
DISTANCE LEARNING BY INTELLIGENT TUTORING SYSTEM
Part I: Agent-based architecture for user-centred adaptivity
Antonio Fernández-Caballero, José Manuel Gascueña
Computer Science Reseach Institute of Albacete, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Albacete, Spain
Federico Botella, Enrique Lazcorreta
Operations Research Centre, University Miguel Hernandez of Elche, Elche, Spain
Keywords: Intelligent Tutoring System, Agent system, Arch
itecture, E-learning, E-teaching, Adaptivity
Abstract: Agent technology has been suggested by experts to be a promising approach to fully extend Intelligent
Tutoring Systems (ITS). By using intelligent agents in an ITS architecture it is possible to obtain an
individual tutoring system adaptive to the needs and characteristics of every student. The general
architecture of the ITS proposed is formed by the three components that characterize an ITS – the Student
Model, the Domain Model, and the Education Model. In the Student Model the knowledge that the system
has about the student (profile and interaction with the system) is represented. In the Domain Model the
knowledge about the contents to be taught is stored. Precisely, in this model four autonomous agents – the
Preferences Agent, the Accounting Agent, the Exercises Agent and the Tests Agent - have been defined.
Lastly, the Education Model provides the functionality that the teacher needs. Across this module, the
teacher changes his preferences, gives reinforcement to the students, obtains statistics and consults the
matter.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agent technology has been suggested by experts to
be a promising approach to fully extend Intelligent
Tutoring Systems (ITS). By using intelligent agents
in an ITS architecture it is possible to obtain an
individual tutoring system adapted to the needs and
characteristics of every student (Frigo, Pozzebon &
Bittencourt, 2004). In this article, an agent-based
Intelligent Tutoring System architecture for user-
centred adpativity in e-learning/e-teaching of any
matter is introduced. A detailed description of the
agents which monitor the progress of the students
and propose new tasks is also provided. The ITS
proposed is not tied to any course in particular,
being the only requisite that the course has to be
divided into theory, exercises and tests.
Many learning/teaching computer-based
envi
ronments framed in the form of ITS use agent
technology. For example, Cheikes has developed
GIA (Generic Instructional Architecture), an agent-
based software infrastructure devoted to support
rapid development of ITS applications (Cheikes,
1995). Tang carried out the implementation of a
multi-agent intelligent tutoring system for the
learning of computer programming (Tang & Wu,
2000). Capuano has described ABITS, a highly
reusable Intelligent Tutoring Framework suitable to
several knowledge domains (Capuano, Marsella &
Salerno, 2000). A multi-agent system named
MASPLANG developed for the adaptation of the so-
called teaching support units has been introduced
(Peña, Marzo & de la Rosa, 2002). Hospers et al.
have presented an agent-based ITS for nurse
education (Hospers et al., 2003). And there are many
more approaches in distance learning (e.g., Bello &
Bringsjord, 2003; Mota, Oliveira & Mouta, 2004;
Kinshuk et al., 2001; de Antonio et al., 2003; Dorça,
Lopes & Fernández, 2003; Pesty & Webber, 2004;
Baldoni, Baroglio & Patti, 2004).
An ITS usually also incorporates pedagogical
agents
(animated characters) to do learning more
attractive and effective. For example, there is Adele
for medical education (Shaw et al., 1999), and
AutoTutor for the students to learn the fundamentals
of computer hardware, the operating system, and the
Internet (Person & Graesser, 2000). SONIA is the
animated agent incorporated in MASPLANG. The
75
Fernández-Caballero A., Manuel Gascueña J., Botella F. and Lazcorreta E. (2005).
DISTANCE LEARNING BY INTELLIGENT TUTORING SYSTEM - Part I: Agent-based architecture for user-centred adaptivity.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 75-82
DOI: 10.5220/0002519500750082
Copyright
c
SciTePress

architecture that we introduce in this article does not
incorporate at present any animated agent.
The layout of the paper is as follows. In section 2
a definition of ITS is provided as its most common
features are introduced. In section 3 we define what
an agent is. In section 4 the aims of our agent-based
ITS are explained. From section 5 on, the ITS
architecture is introduced. Lastly, some conclusions
are provided.
2 DEFINITION OF AN ITS
ITS are programs that possess a wide knowledge on
a certain matter, and their intention is to transmit this
knowledge to the students by means of an interactive
individualized process, trying to emulate the form in
which a tutor or human teacher would guide the
student in his learning process (Millán, Agosta &
Pérez, 1999).
Thus, ITS for sure are systems of knowledge
communication. They can be defined that way
because the principal emphasis in the development
of these systems is to provide them with access to
the representation of the knowledge that the system
tries to communicate to the student.
In an ITS the emphasis is put in the knowledge
(what) to being communicated to the student and not
in the mechanism (how) of communication used to
present the knowledge to the student.
Generally speaking, ITS are characterized for
incorporating three models corresponding to three
knowledge levels (see figure 1). Firstly, there is a
Domain Model where the Knowledge of the Domain
is gathered, that is to say the knowledge of what has
to be taught. A Student Model represents the
Knowledge of the Student, that is to say all things
the student knows on the domain. Finally, there is a
Pedagogical Model where the Knowledge of the
Instructional strategies is described; that is to say,
how to teach the Domain Knowledge.
Figure 1: Components of an ITS
3 DEFINITION OF AN AGENT
There is no universally accepted definition for the
term agent, but there are is a wide range of
perspectives in function of the application domain,
the author, and so on.
Franklin and Graesser state: “An autonomous
agent is a system situated within and a part of an
environment that senses that environment and acts
on it, over time, in pursuit of its own agenda and so
as to effect what it senses in the future.” (Franklin &
Graesser, 1996).
Any agent, in accordance with this definition,
satisfies the four properties as indicated next:
• autonomy: agents operate without the direct
intervention of humans or others, and have
some kind of control over their actions and
internal state;
• social ability: agents interact with other agents
(and possibly humans) via some kind of
agent-communication language; agents
collaborate for the sake of performing tasks;
• reactivity: agents perceive their environment,
(which may be the physical world, a user via a
graphical user interface, a collection of other
agents, the Internet, or perhaps all of these
combined), and respond in a timely fashion to
changes that occur in it; in order to respond
effectively to changes, agents have to know at
each instant their surrounding “world”;
• pro-activeness: agents do not simply act in
response to their environment, they are able to
exhibit goal-directed behaviour by taking the
initiative.
4 OBJECTIVES OF THE AGENT-
BASED ITS
The ITS proposed in this paper creates an
infrastructure for distance learning/teaching of a
matter. In accordande with our experience, and in
order to obtain good results, we propose to
decompose the matter to be taught into theory,
exercises and test questionnaires (see figure 2). The
alumni study each topic of the matter reading theory
first, then making exercises and finally answering to
a test. The system will provide help the students
whenever it will be felt necessary.
ICEIS 2005 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
76
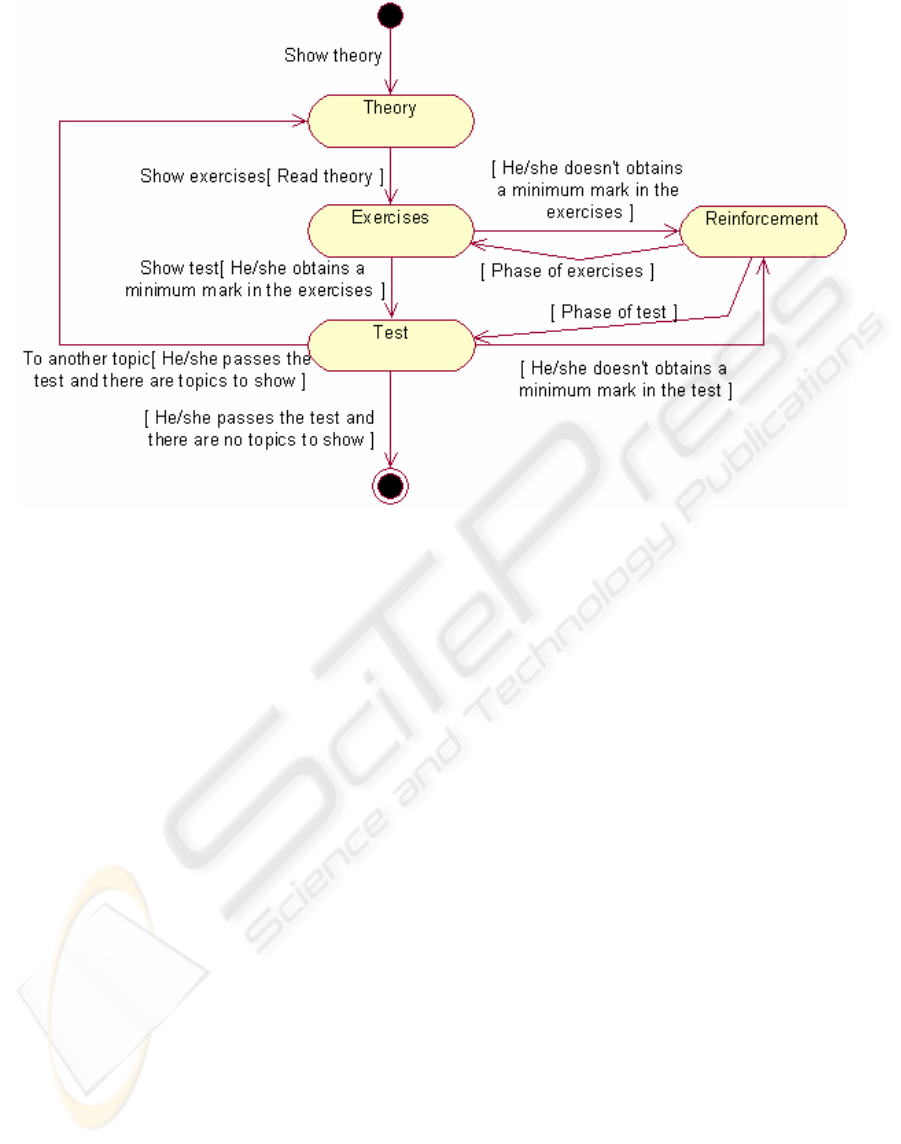
Figure 2: Decomposition of the matter
The first goal of the ITS proposed is that the
alumni learn more and better, that is to say, the
system has to be able to structure learning matter in
such a way to facilitate learning as much as possible.
One the most desirable characteristic to take into
account in learning is the rhythm the student is able
to learn. Thus, the ITS has to adapt the rhythm in
which it introduces the concepts to the learning
rhythm of each student (for instance, to show more
or less exercises, to show more or less tests, etc.).
Another aspect widely considered in learning theory
is reinforcement by rewarding a correct answer and
penalizing the errors (by means of messages, sounds,
etc.).
The second goal in our environment is to
enhance teaching in the same way as learning. One
of the main problems a professor faces when
teaching is that he does not know the skills of his
alumni. Our proposal leads to conclusions that
“teach how to teach”. Within this objective there is
the need to make the matter more comprehensive for
the overall alumni, but always keeping in mind the
requisites given to the subject.
5 ARCHITECTURE OF THE ITS
The general architecture of our ITS (see figure 3) is
formed by the three components that characterize an
ITS, as explained before – the Student Model, the
Domain Model, and the Education Model. In the
Domain Model four agents have been added to
provide the system of a user-centred adaptivity
capacity.
In the Student Model the knowledge the system
has about the student (profile and interaction with
the system) is represented. The model is composed
of three knowledge databases (KDBs). (1) The
Personal Information KDB stores the necessary
personal information of the student to control his
access to the system. (2) The Profiles KDB stores
the level as well as the presentation styles of the
students. The students are assigned different levels
depending on their learning rhythm. (3) The
Learning KDB stores parameters such as the
exercises and tests proposed so far to the students,
the time spent on answering the questionnaires, the
pages of theory visited and the scrolls performed on
those pages, or the reinforcement material prepared
by the Pedagogic Module.
In the Domain Model the knowledge about the
contents to be taught is stored. This model consists
of four KDBs: (1) the Theory KDB incorporates the
pages of theory that have been prepared for teaching
the matter, (2) the Tests Questionnaire KDB stores
the battery of test questions related to the matter, (3)
the Exercises KDB stores the battery of exercises on
the matter, and, (4) the Reinforcement KDB contains
the information used by the Pedagogic Module to
prepare the material to be shown when a student
needs to be reinforced.
DISTANCE LEARNING BY INTELLIGENT TUTORING SYSTEM. Part I: Agent-based architecture for user-centred
adaptivity
77

Figure 3: Architecture of the agent-based ITS system
The Pedagogic Module provides the necessary
mechanisms to efficiently present the matter to the
student. This module is in charge of carrying out
three tasks: (1) to provide the learning guidelines for
the student (including any necessary reinforcement
provided by the system), (2) to update statistics in
the Domain Model of the exercises and tests
presented, (3) to store into the Learning KDB
important data such as the material prepared to
reinforce the student who needs it, the responses
given by the student to the exercises and tests
proposed, as well as the scores that the student has
gotten and the time that he has spent in reaching the
aims.
The Preferences Agent supervises the user
preferred style of presentation (type and size of
letter, colors, margins, and so on). When the user
changes his style of presentation the Preferences
Agent creates a personalized sheet of styles for the
user and updates the user's interface in accordance
with his new pleasures. The information that this
agent gathers is stored in the Profiles KDB. The
Accounting Agent observes the student interaction
with the interface when the pupil accesses a page of
theory. When the student changes to another page of
theory, the Accounting Agent stores in the Learning
KDB some valuable information (the name of the
visited page, the time that the student has spent on it
and the scrolls performed on it). The Exercises
Agent takes charge of choosing the exercises that
will be proposed to the student in the topic that he is
currently studying. This agent stores the chosen
exercises in the Learning KDB as well. In the same
way, the Tests Agent is in charge of choosing the
test questions that will compose a test questionnaire
proposed to the student in the topic that he is
studying at this moment. The test questions selected
are also stored in the Learning KDB. The Exercises
Agent and the Tests Agent do the selection when the
student finishes the first visit to the first page of
theory of every topic. We may highlight that the
Exercises Agent and the Tests Agent are proactive
because they carry out their tasks in parallel with the
activity that the student performs. Indeed, the
student is reading theory without realizing the work
of both agents.
Lastly, the Education Model provides the
functionality that the teacher of the system needs.
Across this module the teacher changes his
preferences, gives reinforcement to the students,
obtains statistics and consults the matter. This model
is in fact devoted to help the teacher to change the
contents of the matter on the basis of the information
obtained from the Student Model and the Domain
Model.
ICEIS 2005 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
78
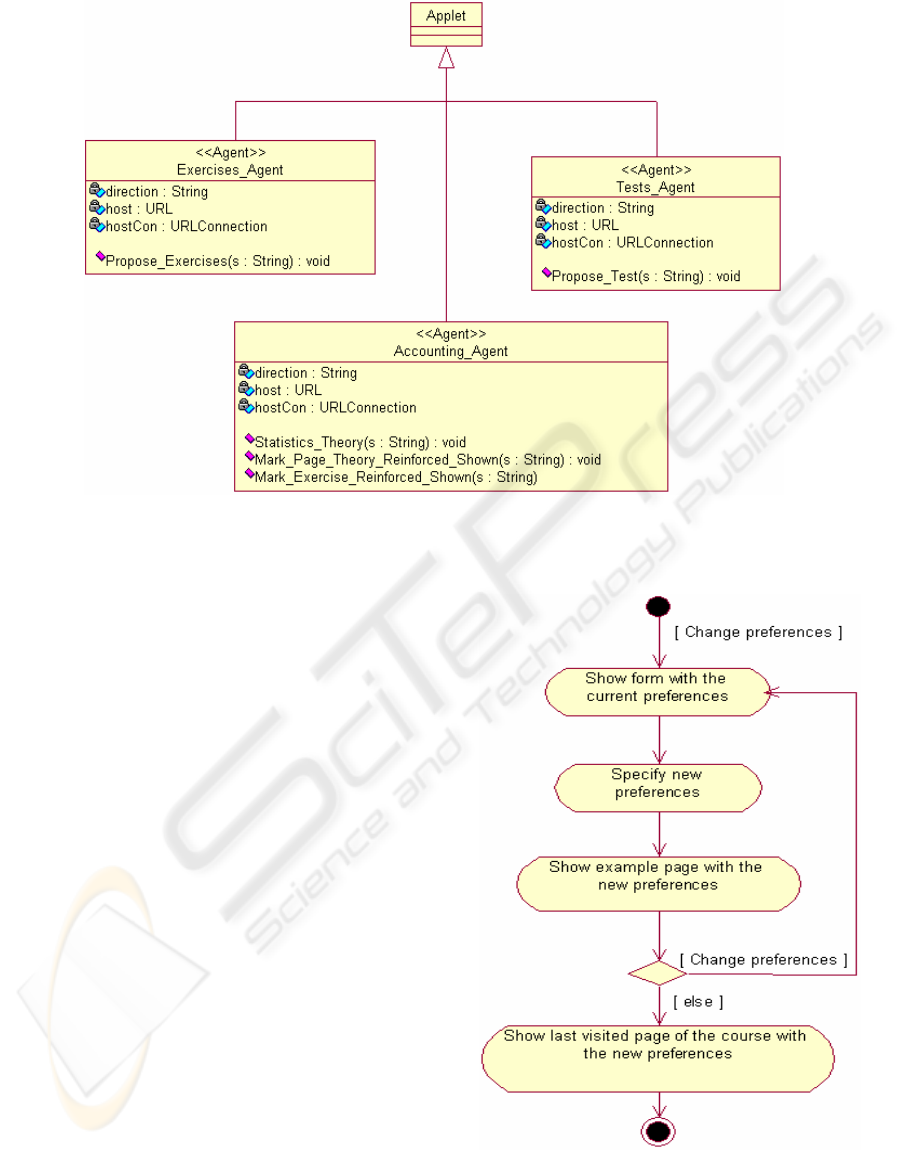
Figure 4: Agent class diagram
6 DESIGN OF THE AGENTS
As it may be observed in figure 4, agents have been
implemented as applets.
6.1 Preferences Agent
The Preferences Agent supervises the style of
presentation that the user likes. The Preference
Agent perceives the interaction of the student with
the user interface and acts when he changes his
tastes. The preference agent is continually running to
know the student’s preferences at any time.
The p
rocess that follows when the user decides
to change his visual preferences is shown in figure 5
as an activity diagram for activiy “Change
preferences”. When the student decides to “Change
preferences”, the Preferences Agent shows him a
form with the preferences that he has selected up to
this moment. This way the user can perform the
changes when he considers that are appropriate.
After having completed the form, the new
selected preferences are updated and an example
page is shown to the student with all the features of
the new selected style of presentation. If the student
does not like the page, he may continue changing his
preferences.
Figure 5: Activity diagram for “Change preferences”
DISTANCE LEARNING BY INTELLIGENT TUTORING SYSTEM. Part I: Agent-based architecture for user-centred
adaptivity
79
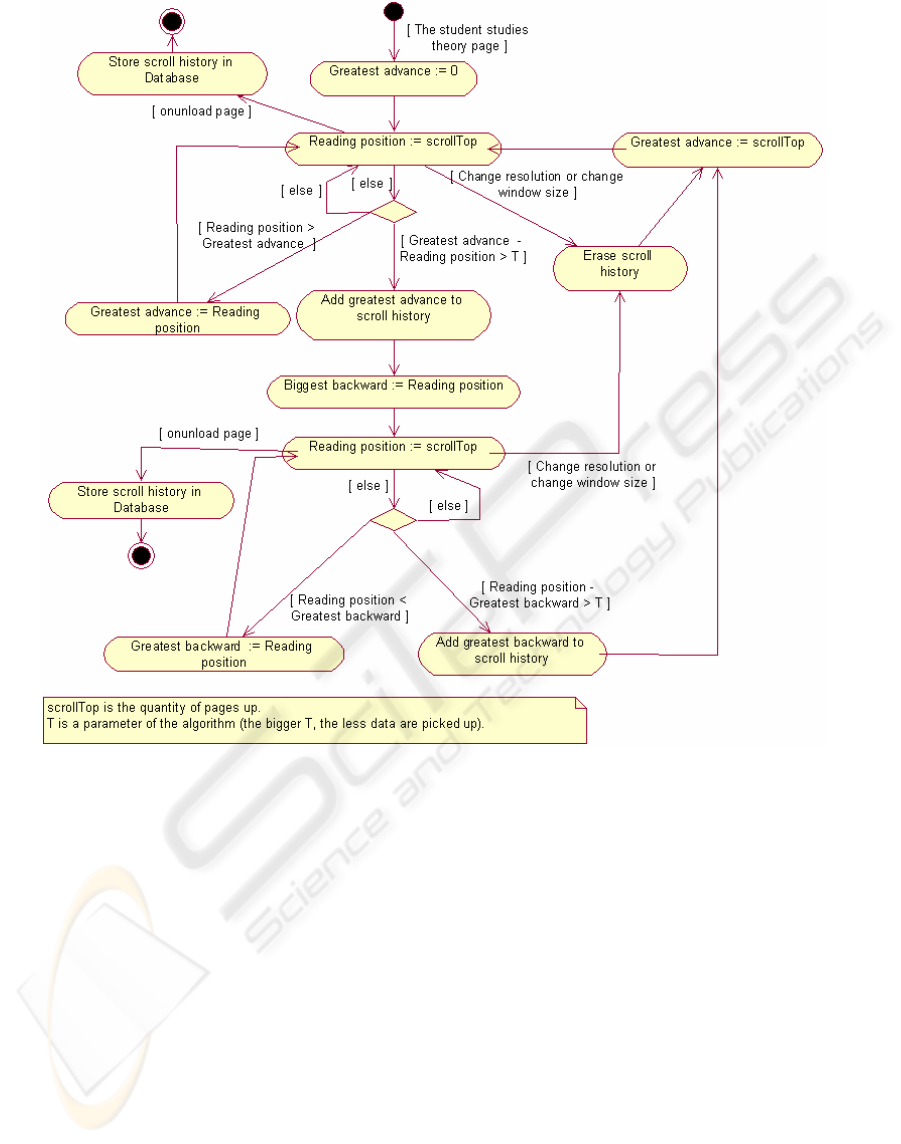
Figure 6: Activity diagram for “Detection of scroll”
6.2 Accounting Agent
The Accounting Agent perceives the interaction
between the student and the user interface and acts
(gets information) when the student changes to
another page of the ITS, scrolls up and/or down a
page, performs an exercise or a test, and so on.
Let us focus on the Accounting Agent when
watching the interaction of the student with the
interface in theory pages. Here, more concretely, the
agent is in charge of watching the scroll that the
student performs on a page of theory as well as the
time that he has remained in that page. When the
student leaves studying a page of theory, the
Accounting Agent stores all parameters gathered
during this time (scroll and time of permanence) in
the database.
In figure 6 the algorithm to detect the scroll that
the student performs when he visits a page of theory
is shown. Once the student has entered a theory
page, he may advance in his reading or go back in
the page. Whilst the student is advancing through the
page, the value of “Greatest advance” is being
updated. Now, when he steps back the value of
“Greatest backward” is updated. Notice how all
steps are stored in the database as “Scroll History”.
6.3 Exercises Agent
The Exercises Agent is in charge of choosing the
exercises that will be proposed to the student in the
topic that he is currently studying. The Exercises
Agent is autonomous as it controls its proper actions
in some degree. The agent, by its own means (pro-
active), selects the set of exercises to be proposed in
the subject studied by the student and adds to each
exercise the links to the theory pages that explain the
concepts (or topics) related to the exercise. When
solicited, it sends the page containing the exercises
to be proposed.
ICEIS 2005 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
80
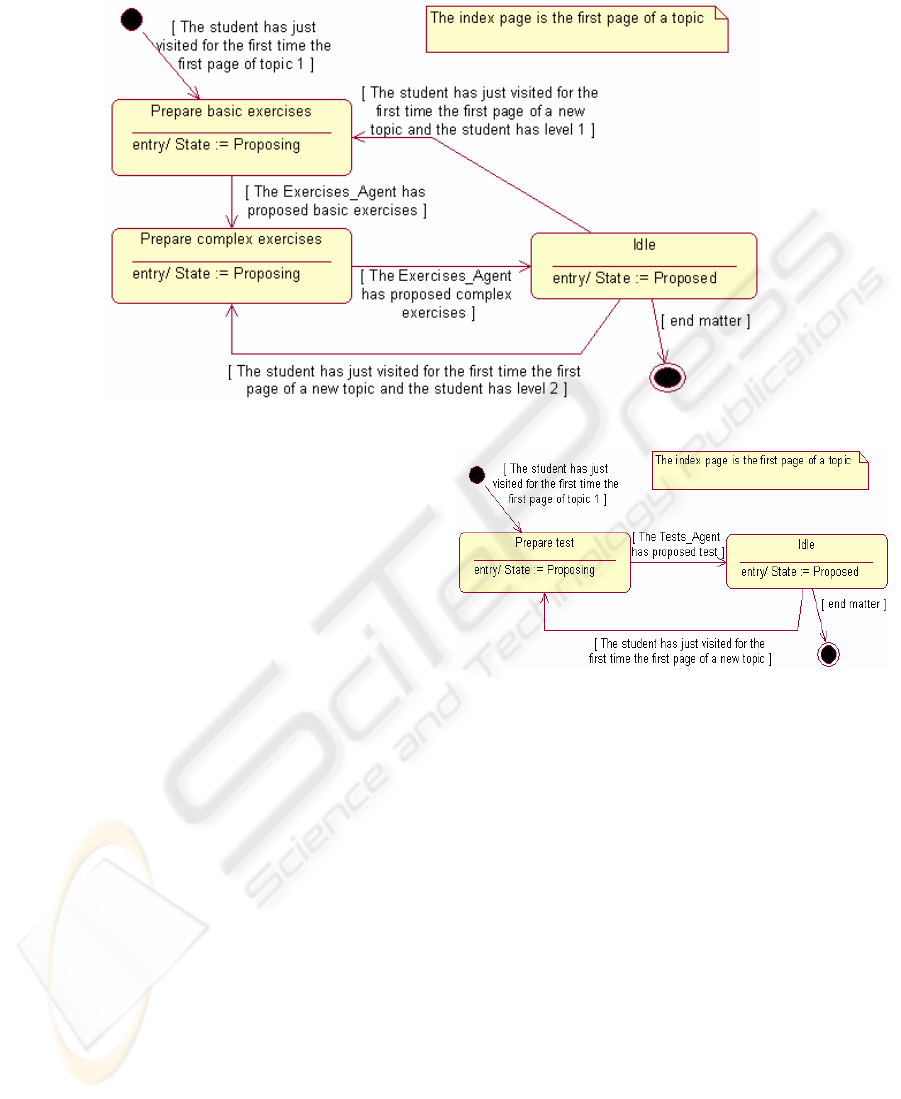
Figure 7: Exercises Agent state diagram
As it may be observed in figure 7, the Exercises
Agent state diagram, when the student has just
visited for the first time the first page of a topic, the
Exercises Agent shows the selection of exercises
that will be proposed to the student for the topic. If
the student is a level-1 student (low level student),
the agent selects the more basic exercises (state
“Elaborate basic exercises”) and later on the more
complex exercises (state “Elaborate complex
exercises”). Now, if the student is a level-2 student
(high level student), the agent is only allowed to
select the complex exercises. Once the agent has
selected the exercises it will remain inactive (in an
“Idle” state) while the student does not go on to the
following topic.
6.4 Tests Agent
Similarly, the Tests Agent is in charge of choosing
the test questionnaires that will compose the test that
will be proposed to the student in the topic that he is
studying. The Tests Agent is also waiting until it is
asked for tests questionnaires pages. The agent by its
own means (pro-active) goes on designing a set of
tests for the subject the student is engaged in.
Figure 8: Tests Agent state diagram
As you may observe in figure 8 – the Tests
Agent state diagram -, the Tests Agent performs the
selection of test questionnaires at the same time that
the Exercises Agent performs the selection of
exercises. Once it has selected the test
questionnaires, the agent will remain inactive (“Idle”
state), while the student does not go on to the next
topic.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have proposed an architecture that
considers the high diversity of users’ skills and
preferences: a user-centred and adaptive interaction
multi-agent system. Our model proposed has been
applied to e-learning/e-teaching by taking advantage
of the current state of the art of ITS. A way to insert
user adaptivity into an ITS is by using agent
technology. This is due to the characteristics that
DISTANCE LEARNING BY INTELLIGENT TUTORING SYSTEM. Part I: Agent-based architecture for user-centred
adaptivity
81

intelligent agents possess – autonomy, social ability,
reactivity and pro-activity. I this article, we have
introduced an agent-based ITS architecture that
enables a better learning to the students and a better
teaching to the professors.
In this sense, in our distance learning system we
have introduced a Student Model, a Domain Model,
and an Education Model. In this latter model four
agents – the Preferences Agent, the Accounting
Agent, the Exercises Agent and the Tests Agent -
have been proposed. To conclude, the multi-agent
system described in the paper gets data obtained
from the profiles to adequate the contents shown to
the concrete student that accesses the distance
learning ITS. On the other hand, the multi-agent
system obtains measures that permit to get
recommendations to enhance the course. This way,
jointly e-learning and e-teaching are greatly
enhanced.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported in part by the Spanish Junta
de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha PBC-03-
003 and the Spanish CICYT TIN2004-08000-C03-
01 grants.
REFERENCES
Baldoni, M., Baroglio, C., Patti, V., 2004. Web-based
adaptive tutoring: an approach based on logic agents
and reasoning about actions. Artificial Intelligence
Review, 22(1):3-39.
Bello, P., Bringsjord, S., 2003. HILBERT & PATRIC:
Hybrid intelligent agent technology for teaching
context-independent reasoning. Educational
Technology & Society, 6(3):30-42.
Capuano, N., Marsella, M., Salerno, S., 2000. ABITS: An
agent based Intelligent Tutoring System for distance
learning. Proceedings of the International Workshop
on Adaptive and Intelligent Web-Based Education
Systems, ITS 2000.
Cheikes, B.A., 1995. GIA: An agent-based architecture for
Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Proceedings of the
CIKM'95 Workshop on Intelligent Information
Agents.
de Antonio, A., Imbert, R., Ramirez, J., Mendez, G., 2003.
An agent-based architecture for the development of
intelligent virtual training environments. Second
International Conference on Multimedia and ICTs in
Education, m-ICTE 2003.
Dorça, F.A., Lopes, C.R., Fernández. M.A., 2003. A
multiagent architecture for distance education systems.
Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference
on Advanced Learning Technologies, ICALT’03, page
368.
Franklin, S., Graesser, A., 1996. Is it an Agent, or Just a
Program?: A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents.
Intelligent Agents III, Agent Theories, Architectures,
and Languages, ECAI '96 Workshop (ATAL), Lecture
Notes in Computer Science 1193:21-35.
Frigo, L.B., Pozzebon, E., Bittencourt, G., 2004. O papel
dos agentes inteligentes nos sistemas tutores
inteligentes. World Congress on Engineering and
Technology Education, page 86.
Hospers, M., Kroezen, E., Nijholt, A., op den Akker,
H.J.A., Heylen, D., 2003. An agent-based intelligent
tutoring system for nurse education. In Applications of
Intelligent Agents in Health Care, J. Nealon and A.
Moreno (eds), pages 143-159.
Kinshuk, Han, B., Hong, H., Patel, A., 2001. Student
adaptivity in TILE: A client-server approach.
Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on
Advanced Learning Technologies, ICALT2001, pages
297-300.
Millán, E., Agosta, J.M, Pérez J.L., 1999. Application of
bayesian networks to student modelling. Proceedings
of PEG'99: Intelligent Computer and
Communications Technology: Teaching & Learning
for the 21st Century.
Mota, D., Oliveira, E., Mouta, F., 2004. MyClass: A Web-
based system to support interactive learning in virtual
environments. Workshop on Modelling Human
Teaching. Tactics and Strategies.
Peña, C.I., Marzo, J.L., de la Rosa, J.L., 2002. Intelligent
agents in a teaching and learning environment on the
Web. Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies,
ICALT2002.
Person, N.K., Graesser, A.C., and the Tutoring Research
Group, 2000. Designing AutoTutor to be an effective
conversational partner. Fourth International
Conference of the Learning Sciences, pages 246-253.
Shaw, E., Ganeshan, R., Johnson, W., Millar, D., 1999.
Building a case for agent-assisted learning as a
catalyst for curriculum reform in medical education.
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Artificial Intelligence in Education, pages 509-516.
Tang, T.Y., Wu, A., 2000. The implementation of a multi-
agent intelligent tutoring system for the learning of
computer programming. Proceedings of 16th IFIP
World Computer Congress-International Conference
on Educational Uses of Communication and
Information Technology, ICEUT 2000.
Pesty, S., Webber, C., 2004. The Baghera multiagent
learning environment: an educational community of
artificial and human agents. Upgrade, Journal of
CEPIS (Council of European Professional Informatics
Societies), 4:40-44.
ICEIS 2005 - HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
82
