
Transference and Storage of Spatial Data in
Distributed Wireless GIS
A.K.Ramani
1
, Sanjay Silakari
2
, Sudheer Koppireddy
2
1
Department of Computer Science & Engineering,
Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, R.N.T. Marg, Indore – 452001
(M.P.), India.
2
Department of Computer Science &Engineering,
Samrat Ashok Technological Institute, Vidisha-464001,
(Madhya Pradesh), India,
Affiliated to Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya,
(University of Technology of Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal)
Abstract.
There has been a great development in Wireless GIS (WGIS) new
century. Spatial data transferring and storage in GIS are developed from wired
to wireless network. This paper first briefly introduces the technologies and
strategies of spatial data transferring and storing in distributed Wireless GIS.
Secondly, the schemes of spatial data transferring modes in wireless GIS for
improving the network transfer rates are introduced emphatically, and the dis-
tributed transferring process technology of GIS spatial data are also discussed.
Based on these, we present the storage strategies in wireless database, and in-
troduce mobile computing conception and three-tier wireless replication data-
base. Here, we emphasize on dynamic replication strategies and methods in
wireless environment. Finally, we compare several data storage strategies in
WGIS databases and the dynamic multi-tier replication strategy is proposed for
wireless database storage…
1 Introduction
Stand-alone and wired GIS may not meet the requirements of all the GIS (Geographi-
cal Information Systems) applications appropriately, especially when users need to
access a GIS, time and location independently. Therefore, there is a need to move
towards ubiquitous GISs, which can serve users anywhere and anytime.
These days, not only GIS experts but also ordinary people tend to access spatial in-
form
ation using wireless equipments. With the rapid development of new integrated
techniques, there are also many new achievements in GIS. The development of the
handheld devices, such as Personal Digital Assistants(PDA), Java-enabled mobile
phones, laptop and Internet techniques, and the application field of GIS has been
enlarged and furthermore, lead to the new challenges to GIS techniques. GIS based
on wireless devices -- wireless GIS (WGIS), will become new branches of GIS and
bring the GIS into a new stage of development. The technology of spatial data trans-
K. Ramani A., Silakari S. and Koppireddy S. (2005).
Transference and Storage of Spatial Data in Distributed Wireless GIS.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Wireless Information Systems, pages 114-123
Copyright
c
SciTePress

ferring and storage in GIS is developed from wired to wireless network at present. It
is feasible for itinerant or peripatetic users to travel from one place to another by
using the wireless network.
However, in the applications of wireless network, the speed of transaction is get-
ting faster, and the capacity of storage is getting larger. However, there are limitations
in wireless GIS.It is a challenge task to connect network elements by radio waves
instead of wires. [1, 3, 4, 5, 6] For example, GIS spatial data transfers and storage
based on wireless LAN are restricted to spatial data capacity and transferring dis-
tance. Therefore, there exists deficiency on the data processing. It is potential to solve
the problem by using distributed dynamic multi-tier spatial data transferring.
Wireless GIS technologies offer a lower time-to-market comparing too many
wired technologies, which require the deployment of large amounts of new network
equipments. The wireless GIS, not only satisfy the network demand of various per-
sonal digital assistants (PDAs),portable computers at anytime and anywhere, but also
be regarded as the compensative means for traditional wired GIS. The data process is
promoted by improving the transferring rate.
2 Characteristics of WGIS
In the mobile communication area, GIS network were usually divided into two types
according to the wireless connection technologies. One is based on the Cellular Infra-
structure connection technique, which is also used for Mobile GIS.The other is based
on wireless LAN techniques. Wireless network is a network, which is built, in a mo-
bile environment, or the environment-combined wireless with wired. It is quite con-
venient for data-transferring network. Therefore, we first need to consider the charac-
teristics of wireless GIS that will likely affect our way of working and thinking on the
current GIS technology.
Fig.1. Wireless GIS Framework
As illustrated in Fig.1, WGIS is composed of mobile equipments, wireless GIS
server and GIS spatial database. The mobile equipments, i.e., PDA, laptop, and mo-
bile phones etc. should be comprised with mobile databases and mobile computing
environment. Wireless GIS server is the main part of WGIS, it deals with all kinds of
115

processing in wireless transfers, including ‘read’, ‘write’, ‘delete’, ‘update’ and ‘com-
mit’ etc.
As the wireless communication the factors considered are, for example, communi-
cation cost, communication time, power supply etc., so the wireless server should
take into account the problems mentioned above and should provide an optimal
search for wireless users.[2,5,7,8,9] GIS spatial database (DB) is used to manage all
types of massive GIS data, while the conventional DBMS could fit the function.
Between the GIS DB and wireless server, a spatial database engine, which could be
ODBC or SDE, should be produced in order to provide services for users.
The wireless GIS is the management and application system of functional and
wireless Geo-spatial data. In this system, we can realize tremendous Geo-spatial data
storage and management in GIS, fast queries of multi-dimensional spatial data and
search in wireless network, wireless station over switch, wireless vendor’s authentica-
tion and management, encrypted wireless data transferring etc.
Being compared with the conventional LAN, the wireless network technology is
possessed itself with overwhelming predominance.However, wireless couldn't be
absolutely replaced by the wired environment and is used to make up the restrictions
of wired, with it’s purpose of the extension of the wired. [10]The Geo-science is now
facing a shift in the way for GIS development in human works and in their access.So
the question becomes how to give GIS clients accessing any type of Geo-Information
quickly, securely, at anytime and in anywhere.
The development of Wireless GIS is served the first and top priority to the devel-
opment of the mobile computing technology. Mobile computing technology is a revo-
lutionary technology, born as a result of the remarkable advance in the development
of computer hardware and wireless communication. It enables us to access informa-
tion at anytime and anywhere even in the absence of physical network connection. It
is essential in a mobile computing environment to serve mobile clients to access re-
mote information at anytime and at any place. In the process of accessing files on
remote servers by the clients, requests are sent by them to mobile support stations
from where the files are thus received from the remote servers and are then are deliv-
ered back to the clients. The high mobility of mobiles for mobile hosts and the narrow
bandwidth in the wireless network may cause certain delay in accessing files. Also,
because mobile clients may request the services of accessing file too often and give
rise to bandwidth contention among them, latencies can be caused on the whole.
The important characteristics in wireless GIS transfer and storage that are needed
to be considered are as follows:
(1) The environment, in which wireless GIS is deployed, is the mixture of two differ-
ent networks, the fixed and the wireless networks. The fixed network is characterized
by the fixed hosting location, relatively high capacity, high reliability and low con-
nection cost. In contrast, the wireless network is to support dynamic network topol-
ogy but with relatively low capacity, low reliability and high connection cost. In order
to avoid compromising database performance due to the use of the wireless network,
recently some techniques have been proposed, including:
• Reducing the number of data exchanged via mobile network;
116

• Reducing the response time of accessing data via mobile network;
• Providing data cache on mobile host;
(2) The resources available to mobile users are generally very limited. As a result,
mobile hosts will tend to be highly personalized. From the data management’s point
of view, mobile users will likely and solely bring the fraction of data they need to
access frequently in mobiles. A new challenge arises for coping with the requirement
of consistency on databases (both on mobile and fixed hosts) especially when those
fractions are not completely independent to each other. Actually many techniques
have already been proposed to address this problem, including:
• Transaction management for wireless transfer;
• Allocation of mobile database replication (materialized view) on the fixed
network;
(3) In general, wireless communications are consisted of low security. The worst case
is, for example, that our data on the mobile hosts would be completely lost if the
mobile hosts become the subjects of thieves.
The consequence of the above characteristics is concluded that wireless GIS, in
general, contains a high degree of unavailability. It is not to say that most data man-
agement issues in mobile information systems are related, directly or indirectly, to the
problem of low data availability. Thus, data availability is the central issue in trans-
ferring mobile spatial data. Accordingly, addressing the problem of low data transfer-
ring speed and management would have significant contribution in the establishment
of wireless GIS technology.
3 Distributed Data Transferring Strategies
Wireless GIS impulses Geo-science and wireless communication technique to a new
era through enlarging the network's carrying capacity and application domain. Nowa-
days, since the application of wired network is gradually saturated, the wireless appli-
cation has become wider and wider. Meanwhile WGIS provides some newly hot spot
applicable strategy.
The data is the most unvigorous segment in GIS, whereas spatial data, which is re-
lated to GIS, is multi-original and complicated, in terms of data types and formats,
i.e., gigantic grid image data, spatial vector data, metadata, etc. It is an essential mat-
ter in WGIS operation for constructing geographic entity objects, organizing and
transferring spatial data, and realizing data share in the Internet. Integrating the char-
acter of wireless transferring, WGIS spatial data transferring strategy should consider
the following facts:
117

(1) Unrestricted by time and location. It is also the predominance for wireless net-
work to realize WGIS from preventing disturbances from outside conditional envi-
ronment and atrocious weather. In the area where the wired is untouched, for exam-
ple, in a hard, badly, dangerous environment, the WGIS could still work well.
(2) Wireless applicability. Being compared to the wired network, the wireless net-
work has a more comprehensive employment and configure mode; otherwise, it isn't
involved in the situation of stations. Thus, the use of GIS becomes more flexible.
Wireless GIS could be realized as the convenient GIS by clients as it is applied to the
traditional GIS and prevalent mobile GIS contemporarily.
(3) WGIS should provide a more extensive GIS service for users. Location Based
Service (LBS) and Mobile Based Service (MBS) provide a realistic model for our
practical world. At different times and in different locations, the model dynamically
offers distinct information service.
(4) WGIS should improve the security for data transferring. The wireless GIS is
utilized an electromagnetic wave transferring in the air instead of cables, to dispatch
spatial data. The frangibility of transferring medium makes the data transfer easily to
be disturbed by the outside environment. Meanwhile the uncertain factors of a trans-
ferring process make wireless data easily to be listened and captured to enough pack-
ets by hackers. Hence, the increase of the wireless security for data transfer is an
important factor for our design.
(5) Transferring velocity of WGIS is restricted by the existing standard. Although
the wireless velocity has been made a great progress in 21st century, for example the
new standard for wireless, i.e. CDMAX, IEEE802.11a and IEEE802.11g, is protru-
sive recent. The velocity of wireless couldn't be exactly and completely compared
with the wired network. From considering the wired cable transferring, the gigantic
GIS data transferring velocity is hard to satisfy the demands. Therefore, improving
GIS transferring velocity is a persistent requirement for WGIS.
(6) WGIS should solve the low efficiency of the visits of spatial database ex-
change. Data organization is still the GIS bottleneck for accesses of users. In the
wireless environment, there also exist the factors for confining exchange visits, for
example restriction of data access and uncertainty of client location. Considering the
interoperability of GIS data, it is important to enhance the efficiency of data transfer.
As a consequence of the above strategies, in the wireless GIS, there is generally a
high degree of unavailability; thus, data transferring is the central issue in this field.
Accordingly, there will be a significant contribution in the establishment of WGIS
technologies from solving the problem of low data availability and velocity depend-
ing not only on spreading software protocol standard, but also on improving hardware
technology.
4 Spatial Data Storage for Mobile GIS
As we all know, the character of GIS data including vector data, grid data and image
data is gigantic and multi-resource. In mobile environment, for the limitation of trans-
118

ferring velocity, we should consider appropriate strategy to storage and manage GIS
data in the wireless server.
4.1 Mobile Computing
Mobile Computing and wireless networks are fast-emerging technologies to make an
environment conducive for ubiquitous computing. In this environment, mobile users
equipped with compact battery-powered palmtops or laptops need to access the large
volume of GIS data stored in the fixed network through Mobile Support Station
(MSS) by the wireless communication. In order to realize the GIS data storage in
MSS, it is essential to adopt mobile database technology.
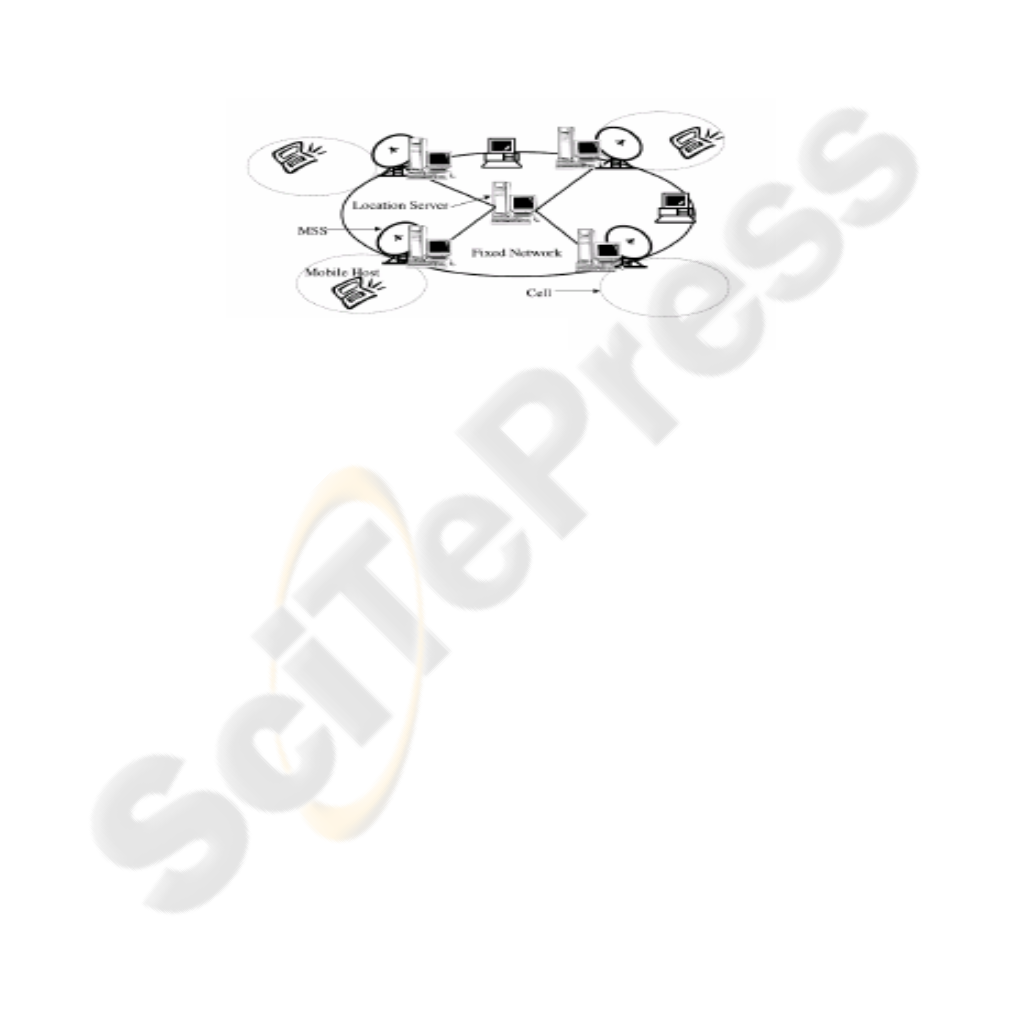
Fig.2. The model of Mobile Envinment
Fig.2 presents the model of a mobile environment. A mobile environment con-
sists of two distinct sets of entities: mobile hosts and fixed hosts. Some of the fixed
hosts, called MSS, are augmented with wireless interfaces to communicate with mo-
bile hosts, that are located within its radio coverage area called a cell. Mobile hosts
are connected by wireless connections to the MSS of the cell where they currently
exist. A mobile host can move within a cell or between two cells while retaining its
network connection. Further, every host and cell in the system is assumed to be asso-
ciated with a unique identifier.
The mobile computing environment is a distributed computing platform with the
following differences: the mobility and access devices of users, frequent disconnec-
tion, limited bandwidth and the mobile resource constraints - limited computational
and power sources.
As a part of a mobile database system, a mobile host acts as a data client and a
data server at the same time. A mobile host, as a data server, is to support basic trans-
action operations such as ‘read’, ‘write’, ‘commit’ and ‘abort’. WGIS should deploy
mobile database as data management, and the use of multi-ties, dynamic replication
technology is available.
119
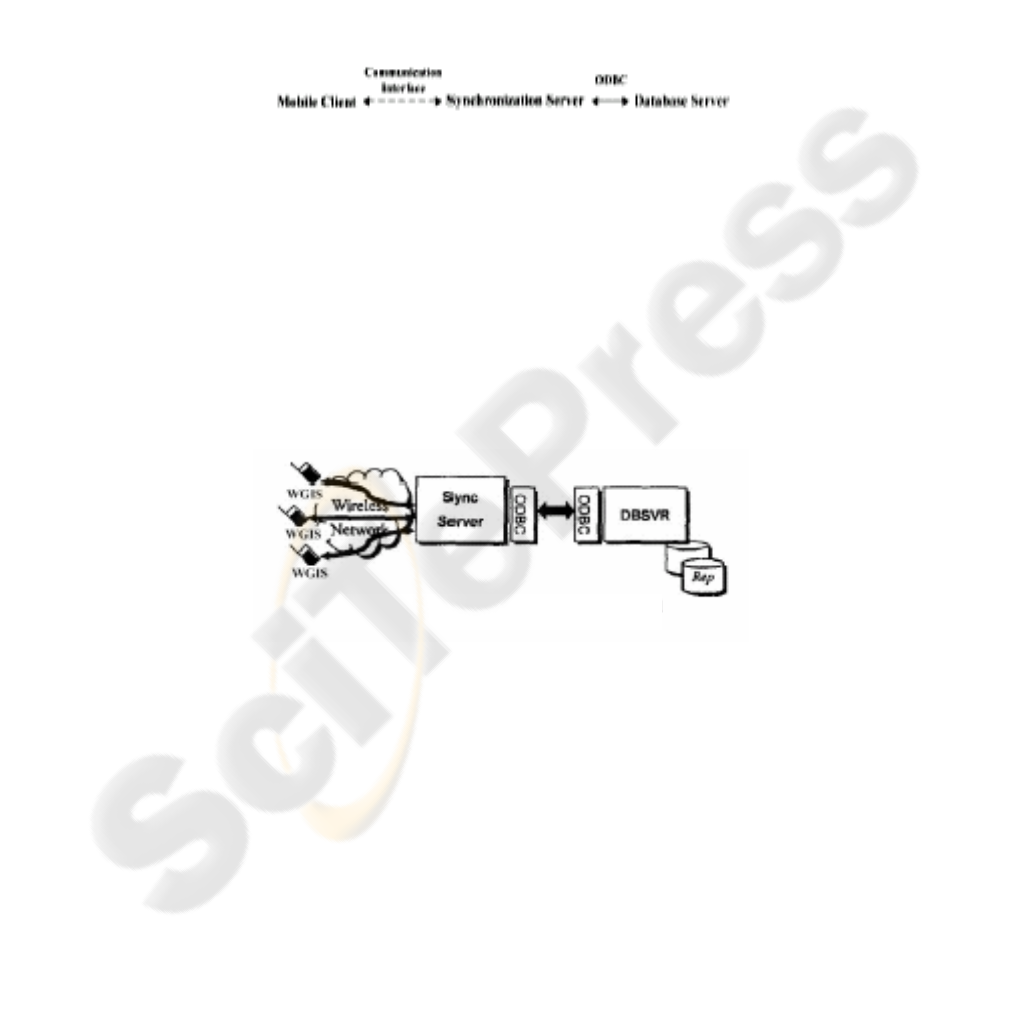
4.2 Three-Tier Replication Model in Mobile Database
In mobile computing environment, users can access information through wireless
connections regardless of their physical location. In mobile database systems, new
features, such as mobility, disconnection, low bandwidth, high bandwidth variability,
heterogeneous networks and security risks, make traditional database processing
schemes no longer well suitable.
Replication is one of the key technologies in promoting the performance of mobile
database systems. In WGIS mobile database system, the three-tier replication archi-
tecture, which is shown in Fig.3, is used to solve the synchronization problem, as
Fig.3. The three-tier architecture of wireless GIS database
Fig.3 and Fig.4 shows, WGIS mobile database is utilized as a synchronization
server to promote the efficiency of spatial data synchronization. It provides a replica-
tion model for database server (DBSVR) and WGIS. Besides, it ensures serializability
and consistency of the mobile database system through the reconciliation of transac-
tion-level conflict.
The function of Sync Server which is connected wireless communication interface
is making distributed processing, controlling spatial data exchange with WGIS and
database server, and sustaining a wireless cell. Mobile client conserves a database
duplicated copy, and through the GIS manages local geographic database. With the
ODBC interface, sync server could exchange spatial data with database server.
Fig.4. The three-tier WGIS replication model
4.3 Replication Dynamic
Replication is a general technique to increase the data availability. However, the gen-
erally available replication technologies assume the deployment on a fixed distributed
environment.
120

According to the behavior of replicas in replication schemes, we can categorize the
schemes into two replications, static replication and dynamic replication. In this pa-
per, dynamic replication for wireless GIS database is considered.
In static replication schemes, the location and the number of replicas are chosen
prior to the deployment. For example, traditional replication schemes, fall into this
category. Manual recalculation of the access cost and redistribution of replicas are
necessary to reflect newly accessing patterns. However, in a mobile environment,
static replication schemes may not perform well since the assumptions about fixed
locations and static accessing patterns are no longer held.
On the other hand, in dynamic replication schemes, the location and/ or the number
of replicas are changed to follow the accessing patterns to data being replicated. Dy-
namic replication schemes try to overcome the problems mentioned above by con-
tinuously maintaining statistics about accessing patterns and/or system workload so as
to dynamically recalculate access cost and reconfigure the replication structure to
adapt to the changes in accessing patterns. In general, this is desirable for a mobile
environment.
In a mobile environment, however, mobile hosts are dynamic. They could move to
anywhere and for unpredictable length of time. Furthermore, the users of replicas
may need to work at several ‘well-known’ sites. In such cases, it may be more advan-
tageous to deploy multi-replication, i.e., placing a replica on each ‘activity centre’ of
its users.
In a mobile computing environment, however, mobile hosts can move anywhere
and anytime, resulting in a highly dynamic system. Accordingly, the centre of activity
of replica readers is not static in general. Not only that, the ability of mobile users to
move can also make it more costly to find current location of mobile users and of
course the replicas if they are dynamic. In this sense, it is necessary to take a balance
between the cost of finding location and replica maintenance.
5 Comparisons of Various Data Storage Strategies in WGIS
In this section, we compare the dynamic multi-tier replication and dynamic-single
replication strategy strategies for wireless databases, which combine the two aspects
of replication policies mentioned above. We intend to show how some important
parameters related to the characteristics of data access in wireless environment affect
the performance of these strategies.
As the performance measure, the average access cost of data is used. In a network
environment, cost is mostly associated with the number of network packets trans-
ferred to do an activity which is observed until it is completed. In a mobile computing
environment, generally, network packets can be divided into two classifications, i.e.,
the data packet and the signal packet. The data packet consists of user data transferred
from the server to the client and vice versa. On the other hand, the signal packet con-
sists of data such as routing information, location lookup, and location update used by
the system,. However, for the reasons mentioned below, we simply ignore the signal
packet from our model.
121

Generally, the size of the signal packet is much smaller than that of the data
packet. Thus, when considering both of them, ignoring the signal packet will improve
the clarity of analysis and the resulting observation on the characteristic of each strat-
egy. In a mobile environment, signal packets are exchanged using a separated channel
from data packets. Therefore, separating the analysis of these two kinds of packets is
more logical and makes our model closer to the real situation in mobile computing
environments.
Without losing the generality, 50 mobile users are assumed to be sharing their da-
tabases with each other. The accesses include both ‘read’ and ‘update’. Access re-
quests arrive according to the Poisson distribution and the access configuration, i.e.,
the portions of ‘read’ and ‘update’, are determined by the ‘write’ ratio. We assume
that an ‘update’ operation will be preceded by a ‘read’ operation.
As for dynamic replication strategies, the implementations are as follows. As indi-
cated by the name, the dynamic-single replication strategy is implemented by making
each master database to only have single replica. In this strategy, each replica is ini-
tially allocated on the home location. As the simulation runs, mobile users start to
move and access the shared data. The replication manager in the registration area
where the user resides currently records every ‘read’ request from a mobile user.
Periodically, the access statistics from all registration areas are collected and com-
pared. Based on the comparison result, the system makes a replica relocated to the
registration area where the ‘read’ accesses to it are requested mostly, and the statistics
is reinitialized. In this way, the dynamic-single replication strategy is equal to user’s
major replica allocation.
As for the dynamic multi-replication strategy, the adaptive data replication (ADR)
with some modifications is adopted. The original ADR, metaphorically, forms a vari-
able-size that stays connected at all times, and constantly moves towards the 'centre of
read–write activity'. The replication scheme expands as the ‘read’ activity increases
and contracts as the ‘write’ activity increases. In our model, we have assumed that the
replicas are allocated on the replica servers associated with registration areas. That
means, the dynamic multi-replication strategy does not assume any connected situa-
tion.
However, as in the original ADR, ‘read’ the closest replica serves requests and all
access requests (including the updates) are recorded. In each registration area, the
access statistics are periodically tested. A replica of data is made available in a regis-
tration area, if during the access statistic evaluation period, the number of its ‘read’ is
greater than the number of its ‘write’. Otherwise, the registration area will cease
keeping the replica. In this way, the replication level changes dynamically following
the read–write patterns but it is guaranteed that at least one replica for each data exists
in the fixed network. In general, the average access cost increases in all strategies
when the network scales up. However, the way the access cost increases in each strat-
egy is slightly different, depending on the ‘move’ and ‘update’ frequencies.
6 Conclusions
In a wireless GIS environment, it is possible to access data anytime and anywhere
without a fixed network. In this paper, we discussed distributed spatial data transfer-
122

ring strategies and the replication strategies of the wireless GIS.It is possible to im-
prove the availability of wireless GIS which such a technology. Due to the use of
wireless network, WGIS may have very low availability without the effectively trans-
ferring scheme and data storage strategies. This may lead to inefficiency in data shar-
ing and interoperation among mobile users.
In this paper, we introduced the characteristics of wireless GIS transferring and
storage. The basic framework and the environment of WGIS are deployed in an inte-
grated network. By analyzing the distributed wireless data transferring scheme, it was
found that it depends on both software and hardware technologies in order to improve
WGIS transfers and increasing transferring velocity. The possible solutions may
include for example, spreading software protocol and employing new mobile equip-
ments.
The performance of replication strategies depends on many factors, such as net-
work scale, mobility, access ratio and access concentration. It was found that in most
circumstances, dynamic replication strategies excel to static replication strategies, and
the performance of the dynamic multi-tiers replication strategies is the best.
Nowadays, the wireless equipments become more and more excessive and wireless
GIS has been applied in many fields, like business, retailing, medicine, etc. Spatial
data transferring and storage in distributed wireless GIS is a challenge area to be
further developed. More and more comprehensive GIS application with 'wired veloc-
ity, infinity freedom' will be realized.
References
1. Sanjay Kumar Madria, Mukesh Mohania, Sourav S. Bhowmick, Bharat Bhargava, Mo-
bile Data and Transaction Management, Information Science 1411(2002) 279-309.
2. Wireless and Mobile ad hoc Networking and Computing. Journal of Parallel and Distributed
Computing. 63(2003) 1-2.
3. Ouri Wolfson, Moving Objects Information Management: The Database Challenge. Depart-
ment of Computer Science, University of Illinois.
4. Chao-Chun Chen, Chiang Lee, Chih-Horng Ke, Best Movement of Mobile Agent in Mobile
Computing Systems. Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Na-
tional Cheng-Kung University, Taiwan.
5. Cecila Mascolo, Licia Capra, Wlofang Emmerich, Mobile Computing Middleware. Dept. of
Computer Science, Univesity College London.
6. Lin Chengda, Meng Lingkui. New applications and research of GIS in the real estate. Inter-
national Conference on Info-Tech and Info-Net (ICII 2001). 261-266.
7. Meng, T. H, McFarland, B. Wireless LAN revolution: from silicon to systems. Radio Fre-
quency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 2001. Digest of Papers. 001 IEEE, 20-22
May 2001, 3-6.
8. N. Shiva Kumar, J. Jannink, J. Widom, Per-user profile replication in mobile environment:
algorithms, analysis, and simulation results, MONET 2 (2) (1997) 129–140.
9. Y. Huang, A.P. Sistla, O. Wolfson, Data replication for mobile computers, in: Proceedings
ACM SIGMOD-94, 1994, pp. 13– 24.
10. A.A. Helal, A.A. Heddaya, B.B. Bhargava, Replication Techniques in Distributed Systems,
Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1996.
123
