
USING FUZZY LOGIC FOR PRICING
Acácio Magno Ribeiro
Electrical Engineering Department, Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Cidade Universitária, 36036-330 Juiz de Fora,
MG, Brazil
Luiz Biondi Neto, Pedro Henrique Gouvêa Coelho
Electronics and Telecommunications Department, State University of Rio de Janeiro,
R
ua São Francisco Xavier, 524, Bl. A,
Sala 5036, Maracanã, 20550-013, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
João Carlos C. B. Soares de Mello, Lidia Angulo Meza
Production Engineering Department, Fluminense Federal University, Rua Passo da Pátria, 156, São Domingos, 24240-
240, Niterói, RJ, Brazil
Keywords: Pricing, Fuzzy S
ets, Risk Assessment
Abstract
: This paper deals with traditional pricing models under uncertainties. A fuzzy model is applied to the
classical economical approach in order to calculate the possibilities of economical indices such as profits
and losses. A realistic case study is included to illustrate a typical application of the fuzzy model to the
pricing issue.
1 INTRODUCTION
Most of current challenges in electrical system
management issues are concerned to the new
world’s environment i.e. competition and
deregulation. The performance of a company should
be measured not only by its product quality but also
by the efficiency of its business in order to achieve
good contracts with low risks and high profits.
One of the major fundamental tasks related to the
n
ew competitive reality is pricing a contract which
can be a tough challenge.
The objective of this paper is to describe a new
com
putational tool customized for the risk
assessment. The mathematical model is based on the
application of fuzzy sets to the classical economic
theory and the overall solution scheme aims to
provide an effective and reliable help to the Decision
Maker on the new challenges of a competitive
environment.
2 CLASSICAL ECONOMICS
In a very simplified way, the classical economic
theory (Mas-Colell et al., 1995; Sher et al. 1986;
Varian 1992) establishes a product price based on
two main functions illustrated in Figure 1: the
production cost and the consumer utility. It is
important to note that every cost is associated to a
desired (or sometimes regulated) quality (reliability,
security) level. Therefore, the presented function
must be regarded as the minimum total cost
necessary to supply the load under corresponding
quality constraints.
Theoretically, in ideal conditions such as perfect
mark
et, competition, etc., the equilibrium between
offer and demand is achieved when the price equals
production costs – the break-even point corresponds
to demand D* cha
rged at price P*. However, it
should be noted that the future demand will not
necessarily equal to the optimal D*. A good load
management scheme would therefore bring the load
to the “profit” region; any commitment to supply
load at the “losses” region would require
331
Magno Ribeiro A., Biondi Neto L., Henrique Gouvêa Coelho P., Carlos C. B. Soares de Mello J. and Angulo Meza L. (2005).
USING FUZZY LOGIC FOR PRICING.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 331-334
DOI: 10.5220/0002548703310334
Copyright
c
SciTePress

compensation in order to maintain a company
economically healthy.
It is interesting to observe that the utility would
achieve profits whenever the demand is lower than
D* (on the left side of the break-even point, where
the user accepts a price higher than production
costs), and losses if the demand is higher than D*. A
good load management scheme would therefore
bring the load to the “profit” region; any
commitment to supply load at the “losses” region
would require compensation.
Figure 1: Production cost and Utility functions
This paper considers a model that extends the
classical economic theory to accommodate
uncertainties. It uses a specialized optimal
expansion/ operation model to evaluate a family of
possible minimum cost functions associated to each
possible future scenario. One example of such
functions is illustrated in Figure 2, defining the
possibility region of production costs. As may be
seen, each point of the region corresponds to the
optimal operation (or, if desired, operation and
expansion) cost necessary to supply a given load.
The overall optimization algorithm is fully described
in (Camac, 1998). Fast minimum cost flow and
parametric programming algorithms were specially
designed and developed in order to make it possible
to construct the region within a reasonable
computational effort.
Figure 2: Possibility Region of Production Costs
The same reasoning may be used to construct the
family of utility functions and therefore the
possibility region of consumer’s utilities illustrated
in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Possibility Region of Consumer Utilities
The resulting region is illustrated in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Possibility Region of Equilibrium
It may be seen that the equilibrium point will lie
within a region delimited by the possible production/
consumption scenarios.
3 FUZZY MODELING
This paper uses the fuzzy set theory as a basis to
model the possibility regions of costs and utilities
and construct a risk assessment framework. Each
scenario of production cost and consumer utilities is
assigned a corresponding possibility
µ
c
or
µ
u
.
(membership functions in fuzzy set theory). Figure 5
illustrates the possibility cost function for demand
D*.
It may be shown that the possibility of a
future scenario s where cost
and utility
jointly occur is given by
∗
c
∗
d
∗∗
+
=
uc
s
µ
µ
µ
(1)
ICEIS 2005 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
332
Using the same reasoning one could
accommodate uncertainties in load values, growth,
fuel costs, etc. The total scenario possibilities will be
the union of each individual possibility.
Figure 5: Possibility Function for a Scenarios
Energy pricing is a multi-disciplinary task and
involves efforts of many different people in a
company. A realistic price structure is generally
based on complex philosophies, objectives and
goals, and cannot be briefly described, as
commercial interests and contractual constraints
prohibit a comprehensive and detailed report.
Nevertheless, an intuitive reasoning would state that
the price must cover costs and the consumer must be
able to pay the price.
The quality of a business (for instance, a sales
contract) will be measured by indices, such as
incomes, profits, etc. A realistic quality index should
reflect the company’s philosophies and goals, and
may combine more than one component (for
instance, incomes, profits and risks) in order to
suitably represent the company’s aims and
objectives.
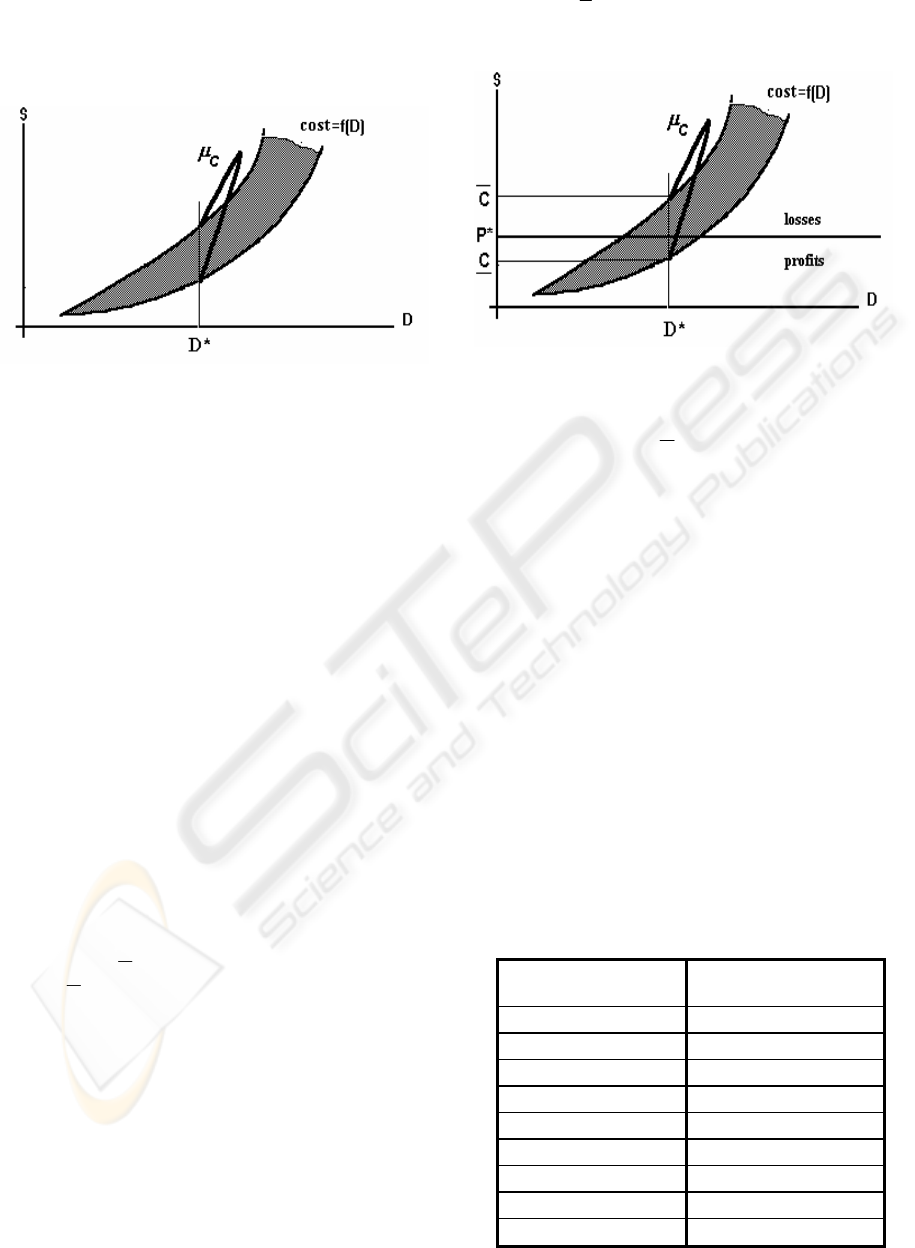
In general, it is better to loose a business than to
do a bad business. Our first analysis will focus on
the first need of a company to recovering expenses.
Suppose, for instance, that the decision maker must
price a supply of D*, whose associated costs are
presented in Figure 6, ranging from lower and upper
bounds
C andC .
Considering a given price P*, it may be seen
that, for scenarios corresponding to costs lower than
P*, there is a positive profit
α
given by
** CP −=
α
(2)
Conversely, the company will experience
losses, or a negative profit, if costs are higher than
sales price. The possibility of losses may be
evaluated by
∫
=
C
P
cl
*
µφ
(3)
Figure 6: Pricing based on Production Costs
where the integral operation is performed under the
D* constraint and represents the accumulated
possibility from P* to
C
.
4 CASE STUDY
The described model was applied to a realistic
Peruvian system. In order to protect confidential
information, only part of the system was modeled
and some key parameters were slightly changed.
Therefore, the obtained results cannot be interpreted
as real and do not reflect company data, targets,
costs or prices. The represented system is composed
by 5 hydrological plants (total installed capacity of
1500 MW) and one thermal plant (total installed
capacity of 250 MW). In this simple case, no
investment costs will be considered. However,
practical applications of the proposed model may
include operation and investment costs.
The nine possible future load scenarios are
presented in Table1.
Table 1: Possible Demand Scenarios
Possible Scenario Demand (GWh)
1 510
2 612
3 734
4 807
5 888
6 933
7 979
8 1028
9 1080
USING FUZZY LOGIC FOR PRICING
333

Table 2: Production Costs for each possible
scenario (Millions of US$)
Table 2 presents corresponding production costs for
ten possible hydrological inflows.
The Decision-Maker must choose an offer
price for a contract of 1000 GWh supply along a
two-year horizon. According to company, pricing it
should follow a Cost-recovering philosophy, and a
5% maximum risk of losses. Figure 7 presents the
fuzzy region of production costs as a function of the
supplied load. For simplicity reasons, a cumulative
scenario possibility function is represented. It may
de seen that the price associated to a 5% risk of
losses is slightly above US$ 4000 million.
Figure 7: Fuzzy Cost Production Region
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented a model for the risk assessment
of an electrical system under a competitive
environment. The proposed approach extensively
used efficient optimization algorithms to build the
regions of possible future scenarios. A fuzzy
reasoning framework then treated these possibility
regions in order to obtain the strategies
corresponding to the company’s objectives. It is
interesting to notice the difference between the
proposed and the classical tools. While the classical
approach requires the user to adopt a given objective
(for example minimum operation costs, minimum
variance, minimum regret, etc.), the new model
adapts to the user targets and philosophies,
producing the adequate results to the new company
needs. The presented model aims to be an effective
and useful tool to risk analysis and management.
HYDROLOGICAL SCENARIOS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 367
3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 2396
4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 22 2724
5 0 0 0 0 5 401 740 1149 1759 5281
6 0 0 0 218 697 1138 1502 2053 2916 6944
7 0 3 241 914 1393 1865 2243 2928 3887 8063
8 1 250 972 1653 2169 2732 3229 4009 5062 9239
9 228 696 1759 2470 3165 3885 4463 5243 6296 10472
REFERENCES
C. J. Andrews, "Evaluating Risk Management Strategies
in Resource Planning", IEEE Transactions on Power
Systems, Feb. 1995, Vol 10, Number 1, pp. 420-426
Mas-Colell, Andrew, Whinston, Michael D. and Green,
(1995). "Microeconomic Theory, Oxford, Oxford
University Press.
Sher, William and Pinola, Rudy, (1986). "Modern Micro-
Economic Theory. North-Holland - New York.
Varian, Hal R. (1992). "Microeconomic Analysis". W. W.
Norton & Company- New York.
D. Camac, “A Model for the Optimal Planning and
Operation of Hidrothermal Systems”, D.Sc. Thesis,
1998 (in portuguese)
COSTS
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
µ
Milions of US$
10
9
8
LOAD
10000
5%
ICEIS 2005 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
334
