
A NEW MODEL FOR DATABASE SERVICE DISCOVERY IN
MOBILE AGENT SYSTEM
Lei Song, Xining Li, Jingbo Ni
Department of Computing and Information Science , University of Guelph, Guelph, Canada
Keywords: Mobile agents, Service discovery
Abstract: One of the main challenges of mobile agent technolog
y is how to locate hosts that provide services specified
by mobile agents. As it is a newly emerging research topic, few research groups have paid attention to
offering an environment that combines the concept of service discovery and mobile agents to build dynamic
distributed systems. Traditional Service Location Protocols (SDPs) can be applied to mobile agent systems
to explore the Service Discovery issue. However, because of their architecture deficiencies, they do not
adequately solve all the problems that may arise in a dynamic domain such as Database Location Discovery.
From this point of view, we need some enhanced service discovery techniques for the mobile community.
This article proposes a new model for solving the database service location problem in the domain of mobile
agents by implementing a Service Discovery Module based on Search Engine techniques. As a typical
interface provided by a mobile agent server, the Service Discovery Module also improves the self-decision
intelligent ability of mobile agents with respect to Information Retrieval. This work focuses on the design of
an independent search engine, IMAGOSearch and a discussion of how to integrate it with the IMAGO
System, thus providing a global scope service location tool for intelligent mobile agents
1 INTRODUCTION
The number of services that will become available in
distributed networks (in particular on the Internet) is
expected to grow enormously. Besides classical
services such as those offered by printers, scanners,
fax machines, and so on, more and more services
will be available nowadays. Examples are
information access via the Internet, music on
demand and services that use computational
infrastructure that has been deployed within the
network (Bettstetter & Renner, 2000). Moreover, the
concept of service in mobile agent systems, which
will be described in this paper, comes into notice
recently.
The mobile agent (MA) model is a new
di
stributed software development paradigm as
compared to traditional client-server model. Instead
of calling operations on servers with some forms of
synchronization, the user passes its goal to an agent
that can migrate within the computational
environment and know how to handle it without
being controlled. In brief, mobile agents are active,
autonomous, intelligent objects that are able to move
between locations in a so-called agent system.
Mobile agents must interact with their hosts in order
to use their services or to negotiate services with
other agents (Song & Li, 2004). There are two
reasons: first, the agents possess local knowledge of
the network and have a limited functionality, since
only agents of limited size and complexity can
efficiently migrate in a network and have little
overhead. Hence specific services are required
which aim at deploying mobile agents efficiently in
system and network management; second, mobile
agents are subject to strong security restrictions,
which are enforced by the security manager. Thus,
mobile agent should find services that help to
complete their tasks. Following this trend, it
becomes increasingly important to give agents the
ability of finding and making use of services that are
available in a network (Bettstetter & Renner, 2000).
Some of the mobile agent systems developed in
the last years a
re Aglets (Lange & Ishima, 1998) by
IBM, Voyager (ObjectSpace Inc, 1997) by
ObjectSpace, Grasshopper (Baumer et al., 1997) by
IKV, and Concordia (Mitsubishi Electric, 1998) by
Mitsubishi. Systems developed for university-based
research are for example D'Agents (Gray et al.,
214
Song L., Li X. and Ni J. (2005).
A NEW MODEL FOR DATABASE SERVICE DISCOVERY IN MOBILE AGENT SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 214-219
DOI: 10.5220/0002512602140219
Copyright
c
SciTePress

1998) and MAP (Puliato et al., 1997). Research in
the area of mobile agents looked at languages that
are suitable for mobile agent programming, and
languages for agent communication. Very much
effort was put into security issues, control issues,
and design issues. However, few research groups
have paid attention to offering an environment to
combine the concept of service discovery and
mobile agents to build dynamic distributed systems.
In this paper, we propose a new service
discovery model DSSEM (Discovery Service Via
Search Engine Model) in mobile agent systems by
using the Search Engine, a global web search tool
with centralized index and fuzzy retrieval. This
model especially aims at solving the database
service location problem in our mobile agent system
IMAGO. In our model, mobile agents are used to
support applications, and service agents are used to
wrap database services. Service providers manually
register their services in the service discovery server.
A mobile agent locates a specific service by
submitting requests to the service discovery server
with the description of required services. Web pages
are used to advertise services. The design goal of our
model is to provide a flexible and efficient service
discovery environment in distributed systems.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we present a brief background related to
this project and bring up the problem of service
discovery in mobile agent systems. Section 3
presents the new model DSSEM and compares it
with several Service Discovery Protocols (SDPs)
currently under development. Section 4 gives an
overview of the IMAGO system and the design of
service discovery module. Finally, we give the
concluding remarks of this paper in Section 5.
2 BACKGROUND AND
MOTIVATION
The general idea of distributed services is that the
application may be separated from the resources
needed to fulfil a task. These resources are modelled
by services, which are independent of the
application. Services do not denote software services
alone, but any entities that can be used by a person, a
program or even another service (Hashman &
Knudsen, 2001). Service discovery is a new research
area that focuses not just on offering plug and play
solutions but aims to simplify the use of mobile
devices in a network allowing them to discover
services and also be discovered (Ravi, 2001).
The service usage model is role-based. An entity
providing a service that can be utilized by other
requesting entities acts as a provider. Conversely,
the entity requesting the provision of a service is
called a requester. To provide its service, a provider
in turn can act as a requester making use of other
services. To form a distributed system, requesters
and providers live on physically separate hosting
devices. Providers should from time to time
advertise services by broadcasting to requesters or
registering themselves on third party servers. From
requests' point of view, it must:
• search and browse for services,
• choose the right service (with desired
characteristics), and
• utilize the service.
Before a service can be discovered, it should tell
a known client about itself. This process is called
Service Advertisement. This work can be done when
services startup, or every time they change their
states via broadcasting to anyone who is listening.
Advertisement can just consist of a service
identifier, or a simple string saying what the service
is, or a set of strings for names plus attributes. An
example is given in Table 1.
Table 1: A Typical Advertisement of Service.
type : printers/postscript/HP20
speed : 24ppm
colour : yes
There are several ways that a client looks up the
service it requires. If the client knows a direct
address of a service, it can make requests directly; or
it can listen to broadcasting advertisements and
select those it wants. The common method is that it
forms a description of desired service and asks a
known discovery server if it knows any service
matching the requests.
A variety of Service Discovery Protocols (SDPs)
are currently under development by some companies
and research groups. The most well known schemes
are: Sun's Java based Jini
TM
(Sun, 1999), Salutation
(Salutation Consortium, 1998), Microsoft's
(Universal Plug and Play, 2000) as well as IETF's
draft Service Location Protocol (SLP) (Guttman et
al., 1999). These SDPs are extended and applied by
several mobile agent systems to solve the service
discovery problem. For example, GTA/Agent
(Rubinstein & Carlos, 1998) addresses the service
location issue by extending SLP, a simple,
lightweight protocol for automatic maintenance and
advertisement of intranet services. Though SLP
provides a flexible and scalable framework for
enabling users to access service information about
existence, location, and configuration, it only
possesses a local function for service discovery and
A NEW MODEL FOR DATABASE SERVICE DISCOVERY IN MOBILE AGENT SYSTEM
215

is not scalable up to global Internet range because it
uses DHCP and multicast instead of a central lookup
(like Jini) mechanism. AETHER (Chen, 2000)
makes an improvement to Jini by building a
dynamic distributed intelligent agent framework.
However, it is reliant on the use of standard Java-
based interfaces implemented by both the clients and
servers in their work. After a study of different SDPs
and mobile agent systems that are adopting these
methods, we found that several problems cannot be
solved by the existing protocols due to their
limitations.
First of all, most existing works support an
attribute-based discovery as well as a simple name
lookup to locate a service. Usually there is only a set
of primitive attribute types in the service description,
such as String and Integer, to characterize a service.
Thus, the service discovery process is primarily
achieved by type matching, string comparison etc.
Here we define service description as: a sequence of
flags or codes that can be multicast to service
requesters or be registered on a third-party server for
advertisement purposes. For example, in SLP, the
value of type tag in its service description should be
“service:printer”; it can also contain some other
property tags to describe this printer in detail, such
as “paper per min. = 9” or “colour-support = yes”
(see Table 2). In the searching phase, much of the
power of SLP derives from its ability to allow exact
selection of an appropriate service from among
many other advertised services with the same tags.
This is done by requesting only the service or
services that match the required keywords and
attribute values requested by the users. These
keywords and attribute values can be combined into
boolean expressions via “&” and “|”, or common
comparators “<=”, “>”, or substring matching.
Table 2: An Example of SLP Service Description
type = service: printer
scope = administrator, bmw
name = lj4050
paper per min. = 9
colour-support = yes
usage = //li4050.com: 1020/queue1
A further step in SDPs is using Extensible
Markup Language (XML) to describe services. An
XML description can be converted to a Java
document model (DOM) object so that it can be
merged into a service registry system. However, no
matter what kind of format is applied, the essence of
lacking rich representation for the service
description has not been changed. The problem
arising directly in our project is that these protocols
are not adequate to advertise some special services,
such as a database service. A database system
already has a well-defined interface and all we
require is a way of finding the location of specific
databases and deciding where to move. In this
situation, the only way we can do is by registering
the database's name and columns for future
discovery. However, for a database service, people
care more about the content recorded in this
database than its name or structure. Considering an
example of a bookstore, before placing an order to
the bookstore, customers would like to know if the
books they require are available in the store by
checking the summary of all books with some
keywords or a fuzzy search criterion. From this point
of view, how can a simple string identifier or XML
identifier meet the requirement?
The second problem is ranking. After requesters
have searched out all services that may be required,
they still need to select the right one for utilization.
Just imagine over the entire Internet, tens of
thousands of providers could publish their services
by their own will. We should be able to know which
ones provide the most realistic and highest quality
services the users want. Apparently moving to their
hosts one by one to find out the required information
is not a wise choice. Therefore, to generate a service
rank is a necessity. However, none of the existing
SDPs has such a mechanism for ranking discovered
services. They are satisfied with finding a service
only, but do not consider whether the service would
be able to serve the requester.
The most significant contribution we make is
that we enrich the service description by using
webpage’s URL (later the search engine will index
the content referenced by this URL) to replace the
traditional string-set service description in mobile
agent systems. Because of their specific
characteristics, such as containing rich media
information (text, sound, image etc.) and being able
to reference to each other, webpages play a key role
acting as the template of the service description.
Since the search engine is an automated indexing
tool that can provide a highly efficient ranking
mechanism for the collected information, it is also
useful for acting as the directory server in our
model.
3 DISCOVERY SERVICES VIA
SEARCH ENGINE MODEL
(DSSEM)
As the most important media type on the Internet
today, hypertext webpages are posted to advertise
the information by industries and individuals.
ICEIS 2005 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
216
Though millions of them are published on the
Internet, these webpages still increase rapidly
everyday for a variety of reasons. They are spidered
and indexed by commercial search engines such as
Google, Yahoo,
AltaVista, etc. Users can easily find
webpages’ locations by submitting the search
request to those search engines. In principle, if we
install a search engine on the service discovery
server that could retrieve webpages posted by
service providers and design a web search interface
for the incoming mobile agents, the problems
described previously could be solved perfectly. In
this situation, service providers don’t need to
register the service description on the service
discovery server. Instead they register the URLs of
their websites that advertise all the information
concerning services. As a middleware on the service
discovery server, the search engine will periodically
retrieve the document indicated in URLs and all
their referencing documents, parse all tags and
words in documents and setup the relationship
between the keywords and the host address of these
service providers. On the other hand, mobile agents
can utilize the system interface by accessing the
search engine’s database and obtain a destination
itinerary that includes a list of ranked host addresses
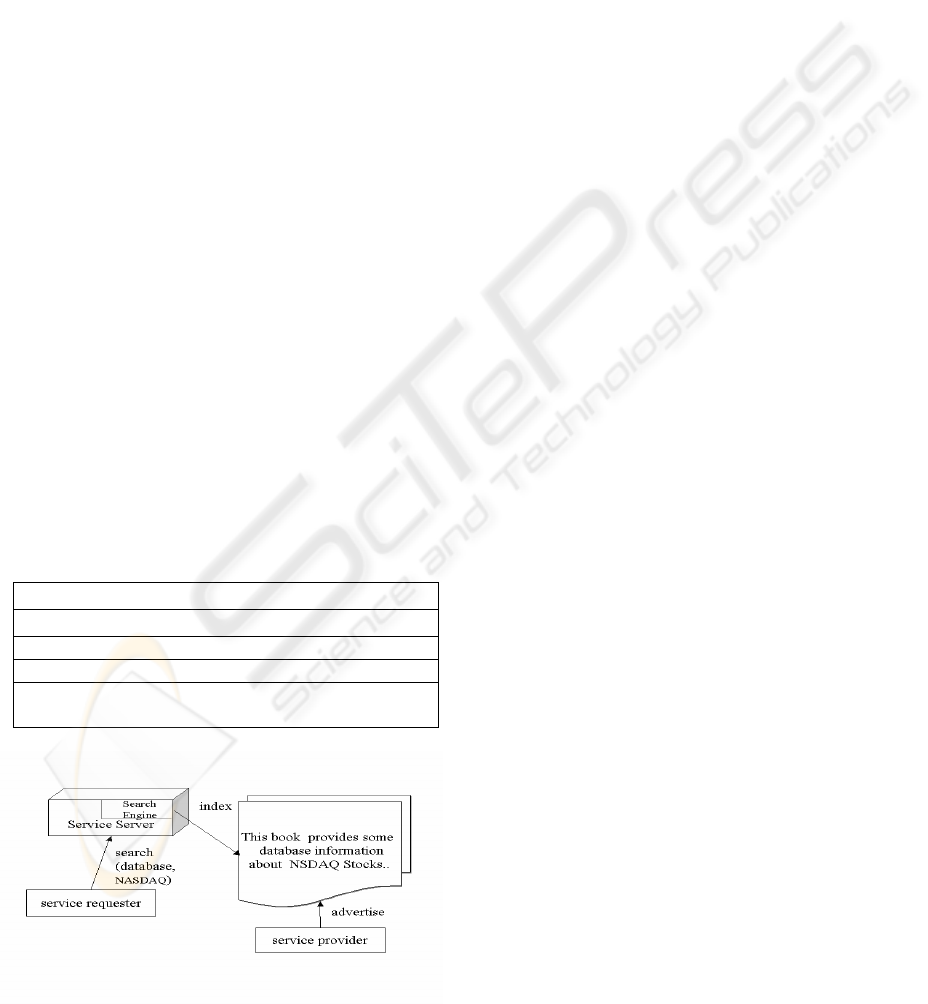
of the service providers (Figure 1).
To use webpages as a medium to advertise
services for the service provider, we should modify
the template in the service description of SLP. The
remarkable change is some properties once
represented by strings or XML language are now
represented by website's home URL. Table 3
illustrates a service description template of the
bookstore example.
Table 3: An Example of DSSEM Service Description
type = service: database
name = bookstore
URL = //www.cis.uoguelph.ca/
location(URL)= www.uoguelph.ca
interface = dp_get_set(Handler, ‘SQL statement’,
Result_handler)
Figure 1: The architecture of DSSEM
The proposed model is similar with SLP and Jini
in the aspect of service discovery process, but
extending those protocols by setting up a
centralized, seamless, scalable framework on the
Internet. Unlike some protocols multicasting
services in the intranet wide, the centralized service
discovery server makes DSSEM service discovery
available on the world wide Internet. The process of
registration and discovery is similar to the lookup
service in Jini technique. Besides that, new features
of mobile agents endow DSSEM with other
incomparable advantages. First, code mobility is
almost impossible in most distributed systems.
Therefore a client must download the device drivers
to use invoke services. To solve this problem, Jini
uses Java Remote Invocation (RMI) to move
program code around network. DSSEM goes one
step further. It makes agents migrate to the
destination hosts and utilize services locally.
Second, the security issue is seldom considered in
current SDPs. However, mobile agent server
requires a strict security concern for authorization
and authentication when they accept the incoming
agents and providing them services for utilization.
4 SERVICE DISCOVERY IN THE
IMAGO SYSTEM
IMAGO is a Mobile Agent System whose
abbreviation stands for “Intelligent Mobile Agent
Gliding On-line”. Imagoes (mobile agents) are
programs written in a variant of Prolog that can fly
from one host on the Internet to another. That is, an
imago is characterized as an entity that is mature
(autonomous and self-contained), has wings
(mobility), and bears the mental image of the
programmer (intelligent agent) (Song & Li, 2004).
The IMAGO project requires two kinds of agent
servers: stationary server and remote imago server.
The stationary server of an application is the server
where the application is invoked. On the other hand,
imagoes of an application are able to migrate to
remote imago servers. Like a web server, a remote
imago server must have either a well-known name
or a name searchable through the Internet name
binder. This kind of server should provide services
for network computing, or interfaces to other
Internet servers, such as web servers, database
servers etc. (Li, 2003).
The IMAGO System is an infrastructure that
implements the agent paradigm. IMAGO Server
(Figure 2) resides at a machine intending to host
imagoes and provides a protected imago execution
environment. Its tasks include accepting agents,
A NEW MODEL FOR DATABASE SERVICE DISCOVERY IN MOBILE AGENT SYSTEM
217

creating a secure run time environment and
supervising agent execution. It must also organize
agent transfer to other hosts, manage
communications among agents, authenticate and
control access for agent operations, and provide
some basic services for the agents, such as Database
Service and Service Discovery Service. To achieve
this, we have considered some issues such as
garbage collection, code migration, communication
mechanism, security and service, etc. Several system
threads are generated on IMAGO Server to deal with
those resident imago threads that are being executed
at different phases. Database Service and Service
Discovery Service are provided by some of these
system threads.
In the early phase of system design, database
operation becomes the major service to applications
in the IMAGO system. Since database interfaces
have been defined as build-in primitives for mobile
agents, the problem of service discovery focus on
how to utilize it.
Before a database service is advertised, the
service provider should fill a registration form and
submit it to IMAGO service discovery server. The
Figure 2: The Process of Web Search Module
contents of this form include: Service Type,
Database Name, URL of the service provider host,
Access Mode, Http URL of their website, interface
function, and the verification information. We
choose URL as the host address since it is
compatible with web browser and independent of
address families (like IP, IPv6 and IPX).
The service discovery module in the IMAGO
system is called Web Search module. The service
discovery server is called service location host. A
search engine called IMAGOSearch should be
independently installed on the service location host.
Search engine is a database system designed to
index Internet addresses (URLs, Usenet, Ftp, image
locations etc). The traditional search engines contain
a special program usually called a spider (or
sometimes a "crawler") which can accept an URL
and then go to that website and retrieve a copy of the
file found there. The search engine will process that
copy of the file later, distilling it down to the bare
essential data to form the database. IMAGOSearch
consists of three main components: Spider, Indexer
and Searcher that are grouped into two modules.
One module includes Spider and Indexer, running at
the background of IMAGO service location host,
and standing alone with IMAGO Server. First, the
Spider gets the URLs from an URL List that stores
initial http URLs of service providers’ websites.
Then, it traverses the hypertext documents pointed
by these URLs in the WWW. These documents are
then loaded and salient words are extracted from the
documents by the Indexer. Some features such as
texts are saved on central unit’s database for user
retrieval. Finally, the Indexer looks for URL anchors
that reference to other documents and adds them to
the URL List. Besides considering the weight of
each word in the query (for example, occurrence in
title should be assigned a higher weight than that in
the body part), IMAGOSearch also pays attention to
positions of each word and their relativity when
ranking. The algorithm we use called shortest -
substring ranking (Charles et al., 2000). Another
module of IMAGO search engine is the Searcher, an
interface function that connects the search engine
and IMAGO Server. Its responsibilities are
accepting the search requests from mobile agents,
querying the database, ranking search results and
finally returning a destination itinerary (Figure 3).
5 CONCLUSION
The most critical issue about search engine's
performance is the quality of search results.
However, we cannot compare it with the major
commercial search engines since they are standing at
different levels. Thus the user evaluation is beyond
the scope of this paper, however a result can be
displayed that illustrates some features of
IMAGOSearch. Table 4 shows IMAGOSerach's
results for a query on keyword “imago lab”. All
results are reasonably high quality pages and, at last
check, none were broken links. An Rw value is a
calculated value returned by the search engine’s
ranking algorithm. We consider the result that has
the highest Rw value as the highest priority result
and assign it a hundred percent rate, the other
results’ percent rates are relative values of it, on a
probated basis.
ICEIS 2005 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
218

Table 4: Search Results of ‘imago lab’
draco.cis.uoguelph.ca Rw= 13.8 100%
( www.cis.uoguelph.ca Rw= 10.65 77%
www.uoguelph.ca Rw= 4.6 33%
www.cas.mcmaster.ca Rw= 4.23 30.6%
When a mobile agent wants to locate certain
services, it first moves to the service discovery
server, then makes a local query and migrates to the
destination hosts after obtaining the itinerary. This
bring us a problem that as the central unit, the
service discovery server becomes a bottleneck when
it is handling thousands of web pages everyday and
simultaneously hosting as many incoming mobile
agents as possible. Can we balance the load in a
distributed environment? The answer is positive. For
this purpose, we installed several service discovery
servers. When an agent begins to search, it moves to
the first service discovery server, if the server is
shutdown or the movement fails, the agent
backtracks and moves to the second one, and so on.
This kind of organization makes our service
discovery mechanism very efficient and reliable.
Finally, we would like to express our
appreciation to the Natural Science and Engineering
Council of Canada for supporting this research.
REFERENCES
Baumer, C., Breugst, M., & Choy, S., 1999, Grasshopper -
a universal agent platform based on OMG MASIF and
FIPA standards, In Proc. of the First International
Workshop on Mobile Agents for Telecommunication
Applications (MATA’99), pp. 1–18.
Bettstetter, C., Renner, C., 2000, A Comparison of Service
Discovery Protocols and Implementation of the
Service Location Protocol, In Proc. of EUNICE 2000,
sixth EUNICE Open European Summer School,
Netherlands.
Charles L., Clarke, A., & Gordon V., 2000, Shortest
Substring Retrieval and Ranking, ACM Transactions
on Information Systems, p 44-78
Chen, H., 2000, Developing a dynamic distributed
intelligent agent framework based on Jini architecture,
Master Thesis, University of Maryland Baltimore
County.
Gray, S., Cybenko, G., & Kotz, D., 1998, D'Agents:
Security in a multiple language, mobile agent system,
Mobile Agents and Security, Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, vol. 1419, Springer, New York.
Guttman, E., Perkins, C., & Veizades, J., 1999, Service
Location Protocol, Version 2, White Paper, IETF,
RFC 2608.
Hashman, S., Knudsen, S., 2001, The Application of Jini
Technology to Enhance the Delivery of Mobile
Services, White Paper, http://wwws.sun.com/.
John, R., 1999, UPnP, Jini and Salutaion—A look at some
popular coordination framework for future network
devices”, Technical Report, California Software Labs.
Li, X., 2003, IMAGO Prolog User's Manual version 1.0,
Technical Report, University of Guelph.
Lange, D., Ishima, M., 1998, Programming and Deploying
Java, Mobile Agents with Aglets, ISBN: 0201325829,
Addison-Wesley.
Mitsubishi Electric ITA, 1998, Mobile Agent Computing
– A White Paper, White Paper.
ObjectSpace Inc., 1997, ObjectSpace Voyager Core
Package Technical Overview: The Agent ORB for
Java, White Paper, http://www.objectspace.com/
voyager.
Puliato, A., Tomarchio, O., & Vita, L., 1997, MAP:
Design and Implementation of a Mobile Agents
Platform, Technical Report TR-CT-9712, University
of Catania.
Ravi, N., 2001, Service Discovery in Mobile
Environments, Technical Report, Department of
Computer Science and Engineering, University of
Texas, Arlington.
Rubinstein, M., Carlos, O., 1998, Service Location for
Mobile Agent System, IEEE/SBT International
Telecommunications Symposium (ITS'98), pp. 623-
626.
Salutation Consortium, 1998, Salutation Architecture
Overview, White Paper, http:// www.salutation.org/
whitepaper/originalwp.pdf.
Song, L., Li, X., 2004, Locating Services for Intelligent
Mobile Agents, In Proc. of 19th International
Conference on Computers and Their Applications, pp.
308-312.
Sun. Technical, 1999, Jini Architectural Overview, White
Paper, http://www.sun.com/jini/.
Universal Plug and Play Forum, 2000, Universal Plug and
Play Device Architecture, Version 0.91, White Paper.
A NEW MODEL FOR DATABASE SERVICE DISCOVERY IN MOBILE AGENT SYSTEM
219
