power market are done after the information passed
from the forecast consumption use case to the
energy management module. Bids are executed by
the retailer market management use case.
In the next section the transactions to the outside
of the retailer model are analyse.
3.2 e-Business transactions
In the traditional electricity industry the company
has to support generation, transmission and
distribution costs besides maintenance. The
company profit is granted by contracts that are made
by the distribution sector with their clients.
Deregulation brought the segmentation of the
electricity industry, all parts from generation to
distribution where separated and new markets where
created. Retailers buy electricity from the
wholesalers which is then sold to the final clients.
Retailer business is well suited to be supported by an
e-Business structure, where a B2B relation is
established between the wholesalers and the retailer,
on the other side a B2C platform is the retailer
solution to improve their competence and services to
the final costumers. Information and communication
technologies are essential for optimal performance
of a retailer. Retailers acquire electricity in two
ways, by a bilateral contract with
ICETE 2005 - GLOBAL COMMUNICATION INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND SERVICES
152

Energy Management
WholeSalers
Accounting Management
Clients Acounting
Management
Retail Market
Management
Clients Load
Management
Consumption
Forecast
Automatic Meter
Reading
ISO
WholeSalers
Power Meter
Loads
Financial Services
Retailer
Clients
Realised Values
Values Needed
Load Control
Service Values
Metering control
Read Values
Traded values
Offers
Power Market
Values
Supply Changes
Sells/Purchases Data
Sales values
Values to analyse
Wholesalers
Meter Read Values
Values Request
Estimated Values
Metering request
System
Operator
Market
Power Market
Management
Bids
Billing
Bilateral
Contracts
the wholesalers or at the wholesale market
posting bids in an auction (Bower, 1999). As
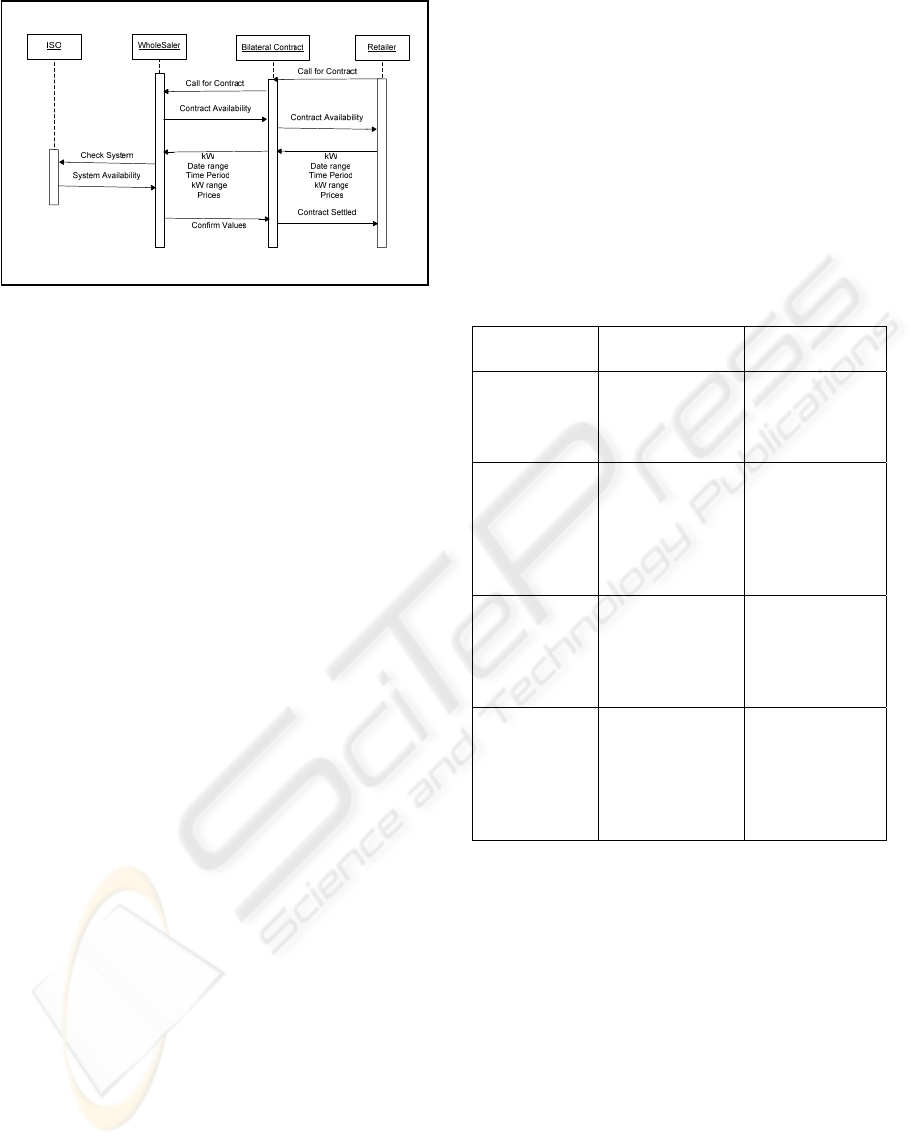
presented in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 the UML sequential
diagrams intends to give a timely perception of the
two forms for the retailer get his commodity
Usually at the power market a reverse auction is
coordinated by the market operator, trying to match
the retailer’s bids with the wholesaler’s offers. As
could be seen in Fig. 3, even in the market where the
Independent System Operator is apart from the
market operator the trades have to be confirmed by
him, usually the day before, because physical
constraints could occur.
Bilateral contracts could have several forms, to
name a few, contracts of fixed price, fixed
quantities, indexed, floating, etc. Nevertheless there
are same parameters and operations that are common
to all. At first, all contracts are settled between two
entities, independent from the system operator.
Prices, quantities, dates and period of time, are the
usual variables. It is possible to join to the contracts
same services for load management, or same
different variables like the temperature or oil price
(Lafferty, 2001). Besides the fact that the contracts
agreements are not revealed, the common
parameters above mentioned, must be sent to
Independent System Operator before the quantities
agreed enter in the power system.
Figure 3: Electricity Power Market
Figure 2: UML model of the electricity retaile
r
syste
m
E-BUSINESS FOR THE ELECTRICITY RETAIL MARKET-A Business to Client perspective
153
To the retailer and his client point of view,
consumption analysis is relevant information. It
helps the costumer to identify his load profile and
behaviour, and gives to the retailer important
information for energy management services (Gaw,
1998).
The different types of tariffs that could be
implemented aren’t all supported by the old power
meters, but open new possibilities for retailer
aggregated services. Real time tariffs are only
available for consumers with smart meters and
costumers that could have an online communication
channel with the retailer. Table 1 presents the four
types of tariffs usually available. It is relevant to
explain the difference between these four tariffs. Flat
tariff is the traditional one. The estimation is based
and time blinded, without any variable
improvement. It is not possible to adapt for the
power market.
On the contrary, Time of Use represents the
natural evolution of the traditional power meter here
we have a internal clock to distinguished the
different periods of a 24 hours day. This way,
allows a transfer of the client’s loads from peak
periods to off peak periods. The price change in a 24
hours day, higher prices naturally at peak periods.
With the evolution of the power metering, the
automatic meter reading have is main support in a
communication channel. Real Time Price tariff
appears and have a direct connection to prices
established at the power market (Reed, 2000). The
power smart meters responds to inputs readings from
the retail centre. This static memory device has
internal algorithms programmed to react to market
prices oscillation. Besides the direct connection of
the Real Time Price tariff, this type is out of phase in
time with the wholesale power market.
Dynamic Tariff is the model that in a more
realistic way represents a real time pricing tariff
varying in periods of half or hour day during the 24
hours of a day. Smart meters could have real time
price changes, the communication structure must be
bidirectional and have additional algorithms for
price adjustment.
To better understand the communication
requirements of a retailer, we will analyse the
communication process of a client with dynamic
pricing tariff. At the first sight, the retailer only
needs to communicate once a day, sending the price
structure for the next day. A more efficient
alternative is to develop a dynamic price web server
for this type of clients. This way costumer could
access the prices list from the retail web server any
time they want.
Type of Tariff Price Costumers
Requirements
Flat Estimation
based. Local
meter reading.
Traditional
meter
TOU - Time
of Use
Prices varying
during a 24
hours day where
fixed intervals of
time.
Traditional
meter with an
internal clock
time periods in
a 24 h day.
RTP - Real
Time Price
Consumer prices
with a direct
connection to
prices at the
power market.
Smart meters
that responds to
inputs readings
from the retail
centre.
DP - Dynamic
Pricing
Prices varying in
periods of half or
hour day during
the 24 hours of
day.
Smart meters
with
bidirectional
communication
.
Suppose the same client is participating in a
load-reduction program, the retailer might want to
know the load reduction as it occurs, in which case
the communication from the customer’s meter to the
retailer needs to be either much more frequent or
based on a system that permits the retailer to poll the
customer’s meter at any time. This second approach
requires a meter with multiple communication ports
that can send dynamic-pricing and load-reduction
programs. The metering communication system
needs to move data and instructions between the
customer and its retailer, and perhaps automatic-
control systems will be needed to answer to time-
varying prices. The answer to these situations brings
us to reflect what should be the better structure to
support these requirements. An e-Business structure
Fi
g
ure 4: Bilateral Contracts
Table 1: Types of Tariffs
ICETE 2005 - GLOBAL COMMUNICATION INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND SERVICES
154

is no doubt, but what type of structure could better
improve this B2C platform.
The answer stills in the model presented in the
second hypothesis of the market model in section 2,
Fig.1 supported by the UML specific model
presented in fig. 2 the electricity retail model. This is
also supported by the Baligh-Richartz effect where
the reduction of number of contacts improves trade
efficiency and reduces its associated costs as shown
in (Wigand, 2003). Mediation overtakes the
incompatibilities between the buyers and the sellers
and focuses the attention on the transaction.
3.3 Security requirements
Any kind of web transaction to be successful must
be secure, surveys indicate the most important factor
that influences an online purchase is the security of
that transaction (Malek, 2004).
An issue of great importance is the security of
the B2C market, from both sides, the access to the
market and the information exchanged are
significant values to preserve. On the contrary to
other electronic markets the break of the security
market not only affects the information but also an
huge amount of resources in a directly or indirectly
way. An intruder that violates the system could
unbalance the market values, and as a consequence
the electrical system is affected as all the framework
that support it. Brownouts and blackouts can occur
affecting all the population served by that market.
The structure presented must answer to the basics
security parameters, authentication, confidentiality,
integrity, non-repudiation in all the online
transactions exchanged in this market.
Specifically the first step from the point of view
of the market operator is to be sure that the markets
participants are who they said to be, to do so an
authentication process must be required.
After this process the market operator must have
means to ensure the confidentiality of the
information exchanged. An encrypted end-to-end
method will increase the reliability of the security
system.
Non-repudiation is a grant that ensures the
responsibility of all market participants, and
consequently push them to take measures for their
security systems.
If besides the above measures an attack succeed
the market security system must have means of
recovery.
Besides the generic security issues there are
some specific of this type of market. As said above it
is allowed that clients could change between
electricity providers but it is necessary to prevent
unfair jumps between retailers without the financial
situation resolved. Each time a new contract is
settled, the verification must be granted by the ISO,
certifying the availability of these new contract
parameters for the physical structure of the electrical
system.
4 DISCUSSION
As we analysed above, retailers are necessary in any
type of electricity market structure and in the near
future their presence will be more essential. The
natural evolution of the electricity industry and
Internet technologies will bring a electricity web
retailer market for costumers with dynamic tariffs. It
makes sense they will have such a market, where the
client could choose between different type of
electricity prices, bundle of products and services.
Price is usually a main parameter to make a choice,
but there are other services that retailers could
associate over the electricity they provide and the
necessary metering. Other types of energy are
common to be bundle like fuel and gas, remote
control of interrupted loads, remote energy audits,
advising and giving support to new and efficient
equipment are some of the services that an
electricity retailer could offer. In fact Great Britain is
starting an electricity client retail market with
several competitors (about 38), from the client side
more than 100.000 per week change from suppliers
(Heath, 2004). Market efficiency is also supported
by retailer web auctions where savings range from 3
to 8% (Wigand, 2003).
5 CONCLUSION
The paper proposed a new electricity retail market
model, on a B2C web platform to clients with
dynamic price. In this model, a client could choose
between retailers (and the associated products and
services) that belong to this e-market. Besides
metering, billing, and remote tariffs control, retailers
provide remote services like energy audits, energy
management programs.
Price spikes at the wholesale market where the
cause of many brownouts and blackouts. In the first
phase of deregulation, prices at the final client
change once or twice a year. Retailers have to
support financially these oscillations. The model
proposed makes possible to solve this problem and
E-BUSINESS FOR THE ELECTRICITY RETAIL MARKET-A Business to Client perspective
155

creates efficient answers in the market. This way it’s
possible to better control demand and it’s resources.
The wholesales markets are trading for some
time and already tested, while retail e-markets are
only making the first steps. The Web is the right
platform for these markets, as for retailer e-
procurements programs. Some issues are raised for
futures improvements in retailer models, such as the
clients segmentation, could be stratified in several
ways, by power, by consumption, by economic
sector. Usually three types are at the top of this
hierarchy, industrial, commercial and domestic
clients. As the influence of on-line auctions grows,
customers are more likely to learn about the
potential savings that can be reaped through
aggregated purchasing via a centralized, low-cost
procurement channel.
We could talk in a second generation of
deregulation where market concentrate an
international electricity retail purchasing system,
which intention is to save money and electricity to
both sides of this web market, retailer and the final
costumer, as said before a win-win relation.
Efficiency is achieved by the competition among
retailers to keep and acquiring costumers. As a result
of this market web structure operational and product
costs are reduced.
REFERENCES
Bower, John, 1999, A Model-Based Comparison of Pool
and Bilateral Market Mechanisms for Electricity
Trading, Energy Markets Group, London Business
School
Cunningham, Paul R. 2001, Buying Energy in a
Deregulated Market, EnergyUserNews.
Gaw, David, 1998, Scalable, Integrated, Real-time Energy
Management Requirements and System Architecture,
Coactive Networks, Inc.
Heath, 2004, E-Business On-line retail energy
marketplaces take off in Britain - Platts Research &
Consulting
Lafferty, R.2001, Demand Responsiveness in Electricity
Markets, Office of markets, tariffs and rates.
Malek, Manu 2004, E-Business Security, Stevens Institute
of Tecnology.
Reed, L. William, 2000, Competitive Electricity Markets
and Innovative Technologies: Hourly Pricing Can
Pave the Way for the Introduction of Technology and
Innovation.
O´Sheassy, Michael, 2003, Demand Response: Not Just
Rhetoric, It can Truly Be the Silver Bullet, The
Electricity Journal.
ICETE 2005 - GLOBAL COMMUNICATION INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND SERVICES
156
