
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH PERFORMANCE SERVO
DRIVE/ANTI DRIVE MECHANISM FOR BACKLASH REMOVAL
I. Askari, S. A Hassan, M. Altaf, A. Azim, M. B. Malik, K. Munawar
College of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering. Rawalpindi. Pakistan
Keywords: 1 Degree of freedom Platform, Backlash Removal, System Modelling.
Abstract: In electromechanical drives, there is always a backlash between any pair of gears. Because of this, it is
almost impossible to realize a high accuracy and high performance drive. However such drives are crucial
in today’s modern electromechanical systems. A high performance drive/anti-drive servo mechanism is
developed to eliminate the effect of backlash. The concept utilizes redundant unidirectional drives to assure
positive coupling of gear meshes at all times. Based on this concept, a methodology for enumeration of
admissible redundant-drive backlash free mechanism has been established. The angular displacement is
achieved as a difference of two torques. These torques can be controlled by a high performance control
system. A controller model will be designed to move a single degree of freedom platform up to a desired
span with a payload.
1 INTRODUCTION
Manipulators use gear trains for power transmission
to allow actuators to be located in some desirable
position. Gear trains are also used for torque
amplification. Backlash is provided for prevention
of jamming of gear teeth due to manufacturing
errors or thermal expansion. However, backlash can
cause momentary loss of coupling between two
matting gears whenever there is torque reversal. It
can result in motion discontinuity, position
uncertainty, and impact in mechanical systems,
which, in turn, make accurate control of manipulator
difficult. End-effecter positioning accuracy is also
compromise due to backlash. Precision gears,
spring-loaded split gear assemblies, and precise
mechanical adjustment are often used to overcome
these difficulties. However, these techniques do not
completely eliminate the backlash and can increase
the cost of manufacturing and assembling.
Many methods such as backlash compensation
(Veitschegger and Wu, 1986), antibacklash gears
(Michalec, 1986), adjustable tooth thickness gears
(Michalec, 1986), adjustable center distance
(Dagalakis and Mayers, 1985) and harmonic drives
(Calson, 1985) have been proposed for the
elimination of backlash. Improvement on problems
caused from gear backlash has been made by using
these methods, e.g., backlash compensation used in
machine tools. However, these methods become
inadequate for robotic systems.
Presently none of these methods can eliminate
backlash in robotics completely. For example, the
method of adjustable center distance has been used
for the assembly of PUMA 560 robot. The backlash
control mechanism supplied by the manufacturer for
the PUMA robot is an eccentric cartridge-bearing
arrangement, as shown in figure1. Adjustable
centers are subject to maladjustments, and in the
field there is no assurance that the quality of a
readjustment will be comparable to the original.
This paper is a continuation of our previous work
where we developed a 2 DOF platform (Tanveer and
Masood et al, 2005), designed the controller (Askari
and Hassan et al, 2005), and finally modeled the
system (Hassan and Askari et al, 2005). Besides the
appropriate position as well as tracking control, the
only flaw of that system was backlash that resulted
in reduced efficiency for the tracking purposes. In
this paper a new concept of drive antidrive
mechanism has been described for one degree of
motion which results in a minimum backlash
between the gears to obtain a stable backlash free
system.
453
Askari I., A Hassan S., Altaf M., Azim A., B. Malik M. and Munawar K. (2006).
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH PERFORMANCE SERVO DRIVE/ANTI DRIVE MECHANISM FOR BACKLASH REMOVAL.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 453-456
DOI: 10.5220/0001199304530456
Copyright
c
SciTePress
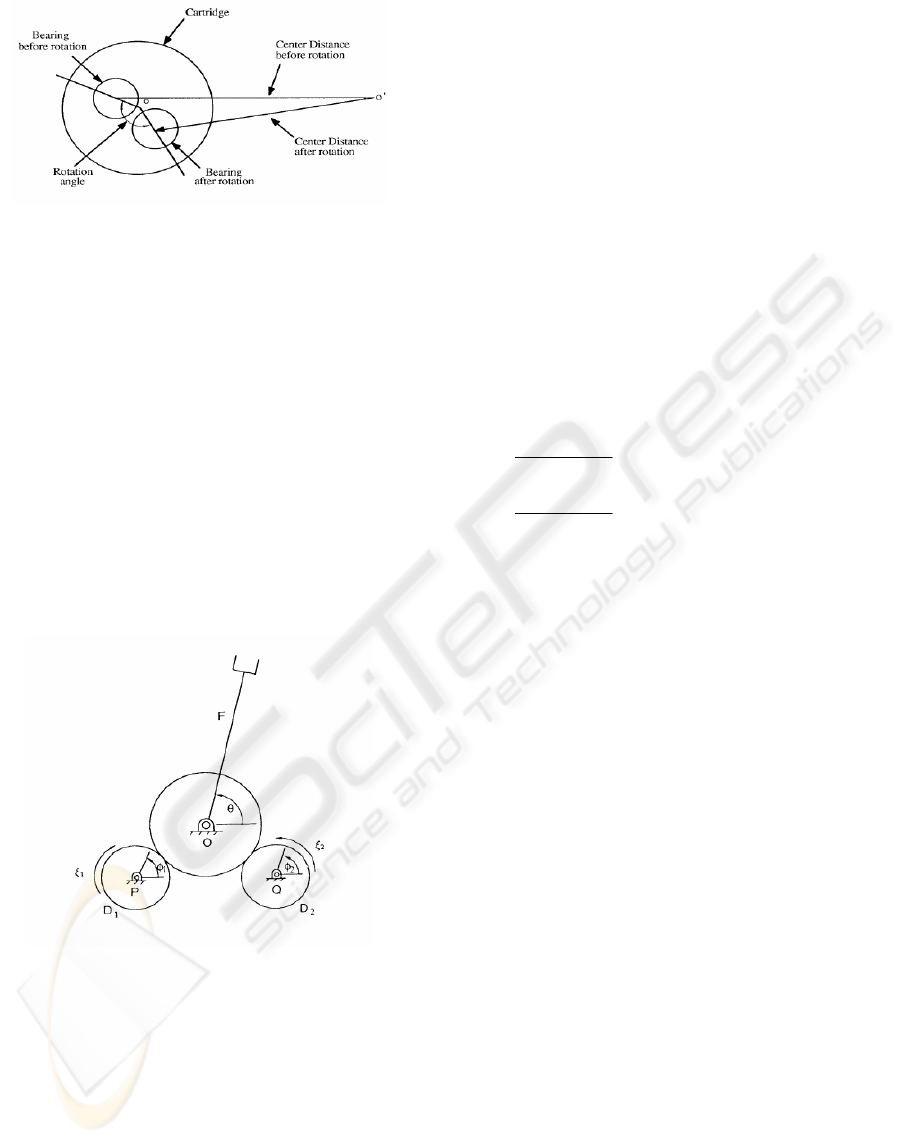
Figure 1: Backlash control mechanism using adjustable
centre distance.
2 THE CONCEPT
Figure 2 shows a simple one-DOF gear train with
two unidirectional drives, where D1 and D2 are the
driving gears and F is the follower. The backlash in
this mechanism can be controlled by applying
torques to D1 in clockwise sense and D2 in a
counter-clockwise sense at all times. The resultant
torque acting on F will be in the counter clockwise
or clockwise sense depending whether torque
contributed by D1 is greater or less than that
contributed by D2. Since no torque reversal is
required to drive F, the effects of gear backlash are
completely eliminated.
Figure 2: One-DOF Mechanism with redundant
unidirectional drives.
The controllability can be analyzed from kinematics
and static point of view. The kinematics equation
for the mechanism shown in figure 2 can be written
as:
()
()
1
1
2
2
/
/
f
f
NN
NN
φ
θ
φ
⎡⎤
−
⎡⎤
⎢⎥
=
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
−
⎣⎦
⎣⎦
(1)
Where
1
φ
and
2
φ
and θ denote the angular
displacements of gears D1, D2 and F respectively,
and,
12
,NN and
f
N represent their tooth
numbers. Note that the negative sign stands for an
external gear mesh.
For such a mechanical system, it can be shown that
the input and output torques are related by following
equation:
()()
1
12
2
//
ff f
NN NN
ξ
τ
ξ
⎡⎤
⎡⎤
=− −
⎢⎥
⎣⎦
⎣⎦
(2)
Where
1
ξ
and
2
ξ
are the torques applied to D1 and
D2 respectively, and,
f
τ
is the output torque on the
follower F. Thus, given the input torques
1
ξ
and
2
ξ
,
the resultant joint torque,
f
τ
is uniquely determined.
However, for a desired output torque
f
τ
, the
required input torques are indeterminate. For
example, the input torques can be expressed as:
()
()
2
12
22
12
11
2
22
12
22
12
f
f
f
NN
NN N
N
N
NN
NN N
ξ
τλ
ξ
⎡⎤
−
⎢⎥
+
⎡
⎤⎡⎤
⎢⎥
=+
⎢
⎥⎢⎥
⎢⎥
−
−
⎣
⎦⎣⎦
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
+
⎣⎦
(3)
Where
λ
is an arbitrary real number. The first term
on the right hand-side of (3) is referred to as the
particular solution and second term the
homogeneous solution. From (3) it is clear that by
selecting proper positive λ, the sense of input
torques
[
]
12
T
ξ
ξ
can be maintained in the
[
]
T
+
−
direction at all times regardless of the value of
f
τ
. Similarly, the sense of input torques can also be
maintained in the
[
]
T
−
+
direction by selecting a
proper negative λ. Hence, the mechanism can be
controlled by two unidirectional drives designed
either in the
[
]
T
+
−
direction or in the
[
]
T
−+
direction.
Since the input torques can be maintained in the
predetermined unidirectional senses at all times,
backlash will never occur.
3 MANIPULATOR
CONSTRUCTION AND
DYNAMIC MODEL
3.1 Construction
A high performance drive/anti-drive servo
mechanism has been developed to eliminate the
effect of backlash. A single degree of freedom
platform has been constructed with gear reduction
ICINCO 2006 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
454
99.231. The selection of DC servomotor has been
done by off shelf parts of second hand parts of
printers and other electric equipments available in
local market. Arrangement of gear selected as
following:
Gear 1= 46: 18 gear ratio; Gear 2 = 41: 17 gear
ratio
Gear 3= 42: 21 gear ratio; Final Gear1= 161 teeth
Actuator Gear = 20 teeth
Total gear reduction =
1
/
f
NN
= 99.231: 1
Actuator is Minertia DC brush less motor with a
supply of 36 volts DC and a Speed of 2000 rpm.
With above specifications the platform can move at
angular speed of 120.9 degree per second. This was
required to move the camera, tracking a target, in
such away that there would be no backlash in the
manipulator.
Two sets of motors and gear arrangements have
been used to construct the drive/anti-drive
mechanism of the manipulator. Figure 3 shows the
simple one-DOF gear train with two unidirectional
drives, where D1 and D2 are the driving gears and F
is the follower.
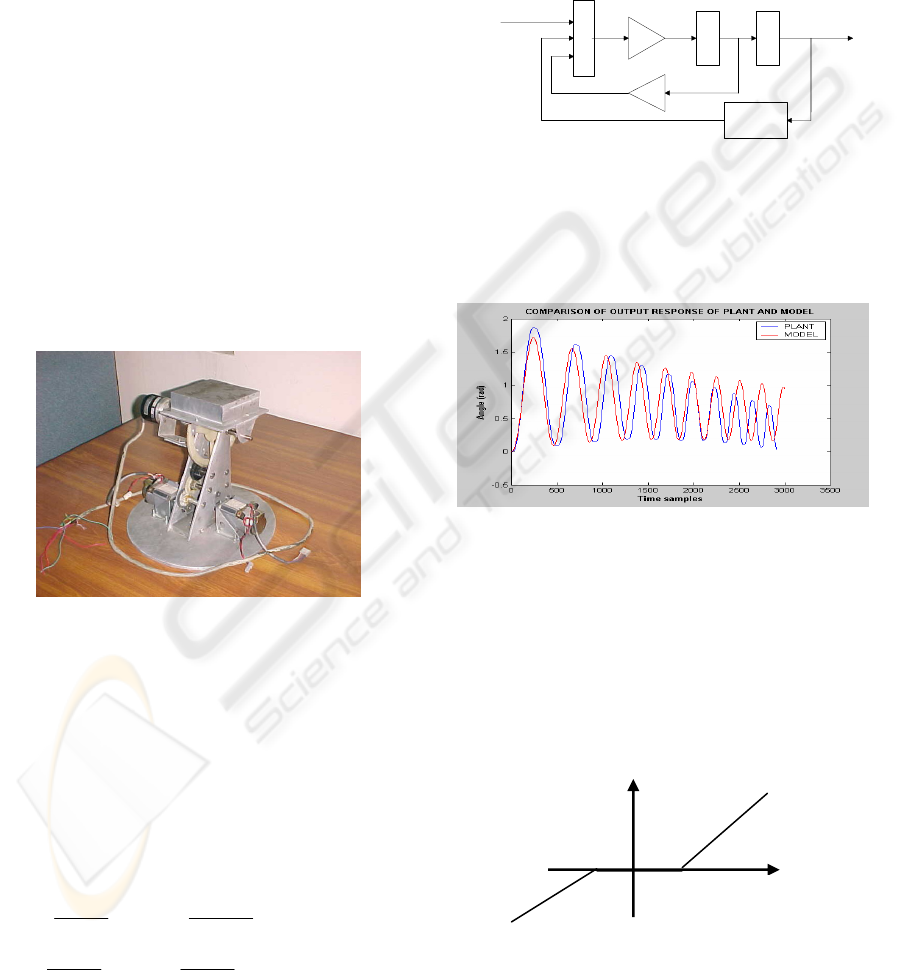
Figure 3: Photographic view of the manipulator.
3.2 Model of the system
Since the system is almost similar in construction
and principle as constructed for the 2DOF platform
(Tanveer and Masood et al, 2005), but here the only
degree of motion is the elevation so using the
previous method of Least Squares (Hassan and
Askari et al, 2005), the continuous and discrete
forms of the model are as follows:
cos (4)Jx x Kx
α
τ
=− − +
2
2
2
[ ] cos [ ] [ 1] (5)
- [ 2] [ ]
TJkT
xk xk xk
JkT JkT
JT
xk k
J
kT J kT
α
τ
+
=− + −
++
−+
++
The parameters of the model are found by giving a
persistently exciting chirp signal at input and the
system is examined on a desired set of frequencies.
The system parameters found are as follows:
J = 2; α = 0.5; K = 0.8
For model validation, a similar model of the
system with above parameters was simulated in
SIMULINK and both the Simulink and actual model
were excited by the same chirp input and response
was calculated.
+
-
-
∫
1/J
∫
1
cos
x
α
2
x
K
input
output
1
x
τ
Figure 4: Simulated model for the plant.
The estimate is approximately close to the actual
values of the parameters for the desired range of
frequencies, as shown in figure 5.
Figure 5: Comparison of output responses of the plant and
model simulations.
4 DEADZONE NONLINEARITY
Deadzone nonlinearity (due to backlash), shown in
figure 6, causes the reduction in the actuator
movement. It is expected in the model whenever
there is direction reversal in the actuator.
Figure 6: Input-output characteristic curve for deadzone
nonlinearity.
slo
p
e=1
Out
p
u
t
in
p
u
t
-D Zone
D Zone
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH PERFORMANCE SERVO DRIVE/ANTI DRIVE MECHANISM FOR BACKLASH
REMOVAL
455
We introduce a deadzone nonlinearity of 0.5 in the
plant model.
By introducing deadzone function h(.), the model
equation will be of the following form:
cos [ ] (6)Jx x Kx h
α
τ
=− − +
Where
[
]
where deadzoneh
ττγ γ
=− =
.
By applying step input,
x
will be zero at steady
state. Hence left hand side of (6) will be zero.
Therefore at steady state
0
s
s
x
x
ω
=
=
Now (6) will become
(
)
cos
cos
ss
ss
Kh x
x
K
ωτα
τγα
ω
=−
−−
=
(7)
By applying three different values of step input
τ
,
result in giving three values of
s
s
ω
. An average of
output angle of the manipulator, is taken as output,
as
av
x
during the steady state region. Hence three
sets of equations results as follows:
11 1
22 2
33 3
cos
cos
cos
s
sav
s
sav
s
sav
Kx
Kx
Kx
τ
ωγα
τωγα
τωγα
=++
=++
=++
(8)
Applying three different values of
τ
and observing
data the values are as following:
1 ss1 av1
2ss2 av2
3ss3 av3
5 5.65 111.5deg
10 11.89 236.05deg
15 18.12 360.48deg
τ
ωθ
τω θ
τω θ
== =
== =
== =
Substituting the above values in (8), the estimates
are:
α = 0.0047; K = 0.8 γ = 0.47
The estimates of
and K
γ
are approximately in
acceptable limits, however
α
is not estimated
accurately. It happened because of taking average of
output angle in (8). We are not interested in it
because
α
has already been estimated by least-
squares method.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have presented a new concept for
controlling gear backlash of an articulated gear
mechanism. A high performance single degree of
freedom platform has been developed with
redundant drives. The concept utilizes redundant
unidirectional drives to assure positive coupling of
gear meshes at all times. One side-benefit of this
class of mechanism is that it is fail safe, i.e., unless
there is loss of backlash control, the mechanism can
continue to function even when one of its actuator
fails to work.
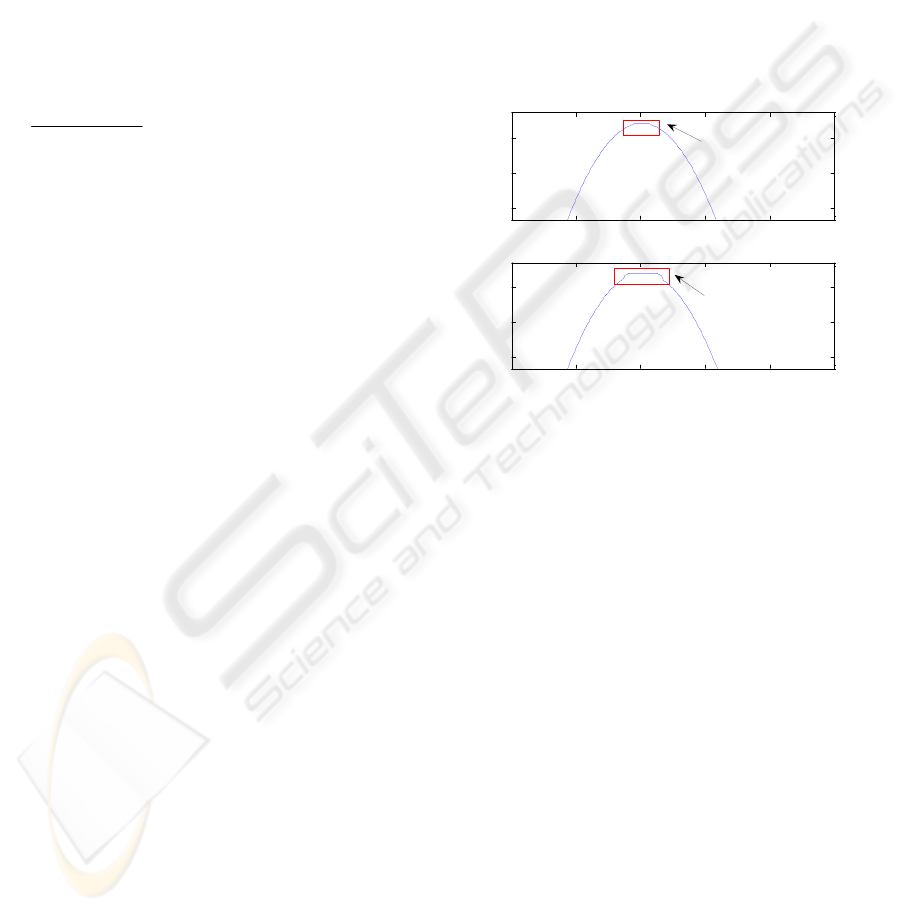
The following simulation shows the result of the
removal of backlash in the system. In figure 7a) the
platform is controlled by using the drive antidrive
mechanism, the deadzone or backlash reduces and
there is just a constant output for 12 time samples
only. But using one actuator, the output remains
constant for approximately 35 data samples at the
position of torque reversal. So there is a remarkable
improvement in the system response and the effect
of backlash has considerably been removed.
2250 2300 2350 2400 2450 2500
0.2
0.205
0.21
Time Samples
Angle in radians
Output of the Platform for both actuators
2250 2300 2350 2400 2450 2500
0.2
0.205
0.21
Time Samples
Angle in radians
Output of the Platform for one actuator only
output remains
constant for less
number of samples
output remains
constant for more
number of samples
Figure 7: Output response for single and double actuators.
REFERENCES
Tanveer Abbas, Muhammad Yasir Khan, Masood-ul-Haq
Barlas, Khalid Munawar, 2005. Development of a
2DOF Tracking system, Part I: Design and
Fabrication. In Proceeding of IEEE - ICET 2005.
Irtaza Askari, Syed Ali Hassan et al, 2005. Development
of a 2DOF Tracking system, Part II: Controller design
and Implementation. In Proceeding of IEEE - ICET
2005.
Syed Ali Hassan, Irtaza Askari et al, 2005.Development
of a 2DOF Tracking system, Part III: System
Modeling. In Proceeding of IEEE - ICET 2005.
Chi-Tsong Chen. 1984. Linear Systems: Theory and
Design. Second Edition. Saunders College Publishing,
Fu, K.S. et al. 1987. Robotics: Control, Sensing, Vision
and intelligence .McGraw-Hill.
Franklin, G.F. et al, 2000. Digital Control of Dynamical
systems. Third edition. Addison-Wesley.
ICINCO 2006 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
456
