
MODEL DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE BASED REAL-TIME
ENTERPRISE INFORMATION INTEGRATION
An approach and impact on businesses
Vikas S. Shah
Advanced Technologies Group, Global Symphony Software (India) Pvt. Ltd. #13 Magrath Rd., Bangalore – 560025, INDIA
Keywords: Enterprise information integration (EII), Model driven architecture (MDA), Real-time enterprise (RTE),
Transformation specification.
Abstract: The rapid advancements of enterprise applications urge organizations to access and process information in
multiple incompatible systems accumulated as massive complex data in diversified formats due to lack of an
accepted common base in the development community. EII solutions must provide interoperability across
various software platforms with an ability to react and adapt enterprise operations in favor of continues
internal and external environmental alterations dealing with time sensitive information. Concept of RTE is
based upon the premise of getting the right information to the right people at the right time in “real time”.
MDA specifications lead the industry towards interoperable, reusable, and portable software components as
well as information models based on standard models. Recently, MDA is considered as another
evolutionary step introducing an engineering discipline to practice pattern-based software development. In
this paper, we present an innovative approach to achieve the notion of intelligent EII through combining
respective strengths of MDA and RTE along with implications over existing business models.
1 INTRODUCTION
EII has steadily gained momentum as a must-have
solution in the arsenal of enterprise architects.
Collecting information from an array of disparate
sources and fusing it together in a unified view is
just the ticket for a range of applications. EII fills the
gap between application and information integration.
It makes possible to insert intelligence to integration
process for the information obtained and arranged in
common context. On-demand intelligence to deliver
information in real-time offers immediate
measurable business benefits through faster and
better decisions as well as enhanced agility and
adaptability.
The distinguishing feature of RTE is to share the
information in real-time reducing cycle-time1
(ENOSYS, 2004) and improving operational
efficiencies. RTE ensures that the information is
current and consistent across all systems,
minimizing batch and manual processes related to
information. RTE solutions must be adaptable to
change and accept change as the process to achieve
their specified goals. Successful RTE focuses
primarily on the function of the enterprise model
that guides the choice of the infrastructure form for
accelerating strategic execution. Since the
technology is relatively novel, there are still some
skeptics related to RTE architectural consistencies.
The Object Management Group’s recent effort to
standardize MDA (OMG MDA, 2003) supported by
number of models, methodologies to prepare
models, and relationships of the different types of
models focusing to produce an enterprise
architecture modeling capabilities that analyst and
developers may utilize to describe EI.
1.1 Our Contribution
We started with the well-known and long established
scheme of separating system operations specification
from details of techniques to utilize platform
capabilities. Our analysis indicates that MDA
presents an approach and enables tools to be
provided for: specifying a system independently of
the platform that supports it, specifying platforms,
choosing a particular platform for the system, and
1
“cycle-time” is relative term and varies depending on the
system’s infrastructure. Generally, it is measured from
operational and transactional activities.
167
S. Shah V. (2005).
MODEL DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE BASED REAL-TIME ENTERPRISE INFORMATION INTEGRATION - An approach and impact on businesses.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 167-173
DOI: 10.5220/0002543801670173
Copyright
c
SciTePress
transforming the system specification into one for a
particular platform.
In order to speed the integration and maximize
the success, there are key capabilities that an
organization must address - access, integrate,
manage, secure, and transact respectively. The
framework and specification method developed
during our research deals with all the capabilities to
deliver single interoperable approach for integrating
all types of information, processes, and
functionalities across applications and architectures.
The MDA approach to achieve real-time enterprise
information integration (REI) enables flexible EII
architecture, spanning major computing platforms
and data stores hiding complexities. We are
presenting consistent REI architecture framework
and transformation specification process with
various case study based on our classification, and
impact of REI solution on business models.
2 ISSUES IN DEVOLOPING REI
SOLUTIONS
Vision of REI solution is an adaptive technology
providing dynamic access to disparate information
in the enterprise, leveraging a metadata and
heterogeneous query infrastructure to dynamically
access information from underlying systems
including ERP, CRM, data warehouses, legacy
systems, and other sources. The true challenges of
integration span far across business and technical
issues. Successful REI (OAGi, 2002) not only need
to establish communication between multiple
computer systems but also between business units
and IT departments supporting day-to-day decision
making across enterprise operations.
Integration has also to be seen as a never ending
process. Over time both the internal and the external
environment changes. The enterprise must react to
these changes in real-time and adapt its operation
accordingly. Present does not yet provide a complete
solution for enterprise modeling (J. Schekkerman,
2004). Existing EII solutions seem to compete with
each other, focus on particular issues and use
conflicting terminology. There are three major
groups of issues (J. Vesterager et al., 2001) that need
to be addressed and resolved during EII.
• Lack of an accepted common base in the
research community
• Limited awareness in the user community
• Insufficient information technology support
Despite the wide-spread need for integration
solutions, only few standards (David C., 2001) have
established themselves in this domain. While
developing an REI solution is challenging in itself,
operating and maintaining such a solution are even
more daunting. The mix of technologies and the
distributed nature of REI solutions make
deployment, monitoring, and trouble-shooting
complex.
Patterns are a constructive approach to convey
experiences and accepted solutions to recurring
problems within a known context. Enterprise
integration patterns assist architects to design and
implement integration solutions more rapidly and
reliably. Primary integration styles are file transfer,
shared database, remote procedure invocation, and
messaging. Asynchronous messaging is
fundamentally a pragmatic reaction to the problems
of distributed systems encouraging design of
components with high cohesion and low adhesion.
The integration patterns are classified as channel,
message construction, transformation, endpoint, and
system management patterns in (Gregor H. et al,
2003) depending on the integration style and
implications of respective EII application.
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF RTE
RTE presents real-time information to employees,
customers, suppliers, and partners and implement
processes to ensure validity as well as consistency of
information across all systems, minimizing batch
and manual processes related to information.
Following are the typical RTE characteristics
recognized during our research from (ENOSYS,
2004), (MetaMatrix, 2001), and (Taylor et al., 2004).
• Produce reusable views
to frequently access
information by various groups within company.
• Universal access
to real-time applications both
within and across corporate firewalls.
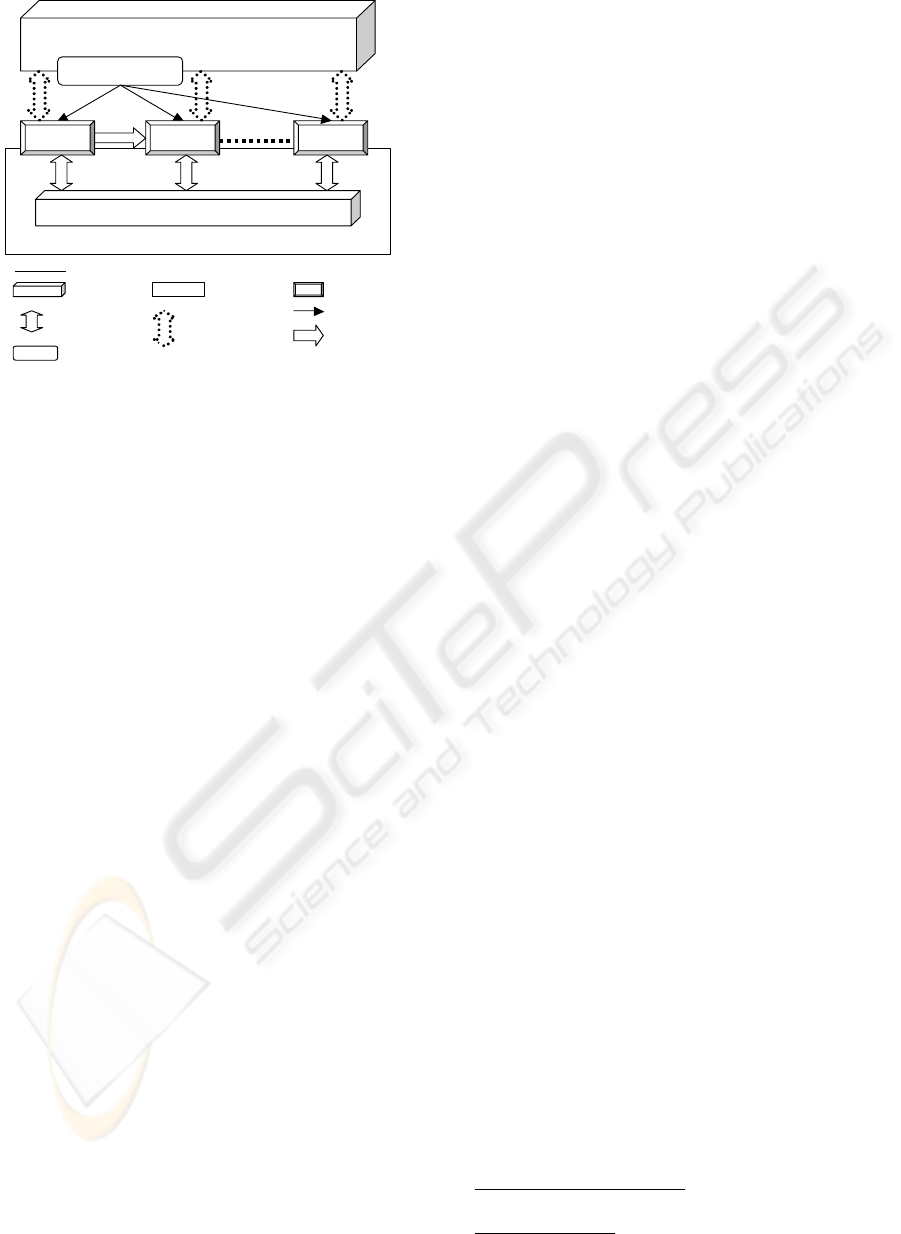
Modeling Framework (Semantic Unification)
Enterprise Model
System
(1)
System
(2)
System
(N)
Integration Service Framework
Integrating Infrastructure
Legends -
Framework
Information
Link
Model
Infrastructure
Concept /
Architecture
Style
System(s)
Control flow
Physical
flow
Figure 1: Concept of model driven REI.
ICEIS 2005 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
168
• Accessible information integration strategy
for
applications to gather the retrieved information
and efficiently delineate application and mission-
critical information from variety of sources.
• Mask the complexity
of underlying real-time
information sources from applications and users.
• Maintain and coordinate access security rules
for
full variety of accessible real-time information
sources since today’s corporations often require
information from partners, suppliers, and
customers in an extended network.
• Rapid information access capabilities
to reduce
the risk due to outdated information that can be
useless or even damaging.
4 MDA – AN APPROACH
In this section, we have categorized MDA (OMG
MDA, 2003) and MOF (OMG MOF, 2002)
specifications in conceptual, logical, and execution
views to illustrate the MDA approach and its
implications during development of REI solution.
4.1 Conceptual View
At the heart of MDA, there are three models CIM,
PIM, and PSM that may also be perceived as
viewpoints to reduce the logical complexities.
Computation Independent Model
- CIM provides
environment of system, and respective requirements.
CIM describes situation in which the system is used.
Such a model is sometimes called a domain or
business model. It may hide much or all details
concerning the use of automated information
processing system. CIM requirements should be
traceable to corresponding PIM and PSM constructs
that implements them and vice-versa.
Platform Independent Model
- PIM focuses on
operation of system while hiding details necessary
for particular platform. PI view illustrates part of the
complete specification that may not change from one
platform to another. PI view may use a general
purpose modeling language. PIM might consist of
enterprise, information, and computational
specifications suited for several architectural styles.
Platform Specific Model
- PSM combines the
platform independent viewpoint with an additional
focus on detail of platform specific use by system.
4.2 Logical View
Model transformation is the process of converting
one model to another model of the same system. An
MDA mapping provides specifications for
transformation of a PIM into a PSM for a particular
platform. The platform model determines the nature
of mapping.
A model type mapping specifies a mapping from
any model built using types specified in PIM
language to models expressed using types from PSM
language. These mappings may also specify
mapping rules in terms of instance values to be
found in models expressed in PIM language. A
metamodel mapping is a specific example of a
model type mapping. In certain cases, mappings may
be expressed as transformations of type instances in
PIM (or meta-classes) into type instances in PSM as
articulated in other languages including natural
language. Another approach to mapping models is to
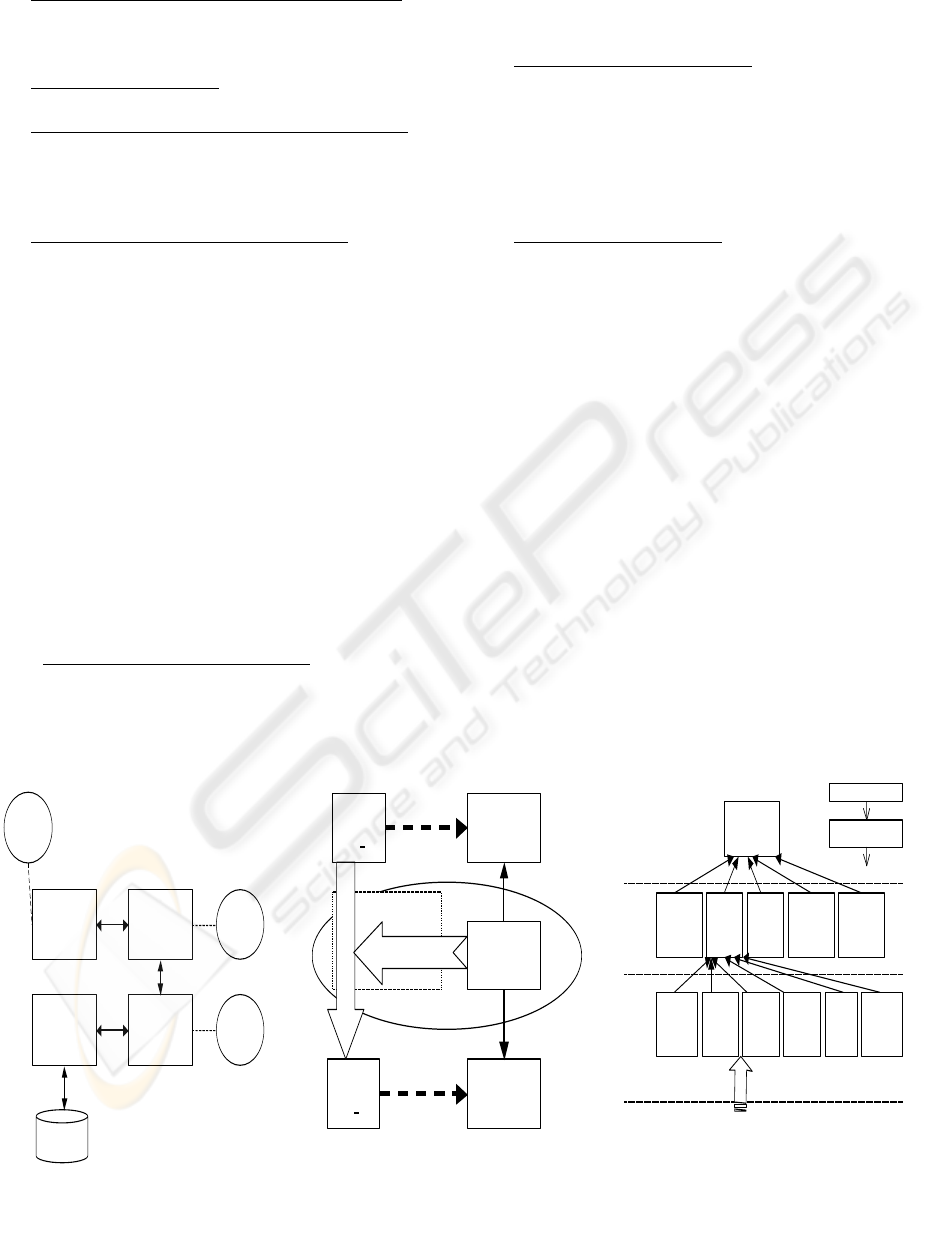
Co mp utation
Independent Model
(CIM)
Platform
Independent Model
(PIM )
Software
Co mponent /
Module
Platform Specific
Model (PSM)
Information /
Data
CIM -PIM
Mapping
PSM-Code
Mapping
PIM-PSM
Mapping
Software
Architect/
Des igner
Software
developer
Analyst
Example:
Process/
Rule/
Ontology
Metamodel
Example:
Class/
Sequence
Diagrams
Example:
State/
Package
Diagrams
Example:
J2EE/
.Net/
CORBA
Mapping
Possible MARK Model
Model
(An
)
Model
(Bn
)
Metamodel (A)
Transformation
Model
Metamodel (B)
Transformation
source language
target language
language used
language used
MOF Meta-
met a mo d e l
Business
Rules
Co mmon
Warehouse
UML
Web
Services
Business
Process
.Net CORBA EJB EA I EDOC Schedule
Information layer
Model
layer -
UML
Profiles
Meta-
model
layer
Meta-meta model
layer
XML
XMI generation rule
XMI Files
Figure 2a: MDA conceptual overview. Figure 2b: Metamodel mapping transformation. Figure 2c: MOF four layers.
MODEL DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE BASED REAL-TIME ENTERPRISE INFORMATION INTEGRATION - An
approach and impact on businesses
169

identify model elements in PIM that should be
transformed in particular mode giving the choice of
a specific platform for PSM. Model instance
mappings should define marks. A mark represents a
concept in PSM and is applied to an element of PIM
to indicate method for transforming element. It is
consider as transparent layer placed over model.
Mappings, however, consists of combination of
the above approaches. The marks may appear from
different sources as identified below.
• Types from a model - specified by classes,
associations, or other model elements
• Roles from a model – patterns
• Stereotypes from metamodel (Ascential, 2002)
• Elements from meta-metamodels (David S. et al,
2003)
• Model elements from metamodels (ISIS, 2004)
The consecutive step is to obtain the marked
PIM and transform it into PSM. A tool might
transform PIM directly to deployable code without
producing PSM. Such a tool might also produce a
PSM for use in understanding or debugging the
code. The results of transforming a PIM using a
particular technique are a PSM and a record of
transformation. The record of transformation
includes a map from the element of PIM. Model
transformation approaches are as follows.
• Marking using array of mapping and marking
• Metamodel transformation using transformation
specification through PI metamodel and PS
metamodel
• Model transformation using transformation
specification through PI type and PS type
• Pattern application
Along with PI and PS marks, additional
information may be supplied to guide the
transformation. Inputs to transformation (TR) are
patterns (AP), technical choices (TC), and quality
requirements (QR) represented as TR [AP, TC, QR].
4.3 Execution View
Meta-Object Facility (OMG MOF, 2002) technology
provides a model repository that may be utilized to
specify models encouraging consistency in
manipulating models in all phases of the use of
MDA. All MDA models are related since they are
all based on a very abstract metamodel – MOF.
Central theme of the MOF approach to meta-
information management is extensibility. The goal is
to provide a framework that supports any metadata
and allows new types to be added as required. In
order to achieve this characteristic, MOF has layered
metadata architecture - information, model,
metamodel, and meta-metamodel layer.
5 COMBIMNING STRENGTHS OF
MDA AND RTE
Meta-information management is a fundamental
element of REI: access to information in a seamless
and uniform manner. REI depends on sophisticated
technologies to collect, manage, and model
metadata, metamodels, and meta-metamodels as
well as query management and connection
technology for available information systems.
Various benchmarks identified for information
integration are categorized in terms of effort spent in
data conversion, lookup transformation, and built-in
function transformation.
MDA makes it possible to practice pattern-based
software development since model compilers
replicates proven patterns more quickly and
accurately. The motivating features offered by MDA
approach for constructing organization wide REI are
multi-platform models, federated systems, multiple
applications of pattern, general model to model
transformations, reuse of mappings, and enables
interoperability.
MDA move up the abstraction ladder caring the
development paradigm inexorably away from
computing platform and towards REI. A key issue is
“how to treat remaining gap?” or the abstraction gap
between REI and software specification.
Transformation technique resolves and achieves the
co-ordination (SOSY, 2004 and iO, 2001).
5.1 Transformation Specification
We have divided transformation specification
process to formally specify the intended behavior of
model transformer in three distinct specifications.
The details of each step are analyzed and identified
with Generic Modeling Environment (ISIS, 2004),
(Aditya et al, 2003) tool set and discussed below.
The pattern specification
– It is at the centre of
transformation specification. Purpose of the phase is
to represent integration patterns in concise and
scalable format and use semantic meaning to
enumerate the implementation details. The pattern is
represented by PAIR of [<class, attribute>,
<association, source<class, attribute>,
destination<class, attribute>>] where “<,>” depicts
the “set of”. Association is distinguished from the
source class to the association class and from
association class to the destination class. Cardinality
(n) should be specified for each pattern with the
semantic meaning that a single pattern (class,
attribute) must match “n” host <class, attribute>.
Pattern matching algorithms supports single, fixed,
and variable cardinality as well as partial matching
to reduce the complexity of transformation.
ICEIS 2005 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
170
Static structural constraint specification
–
Structural integrity is the primary concern in model
transformation. The problem to specify, maintain,
and reference different models conforming various
metamodels is resolved by using source and
destination models to explicitly specify the
temporary PAIR(s). It requires defining rules for
following operations.
• Bind to match objects in the PAIR(s).
• Delete to remove objects after the match.
• New to create objects after the match.
Execution of rule involves matching each pattern
object marked either bind or delete. Upon successful
pattern match, remove the pattern objects that are
marked as delete and create that are marked new.
Control flow specification
– The initial bindings
and application ordering are necessary to increase
efficiency and effectiveness. Control flow
specification allows user to manage complexity of
transformation and control application. Features of
the control flow specifications are rule sequencing,
non-determinism for parallel execution of rules,
hierarchy for primitive transformation rules,
recursion of rules, and test/case to choose between
different control flow paths.
Enterprises utilize and combine various
transformations to define meta-information. The
most frequent transformations during REI are
mathematical, decomposition, union, and decision
transformations. Mathematical transformation
creates a column and computes it from two different
information elements. Information element
decomposition transformation receives a single
value and decomposes it into one or more elements.
The enterprise defines group in the meta-information
using union transformation and integrates
semantically equivalent information from different
sources. It presents information as if they are from a
single source, eventually results into aggregation of
information from different enterprise divisions. An
appropriate example of union transformation is the
result of demand-supply statistics of retail products.
Decision transformations defer the choice of which
information element to use until run-time. It
supports critical real-time business decisions.
Excellent example using decision transformation is
return value of daily activities, and data indicating
variation in the cost of different stocks.
5.2 REI Solution Selection
REI focuses primarily on the function of model that
guides choices of the infrastructure form to
accelerate strategic execution. We have recognized
following dimensions during selection process.
• Principles to construct REI.
• Capabilities offered by REI.
• Extendibility - abilities to enhance for
future harnesses of REI.
The dimensions are subcategorized in Table 1.
At present, only approach to measure success (or
failure) of REI is to distinguish the business before
and after implementation.
Table 1: Selecting REI solution: Dimensions.
Principle Capability Extendibility
Vision
Channels
Awareness
Geographic-
coverage
Business-
drivers
Industry focus
Investment
Volatility
Technology
Services
Pricing
Agility
Financials
Execution
Personnel
Operational fit
Technical fit
Functional fit
Vendor-
support
Experiences
6 CASE STUDY – MDA BASED REI
In this section, we have analysed and indicated the
classification of implementation strategies adapted
by various solution providers to resolve domain
specific problems for explicit industry segment and
their experiences. Typical approaches to introduce
MDA and RTE concepts are - profiling, middleware,
and information base layer.
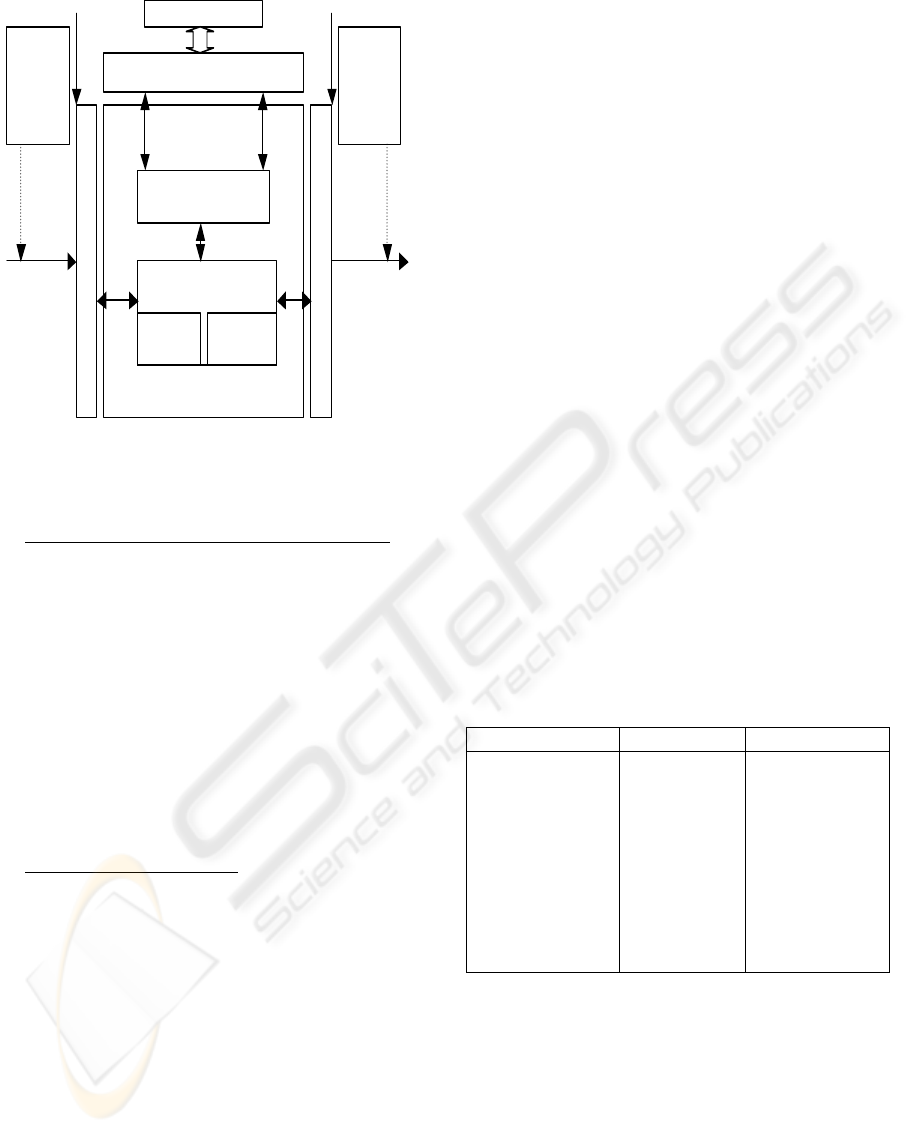
Transformation M odel A PI
Transformation M odel A PI
Rule and Constraint Manager
Transformation Engine
Egres s
Meta-
model
Ingress
Meta-
mo de l
Rule Interpreter
Execution Manager
Rules
Pattern
Matcher
Evaluation
Manager
Ingress
specification
Egress
specification
Describes
Describes
Figure 3: Run-time model transformation.
MODEL DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE BASED REAL-TIME ENTERPRISE INFORMATION INTEGRATION - An
approach and impact on businesses
171
ARTiSAN Software’s Real-time studio
(Matthew, 2002) provides modeling the system in its
environment by creating a context diagram defining
a high level view of the system without constraining
to implementation platforms and configurations in
terms of profile. One of the key concepts is the
modeling of systems from different viewpoints
persistent on particular concerns or an area of
functionality or an area of interest to the system.
Viewpoints can be reused on different systems.
Real-time studio allows packages to be exchanged
between models. The profile can be used across
many projects.
Component Synthesis with Model Integrated
Computing - CoSMIC (K. Balasubramanian, 2003)
is MDA tool suite tailored to the requirements of
real-time systems. It addresses following unresolved
challenges in using middleware to build mission-
critical systems with time and space constraints.
• Lack of middleware composability to
support multidimensional Quality of
Services (QoS).
• Accidental complexities during integration.
• Lack of principled methodologies to
support reflective middleware capabilities.
• Accidental complexities during
configuration.
The CoSMIC activities involve developing
aspect-oriented modeling tools for high-level
specification, tool to analyse end-to-end QoS and
time/space constraints, mapping constraints
specified in the models to target-specific middleware
configuration parameters, generators that compose
optimized and fine-tuned middleware components to
meet the end-to-end constraints, program
transformation tools that weaves in application QoS
requirements to compose customized middleware
from fine-grained QoS enabled components, and
additional aspect weavers that instrument
synthesized code to collect, organize and present
QoS meta-information to the QoS adaptation layer
controlling middleware infrastructure.
MetaBase EII (MetaMatrix, 2001) suite
integrates information from various sources and
systems across the extended enterprise using model
driven approach. The enterprise applications gain
access to integrated sets of real-time information
through the virtual data layer by submitting a single
request to server. The identified advantages over
other integration approaches are described below.
Data Warehousing, Data Marts, and Data Staging
creates new complex data structure that is specific to
limited number of applications. Data is updated from
native store in batch processes such that real-time
information is not available.
Content Integration method
is lacking to provide
back-end integration to information processing.
Enterprise Application Integration
lacks to address
the need for enterprise-wide information integration
rather it is hard-coded into the process of each
specific solution.
7 IMPACT OF REI ON BUSINESS
MODELS
The correlation between REI and business decisions
can be identified from the impact on businesses due
to adaptation and utilization of REI solution by
various organizations. (Dr. Y. Malhotra, 2004) briefs
the impact of REI on business models. IT analysts
have attributed Wal-Mart’s success to its investment
in REI technologies, classical example of setting the
benchmark of doing more with less. Dell has
developed and perfected its REI by strong ties with
its customer. Dell’s early innovations in passionate
pursuit for being the low cost ‘build on demand’
leader for consumer computing products has yielded
it the advantage of real-time business performance.
GE business model defined for maintaining quality
standards has been extended to control costs by
minimizing response time to problems affecting
products purchased by its customers. The critical
variables including sales, daily order rates, and
inventory levels can be tracked in real-time.
Cisco prided itself about the REI technologies
that offered apparently seamless integration of real-
time data within and across its supply-chain and
customer ordering system but ignored the
consequences that the past may not be accurate
predictor of future. Cisco ended up writing off
$2.2Billion in inventories and sacking 8500
employees demonstrates that even the best
technology offer no protection against appalling
business decisions, especially when the assumptions
embedded in the dominant logic are taken for
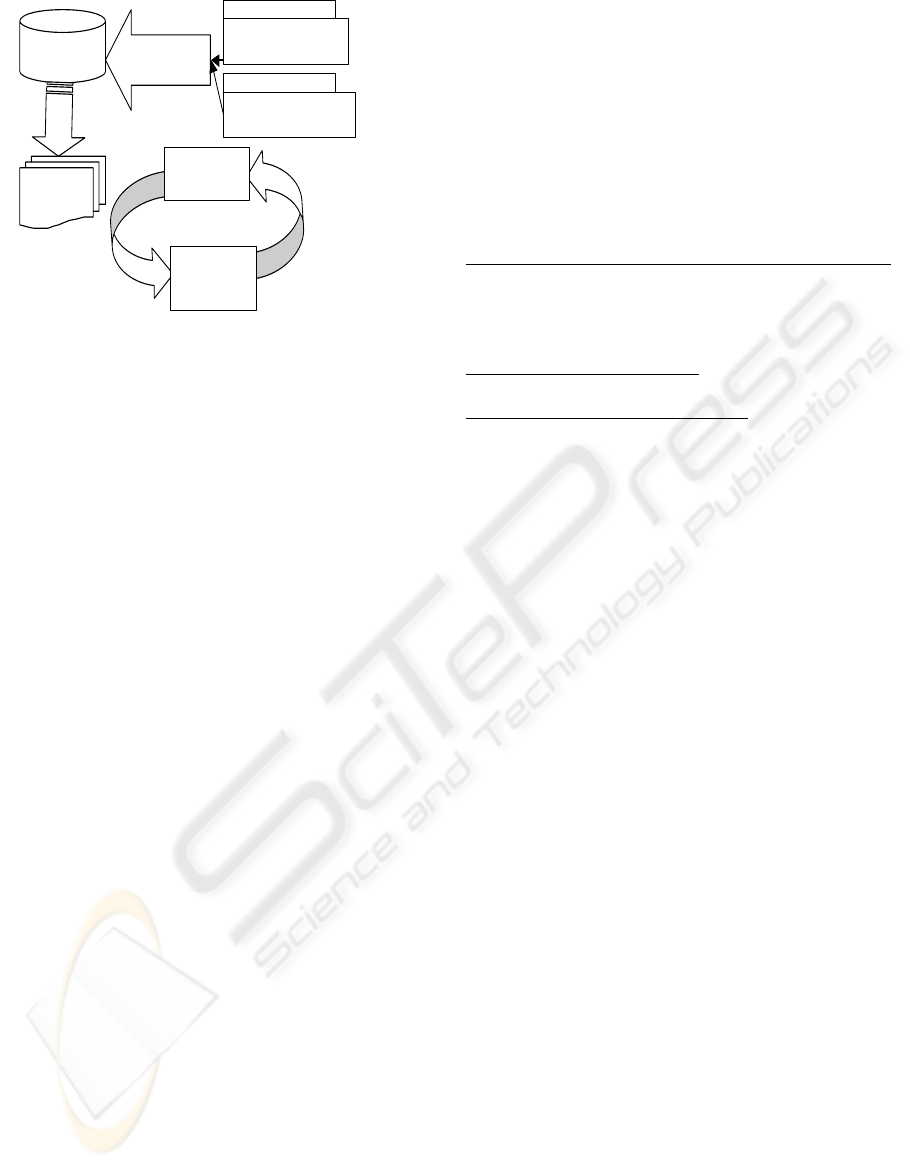
Platform
Specific Model
Use Platform
Specific
Extensions
C++ Profile
Real-Time Profile
Applications
Parse source
code into model
Model to source
code pattern -
templates
Synchronization - PSM &
Application source code
Figure 4: Round-Trip Engineering with UML-Profiling.
ICEIS 2005 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
172

granted. Enron had emphasized that efficiency gains
made possible by dynamic pricing, the company
deployed REI sought out new technology wherever
possible. Unfounded and overly optimistic belief in
technology as the means for generating profits led to
Enron’s downfall.
8 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we represented strengths of MDA and
RTE to achieve REI architecture framework. One of
the major problems analyzing behavior of REI
processes is to identify unpredictability of various
components or modules within a specified system
infrastructure. It is challenging to estimate
interactions between different enterprise applications
and establish appropriate mapping and
transformation techniques as described in MDA
specification. Our approach also resolves
architectural dependencies in very initial stages of
software development life cycle.
Ideally, REI initiative position users and model
driven information together not by swapping them
but alerting with relevant modifications enabling
analysis mode and act to achieve specific objective.
Real-time capabilities of EII provide efficient risk
management, accurate information, and precise
forecast due to various real-time collaboration
techniques. Reducing the cycle-time and latency of
information flow within an enterprise and its supply-
chain is meaningless without the context of terms
and conditions that outline permissible actions by
supply-chain partners that is provided through the
MDA based approach. Implementing real-time
analytical capabilities to MDA ensures timeliness,
pervasive connectivity, ubiquitous delivery, high
availability, and scalability.
OMG’s QVT (Queries, Views, and
Transformations) (OMG MDA, 2003) proposal
utilizes pattern matching as one of the key factor
providing single language for relations and mapping
that lowers entry barrier to transformation use.
REFERENCES
Aditya Agrawal et al., 2003. An End-to-End Domain-
Driven Software Development Framework. Object
Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages, and
Applications - OOPSLA’03, pp 26-30.
Ascential Software., 2002. Enterprise Data Integration
Benchmark Summary Whitepaper – WP-3004-0202.
http://www.ascentialsoftware.com/
David Chen., 2001. Standards on Enterprise Integration
and Interoperability: A Survey. KM in Inter- and Intra-
Organizational Environment Workshop, EADS Central
Research Centre, Paris, France.
David S. Frankel et al., 2003. The Zachman Framework
and the OMG’s Model Driven Architecture. Business
Process Trends Whitepaper.
Dr. Yogesh Malhotra., 2004. Integrating Knowledge
Management Technologies in Organizational Business
Processes: Getting Real Time Enterprises to Deliver
Real Business Performance. Journal of KM Special
Issue on ‘KMT’, Q3.
ENOSYS Software., 2004. Enterprise Information
Integration: Integrating the Real-Time Enterprise –
Business Whitepaper.
Gregor H, et al., 2003. Enterprise integration patterns:
designing, building, and deploying messaging
solutions. The Addison Wesley Signature Series.
iO Software, 2001. ArcStyler: Model Driven Architecture
Whitepaper. Architecture Board ORMSC.
Ormsc/2001-07-02. http://www.io-software.com/
ISIS, 2004. Generic Modeling Environment (GME) 4
User’s Manual. Release 4-3-12., Vanderbilt University,
USA. http://www.isis.vanderbilt.edu/Projects/gme/
J.Schekkerman, 2004. Enterprise Architecture Tool
Selecting Methodology - Version 2.1. Institute for
Enterprise Architecture Development.
J.Vesterager, et al., 2001. "Use of GERAM as Basis for a
Virtual Enterprise Framework Model", Proceeding of
DIISM2000, J. Mo, L. Nemes (Eds) Kluwer,
Dordrecht, pp.75-82.
K.Balasubramanian et al., 2003. Model Driven
Middleware: A New Paradigm for Developing and
Provisioning Large-scale Distributed Real-time and
Embedded Applications. Elsevier Journal Special Issue
on Model Driven Architecture.
Matthew Hause, 2002. ARTiSAN Real-Time Studio
Support for Model Driven Architecture. ARTiSAN
Software Tools. http://www.artisansw.com/
MetaMatrix, Inc., 2001. Enterprise Information
Integration, http://www.metamatrix.com/
OAGi - Open Applications Group, 2002. OAGIS Open
Applications Group Integration Specification Release
8.0 Document number 20020405.
OMG MDA, 2003. MDA Guide Version 1.0.1. Omg/2003
-06-01. http://www.omg.org/mda/
OMG MOF, 2002. Meta Object Facility Specification
Version 1.4.
SOSY Inc., 2004. Justifying New Technology: Making
Qualitative and Quantitative Arguments for MDA
Whitepaper. http://www.sosyinc.com/
Taylor et al., 2004. Standards on enterprise integration and
engineering--state of the art. International Journal of
CIM, Volume 17, Number 3, p 235 – 253.
MODEL DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE BASED REAL-TIME ENTERPRISE INFORMATION INTEGRATION - An
approach and impact on businesses
173
