
Syntactic, Semantic and Referential Patterns in
Biomedical Texts: towards in-depth text comprehension
for the purpose of bioinformatics
Barbara Gawronska, Björn Erlendsson
School of Humanities and Informatics, University of Skövde, Sweden
Abstract. An es
sential part of bioinformatic research concerns the iterative
process of validating hypotheses by analyzing facts stored in databases and in
published literature. This process can be enhanced by automatic in-depth text
understanding. A prerequisite for this is an adequate syntactic and semantic
analysis. The paper presents the results of syntactic, semantic, and textual
analysis of a corpus of biomedical abstracts. It focuses on the ways in which
relevant molecular interactions are referred to in the abstracts, and proposes a
strategy for linking natural language expressions to the standard notation used
in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
The syntactic and semantic regularities observed in the language of biomedicine
are also discussed from the cognitive point of view.
1 Introduction and Background
1.1 Natural Language Understanding for the purpose of bioinformatics: main
challenges
One of the most serious problems that researche
rs within the field of bioinformatics
have to deal with is the textual information overload [1], [2], [3]. This is a generally
acknowledged difficulty, and serious attempts to overcome it, or at least diminish it,
are in progress. A very informative survey of the area is presented in [4].
The large medical literature databases MedLine and PubMed
(http://m
edlineplus.gov, http:// www.pubmedcentral.gov¸ [5], [6], [7].) provide access
to electronic medical lexicons, encyclopedias, document retrieval systems, and a
limited possibility of automatic query answering. Still, researchers in the field of
bioinformatics have to cope with several serious problems:
1. The s
hortage of integration tools: specialized databases, dictionaries,
encyclopedias, and literature are available in electronic form, but there are not
enough tools for synchronization of information coming from these sources. There
is also a need and for developing an ontology of different kinds of relationship. [8],
and [9], are an important step towards this goal.
2. Term
inological discrepancies: information about the same gene/protein is stored
under different names/codes in different databases. [1]
Gawronska B. and Erlendsson B. (2005).
Syntactic, Semantic and Referential Patterns in Biomedical Texts: towards in-depth text comprehension for the purpose of bioinformatics.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Natural Language Understanding and Cognitive Science, pages 68-77
DOI: 10.5220/0002566900680077
Copyright
c
SciTePress

3. Problems with coreference identification. The importance of anaphora resolution
is generally acknowledged [9]. Hahn et al. [5] present an algorithm for coreference
identification between hyper - and hyponyms, based on the Centering Theory [10].
However, only a few systems include such component
4. Problems with identification of relations between biological objects
(chromosomes, genes, proteins, diseases, distortions...). Most existing text retrieval
and text mining devices can inform the researcher that there seems to be some
relation between e.g. a gene and a disease, but in most cases they do not specify
what kind of relation it is. For current research aimed at improving extraction of
relations, see [11], [12], [9], [13], and [14].
5. Problems with distinguishing between relations reported as being true,
hypothetical, or absent, as in It is beyond any doubt that the lack of gene X in
chromosome Y causes disease Z, vs. The findings suggest that the loss of gene X
may play a role in the development of disease Z. vs. Gene X is not involved in the
development of disease Z.
What is needed for efficient, high-quality Information Extraction from biological
literature is more sophisticated Named Entity Recognition, better discourse
interpretation, and more reliable identification of objects and relations. The currently
available systems suffer from a shortcoming that many researches in the field of
bioinformatics complain about: the output contains too many false positives. The
users would be more benefited by a system that would deliver extractions with very
high confidence values, and which would leave more difficult/ambiguous texts or
sentences to be processed by humans.
1.2 The aims of the current project
This work is a part of a larger project, conducted in cooperation between
computational linguists and computer scientists working in the field of bioinformatics.
The project aims at creating an Information Fusion system for bioinformatic research
that should combine information coming from different sources: specialized
databases, ontologies, text databases, and lexical and grammatical resources [15].
Our approach to Information Extraction is based on the conviction that a careful
syntactic and semantic analysis is a prerequisite for high-quality text understanding.
Objects mentioned in a text cannot be identified, and thus relations between them
cannot be correctly extracted if the NLP component is not able to delimit the noun
phrases in the text. One of the most advanced commercial bioinformatic IE-tools of
today, MedScan [16] seems to suffer mainly from problems concerning the
delimitation of noun phrases (although the system is in many respects very
impressive). For example, a process that in the text is described as causing “cell
death” is by the system interpreted as causing death, just to mention an example. To
avoid this kind of errors, we decided to perform a syntactic, semantic and textual
analysis of a sample corpus of biomedical abstracts. The goal was to investigate the
repertoire of semantic and syntactic patterns in biomedical texts, and to state what
modification of already developed IE tools and resources are required in order to
make the output from a text comprehension system compatible with the notation used
in bioinformatic research.
69

2 The Method
We analyzed a corpus of biological abstracts from PubMed consisting of totally 14
090 words. The texts were POS-tagged by means of tools and resources that have
been developed for the purpose of information extraction from more general texts
(news reports). As lexical resources, we utilized parts of WordNet (the noun part and
the closed category words), and a lexicon of verbs and adjectives constructed during
the work on news reports. The only modification we employed was an addition to the
Named Entity Recognition procedure. We enriched it by a rule connecting acronyms
to full object names in order to handle cases like loss of heterozygosity (LOH).
After the first run of the tagger, we found that about 18% of the words (tokens)
remained unclassified. This was expected, since we did not use any specialized
medical lexicon. After completing the lexicon semi-automatically (by adding the
lacking terms and providing them with part-of-speech information) we tagged the text
again, removed the lines containing the names of the authors and their affiliations, and
performed a syntactic analysis of the remaining text (12 911 words).
The texts were analyzed by a parser based on Categorial Grammar and Referent
Grammar. About 70% of the sentences were parsed reasonably correctly. The
remaining 30% were analyzed manually. The results of the syntactic analysis were
then examined from a semantic perspective in order to find answer to the following
questions:
• what linguistic patterns indicate the difference between the background
information (references to previous research, already known facts etc.) and the new
information to be extracted?
• what linguistic markers are most frequently used to indicate the epistemic status of
a relation (i.e. how to distinguish between a claim, a hypothesis, a negation of a
previously mentioned claim etc.; cf. [17]) ?
• is the main verb in a sentence a good clue to identification of the relation between
biological objects, or is this information stored elsewhere in the syntax?
• how easy/difficult would it be to map the parsing results onto the set of relations
between biological objects that is utilized in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and
Genomes [18]; [19]?
3. The Results of Corpus Analysis
3.1 Noun Phrases
The analysis has shown that the texts were very NP-heavy. 74% of the total number
of words (tokens) in the material occurred within noun phrases. Personal pronouns
were relatively infrequent – only 80 occurrences, i.e. 0.6% of the word tokens. The
dominating pronoun was we (57 instances). We found only 12 instances of anaphoric
pronoun (this, they, and it). The following types of noun phrases were represented in
the material:
70

1. Quantifier-less phrases, consisting of a single noun (cancer, methylation) or a
single acronym (code of a protein, or a gene, like Mdm2 , p53) optionally preceded
by an adjective phrase – (17% of all NPs)
2. Nouns preceded by a quantifier or a determiner, with optional adjective attributes,
but without postnominal attributes (this locus, no aberrant bands) – (12%)
3. Phrases with a nominal compound as their kernel (with optional quantifiers,
determiners, and/or adjectives): cell death, gene-specific TSG methylation – (12%)
4. Phrases consisting of NPs enumerated under (1)-(3), followed by one or more
prepositional phrase(s) – (35%)
5. Phrases where a quantifier functions as the syntactic kernel (one of the 12 cases,
four of seven cases) – (4%)
6. Phrases containing an NP of type (1)-(3) or (5), followed by a relative clause –
(10%). Phrases with postnominal participle attributes were analyzed as equivalent
to phrases with relative clauses. This means that an NP like clones carrying
malignant alternations gets the same syntactic representation as clones that carry
malignant alternation.
7. NPs involving coordination (NP* and NP), disjunction (NP* or NP), and/or
apposition: two cell-cycle regulators, CDKN2A/p16/INK4A and INK4A-p14(ARF)
– (ca 11%).
A striking characteristics of the NP:s is the high frequency of nouns formed from
verbs. In the noun phrases, we found 414 deverbal nouns with the most productive
suffixes (-ion: expresssion, methylation; -ence/-ance: occurence; -ent: development,
impairment), and 122 -ing participles with either nominal function or involved in
attributive clauses (not following the auxiliary “be”). About 50% of the noun phrases
involved reference to a process/state. The three dominating semantic classes were: 1)
concrete biological objects/substances (cells, genes, chromosomes) 2)
biological/biochemical processes/states (activation, inhibition), and 3) research
activities and research results (investigation, study, finding). NP:s referring to human
beings were practically restricted to the first person plural pronoun meaning the
authors, apart from a couple of sporadic references to patient groups.
3.2 Auxiliaries, tense and modality
The most frequent verb in the material was be: 285 occurrences (infinitives, past
participles and simple tense forms). Out of these, 135 were used as auxiliaries in
passive constructions (be+past participle).The remaining instances occurred in the
context “NP be NP”, “NP be A”, or in semi-lexicalized phrases. Be was the clearly
dominating auxiliary, and the dominating tense forms were simple past and simple
present. It is worth noting that we did not find any occurrence of continuous tenses
(be + present participle).
There seem to be some cognitive reasons for the observed distribution of tense and
voice, especially the absence of continuous forms. A scientific text, in contrast to a
news reporter, does not focus on a single event that is going on in the time that
overlaps the time of writing. Thus, present continuous is not a tense form to be
expected in a scientific abstract. A researcher is primarily interested in regularities,
and general laws – thus, the simple present, which is the unmarked, “timeless” tense
form, is often the natural choice when talking about the properties of the biological
71

objects and processes. “When we wish to express, not validity or duration, but
validity at al times, we use the present tense” [20].
The simple past tense is used for reference to the parts of the experimental
procedure. Reichenbach’s [20] interpretation of the English simple past fits in with
the distribution of this tense in our material. In Reichenbach’s classical model, simple
past covers the situations where the event point E precedes the speech point S in time,
and the reference point R (corresponding to the sender’s perspective) coincides with
the event point. This means that the event referred to is regarded as distanced from the
speech act (or writing act) point. The past event is, as Pettersson [21] expresses it “in
another space” than the speech act. The distance and the perspective from outside are
no doubt suitable for expressing a scientific point of view.
Modal verbs were not very frequent in the material (36 occurrences, restricted to
can/could, may/might, and must). Despite the quite low number of occurrences, the
modal verbs cannot be ignored in the context of information extraction, since the
difference between facts and hypotheses is of crucial importance.
A practical conclusion to be drawn from the distribution of tense forms and
auxiliaries is that, when parsing the biomedical texts, we should get a higher
preference to rules handling verb phrases in simple tenses and in passive voice. The
ambiguous -ing participles should, be interpreted in the first hand as adjectives or
nouns.
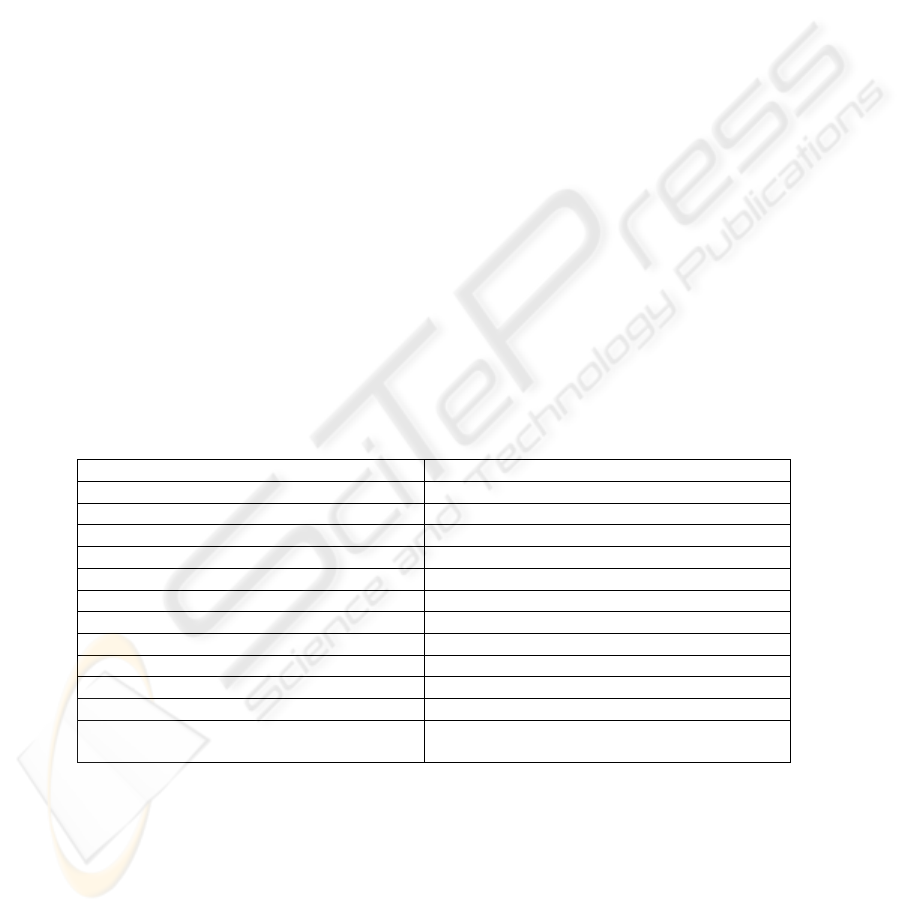
3.3 Content verbs: classification
Totally, we found 136 lexical verbs in the material. The verbs were classified
semantically into three main groups and then divided into subgroups on the basis of
shared syntactic and semantic patterns. The two largest groups are presented in tables
1-2. The distinguishing factor was whether the verbs occurred as referring to research
activity or to interactions/states involving objects in the world of molecular biology
(genes, proteins etc.). The third group consisted of verbs displaying different syntactic
valency patterns, but sharing the semantic feature “behaviour/manifestation”. The
verbs in this group were e.g. show, display, reveal. These verbs could appear with
reference both to the world of the researchers (Our results show that...) and the world
of biological objects (The two RIPs (...) show a protein segment…).
Further sub-classification of verbs in groups 1 and 2 was governed by the
semantico-syntactic valency patterns observed in the material.
The relations that are of most interest for the bioinformatic research conducted
within the current project are those denoted by verbs in group 2.1 and 2.3. This was
stated by asking the members of the bioinformatics research group to mark the
"interesting" verbs on the list of all lexical verbs in the material. The verbs they had
chosen belonged all to groups 2.1 and 2.3.
72

Table 1. Verb classes (1)
Group 1: Events in the world of the researchers
Valence and Occurrence Patterns Examples
Occurr-
ences
Lexical
Entries
1.1 Verbs of cognition and communication
a BObj/BProc is V + PastPrt report, understand, consider, 24 5
b Researcher V BObj/BProc analyze, examine, investigate,
realize, hypothesize
89 12
c Researcher V Study/Result present, restrict, extend 22 5
d Result V confirm, demonstrate, indicate 121 13
1.2 Verbs of manipulation
a Researcher V BObj add, expose, extract, knock,
generate, collect, infect,
32 14
b Researcher V Tool to/for BProc use, employ 24 2
Total 312 51
Table 2. Verb classes (2)
Group 2 Events in the world of the biological objects
Valence Pattern Examples
Occurr-
ences
Lexical
Entries
2.1 Interactions between biological objects (BObjs) and or biological processes (BProcs)
a Affect/cause verbs:
BObj1/BProc1 V BObj2/BProc2
Clear Agent and Patient roles
affect, activate, control, elevate,
inactivate, inhibit, induce,
regulate, enhance, methylate.
203 39
b Affect/cause verbs with
prepositional objects
BObj1/BProc1 V P BObj2/BProc2
lead, result 12 2
c Participation verbs; mostly
BObj1/BProc1 V P BObj2/BProc2
No clear Patient role
associate, combine, correlate,
contribute, include, involve,
play (a role), relate, coincide
88 10
d Resemblance verbs
BObj1/BProc1 V BObj2/BProc2
resemble, match, reflect 7 3
2.2 Verbs of location, existence, appearance, and state change
a Location verbs 1:
BObj1 is V+PastPrt in/of/at/by
BObj2
locate, compose, construct,
maintain, organize
14 5
b Location verbs2:
BObj1/BProc1 V BObj2/BProc2
harbour, contain, carry,
encapsulate
11 4
c Verbs of existence and appearance:
BObj/BProc V
appear, exist, occur, arise,
reappear
11 5
d Verbs of state change
BObj/BProc V (A)
elevate, decrease, increase,
vanish, disappear, become, vary,
remain
53 8
Total 399 76
It is of course of importance to provide these central relations with markers of their
epistemic status, extracted from the verbs of cognition and communication (group
1.1), modal verbs and adverbs, and negation particles. We assume that this can be
made in accordance with the model presented in Gawronska et al. [17]. The very
73
interactions between biological objects, however, should be mapped onto some
format that is generally accepted by the bioinformatic community. The first step
towards an adequate output format from the text comprehension system should thus
be to investigate how the verbs relate to the concepts employed in standard
bioinformatic reference sources.
3.4 Content verbs in the biomedical texts and biological relations in KEGG
In the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), knowledge about
interactions between genes, proteins and enzymes in various cellular processes is
represented in form of so-called KEGG pathway maps. Objects are divided into three
categories: 1) gene products 2) other molecules 3) "other maps" (i.e. networks of
relations). There is also a possibility of representing clusters of objects (so-called
object complexes).
The KEGG pathway maps employ a finite set of relations: In the descriptions of
cell cycle, for example, KEGG enumerates 11 protein-protein relations, 4 gene
expression relations, and 1 enzyme-enzyme relation. Five of the protein-protein
relations are highly specific ("phosphorylation" and "dephosphorylation"). Other are
not restricted to processes involving a specific molecule: "activation", "inhibition",
"association", "dissociation". Two subgroups are quite general: "state change" and
"indirect effect".
It is not entirely clear whether the concept of "state change" even includes "change
of amount". If yes, then all verbs classified as belonging to group 2.2.d in Table 2
would map onto this relation. Other relations would correspond to the verbs in
category 2.1.
Table 3. Relations between verbs from the corpus and KEGG gene/protein interaction classes
VERBS (examples) INTERACTIONS in KEGG
methylate methylation
activate, induce, promote, trigger, stimulate activation/expression
translated (part of) expression
inhibit, inactivate, block, suppress inhibition/repression
bind binding/association
disassemble dissociation
complicate, correlate, contribute, involve indirect effect
enhance, destroyed, kills, reduce, elevate state change
mediate (part of) expression or (part of) repression
affected, control activation or inhibition
regulate, modulate activation/expression or inhibition/repression
elicit, cause, allow, yield, produce, provoke,
release, undergo, associate, combine, lead
may correspond to different KEGG interactions
depending on the semantics of the arguments
On the basis of our corpus study, we established a set of most probable links between
the verbs in groups 2.1 and 2.2.d, and the KEGG interaction types (Table 3).
The last row in Table 3 contains verbs that - for different reasons - are ambiguous
in relation to KEGG interactions. associate and combine may refer to "true"
biochemical combinations of two objects ("binding/association"), or just to
coocurrence of objects/processes. Disambiguation would require checking the
74

semantic classes of the arguments of the verb. Other verbs in this category (lead,
cause, result) are semantically light and cannot be mapped onto some specific KEEG
interaction. These verbs merely indicate that there is a cause-result relation, but the
more specific information is to be extracted from the NPs, e.g. X causes methylation
of Y should be interpreted as “methylation”.
3.5 Coreference patterns in biomedical texts
Most efforts concerning intersentential anaphora resolution focus on pronominal
anaphora [22]. In the domain of bioinformatics, however, pronominal anaphora seems
of marginal interest. Personal pronouns are, as already mentioned, infrequent (only 12
anaphoric pronouns in a corpus of almost 13 000 words). The most frequent
anaphoric expressions are nouns preceded by this/these. About 30% of the
coreference cases we found were quite trivial, following the pattern: N X – this/these
N(s), like chromosome 9 – this chromosome. Other frequent patterns are of the type: a
sequence of coordinated acronyms – a noun referring to the type of biological objects
the acronyms denote, like: CDKN2A, CDKN2B and p14 – these genes. Such
anaphoric constructions are less trivial, but still possible to resolve automatically,
provided that the acronyms are correctly classified (in this example, as names of
genes) by the Named Entity Recognition component.
Another pattern that can be handled automatically is the one where NPs like this
question or this problem refer back to the preceding predication, like in: The pathway
through which hSNF5 acts remains unknown. To address
this question, we generated
MRT-derived cell lines. Phrases like unknown or not well understood are reliable
indicators of reference to a question or problem.
The classification of verbs employed here should also - in the future - facilitate
automatic resolution of cases where an abstract noun derived from a verb points back
to a predication containing one or more verbs belonging to the same semantic class,
like in Expression of p16(INK4A) was significantly elevated in the immortalized cells
but gradually disappeared during the accelerated growth phase. This alteration
correlated with loss of the contact inhibition response..., where the NP this
alternation points back to two predications with change-of-state verbs.
Reliable intersentential anaphora resolution in this domain requires access to
specialized databases (in order to classify the acronyms and names of biological
objects), which is a matter of future work.
4 Conclusions and Plans for Further Research
The syntactic, semantic and textual analysis of biomedical abstracts indicates that
tools, resources, and methods developed for the purpose of automatic understanding
of general language texts (WordNet, at least its noun part; POS-taggers, general
computerized grammars) can be to a considerable extent used for processing
specialized texts. The tagger and the syntactic parser developed for general texts
required certain domain-specific additions (concerning long acronym sequences and
mathematical symbols), but could successfully process the majority of input. Many
75

syntactic and morphosyntactic rules that were did not need to be activated when
parsing the biomedical texts: for example, rules handling continuous tenses had never
to apply. Adapting a general parser to a new domain seems to be rather a matter of
weighting the rules than of changing them in an essential way.
The lexical representations of verbs of cognition and communication that are of
crucial importance for understanding e.g. news reports [17] are of use also in the
domain of biomedicine. Many lexical verbs in the analyzed material belong to the
cognition and communication category. These verbs (and their interplay with modals
and negation) function as significant indicators of the distinctions between
foreground/background information, or between hypothetical vs. 'real' states-of-
affairs.
The linguistic classification of content verbs, based on semantic and syntactic
patterns, seems to be useful for the purpose of IE in general. The verbs that have been
marked as relevant vs. irrelevant by our colleagues from the field of biology and
bioinformatics corresponded almost in 100% to the classes we identified on purely
linguistic basis. This indicates that the domain-specific classification of objects and
relations is probably governed by the same cognitive patterns as the semantics of
general language.
The biomedical texts are very NP-heavy. Nouns derived from verbs are very
frequent. The frequency of relative clauses and attributive participle constructions is
also quite high. This means that relations between biological objects are encoded not
only by main predicate verbs, but also within noun phrases. A correct analysis of
noun phrases is hence very important for text understanding. The most serious
problems in parsing noun phrases are caused by ambiguous coordinated constructions
with and/or. Since these constructions are difficult to understand even for human
informants lacking deep domain knowledge, it is questionable, whether it makes sense
to try to resolve them automatically (and risk to produce false positives), or whether it
would be better just to mark such constructions as ambiguous and let the specialists in
biomedicine interpret them.
The coreference patterns in the investigated corpus involve almost no cases of
pronominal anaphora. Anaphoric links between whole predications and nouns formed
from verbs is frequent. This confirms the need of detailed representation and
classification of verbs and deverbal nouns.
The investigation performed here focused on syntax, coreference patterns, and verb
semantics. We did not address the question of detailed classification of biological
objects. We are aware that the WordNet categorization is far too general to be utilized
for IE in bioinformatics. A way to overcome this problem would be to identify and
annotate WordNet nodes with respect to different hierarchy types, and to connect
these annotated nodes to the information stored in bioinformatics databases, (like the
Gene Ontology). We plan to investigate this possibility in cooperation with a research
group in bioinformatics.
References
1. Narayanan, A., 2003. Document Technologies for Bioinformatics, Ms, Dept. of Computer
Science, University of Exeter, GB.
76

2. Narayanan, A., Keedwell, E.C., Olsson, B., 2002. Artificial Intelligence techniques for
bioinformatics. In Applied Bioinformatics, Vol. 1 Nr. 4, pp. 191-222.
3. Narayanan, A., Keedwell, E., Tatinneni, S.S., Gamalielsson, J., 2003. Artificial Neural
Networks for Gene Expression Analysis’, 19 March,
www.dcs.ex.ac.uk/~anarayan/publications/combined_gene_expression_paper.pdf
4. Hirschman, L., Park, J.C., Tsujii, J., Wong, L., Wu, C.H., 2002. Accomplishment and
challenges in literature data mining for biology. In Bioinformatics, Vol. 18, Nr. 12, pp.
1553-1561.
5. Hahn, U., Romacker, M., Schulz, S., 2002. Creating knowledge repositories from
biomedical reports: The MEDSYNDIKATE text mining system. In Pacific Symposium on
Biocomputing 2002, Kauai, Hawaii, USA, pp. 338 - 349.
6. Gene Ontology general documentation, 2004. An Introduction to Gene Ontology, 18
March, http://www.geneontology.org/GO.doc.html
7. Smith, B., Williams, J.,Schulze-Kremer, S., 2003. The Ontology of the Gene Ontology. In
Proceedings of AMIA Symposium 2003, Ottawa, Canada, pp. 609-613
8. Putejovsky, J., Castano, J., 2002. Robust relational parsing over biomedical literature:
Extracting inhibit relations, Proceedings of PSB 2002, Hawaii, USA, pp. 362-373.
9. Park, J.C. Kim, H.S., Kim, J.J., 2001. Bidirectional incremental parsing for automatic
pathway identification with combinatory categorical grammar. In Proceedings of PSB
2001, Hawaii, USA, pp. 396-407.
10. Sidner, C., 1983. Focusing in the comprehension of definite anaphora. In Brandy, M. and
Berwick, R. C. (eds.) Computational Models of Discourse, pp. 267-330. MIT Press,
Cambridge.
11. Ding, J., Berleant, D., Nettleton, D., Wurtele, E., 2002. Mining MEDLINE: Abstracts,
sentences or phrases?, In Proceedings of PSB 2002, Hawaii, USA, pp. 326-337.
12. Stapley, B., Benoit, G., 2000. Biobibliometrics: Information retrieval and visualization
from co-occurrences of gene names in Medline abstracts. In Proceedings of PSB 2000,
Hawaii, USA, pp. 529-540.
13. Friedman, C., Kra, P., Yu, H., Krauthammer, M., Rzhetsky, A., 2001. GENIES: A natural-
language processing system for the extraction of molecular pathways from journal articles,
In Bioinformatics, Vol. 17.
14. Rindflesch, T., Tanabe, L., Weinstein, J., Hunter, L., 2000. EDGAR: Extraction of drugs,
genes, and relations from biomedical literature. In Proceedings of PSB 2000, Hawaii, USA,
pp. 517-528.
15. Gawronska, B, Olsson, B, de Vin, L., 2004a. Natural Language Technology In Multi-
Source Information Fusion. In Proceedings of the International IPSI-2004k Conference,
Kopaonik, Serbia, April 2004, Published on CD with ISBN 86-7466-117-3
16. Novichkova, S., Egorov, S., and Daraselia, N., 2003. MedScan, a natural language
processing engine for MEDLINE abstracts. In Bioinformatics, vol. 19:13, pp. 1699-1706.
17. Gawronska, B., Torstensson, N., Erlendsson, B., 2004b. Defining and Classifying Space
Builders for Information Extraction. In Sharp, B. (ed.): Proceedings of NLUCS- (Natural
Language Understanding and Cognitive Science), Porto, Portugal, April 2004, pp 15-27
18. Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes. http://www.genome.jp/kegg/, 2005-02-14
19. Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima, S., Okuno, Y., and Hattori, M., 2004. The KEGG
resources for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D277-D280
20. Reichenbach, H., 1947/1966. Elements of Symbolic Logic, Collier-Macmillan Canada,
Toronto, Ontario.
21. Pettersson,T., 1994. Tense. In Working Papers 42, Dept. of Linguistics, Lund University,
Sweden, pp. 179-196.
22. Mitkov, R., 2003. Anaphora Resolution. In Mitkov, R. (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of
Computational Linguistics, Oxford University Press.
77
