
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT
WITH DOCBOOK
Alberto González Téllez
Department of Computer Engineering, Polytechnic University of Valencia, E.U. Informática, Valencia, Spain
Keywords: Teaching document production, document management, Docbook, XML.
Abstract: Document production is an important aspect of academic activity. Nowadays the most common tools used
to create teaching documents are office suites and e-learning oriented authoring applications. We found that
none of these options fulfill our requirements of content repository management, content filtering and
presentation format selection, and last but not least being open and free. Docbook is a book production
oriented XML compliant language, so it has the capability of using the standard XML processing tools like
XSLT, XPath, XInclude and XQuery. The main parts of Docbook (DTD and stylesheets) are open source.
These basic components can be customized and complemented in order to get adapted to application
requirements and final users. After some years of experience using Docbook to produce our teaching
material we found productive tools and we developed some Docbook customizations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional teaching based on blackboard and
lecturer speech is nowadays dying due to the
availability of computers and the Internet. The use of
these technologies requires new tools to create
learning and teaching material.
The most common tools are office suites like
Microsoft Office and Open Office. This is the case
for example in our university. Office suites have a
good user interface and are flexible enough to cover
many requirements of authoring learning/teaching
content. But after years of work lecturers find
themselves with piles of documents, many of them
redundant, and in spite of being in electronic format
it is difficult to reuse them because almost
everything has to be made by hand. Another
inconvenient is that document formats are
proprietary so users become linked to software
companies and products.
There are many authoring tools specifically
oriented to e-learning (e-learning, 2006). This
market has expanded mainly because of the interest
of business organizations in creating their own
learning resources. These tools are very productive
and fulfill almost all the e-learning platform
requirements. But they use to be very expensive and
they also create a strong link between users and
software companies. Like office suites, these
applications have their own data formats. In spite of
being able to export open formats, it is impractical to
work on them directly. Also a big effort is required
in order to port these formats to another application.
We decided to get another way and try to find an
authoring environment that was productive, open
and flexible. Some attempts have been made in this
direction (Kirsch-Pinheiro, K., 2001 and Süß, Ch.,
2002) but we have found them unsatisfactory
because they rely on unstable applications, they do
not focus on the aspects we are more interested on
(exercise management, exam generation, multiple
presentation formats, etc) or they use non standard
formats.
1.1 XML and Docbook
In 1998 the World Wide Web consortium published
the XML specification (W3C rec 04, 2004) with the
aim of becoming an open standard to data
representation and application interoperability. This
specification was complemented with a set of
standard tools to support data processing. The main
XML tools are:
– DTDs and schemas: Techniques to define XML
languages (W3C rec 28, 2004).
188
González Téllez A. (2006).
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT WITH DOCBOOK.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and
e-Government / e-Learning, pages 188-195
DOI: 10.5220/0001238901880195
Copyright
c
SciTePress

– XSLT stylesheets: XML processing language
(W3C rec 16, 1999).
– XPath: XML data climbing language (W3C rec
16, 1999).
– XQuery: XML data querying language (W3C
cand 3, 2005).
– XLink (W3C rec 27, 2001) and XInclude (W3C
rec 20, 2004): XML data linking and modular
composing.
Every markup language that is XML compliant
can benefit from all of these techniques. The
particular language we choose will depend on the
application we are involved with. There are XML
languages defined for many applications:
– SVG for vector graphics (W3C rec 14, 2003).
– MathML for mathematical equations (W3C rec
21, 2003).
– XHTML for web pages (W3C rec 26.1, 2002).
– SMIL for multimedia presentations (W3C rec
13, 2005).
– Web services (SOAP, WSDL)
– Business interoperability (ebXML)
– Etc…
Docbook (Docbook, 2006) is an XML language
oriented to book production and management that
we found very well suited for producing and
organizing teaching content. The basic Docbook
tools are the DTD and the XSLT stylesheets to
produce web and printing formats. Both of them are
open source and can be found on the Docbook site.
These basic tools have to be complemented with
authoring tools and some customizations in order to
fulfill application requirements. Either DTD and
stylesheets are fully customizable at several levels of
complexity (Walsh, N., 2003 and Stayton, B., 2005),
usually simple customizations will suffice.
End users have to be kept completely away from
XML details, so user friendly tools have to be
offered. Nowadays this is not so well accomplished
in Docbook as in office suites, but some tools are
evolving quickly in this direction. The authoring
toolset we use includes:
– Content editor. We have found XXE (XXE,
2006) a good choice, but many others are
available.
– Format generator. XFC (XFC, 2006) is a
general application with a GUI interface. We
think that a more customized one is desirable.
– Content manager. Qizx (Qizx, 2005) is a freely
available XQuery tool.
After some years using Docbook to produce and
manage teaching documents, we raised the
conclusion that the effort of customizing Docbook
and developing user friendly tools is worthwhile. In
this work we first describe briefly Docbook basic
tools and customization techniques. Next we
describe some customizations we have implemented
and the tools that we selected and developed to
produce and manage documents. Finally some
conclusions and future work directions.
2 BASIC TOOLS
Docbook DTD and XSLT stylesheets are available
on Docbook source forge project (Docbook, 2006)
whose main administrators are Norman Walsh and
Bob Stayton. The DTD and stylesheets main books
are public in web format. Authoring tools usually
include these basic tools.
2.1 Docbook DTD
There are two techniques to validate XML
documents: DTDs and schemas. DTDs are inherited
from SGML and they are a compact way to specify
XML syntax. However they have light control over
some syntax aspects. Schemas have a stronger
syntax control capability but they are more complex.
DTDs simplicity has avoided their complete
replacement by schemas and many XML languages
are still specified by means of DTDs. DocBook
specification is available in DTD and in the schema
language RelaxNG.
Docbook elements can be classified as:
– Hierarchical elements
– Sets
– Books
– Divisions
– Components
– Sections
– Meta-information elements
– Content elements
– Block elements
– Inline elements
Sets are collections of books. A book can begin
with a dedication element followed by navigational
components (tocs, lots and indexes). Divisions are
the first hierarchical level after book, they include
part elements and reference elements. Parts contain
components which include the book content and
reference elements contain refentrys. Components
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT WITH DOCBOOK
189

are chapter-like elements: preface, chapter,
appendix, glossary and bibliography. Sections
organize the chapter contents, there are several kinds
of sections: sect1…sect5, section, simpesect,
bridgehead, refsect1…refsect3, glossdiv, bibliodiv
and indexdiv. Sect, section and refsect elements can
nest. All elements in the section level and above
include a wrapper for meta-information about the
content.
Immediately below the sectioning elements
Docbook defines block elements that are paragraph-
level elements. Some examples of block elements
are: paragraph, lists, admonitions, examples, figures,
tables, etc. Inside block elements we can define
inline elements like emphasis, quote, subscript,
superscript, crossreferences, etc. There are several
kinds of block and inline elements.
All Docbook elements also have attributes that
define specific element features like list bullets and
numbering, table lines and sizes, etc.
The next is a simple example of Docbook
document structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE book PUBLIC "-//OASIS//DTD DocBook XML
V4.3//EN"
"http://www.oasis-
open.org/docbook/xml/4.3/docbookx.dtd">
<book>
<title></title>
<chapter>
<title></title>
<section>
<title></title>
<para></para>
</section>
</chapter>
</book>
First we find the XML processing instruction
that is the required first line in every XML
document. Next there is the DOCTYPE declaration
that identifies the root element and the DTD using a
public identifier. These identifiers can be resolved
on the web or locally by means of a catalog 0. The
book element is the document root and it has a title
and a chapter children. The chapter element only has
a section with a title and a paragraph. Titles and
paragraphs are examples of block elements that
include final content.
2.2 Stylesheets
Once we have written a Docbook document we have
to deliver it in some presentation format. The most
frequently used formats are HTML for the web and
PDF for printing. To get our book in this ways we
have to apply some transformations, these
transformations are performed by XSLT stylesheets.
The engine that executes stylesheets over XML
data is an XLST processor. Many of them are freely
available: xsltproc (Xsltproc, 2006), Xalan (Xalan-J,
2005), XT (XT, 2005) and Saxon (Saxon, 2005).
Xsltproc is implemented in C and then it is faster
than Xalan, XT and Saxon that are implemented in
Java. The user interface to these utilities is a console
command but they also offer APIs to use them from
applications.
HTML is obtained by simply applying the
corresponding stylesheet. PDF generation requires
two steps, first Docbook is converted to XSL-FO
(W3C rec 15, 2001) applying XLST, and then a FO
to PDF converter is required. FOP (FOP, 2006) is an
open source option but it does not implement the
whole FO specification. XEP (XEP, 2006) is a
commercial product fully compliant with XSL-FO.
Recently XEP has become freely available for non
commercial use.
3 DOCBOOK CUSTOMIZATION
Docbook customization can be done in two aspects:
markup and presentation. Markup customization
means to change, extend or reduce the markup
defined by Docbook DTD. Presentation
customization deals with Docbook stylesheets.
3.1 DTD Customization
Customizing Docbook markup is generally not
recommended because when the markup is modified
compatibility is lost; but sometimes applications
demand some customization level.
When Docbook is customized we say that we
create a customization layer (Walsh, N., 2003). A
markup customization layer consists of a file with
the next content:
(1) Overrides of Entity Declarations
(2) <!ENTITY % orig-docbook "-//OASIS//DTD
DocBook V3.1//EN">
%orig-docbook;
(3) New/Modified Element and Attribute
Declarations
“Overrides of entity declaration” means to assign
values to Docbook DTD parameters. These
parameters are defined in the DTD in order to allow
some kinds of usual customizations like:
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
190

– Adding a new kind of already existing elements
(%*.class; parameters).
– Changing the content model of some kind of
elements (%*.mix; elements).
– Ignoring or redefining an element (%*.module;
parameters).
– Control marked sections around individual
element declarations or attribute list declarations
(%*.element; and %*.attlist; parameters).
– Making global changes to the inclusions and
exclusions in the DTD (%*.inclusion; and
%*.exclusion; parameters).
– Adding markup to most entity declarations
(%local.*; parameter entities).
The Docbook DTD is included by means of an
ENTITY declaration. Finally the new or redefined
elements are declared. An example of a markup
customization layer is:
<!-- Add MethodName element -->
<!ENTITY % local.tech.char.class |MethodName">
<!-- load DocBook -->
<!ENTITY % DocBookDTD PUBLIC
"-//OASIS//DTD DocBook V3.1//EN">
%DocBookDTD;
<!-- Define MethodName element -->
<!ELEMENT MethodName ((%smallcptr.char.mix;)+)>
<!ATTLIST MethodName
%common.attrib;
%classname.role.attrib;
%local.classname.attr
To use a customization layer in a document we
have to include a DOCTYPE declaration that
references the file that defines the customization.
The reference can be done using a system or a public
identifier. In case of a public identifier a new one
has to be created in order to avoid confusion with
the original DTD.
3.2 Stylesheets Customization
A common need when using Docbook is to
customize presentation, either HTML or printing
formats. Presentation is generated from Docbook by
means of XSLT stylesheets. In order to facilitate
customization many parameters are defined in
Docbook stylesheets.
Setting parameter values is the most straight
forward customization method. This can be done on
the XSLT processor command line or using a file.
Parameter setting in the command line depends on
the XSLT processor command syntax. If a file is
used then it will be an XSLT stylesheet like the next:
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform
" version="1.0">
<xsl:import
href="/usr/share/xsl/docbook/html/docbook.xsl"/
>
<xsl:param name="html.stylesheet"
select="'corpstyle.css'"/>
<xsl:param name="admon.graphics" select="1"/>
</xsl:stylesheet>
First we import the Docbook stylesheet and then
we set parameter values. There are many parameters
available and then many format customizations can
be performed in this way. A complete parameter
reference can be found in Stayton, B., 2005.
When parameter setting is not appropriate other
more sophisticated methods are available:
– Setting attribute sets.
– Completing placeholder templates.
– Generating new templates.
– Customizing generated text.
– Replacing templates.
XSLT attribute sets are similar to parameters. As
an example you can turn off boldface and left-align
sections titles with the next attribute set setting:
<xsl:attribute-set
name="section.title.properties">
<xsl:attribute name="font-weight">Normal
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:attribute name="text-align">left
</xsl:attribute>
</xsl:attribute-set>
An example of placeholder template is
user.header.content that is called by chunking
HTML stylesheet at the beginning of every HTML
page:
<xsl:template name="user.header.content">
<p><b>Hi all!</b></p>
</xsl:template>
New templates generation is a mechanism that
allows redefining some format properties (for
example title pages). There are some XML
templates that can be modified and then an XSLT
stylesheet will replace the original Docbook
stylesheets by the new ones (XLST is itself XML).
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT WITH DOCBOOK
191
By customizing generated text we can change
some text that is not present in the input document
but appears in the presentation, this is because
stylesheets create it. Generated text can be
customized on the stylesheet distribution files for all
the languages supported (for example English file is
common/en.xml). Customization can also be
included in a customization layer leaving
distribution files unmodified.
Replacing templates is simply to rewrite the
XSLT templates we want to customize. This is done
after the main stylesheet import in the customization
layer. This kind of customization requires a deep
understanding of Docbook stylesheets and XSLT
itself because there are many subtleties that can get
into errors.
4 AUTHORING TOOLS
Creating content in a user friendly way is perhaps
the user most important demand. Docbook as any
other XML compliant language can be edited using
a raw text editor. From the point of view of
authoring production it is not the most adequate
option. Fortunately there are many editors that offer
a more specific environment.
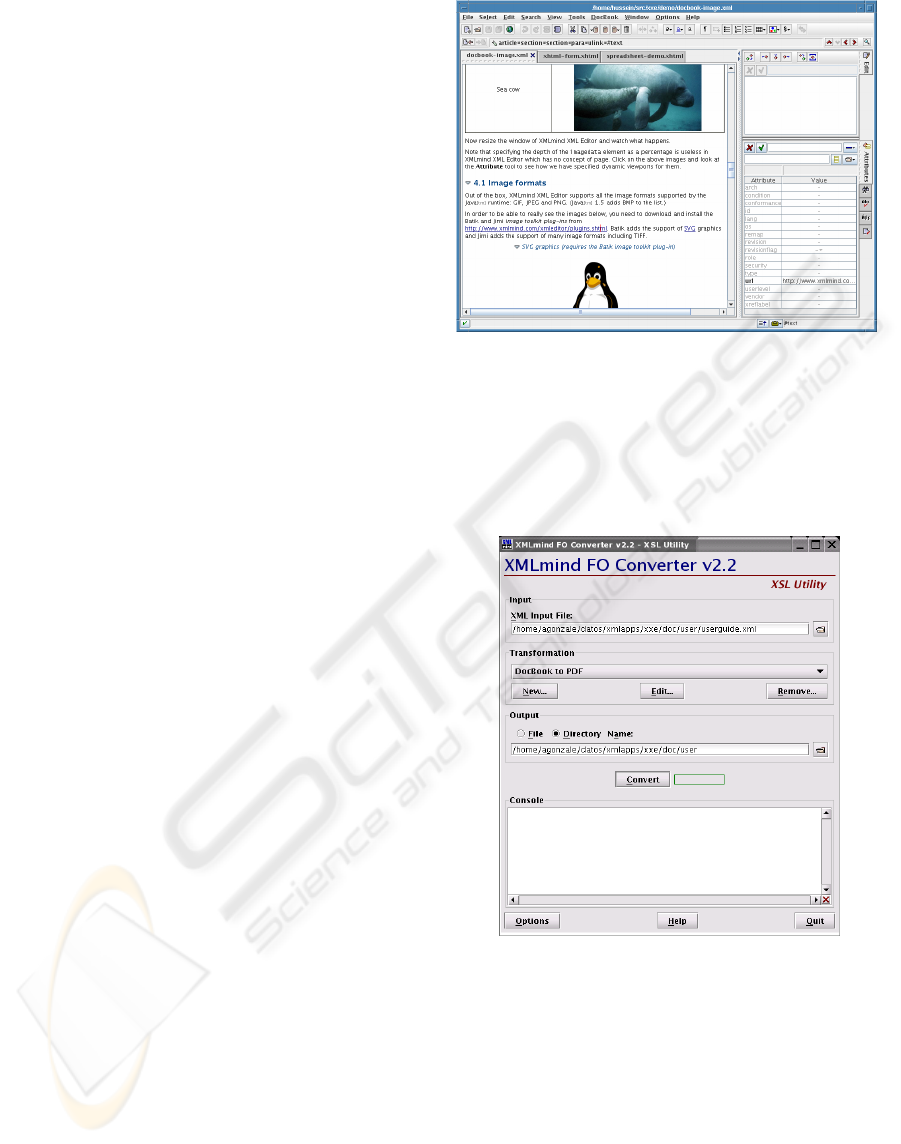
XXE (XMLMind XML Editor at XXE, 2006) is
a particularly interesting editor because it offers a
WYSIWYG like interface that hides the markup to
the user (Figure 1). It is a Java application and then
it runs on many platforms. Besides of being a
general XML editor it has been completely
customized to Docbook. It is a commercial product
but XMLMind offers a standard version that is
freely distributed an only lacks for some
functionalities. The most relevant is that it does not
support schemas. In our experience we have found
standard version adequate.
We include non textual content (images,
graphics, equations and plots) using JPEG format by
means of ‘fileref’ attribute. JPEG seems to be the
most universally supported image format. We hope
that in the near future there will be better support for
non-textual information XML languages, mainly
MathML and SVG. The tool we use to edit non
textual content is OpenOffice suite.
Figure 1: Editor XXE.
To generate presentation XMLMind offers XFC
(XMLMind FO Converter at XFC, 2006). It is a Java
application that generates several format from
Docbook: HTML (one page or chunked), PDF, RTF
and WordML (Figure 2). It uses Saxon as XLST
processor and FOP as default PDF generator.
Figure 2: XMLMind FO Converter.
4.1 Collaborative Authoring
Docbook documents are plain text this allows to use
concurrent versioning systems like CVS to
collaborative authoring teaching material. We use a
CVS server on Linux and the java client SmartCVS.
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
192

Figure 3: SmartCVS client.
To avoid conflicts between versions the author
team has to agree which document part every
member is going to work on. In this way CVS
merges changes automatically in a common
document.
All auxiliary content is declared as binary format
and concurrent edition of this material is not
possible. This is not an issue because in our
approach text is the backbone content.
5 TEACHDB
We are developing markup and stylesheet
customization layers taking account of our previous
experience with Docbook as teaching content
production framework. We call the customized
markup TeachdB. The requirements we want to
satisfy are:
– Class material repository building.
– Lab guides repository building.
– Class material and lab guides generation from
repositories.
– Class and lab exams generation from
repositories.
– Printing format and slides format generation
from the same content.
5.1 TeachdB Markup
We have minimized markup customization in order
to maintain the maximum compatibility level with
Docbook. This means to avoid creating new
elements and attributes if Docbook existing ones are
usable. TeachdB markup extensions can be
summarized as:
– ‘Role’ attribute of element ‘article’ is restricted
to ‘class’ and ‘lab’ values.
– A new root element ‘exam’ is added through
local.article.class parameter.
– Exercises are implemented using Docbook
‘qandaentry’ element with some extensions:
– Two new attributes ‘lastusetype’ and
‘lastusedate’ are added to ‘qandaentry’.
– A new element ‘options’ is added to
‘question’ in order to implement test
questions.
– A new attribute ‘type’ is added to ‘answer’
elements, with values ‘response’ and
‘solution’.
As you can notice the most significant
customization is related to exercises. This is not by
chance because we think that exercises are the most
important component of a learning material.
Exercise management is the most complex process
to implement. Exercises will be used in three ways:
– Class or lab examples.
– Class or lab exercises.
– Exam exercises.
In order to reuse already authored exercises some
information is required: last use type and last use
date. This information is included in two new
‘qandaentry’ attributes: ‘lastusetype’ and
‘lastusedate’. These attributes permit to select
exercises automatically, according to a certain
criteria, by means of XLST or XQuery.
The new element ‘exam’ introduces a structure
specifically oriented to exam authoring. It has two
children: ‘header’ and ‘questions’. Element ‘header’
includes information about the exam (subject, date,
etc). Element ‘questions’ is a sequence of ‘Question’
elements that have attributes to implement exam
version. These attributes define question and
response options orderings for every exam version.
A ‘qandaentry’ child defines the question content.
An important requirement is content reuse.
Content repository management can be implemented
in two ways:
– Content filtering based on attribute values.
– Content selection with XInclude.
Content filtering is adequate if the final
document is a single document subset, otherwise
content selection from several sources can be
implemented with XInclude.
When repositories grow in size it is convenient to
automate content location. This can be achieved
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT WITH DOCBOOK
193

using XQuery over metadata elements and element
attributes.
5.2 TeachdB Stylesheets
In order to get presentation formats adapted to
document use, we have developed some stylesheet
customizations. In particular we have defined
formats for:
– Student class notes (PDF).
– Lecturer class presentation (chunked HTML).
– Lab guides (PDF).
– Class exams (PDF).
– Lab exams (HTML forms).
Student class notes have a printed book like
format: header, footer, page number, numbered
sections, etc (Figure 4). All this customizations are
documented in 0.
To generate lecture presentation we have
converted Docbook to Slides. This is fairly easy
because Slides and Docbook have the same content
elements; they only differ in hierarchical elements.
Slides offer several chunked HTML templates that
include navigation controls and appropriate font
sizes (Figure 5).
Figure 4: Example of class notes PDF format.
Lab guides have similar format than class notes
but they include a question set that is used to
generate lab exams from a web server. When the
PDF lab guide is generated the exam question set is
filtered. The question set is obtained by means of an
XSLT transformation and it is put on the server as a
question repository. Students perform the exam
accessing to the exam URL after the lab session and
the web server delivers a question subset in HTML
form format (González, A., 2005).
Figure 5: Example of class session slide.
Class exams are generated in two steps, first the
exam markup is translated to Docbook, then a
customized stylesheet is applied to generate PDF.
There are two options: exam without solution and
exam with solutions.
5.3 Format Generation
In order to facilitate format generation we have
implemented a Java application that is specifically
customized to our needs. It is a front-end to shell
scripts that execute xmllint parser to solve
XIncludes, xlstproc to transform XML, XEP to
generate PDF and web clients or PDF visors to
shown the result. The use of native parser and XLST
processor gives a satisfactory response time.
Figure 6: Customized format generator.
The application use is very simple. First the
content document is specified. Then the type of
presentation desired is set by means of fixing the
mark in a radio button group. Finally the
presentation document is generated by pushing a
button.
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
194

6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We consider Docbook an interesting tool for
teaching document authoring and management.
Being XML compliant it allows using all the
standard XML document processing technologies.
Simple markup and stylesheets customization permit
to get some capabilities like several formats from
one source, content filtering and repository
management; that are not available in other more
widespread tools.
Docbook weakest point has been the lack of user
friendly editors. Nowadays the situation is changing;
XXE is a good example of a Docbook productive
editor. Nevertheless there is a long way in this
respect to compete with office suites.
As future work we will try to achieve the next
goals:
– To customize Qizx to locate repository content.
– To include LOM markup (LOM, 2002) in
Docbook elements metadata in order to integrate
documents in LMS environments (Dhraief, H.,
2001; Allert, H., 2002).
– To use XML for as much content types as
possible, particularly graphics (SVG) and math
equations (MathML).
REFERENCES
e-learning, 2006. e-learning center site.
http://www.elearningcentre.co.uk/eclipse/vendors/auth
oring.htm
Kirsch-Pinheiro, K., 2001. A Cooperative Environment for
E-Learning Authoring. In Documents Numériques :
Espaces d'Information et de Coopération, vol. 5, n. 3-
4, pp. 89-114, Hermes Science, France.
Süß, Ch., 2002. LMML – The Learning Material Markup
Language Framework. In Int. Worshop ICL, Villach,
Austria.
W3C rec 04, 2004. XML specs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml/
W3C rec 28, 2004. W3C schema. Specs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/,
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/
W3C rec 16, 1999. XSLT and XPath specs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt
http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath
W3C rec 15, 2001. XLST-FO specs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xsl/
W3C cand 3, 2005 XQuery apecs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xquery/
W3C rec 27, 2001. XLink specs.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xlink
W3C rec 20, 2004. XInclude specs.
ttp://www.w3.org/TR/xinclude/
W3C rec 14, 2003. SVG language.
http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/
W3C rec 21, 2003. MathML language.
http://www.w3.org/TR/MathML/
W3C rec 26.1, 2002. XHMTL language.
http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/
W3C rec 13, 2005. SMIL language.
http://www.w3.org/TR/SMIL2/
Docbook, 2006. Docbook main sites.
http://www.docbook.org
http://docbook.sourceforge.net/
Walsh, N., 2003. DocBook: The Definitive Guide. O'Reilly
Stayton, B., 2005. DocBook XSL: The Complete Guide.
Sagehill Enterprises.
XXE, 2006. XMLMind XML Editor site.
http://www.xmlmind.com/xmleditor/
XFC, 2006. XMLMind FO Converter site.
http://www.xmlmind.com/foconverter/
Qizx, 2005. Qizx open site.
http://www.axyana.com/qizxopen/
Xsltproc, 2006. Libxslt site. http://xmlsoft.org/XSLT/
Xalan-J, 2005. Java implementation of Xalan site.
http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/
XT, 2005. XT site. http://www.blnz.com/xt/
Saxon, 2005. Saxon site. http://saxon.sourceforge.net/
FOP, 2006. Apache Formatting Objects Processor site.
http://xmlgraphics.apache.org/fop/
XEP, 2006. RenderX site for XEP.
http://www.renderx.com/
González, A., 2005. Entorno web para la generación y
corrección automatizada de exámenes basado en XML
y Java, I Congreso Español de Informática, Granada,
Spain,
LOM, 2002. Learning Object Metadata specs.
http://ltsc.ieee.org/wg12/20020612-Final-LOM-
Draft.html
Dhraief, H., 2001. Open Learning Repositories and
Metadata Modelling, in Proc. of Int. Semantic Web
Working Symposium, Stanford, USA
Allert, H., 2002. How are Learning Objects Used in
Learning Processes? Instructional Roles of Learning
Objects in LOM. ED-MEDIA 2002, World Conference
on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia &
Telecommunications, Denver Colorado, USA
TEACHING DOCUMENT PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT WITH DOCBOOK
195
