
A CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR SUSTAINING COMPETITATIVE
ADVANTAGE IN DIGITAL ECONOMY
Swapan Kumar Majumdar
School of Business Administration, Al Akhawayn University, Ifrane 53000, Morocco
Keywords: Business Model, Competitive Advantage, Connected Organizations, Digital Economy, Governance,
Internet, Web Technology, Sustainability.
Abstract: As high speed Internet is connecting citizens and businesses around the world, social and economic mode of
interactions among citizens, governments, customers and businesses are changing rapidly. Governments and
businesses are using web information systems to provide highest quality services at affordable cost to their
citizens and customers. Citizens and customers are becoming more demanding. Businesses are experiencing
intense pressure of global competitors, and are in constant search for strategies and models for better
governance and sustaining growth. This paper examines the impacts of Internet and web-technology on the
functions, processes, structure and behaviour of connected-business organizations, and their effects on the
competitive landscape and sustainability of eBusiness organizations. As a final point, it provides a
conceptual model for sustaining competitive advantage in digital economy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internet has revolutionized the ways and means of
connecting, inter-operating and exchanging
messages, goods, services and money. The emerging
new media and the channels of communication is so
powerful, convenient, cost-effective and far-
reaching that they are consistently attracting millions
people of all class, hundreds of businesses of all
kinds, from all over the world every day. This
revolution of communication has created an
evolution that is transforming business, society and
the economy. It has transformed the economy into
digital economy, society into eSociety and the
businesses into eBusiness. The size of digital
economy is growing in leaves and bounds. In digital
economy citizens, customers, governments and
businesses, use Internet and Web technology tools as
the enablers of business.
The boom, bust and return (Johnson, 2002, US
Census Bureau 2005, European eBusiness Market
Watch 2005) of ePhenomenon might be confusing at
its manifestation. In fact, these are symptoms of
evolutionary characteristics of digital business
ecosystems (Peltoniemi 2004). The eEvolution
reminds us the stories of automobiles and aviation
industries. In the early days of automobile industry,
there were more than 2000 carmakers, but now there
are only three car companies left in the United
States. Likewise, hundreds of aircraft manufacturers
have gone bust, some very recently. The eSociety is
a fully connected society. Its members use
technology and the digital network for
communication, intermediation, evaluation and
completion of business transactions. The processes
are automated, ubiquitous and access able from
anywhere by anyone at any time and by many
devices. This being scope and scale operation of
connected-business (eBusiness) the success of a
networked company—depends on — how one uses
the emerging technology to create competitive
advantage for their companies and how renewable
are those advantages. The core intents of eBusiness
are similar to any other business, but the mode and
rules of operations and competition are very
different (Porter 2001).
The competitive advantage of digital business
entity does not come from having computers and
connectivity with the global network, but by using
them to create, deliver and realize superior value.
The challenge is how to create superior value for
customers and remain closer to the customers, who
are also members of the same connected society and
have many options. The Internet provides equal
opportunity to all to customers and competitors,
59
Kumar Majumdar S. (2006).
A CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR SUSTAINING COMPETITATIVE ADVANTAGE IN DIGITAL ECONOMY.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and
e-Government / e-Learning, pages 59-65
DOI: 10.5220/0001243700590065
Copyright
c
SciTePress

suppliers and distributors. Customers of connected
economy are well aware of their options, and
demand excellence. Everyone (customers and
competitors) sees everything from everywhere. The
web-based digital economy provides global
visibility.
The biggest challenge of eBusiness is how to
maintain differentiation and remain competitive in
fully connected and transparent society. Protecting
uniqueness in open, transparent and borderless
economy requires in-depth analysis of contributors
of differentiation. What resources, actions and
behaviours of firms will lead to sustainable
competitive advantage? A competitive advantage
can result either from implementing a unique value-
creating process or through superior execution of the
same strategy as competitors (Bharadwaj,
Varadarajan, and Fahy 1993). The competitive
advantage is sustained when other firms are unable
to duplicate the strategy (Barney 1991).
Sustainability means durability and durability of
competitive advantage is like the competitive
survivability of the firm.
Success brings rewards as well as competitors,
who try hard to develop new technologies and new
business processes that can upset the initial
competitive status quo. Only those competitive
advantages lead to extraordinary growth and
profitability, which can create big barriers around a
business to fend off the competitors. The best long-
term investments are those companies whose walls
are not only high, but also getting higher and thicker
over time.
The innovative character of ICT, ubiquity of
Web, and speed of digital network has changed
sustainability into nightmare of survivability.
Customers and competitors instantly receive the
same information, thereby provide impetus to the
competitors and challengers to learn and readjust
their competitive strategy, and have made eBusiness
as hyper-challenging. Who will equal or outperform
whom and when, depends on who learn and readjust
their business processes, organizational structure and
their work culture to the requirement of the
competitive landscape of digital economy fast?
This raises many questions about the impact of
the Internet technology on functions and processes
of business, structure of organizations, and work
culture of organizations and competitive landscape
of the business. What framework or eBusiness
model (Majumdar 2005), will help eBusiness firms
to retain their competitive advantage in this
hypercompetitive business environment of digital
economy.
2 FEATURES OF DIGITAL
ECONOMY
The potential of digital connectivity to boost
productivity, convenience and lowering the costs of
operation and transaction is compelling developed
and developing countries to focus on the e-potentials
for growth and modernization of the public and
private services. Industries and organization across
the world operate like a massively interconnected
network of organizations, technologies, consumers
and products. The success of a business is no longer
dependent on the size of its internal and external
operations, but on the associations and relationships
established among the participants in the digital
Business Ecosystem.
The questions are, how can we predict, which
organization will survive for how long and which
organization will perish over time and why. What
are the rules of the emerging digital business
ecosystems? Creating sustainable business models
seems unworkable without knowing the unique
features of digital economy and the keystones of
eBusiness model.
Firms and individuals of digital economy use
Internet and web to transact business. Technology
converts all information, processes and transactions
into digital forms and allows business transactions
with minimum human intervention. Internet and web
are the backbone of digital economy and together
they provide the technological platforms that allow
business and entrepreneurs to communicate with
their stakeholders in ways not previously possible.
The ease with which information can be exchanged
over these channels fundamentally changes the
relationships with an organization's stakeholders.
Seven unique features of eBusiness technology
(Laudon 2004) are:
•
Ubiquity - Internet/web technology is
available everywhere: at work, at home,
and elsewhere via mobile devices, anytime.
Digital goods and services are visible and
accessible from “marketspace”. Anyone
from anywhere at anytime can access and
conduct business using Internet.
• Global Reach – The technology reaches
across national boundaries, around the
earth. Business is enabled across cultural
and national boundaries seamlessly.
Information can reach all connected
customers or business partners through the
Internet without sacrificing the richness of
the contents.
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
60

• Interoperability – Internet provides an
open and nonproprietary platform for
communication and collaboration and
allows enterprises to integrate and
interoperate ubiquitously. There is one set
of technical media standards across the
globe, Internet standard.
• Interactivity – Instant messaging
capability of eBusiness technology enables
close connections, online dialog, with
customers and among supply chain or
business ecosystem partners' information
systems. The benefits include real-time
pricing and negotiation, and online flexible
customer servicing.
•
Information Density – Technology
reduces information costs and raises
quality. Information processing, storage and
communication costs drop dramatically,
while currency, accuracy and timeliness
improve greatly. Information becomes,
plentiful, cheap and accurate.
• Speed - Change is fast and frequent in the
digital economy. Digital firms must learn
to learn and adapt quickly to changing
business and economic environments.
Adaptation is sensing the shape of next
wave, and positioning the company to take
advantage of it (Arthur, 1996).
•
Personalization – Technology allows
personalized messaged to be delivered to
individuals as well as groups. A firm or
business ecosystem (Gossain and Kandiah,
1998) can provide unique (and customized)
"solutions" (as opposed to single product or
service) to individual customers.
In digital economy, ICT is the enabler of
business. The design of “business models” of digital
economy is articulation of firms’ strategy to create
and deliver of unique value to its customers and
shareholders in a given segment of the business
ecosystem by using the right technology and
resources, aligning people and the processes for
achieving the desired level of performance.
The goodness of a business model depends on
the power of the value proposition, correctness of
execution and governance processes (Majumdar,
2005). To thrive in global marketspace, an
organization have to study the impact of Internet and
web technology on connected organizations before
developing a framework to construct a resilient
business model for the organization.
3 IMPACT OF INTERNET &
WEB TECHNOLOGY ON
BUSINESS
Sustainability of “business entities in digital
economy” depends on how effectively firms
formulate strategies to blend the technology and
other corporate resources, to design business
processes, develop organizational structure and work
culture not only to combat the competition, but also
to maintain the competitive edge. To develop a
resilient framework for sustaining competitive
advantage in digital economy requires understanding
of the impact of Internet and Web technology on: (1)
the functions of business, (2) the processes of
business, (3) the on structure of organizations, (4)
the work culture and behaviour, (5) the competitive
landscape of eBusiness, and (6) the sustainability of
eBusiness.
Figure 1 illustrates the impacts of Internet and
Web technology on eBusiness application
management.
Impact of Internet and web technology can be
assessed in several ways. In this case, the results of
Momentum Research Group (MGR 2002, 2003,
2004 and 2005), European Union (EBW 2003 and
2005) and others secondary sources were used to
examine the impact of Internet and Web technology
on sustainability of competitive advantage.
3.1 Impact of Internet on Business
Functions
The results of Net Impact research (MRG 2002,
2003, 2004, and 2005) and the report of European
Union’s eBusiness Market Watch (EBW 2003 and
2005) demonstrate that Internet and Web
technologies have substantially changed the
functions and processes of private and public sector
organizations across US, EU and Latin America.
The Internet technology is influencing almost all
functions of contemporary organizations.
Organizations of all sizes across industries, across
countries either have adopted or actively trying to
adopt Internet business solutions as a tool to lower
operating costs, increase revenue, increase
operational productivity, increasing customers’
satisfaction and harvesting rich dividends.
A CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR SUSTAINING COMPETITATIVE ADVANTAGE IN DIGITAL ECONOMY
61
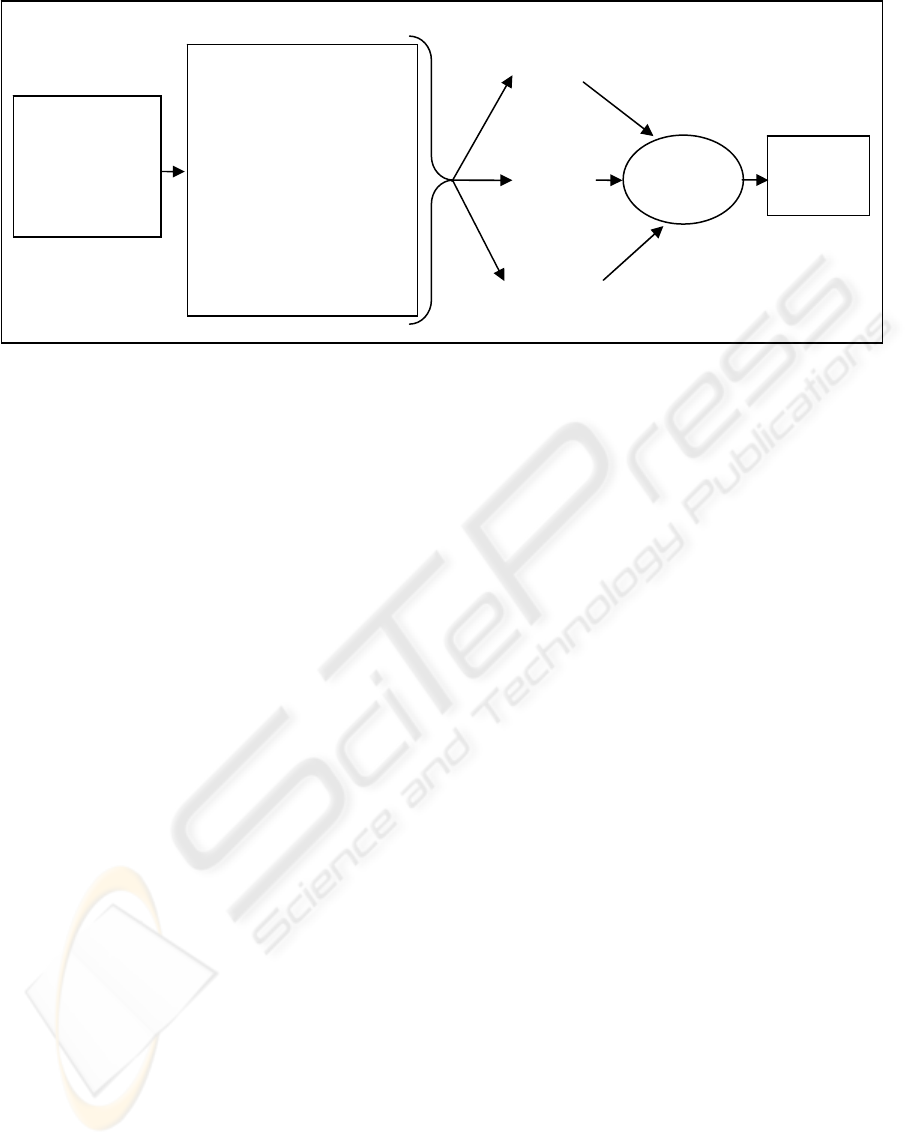
Figure 1: Impacts of Internet and Web Technology on Management of eBusiness Applications.
30-60% of European public sector organizations
(MRG 2004, p-2) have been able to automate the
typical business processes involved in their delivery
of citizen services. The automation of these
processes not only increase the speed of service
delivery, but also reduce data-reentry errors, and
facilitate the transmission of data to other
complementary services. The public sector
organizations are focused to extend the capabilities
of existing citizen services, to introduce new
services, to reduce costs of operations and increase
citizen satisfaction. The level of network-enabled
adaptation of Latin America 2005 is strikingly
similar to the network-enabled adaptation behaviour
of US 2003 (MRS 2005, p-16).
Web enabled applications account for a greater
percentage of deployed applications in Latin
American Networked-organizations than that was
observed in US in 2003 (MRS 2005 p-17). Smaller
organizations (less than 100 employees) had high
level of applications that use web-based technology
and the same is expected to observe in US (MRS
2005 p-18). This shows that small organizations are
smart, flexible, and are adapting web technology to
e-enable their business functions.
3.2 Impact of Internet on Business
Processes
The process and business functions are interlinked.
With the progress of automation, many of the old
business functions have been subsumed within the
activities of back-office. Thus business processes
have become more important than functions. The
Internet and Web technology is transforming all
processes into automated web-enabled processes.
The result of repeated Net Impact study (MRG 2003,
2004, and 2005) shows that business processes have
to to be reengineered to leverage new technology
capabilities. However, the timing of process
reengineering can significantly influence the final
results. Research results demonstrate that
organizations do not accomplish their desired
results, if they do not reengineer their business
processes before implementation of the technology.
Process reengineering after application deployment
tend to increase in operating costs significantly. This
reveals the fact that Internet / Web technology is a
general-purpose tool; results of application depend
on the correctness of the application process. It is
hard to change the meal, once it is cooked.
Secondly, technology does not guarantee results, if it
is not managed well.
3.3 Impact of Internet on
Organizational Structure
Internet is changing the structure of organizations
from hierarchical to flat task-based. The middle
managers’ positions are being eroded. Big
organizations are being disintegrated as smaller task
focused connected business units with specific
responsibility sharing common organizational
resource pull like human resource, IT resources.
Conversely, small organizations are forming task-
driven umbrella organization and operating like a
big corporation, but maintaining their individual
identity and profit centers. The bigger the world
economy, the more powerful is the smallest players.
Like globalization, Internet is molecularzing the
Structure of
organization
Ubiquity
Global Reach
Universal Standard
Interactivity
Speed
Neutrality
Customizability
Internet & Web
Technology
•Production process
•Service Process
•Information & Communication
•Products & Service Delivery
•Negotiations
•Buying and Selling Process
•Payment Collection Process
•Coordination & Collaboration
•Status Tracking
•Customer Relationship
Sustainability
of eBusiness
Business Functions
Work Culture
/Behaviour of
organization
+
Business
Process
+
H3
H2
H4
Competitive
Landscape
H5
H5
H5
H6
H1
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
62

organizations. The relationships grow more
business-like between employers and employees, the
traditional chain of command is breaking, and the
hierarchy-linked authority and power that used to be
taken for granted are now being questioned (Malone
1998).
3.4 Impact of Internet on
Organizational Behaviour
Behavior and culture of organization has significant
impact on the technology driven performance (MRG
2005 p-27). This point out that value realization
(implementation and governance) from digital
process requires different mindsets and cultural bent.
The results Net Impact study (MRG 2003, 2004 and
2005) reveals that “desire to improve customers
satisfaction” is the number one objective of using
ICT driven processes. Both the Net Impact 2003
study and European Public Sector 2004 study
revealed that customer or citizen satisfaction was the
most frequently cited driver of technology
investments. Net Impact study of Latin America
(MRG 2005) exhibits that the urge for achieving
completive advantage by accelerating organizational
speed, improving customer satisfaction or lowering
costs are common mindsets of networked
organizations.
3.5 Impact of Internet on
Competitive Landscape
By design all networked organization are global
entities. The struggle for opportunity sizing is also
global—and the winners are those—that have
highest ability to deliver on time, within budget and
according to the preferences of the customers. What
defines this “new world,” and the competitive
landscape of business? The four key elements that
make the current business landscape different are:
globalization, Internet, importance of knowledge,
and collaboration across organizational
“boundaries.”
The major challenges are: What are the fundamental
issues needs to be addressed to create sustainable
organizational improvement. How to determine what
is the right eBusiness opportunity? How can an
organization move from where it is to where it wants
to be? What are the transitional issues? Why do
some organizations execute successfully, while other
organizations fail to do so? What are the key factors
that make the most differences?
3.6 Impact on Sustainability
In digital economy, the distance is dead. Work never
sleeps. Value chains and boundaries of industry are
blurring. Profits proved hard to come by, and many
high-flying companies came crashing down. In little
more than one year, many companies have fallen,
the business world changed dramatically. The dot-
com bubble burst, a recession came, and economic
uncertainties snowballed (Kaplan 2002).
Sustainability depends on speed correctness of
the business model and soundness of execution and
governance. The new business ecosystems are
compelling organizations to rethink their directions
and revamp their business models.
Successful organizations of US, EU and Latin
America are first focusing on back-office
applications like finance and accounting, human
resource and inventory management before shifting
to customer-facing applications that improve
employees, partner, customer, client or citizen
(public sector) interactions (MRS 2005). The
message is that organizations must be internally
efficient to meet the divergent needs of their
customers and other external business partners.
4 FRAMEWORK FOR
COMPETITIVE
SUSTAINABILITY
The pace technological change is continuous in
digital business ecosystem. How long will a
distinctive competitive advantage of a firm last,
depends on what actions the firm takes to enhance
and protect its capabilities and what actions the
competitors take to replicate them. In connected
economy news move fast and provokes competitors
to take counter actions to match, alter or to supersede
them. How long a firm can uphold its key strategic
advantages?
Lucas (Lucas 2005) suggests that in digital
business ecosystem only those competitive
advantages will last for a while if they are rare,
inimitable, non-substitutable and protect-able. Long-
term sustainability of competitive advantage depends
on organization’s ability to add additional resources,
which are valuable, inimitable and non-substitutable.
Protecting competitive advantage in Internet
economy is impossible, unless it is complementary to
the characteristics of connected economy.
Conversely, eBusiness firms cannot survive, if it does
not have any competitive advantage (Barney 1991).
A CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR SUSTAINING COMPETITATIVE ADVANTAGE IN DIGITAL ECONOMY
63
The continuity of success depends on how
complementary and resilient is the firm’s plans to
transform dodging power of Internet into a unifying
force to beat or equal the competition in terms of
cost, quality, speed and innovation.
The endurance of competitive advantage of
eBusiness depends not only on the worth of the
advantage and the degree of difficulties of duplication
or imitation, but also on the worth of imitation and on
the strategy of protection as well as conversion of
challengers and competitors into contributors and co-
operators. Another theory of protection is
development of capsules, modules and devices that
can embed/encapsulate complex operations into
simple capsules, modules or devices, which could be
used by many for many different things and pulled by
large number of users. Moreover, sustainability of
eBusiness depends on pull-worthiness of the business
rather than push power of the promoters.
First movers’ advantages are short-lived (Barney
1991). In digital economy, “knowledge” is the key
resource and success factor of digital economy.
Nevertheless, knowledge is not static; it requires
continuous updating and creation. To sustain in this
knowledge economy, one has to be fast learner, talent
attractor and continuous addition of resources and
refreshing of their capabilities. Organizations have to
be the homes of innovators and knowledge creators,
who would be able to continuously develop new
solutions and advantages. To survive and thrive in
this ever changing world of digital economy,
organizations have to develop superior and resilient
supply / demand matching capabilities that are more
responsive to changing market conditions and have to
have multiple sources of revenue.
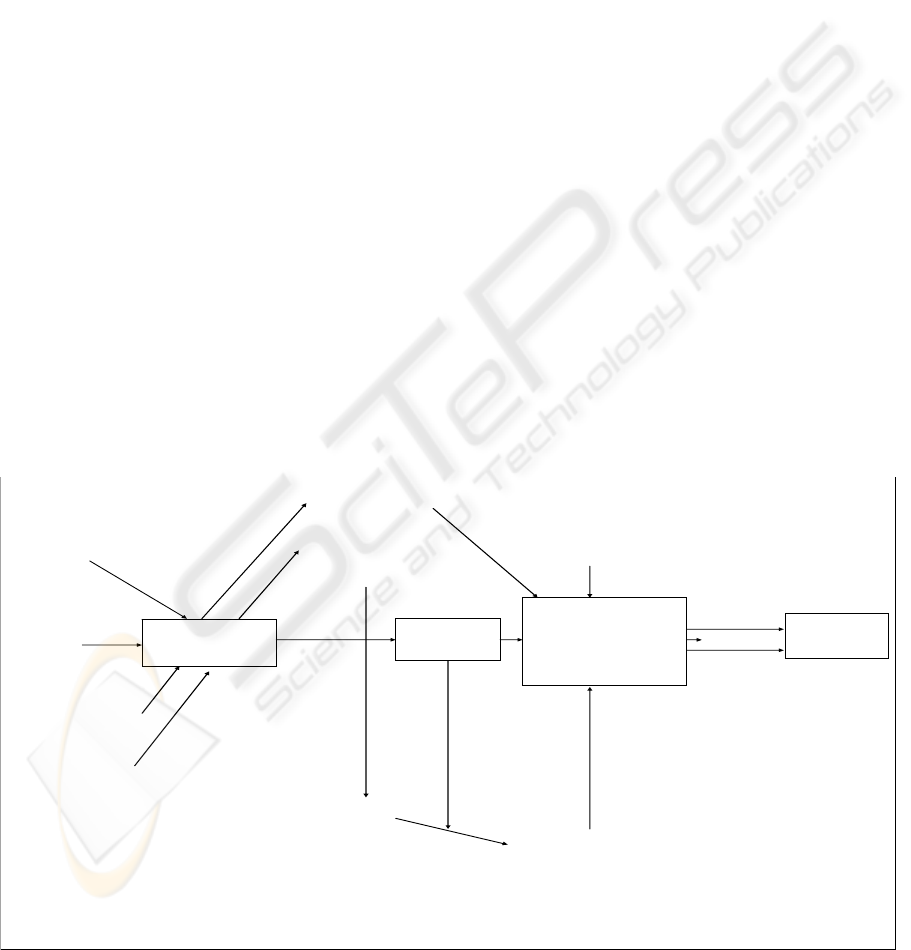
Figure 2 exhibits a framework for sustaining
competitive advantage in networked economy. It
illustrates that to pull initial advantage organization
must have a distinctive competency, a worthy
network, rare resources and unique capability.
Nevertheless, to remain successful, eBusiness
initiating organization must be able to pull enterprises
with complementary values and create a talent pull.
Moreover, add additional resources and capabilities
develop efficient and effective integrated operating
models and create strong high performance work
culture to become a superior provider of products and
services and respond quickly with diverge needs of
the customers and markets. To ascertain sustainability
in uncertain and ever changing business environment,
one has to have superior and capabilities, which are
resilient, inimitable and renewable. To haze the risks
of failure, one should have multiple sources of
revenue rather than a single source of revenue.
Best-fit business plans call for assessment of the
worth-of-the-network. Lucas (Lucas 2005) mentions
about network externalities. However, from
networked organizations’ viewpoint, worth of a
network is more important rather than “network
externalities”.
Figure 2: A Conceptual Model for Sustaining Competitive Advantage in Digital Economy.
Sustainable
Advantage
Multiple
Sources of
Revenue
ST ART
Distinctive
Competencies
Worthy
Network
Rare
Resources
Unique
Capabilities
Additional Capabilities
and Resources
Valuable
Not Easily Imitable
Proctab-able
Collect & Create
A Resource &
Talent Pool
Pull Enterprises with
Complementary Assets
Go for Cooptation
Pull Enterprises
and Talents wi th
Comp lemen tar y
Assets, Develop
Skills Managing
Community
Pull Initial
Advantage
Encapsulate Key
Processes
Superior Supply/
Demand Matching
Capabilities and
Resources
Develop
Integrated
Operational Model
Develop High
Performance
Mindsets and
Work Culture
Superior
Resilient
Inimitable
Renewable
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
64

Worth-of-a-Network can be estimated by the
formula as given below.
WN = N * C * G + ∑P
WN = Worth of a Network,
N = Number of Customers Use the Network,
C = Per Capita Consumption,
G = Growth Potential,
P = Number of Potential Contributors
Connected with the Network and their Worth
5 CONCLUSIONS
In digital economy initial opportunities are short
lived. Changes are continuous. Challenges are
endless. To haze through the maze of eBusiness, has
to have comprehensive roadmap for value creation
and delivery. This paper provides a dynamic
framework for sustaining competitive advantage in
digital economy.
This model advocates the need of network of
complementary capabilities for continuation. The
initial success depends on the worth of the network
and the distinctiveness of the competencies.
Continuity of success depends on capability
building, effectiveness of operational model,
performance “mindsets” and the work culture of the
organization.
Continuity of competitive advantages requires
continuous scanning of the opportunity as well as
reviewing the strategies of technology-enablement
of the processes, monitoring execution, and critical
examination of the performance of the competitors.
Continuity demands continuous process
improvements and innovation. Sustainability can no
longer ensured without adding more recourses and
creating pool of talents and resources, and
discovering new sources of revenues. Successful
eBusiness management demands continuous
learning. The other fundamental elements of success
are collaboration and leadership.
REFERENCES
Arthur, W. B. (1996). Increasing Returns and New World
of Business. Harvard Business review, 74 (3), 100-
109.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm Resources and Sustained
Competitive Advantage. Journal of Management, 17
(1), 99-120.
Bharadwaj, S. G. P. et al. (1993). Sustainable Competitive
Advantage in Service Industries: A Conceptual Model
and Research Propositions. Journal of Marketing, 83-
99.
EBW (2003). European Union’s eBusiness Market Watch.
A Pocket Book of eBusiness Indicator.
http://info@ebusiness-watch.org.
EBW (2005). European Union’s eBusiness Market Watch.
A Pocket Book of eBusiness Indicator.
http://info@ebusiness-watch.org.
Gossain, S. and Kandiah, G; (1998); Reinventing Value:
The New Business Ecosystem. Strategy & Leadership,
26 (5), 28-33.
Johnson, C (2002). US eCommerce: The Next Five Years.
Forrester Research Report (January 27, 2002).
Kaplan P. J. (2002). F’s Companies: Spectaculars Dot.com
Flameouts. NY; Simon and Schuster.
Laudon, K. C. et al (2003). E-Commerce: Business,
Technology, Society. Pearson Addison Wesley, NY.
Lucas, H. C. (2005). Information Technology: Strategic
Decision Making for Managers. Wiley & Sons.
Majumdar, S.K (2005). MAP-STEPS: A Framework for
Formulation and Governance of eBusiness. Presented
in the 7
th
International Conference, “The Emergence
of Novel Organizational Forms in the Globalizing
Planet: Towards the Business Ecosystems” 6-9 July
2005, Italy, as Keynote Speaker.
Malone, T. et al (1998). The Dawn of the E-lance
Economy. Harvard Business Review, 76 (5), 144-152.
MRG (2002). Momentum Research Group. Net Impact
Study: The Projected Economic Benefits of the
Internet in US, UK France and Germany, January
2002.
MRG (2003). Momentum Research Group. Net Impact:
Driving Networked Business Productivity in US, May
2003.
MRG (2004). Momentum Research Group. Net Impact:
Driving Networked Business Productivity in
Germany, France, Italy, Netherlands, Poland, Spain,
Sweden and UK, April 2004.
MRG (2005). Momentum Research Group. Net Impact:
Driving Networked Business Productivity in Latin
America, April 2005.
Porter, M E (2001). Strategy and the Internet. Harvard
Business Review, 79 (2), 63-78.
UCB (2002). US Census Bureau . Statistical Abstract of
the United States.
A CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR SUSTAINING COMPETITATIVE ADVANTAGE IN DIGITAL ECONOMY
65
