
SYSTEMATIC GENERATION IN DCR EVALUATION
PARADIGM
A
pplication to the Prototype CLIPS system
Mohamed Ahafhaf
Laboratoire CLIPS-IMAG, Université Joseph Fourier
385, rue de la Bibliothèque - B.P. 53 - 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9 - France
Keywords: Evaluation, speech understanding, dialog system, systematicity, objectivity
Abstract: In this paper we present an extension of DCR evaluation method tested on a spoken language understanding
and dialog system. It should allow a deep evaluation of spoken language understanding and dialog systems.
The key point of our method is the use of a linguistic typology in order to generate an evaluation corpus that
covers a significant number of the linguistic phenomena we want to evaluate our system on. This allows
having a more objective and deep evaluation of spoken language understanding and dialog systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decade, there was an increased
interest in s
poken language dialogue systems and
especially in their Spoken Language Understanding
(SLU) components. Manyapproaches of spoken
language with different theoretical backgrounds
were proposed and
implemented.
In order to test the effectiveness of these
di
fferent approaches, different evaluation methods
have been developed and used. Among these
methods, ATIS like quantitative evaluation methods
are probably the most commonly used. In such
quantitative methods the performance of the tested
system is measured by comparing its real output
with a corresponding analysis
by hand. Despite their interest, these methods do not
pr
ovide a detailed diagnosis of the negative and
positive aspects of an SLU system in term of
linguistic phenomena processing.
Further more, it requires a lot of adaptations (precise
t
ask, system’s output format, etc.) in order to make
an objective comparison between different systems.
To avoid the limitations of quantitative methods,
several
deep schemes were proposed. Among these
schemes, the DCR (Declaration, Control, Reference)
method seems the most ambitious to provide a
general framework for a qualitative evaluation of
spoken language systems (Zeiliger et al., 1997),
(Antoine et al., 1998). However, despite the
improvement of the evaluation quality with this
method, it lacks of systematicity, as we will see
later. This makes the comparison of the results of
different systems hard to do.
In this paper we present an extension of the DCR
m
ethod that allows to provide both deep and
systematic evaluation. The outline of this paper is as
follows: in section two we present the major
requirements of an objective evaluation method of a
SLU system. In section three, we present the main
aspects of the DCR method. Our method is
described in section four. In section five we provide
a description of our experiments and results and
finally conclusion and perspectives will close the
paper.
2 MAJOR REQUIREMENTS FOR
AN OBJECTIVE EVALUATION
METHOD OF SLU SYSTEMS
The major requirements for an objective and generic
method of SLU systems evaluating are:
Task independence: the method should be applied
to di
fferent systems whatever are their tasks.
Output format independence and analysis level
independence: one
of the major problems that face
a generic evaluation method is to be able to compare
systems with different output formats or to test
systems with different analysis level (syntactic
parsing or semantic analysis).
374
Ahafhaf M. (2005).
SYSTEMATIC GENERATION IN DCR EVALUATION PARADIGM - Application to the Prototype CLIPS system.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 374-380
DOI: 10.5220/0002520603740380
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Predictivity: the method should provide a detailed
diagnosis of the errors of the system. This allows to
drive future improvements of the system.
Objectivity: the evaluation corpus should contain
representative linguistic phenomena of the language
it is designed to process.
Flexibility: partial evaluation should be possible.
For example, one should be able to evaluate his
system on a specific phenomenon or a small set of
phenomena that he consider as particularly
interesting for his system.
3 DCR METHOD
The DCR method was proposed as an attempt to
satisfy the requirements presented above. It is based
on the generation of derived test sentences on the
basis of initial ones extracted from the corpus on
which the system is built. The derived corpus
contains a set of groups where every group is
dedicated to the evaluation of a unique linguistic
phenomenon. Every DCR test consists of three
components (Antoine et al., 2000):
1. The Declaration D: it corresponds to an ordinary
utterance that may be uttered by the system’s users.
2. The Control C: it consists of a modified version of
the utterance D usually with a focus on a precise
phenomenon that is present in D.
3. The Reference R: it consists of a Boolean value
which accounts for the coherence of the utterances C
and D.
Here is an example of the DCR test:
<D> I want a double room with with Internet euh
Internet connection
<C> I want a double room
<R> False
The main problem of this method is that it does not
provide a linguistic framework for the derivation of
the D utterances (initial utterances) into C utterances
(derived utterances). In fact, the derived utterances
are generated following quasi-subjective and task
dependent criteria without any guaranty of
production systematicity.
4 OUR METHOD
In order to overcome the systematicity and
derivation objectivity problems in the DCR method,
we propose an extended version of it that allows to
generate the derived utterances following an a priori
defined linguistic typology. The key features of our
method are
presented in the following paragraphs:
4.1 Initial corpus
The initial corpus consists of a set of representative
utterances selected following two criteria:
on the one hand, they have to cover the different
semantic aspects of the application domain and on
the other hand, they should provide a riche syntactic
base for the derivation operations (they should
contain different syntactic structures).
4.2 The derivation grammar
The derivation grammar is built on the basis of
syntactic typology that has two main resources:
1. Existing grammars: the existing classical
grammars and linguistic typological descriptions of
the language of the system we want to evaluate are
valuable source for the creation of the derivation
grammar. They are particularly important because
they provide a general and almost exhaustive
description of the different standard syntactic
phenomena.
2. Existing linguistic resources: spoken language
corpora are analysed in order to extract the
occurrences of different forms of the phenomena we
want to test. The major motivation of extracting a
part of our rules directly from these corpora is to
take into consideration the linguistic phenomena of
spoken language that are not systematically
considered in the classical grammar books and
linguistic typological studies (since they are
mainly concerned with written language rather than
spoken one).
We distinguish between two types og grammar: the
first one is based on transformations, the second one
on simple rewriting rules:
- Transformation grammar: is derived from
syntagmatic rules and consists of the rewriting of
each syntagm with an insertion of a linguistic
phenomenon (Kurdi & Al, 2003).
- Rewriting grammar : it starts at (D) utterance
containing the linguistic phenomenon to derive
systematically (by applying the built rules) one or
more (C) utterances. They are derived from a
typology built for each phenomenon. Derivation
process is made according to syntagmatic rewriting
rules. The transformation grammar will not be
approached here because it was already published
(Kurdi & Al, 2002), (Kurdi & Al, 2003). We will
treat the rewriting grammar which, in our opinion, is
most compatible DCR method.
SYSTEMATIC GENERATION IN DCR EVALUATION PARADIGM : Application to the Prototype CLIPS system
375

Rewriting example rules :
We gine below an example of this grammar applied
to a dialogue. The strating point is a dialogue
stopped at precise time to question the machine
understanding on a precise element (linguistic,
rhetoric or dialogical phenomenon, etc). The
advantage of this exercise is that it makes possible
having a diagnosis within a dialogue and at any
time. Here an example of stopped dialogue:
M : Bonjour, ici l'assistante virtuelle Vocalisa. Quel
est le motif de votre appel, s'il vous plait (Hello, here
the virtual assistant Vocalisa. What is the reason for
your call, please?)
U : oui bonjour vocalisa hervé blanchon euh non
pardon dominique blanc euh je voudrais joindre
dupond s' il te plaît (hello vocalisa Herve blanchon
euh not Dominique Blanc pardon euh I would like to
join dupond please )(PVE, Dialogue 5) (M -
machine, U – user (utilisateur)).
At this stage we stop the dialogue to question the
system in order to test the auto-correction
understanding phenomenon. In despite of its less
importance on the user request the autocorrection is
a rhetoric phenomenon which poses many
understanding problems to a (SLUD) system. The
fact here is to know if the machine understood Herve
Blanchon or Dominique Blanc.
In accordance with DCR method the (U) utterance
above would correspond to the Declaration (D). To
generate (C) control utterance according to definite
typology we have the following rules:
(1) NP PP (PP = Personal Pronoun)
VP V + Name1 (Name2)
VP Aux.etre + Name1 (Name2)
NP + VP je + suis + Hervé blanchon (Dominique
Blanc)
The utterance generated from the rule (1) is : je suis
hervé Blanchon (I am Herve Blanchon ).This
utterance corresponds to the control one in DCR
method.
Resulting DCR test is:
D : oui bonjour vocalisa hervé blanchon euh non
pardon dominique blanc euh je voudrais joindre
dupond s' il te plaît (yes hello vocalisa Herve
blanchon euh not Dominique Blanc pardon euh I
would like to join dupond please)
C : je suis Hervé Blanchon (I am Herve Blanchon)
R : no
According to the correction phenomenon typology
the (Name1) would correspond to the autocorrected
i.e. Hervé Blanchon. The awaited answer in this case
is negative (R = no).
To generate (Name2) which corresponds to the
substitued information, we apply the same rule (1)
but on inserting (Name2) (Dominique Blanc):
The generated utterance is: je suis Dominique Blanc
(I am Domenica Blanc) who corresponds to the
substitued information (the user final information).
Resulting DCR test is:
D : oui bonjour vocalisa hervé blanchon euh non
pardon dominique blanc euh je voudrais joindre
dupond s' il te plaît (yes hello vocalisa Herve
blanchon euh not Dominique Blanc pardon euh I
would like to join dupond please)
C : je suis Dominique Blanc (I am Dominique
Blanc)
R : no
4.3 Process of derivation
The Derivation consists in a first phase of the
rewriting of the initial utterance syntagm. The
utterance segmentation is made according to a
communicative criteria suggested in the formalism
Sm-TAG (Kurdi, 2001).
Each unit evaluation corresponds to only one
conceptual segment. A conceptual segment is a set
of words with a particular role
(semantique/pragmatic) within the utterance. These
roles imply a large variety of cognitive and
linguistics considerations such the utterance
topicality, its importance, etc (Androws, 1985). In a
second phase we carry out a systematic application
of derivation by generating from the grammatical
category the word or the lexeme which corresponds
to him either on referring to the initial utterancel or
to the whole of the corpus.
For example, let us consider the following D initial
utterance:
D- Je veux réserver une salle euh avec un vidéo
projecteur ( I want to reserve a room euh
with a video projector).
To test the hesitation morpheme "euh" in its Post-
object position we refer to the rule below to generate
C utterance :
(2) SV V + SN
The generated utterance from this rule is:
C- réserver une salle (to reserve a room)
ICEIS 2005 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
376

In this architecture, the data flow is not linear: the
speaker pronounces an oral utterance; the automatic
speech recognizer (ASR) performs speech to text
conversion and produces an orthographical string.
This orthographical string is then taken by a
linguistic component (known as Understanding
module) that produces a semantic schema
representing the literal meaning of user's utterance.
The semantic schema thrives progressively with the
contributions of the Interpreter modules to become a
dialogue act. This module is one of the most
importances, it has to resolve the pragmatic problem,
problems of reference, of date/time…for giving a
dialogue act with the semantic schema is clear and
comprehensible by dialogue manager. Then the
dialogue manager with the dialogue act passed by
Interpreter will interact with the task manager to
perform the determination of user's dialogue goal, of
dialogue strategy, and of act of the machine (we will
detail these elements in the next section). These
elements will transfer to the Generator that takes the
role of interpreting them to a character string as a
response of machine. Finally, the Speech synthesis
performs the text to speech (TTS) conversion and
produces the utterance appropriately satisfied with
the user's utterance.
The result use of DCR is a corpus derived by a
systematic and methodical application of the
rewriting grammatical rules. Contrary to the old
DCR procedure, derivation is made by applying a set
of grammatical rules based on syntagms extracted
from the initial utterance.
5 EXPERIMENTATION
5.1 The CLIPS Prototype
CLIPS prototype is a Spoken Language
Understanding and Dialog (SLUD) systme which we
used to evaluate our method. The system was
developed whithin the framework of PVE project
(Vocal Gate of Company, RNRT project) at the
CLIPS laboratory. This project aims at the
development of an interface generation model of
vocal dialogue for a vocal gate compagny. More
precisely, its purpose is to analyse, study and
formalize a generic model of vocal human-machine
dialog, in the optic to propose technological
solutions adapted to the needs of an access to the
information system company compatible with the
mobility (within
5.2 DCR tool
the meaning of circulation) of the personnel inside
and outside. The priority functional elements of a
vocal gate company are the interrogation of the
personnel repertory, the diary of a user group and
the follow-up of the personal electronic mail. These
functions must be activables in an integrated way in
order to allow a useful and powerful dialogue for a
user reaching the service by telephone.
DCR tool is a program which we developed to apply
DCR method on. This program allows in accordance
with the principles of DCR (Declaration, Contrôle,
Référence) to assess the parsing capacities of the
undesrtanding module and to determine the strategy
type by the task manager.
The prototype architecture was designed in a
modular and distributed way. Each module is
considered as an agent. The gray agents are those
which still depend on the task.
Figure 1: Prototype CLIPS architecture
SYSTEMATIC GENERATION IN DCR EVALUATION PARADIGM : Application to the Prototype CLIPS system
377
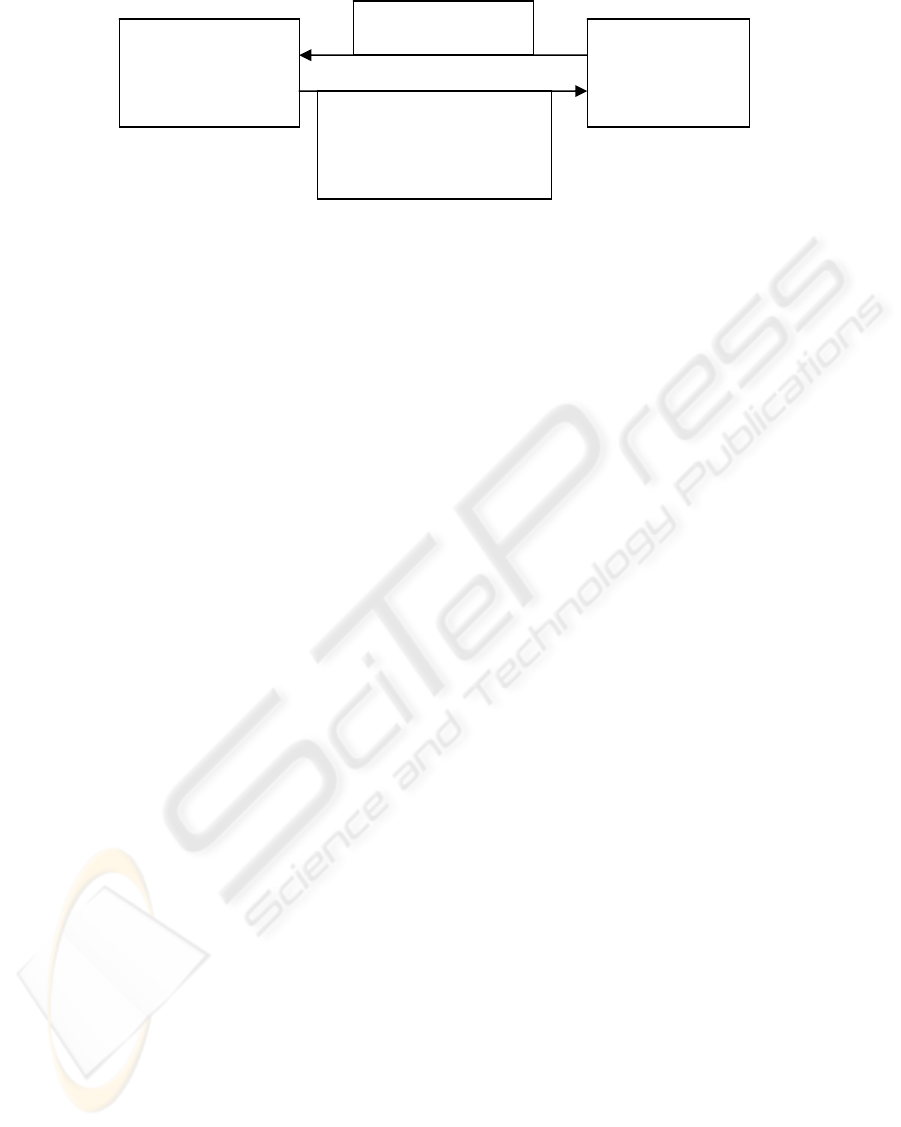
Figure 2: Parsing diagram of the DCR tool
This program is built following conceptual segments
developed for the understanding module and the task
manager. Its role is to parse, to compare two
untterances (D and C) and to synthesize an answer
(R). Thus, a test is known positive if R is positive
(yes) and negative if R is negative (not).
5.3 The considered phenomena
We made an evaluation of this system on two
phenomena that we considered as being particulary
relevant for a spoken dialog system. These
phenomena are: topic (objet in french) to test
understanding module and dialogue strategy to
assess dialogue manager module.
5.3.1 Topic
The topic is not an inherent oral linguistic
phenomenon but a word or a syntagm of language
vocabulary. Semantically speaking, topic is a
signifiant whose significance is contained in a
language dictionary and who is supposed to preserve
in an unspecified use. In the humanmachine
dialogue context this phenomenon governed by a
principle of recognition where it can or must be
taken as key element of a request in an unspecified
application. According to the studied corpora, the
topic can be a noun phrase, a prepositional syntagm
or a name corresponding to syntactic functions
varying according to the phrastic and pragmatic
context.
Our typology retains the noun phrase (NP), the
prepositional syntagm (PS) and the name:
NP: is the noun phrase which a request contains.
Example: j’aimerais réserver une salle (I would
like to reserve a room) (PVE corpus).
PS: corresponds to the prepositional syntagm. It is
also a noun phrase in the beginning of a sentence or
in an isolated context. Example: je veux assister à la
réunion (I want to attend the meeting) (PVE corpus).
Name: corresponds to a proper or usual name that a
request can contain. Example: je suis monsieur Jean
Caelen (I am Mr Jean Caelen) (Prototype CLIPS
corpus).
5.3.2 Dialogue strategy
The dialogue strategy is the form that aims to control
spoken dialogue. It decides directly to the dialogue
efficiency that is calculated by the speed of
convergence of the dialogue acts towards the final
goal. We distinguish the types of dialogue strategy
by two different categories as following (Caelen,
1997):
Non-inference strategies: the strategies that speaker
does not need to finally know the goal of his partner.
Directive strategy: consists in keeping the initiative
to drive the dialogue: maintaining the exchange goal
and keeping the initiative, imposing a new goal.
Reactive strategy: consists in delegating the
initiative to speaker either making him endorse his
goal, or by adopting his goal.
Constructive strategy: consists in moving the current
goal in order to invoke a return, for example to make
notice an error, make a quotation, undo an old fact...
Inference strategies: These strategies are known as
inference insofar as they require a fine knowledge of
respective goals of two partners. In these strategies,
the two interlocutors have more balanced position.
Cooperative strategy: consists in adopting the goal
of his interlocutor by proposing one (or many)
solution which brings to him the most relevant way
to achieve his goal.
Negotiated strategy: can be involved in a situation
where the goals are incompatible and the
interlocutors want to minimize the concessions. The
negotiation is expressed by argumentative sequences
(argumentation/refutation) with proposal for a sub-
optimal solution until convergence or
acknowledgement of failure.
DCR tool
Understanding
D.C Utterances
D.C
Semantic(syntactic,
pragmatic) parsing
ICEIS 2005 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
378

5.4 Generation grammar and derived
corpus
We used different grammatical sources in order to
write the grammar. These sources include many
grammar books like (Gadet, 1989), (Gadet, 1992),
and linguistic typological studies like (Benveniste,
1997), (Blasco-Dulbecco, 1999).We also used a
dialogue test corpus of
prototype CLIPS system (Nguyen & Al, 2003) and
two corpora of oral French: the DALI project corpus
(Sabah, 1997), PVE project corpus.
We obtained a total of 30 rules of which: 19 for the
topic and 11 for the dialogue strategy. Some rules
are hybrid (are applicable at the same time on two
phenomena) and will be also presented in the
evaluation results. With an aim of limiting the
number of the generated utterances for this
experiment, we generated one at three utterances
corresponding to each
rule. A multiple generation is possible but it is
limited, in our case, with the lexicon of the system.
Thus, it is possible to generate a multitude of
utterances when the lexicon of the system is broader.
We obtained 192 derived utterances on the basis of
six basic ones.
5.5 Evaluation results
According to our statistics 37% of the generated
utterances are not parsed which 25% are irrelevant
to the task of the system (nominalizations, etc), and
some of them 12% belong to a constant register or
not natural. 66% are the rate of general performance
of the system.
5.5.1 Topic processing results
Our corpus contains 38 statements corresponding to
the various types of the topic. The evaluation results
are presented in the following table:
Table 1: Our results on the topic cases
The results show that the grammatical category (NP,
PS) corresponding to the phenomenon topic has not
a real significance nor an influence on the utterances
parsing (rate of success 80%). They are treated in a
quasi similar way in spite of their different syntactic
position (first topic, second topic, etc.) (in french:
objet direct, objet indirect) either in D than C. The
NP category parsing is less succeeded (77%)
because some C utterances pose a parsing problem
to either the dialogue system and the DCR tool. For
example, the nominalization of then request
formulate (formule de demande in french) in je
voudrais réserver lafayette (I would like to reserve
lafayette) exceeds their parsing capacities even if the
utterance is correct.
5.5.2 Analyse results of strategies
The number of utterances we obtained for dialogue
strategiy is 132. The results of evaluation tests are
presented in the table below:
Table 2: Our results on the strategy cases
Type of strategy (%) of the correctly
processed cases
Cooperative 63
Constructive 54
Reactive 72
Directive 63
Negotiative 81
Total 66
The dialogue strategies which, recall it, are
determined by the dialogue system show here a
rather promising rate of success (63%). For example,
the parsing capacity is high for the negotiatied
strategy and reactive but enough low with the
constructive and cooperative strategies. This is due,
in one hand to the type of utterances selected in a
dialogue in fact D (for example: an utterance
without ellipsis is parsed more easily than an elliptic
one), in the other hand to the type of interrogative-
utterances C derived: an utterance such est- ce que
cette stratégie est constructive? (is this strategy
constructive?) is easier to parse than la stratégie est-
elle constructive? (the strategy is it constructive?)
although the propositional contents is the same for
the two utterances.
Type of topic (%) of the correctly
processed cases
Noun Phrase 80
Prepositional Syntagm 80
Name 77
Total 79
6 CONCLUSION
In this article, we presented an extension of the DCR
method. Our motivations for this extension are:
To allow a systematic (and by consequent more
objective) generation of the evaluation corpus To
have a major diagnosis of the assessed system.
For satisfying these two conditions, we
defined a derivation method that allows to obtain an
SYSTEMATIC GENERATION IN DCR EVALUATION PARADIGM : Application to the Prototype CLIPS system
379

evaluation corpus build following an a priori defined
linguistic typology of the phenomena we want to
assess our system on. As we saw, this methodology
is task and lexicon independent and allow to
evaluate any system independently of the
representation level of its output (syntactic, semantic
or pragmatic representation).
The application of our method on the
evaluation of an SLUD system showed that it is
realistic and that it allows to obtain a deep diagnostic
of the reasons of success and failure of the system.
As a perspective of our work, we intend to apply our
method to more than one SLUD system (preferably
with different approaches) in order to show that it
may be used to compare not only the involved
systems but also the effectiveness of their
approaches to the SLUD task.
Finally, we are investigating the possibility
of extending our methodology to the evaluation of
more semantic and pragmatic phenomena in order to
enlarge its application domain to the dialogue
evaluation.
REFERENCES
Andrews, A., 1985, The major functions of the noun
phrase, In T. SHOPEN (editor), Language typology
and syntactic description, Vol. 1 Cambridge university
press.
Antoine, J-Y., Siroux, J., Caelen, J., Villaneau, J.,
Goulian, J., Ahafhaf, M., 2000, Obtaining predictive
results with an objective evaluation of spoken dialogue
systems: experiments with the DCR assessment
paradigm, LREC’2000, Athens, Greece.
Benveniste, C-B.,1990, le français parlé : études
grammaticales, Editions du CNRS, Paris.
Benveniste, C-B., 1997, Approches de la langue parlée en
français, Ophrys, Paris.
Blasco-Dulbecco, M., 1999, Les dislocations en français
contemporain : étude syntaxique, Honoré Champion,
Paris.
Caelen, J., Stratégies de dialogue, Conférence
MFI’(Modèles Formels de l’Interaction), Lille,
Cépadues éd, 2003.
Gadet, F., 1992, Le français populaire, Paris : Armand
Colin, 1992.
Kurdi, M.Z., 2001, A spoken language understanding
approach which combines the parsing robustness with
the interpretation deepness, proceedings of the
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence
ICAI01, Las Vegas, USA, June 25 - 28.
Kurdi, M.Z., Ahafhaf, M., 2003, A grammar based method
for systematic and generic spoken language
understanding systems evaluation, In International
Conference on Natural Language Processing and
Knowledge Engineering, Beijing Media Center, China,
October 26-29.
Nguyen H., Caelen J. 2003, Generic manager for spoken
dialogue systems. DiaBruck : 7
th
Workshop on the
Semantics and Pragmatics of Dialogue, Proceedings
pp.201-202.
Picabia, L., 1975, Eléments de grammaire générative :
application au français, Armand Colin, Paris.
Riegel, M., Pellat, J-C., Rioul, R., 1994, Grammaire
méthodique du français, PUF, Paris.
Sabah, G., 1997, Rapport final du projet DALI (Dialogue
Adaptatif: Langue et Interaction),
http://herakles.imag.fr/pages_html/projets/DALI.html
Zeiliger, J., Caelen, J., Antoine, J.Y, 1997, Vers une
méthodologie d'évaluation qualitative des systèmes de
compréhension et de dialogue oral homme-machine,
actes JSTFRANCIL' 97, Avignon, France,4.
ICEIS 2005 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
380
