
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB
BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING ACTIVITY
THEORY ANALYSIS
Chi-Yuh Shen, Gwo-Dong Chen, Kuo-Liang Ou
Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University
No.300, Jhongda Rd., Jhongli City, Taoyuan County 32001, Taiwan(R.O.C.)
Department of Applied Mathematics
National Hisn-Chu University of Education
No. 521, Nan-Da Road, Hsin-Chu City, Taiwan, (R.O.C)
Keywords: Activity theory, intrinsic motivation, educational online game, machine learning, web based mathematic
learning.
Abstract: In this paper, we use activity theory to analyze the process and out come of mathematic learning by using
MEOG (Multi-User Educational Online Game) based on the previous research (Gwo-Dong Chen, Gee-Yu
Shen, 1997) described a multi-user educational online games which can motivate and guide students to learn
and practice courses on the web. In order to reduce the obstacle of MSEOG applying in instructional
activity in classroom, first, we adopt the factors of motivation as outcome and decided the tools and rule by
found the cue in the questionnaires and server log. Second, we consider events of instruction and learning
phrases (Gagne) and using Machine Learning Technique to get the potential rule (activity theory). From
these, we want to develop a methodology to get stability of guiding online game applying in instruction of
classroom.
1 INTRODUCTION
To play the game is the important part of our mental
and social development (Alan Amory, Kevin
Naicker, Jackie Vincent and Claudia Adams, 1998).
There are so many young men and younger adults
volunteer to spend much time to play online
game.(Alexamder E. Voiskounsky, Olga V. Mitina,
Anastasiya A.Avetiso, 2004). Recently, an online
game called “world of war craft” is popular in
Taiwan. It is a obvious evidence. Using game to
support in learning is not new research e.g.
increasing motivation (Westrom, Mary 1992, Gwo-
Dong Chen, Gee-Yu Shen, 1997,Maria M. Klawe
1999),enhancing achievement in mathematics
learning(Maria M. Klawe 1999), effect the cognitive
function (Rieber 1996) and training Skill to play
adventure games includes : logics, memory,
visualization, and problem solving (Quinn, 1994,
1997 Amory et al, 1999b).
In the study of Tom S. Chan (1999) mentions
”Deci and Ryan(1985) noted that making all school
work intrinsically motivating is impossible”.
Few research in game applied in school
activity.From BECTA surveying , Kirriemuir, JK,
McFarlane, A(2003) point out the main obstacle of
apply computer and video game in school is learning
in time, but teacher not allow student spend time in
the control of complex learning.
From E-GEMS project, Maria M. Klawe (1999)
got the result of gaming supporting learning are
effective increasing motivation and achievement.
But, in Muti-user network game, there is “significant
and persistent difficulties in bringing the games to
the level of stability needed to conduct field studies
of the games as a whole” (cited by Maria M. Klawe
1999).
In previous study (Gwo-Dong Chen, Gee-Yu
Shen, 1997), student volunteer to spend more time to
play MSEOG, besides, there are some factors of
motivation decided by T-test, but not study in
achievement and low rate in relearning the CAI.
312
Shen C., Chen G. and Ou K. (2006).
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and
e-Government / e-Learning, pages 312-319
DOI: 10.5220/0001252103120319
Copyright
c
SciTePress
A few study in using activity theory applied in
gaming related work. Activity theory provide a
method to analyzing learning processes and
outcomes (Lucia Rohrer-Murphy)
Kurt Squire 2002 argued the Game-Playing as
Social Practice and activity theory was proposed
under the issue-“how can one theoretical framework
for socio-cultural contexts” by psychologists. Victor
Kaptelinin Michael Cole 2002 adopted activity
theory in the research work about educational
computer game playing.Pippon Barr 2005 think
activity theory may prove a useful analytic approach
to the computer playing, and use activity theory to
develop a conceptual framework which describes the
role of value in computer game.
For this reason, this study based on the
advantage of combination online game and
instruction, issue of educational online game, using
activity theory, consideration events of instruction
and learning phrase (gagne) to develop the next
generation of educational online game applied in
instructional activity of classroom.
2 DEFINITION
Online game: players can interact in the same time.
Educational online game: combining CAI and
online game to achieve the goal of instruction.
Loosely mode educational online game: lower
learning support or intervene, player has the higher
degree of control in the game e.g. previous study
(Gwo-Dong Chen, Gee-Yu Shen, 1997). It let
student spend more time in learning. So, this model
could partial apply in classroom and continue
learning in out of school.
Tightly mode educational online game: higher
learning support or intervene, player has the lower
degree of control in the game e.g. this study. This
model designed to apply in instruction of classroom.
Mix mode educational online game: higher
learning support or intervene, player has the lower
degree of control in the game e.g. this study. This
model designed to apply in instruction of classroom
under tightly mode and adaptive tuning the mode in
out of school.
3 RELATED THEORY AND
RESEARCH
3.1 Intrinsic Motivation
The primary reason of embedding learning materials
into a multi-user computer game is to promote the
learning motivation of the students. Lepper and
Malone (1981) investigated what makes a computer
game fun. Malone,T.W.&Lepper, M.R.(1987)
found that motivation factors can be divided into
two groups: intrinsic motivation and extrinsic
motivation. The motivation factors of a single user
game are mostly related to intrinsic motivation. The
intrinsic motivation factors include:
Challenge: a game always provides missions to
be accomplished or virtual enemies to fight with. It
provides a challenge to the players;
Curiosity: a game always has a fantasy story with
graphic animation and sound. The missions provided
are like puzzles. A player is always trying to find
how to solve and what is in the fantasy scene;
Engagement: a game provides a simulated
environment. The players feel like they are the role
in the game for they always get response quickly
after they take actions. This keeps the players
focusing on the game. And, the players feel like they
are involved in the missions and environment;
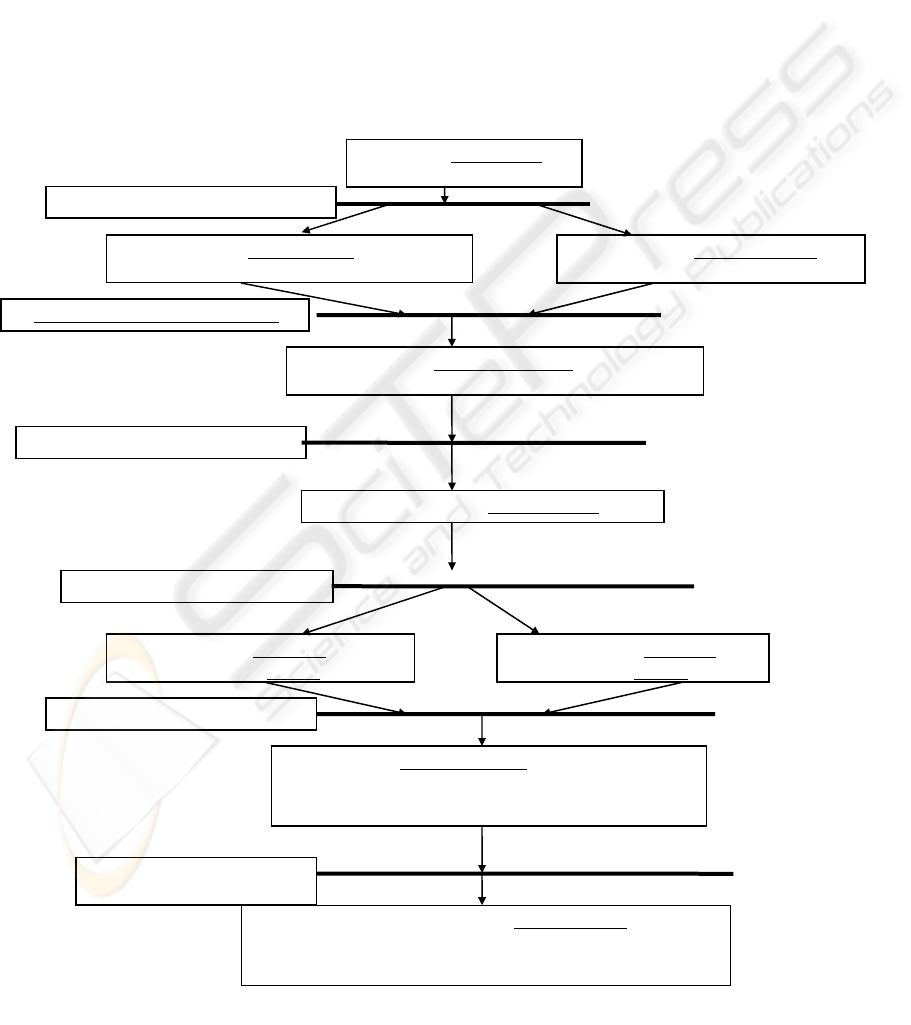
Autonomy: a game provides a simulated
Tool
Rule
Division of labour
Sub
j
ects
Out Come
Communit
y
Figure 1: Yrjö Engeström’s activity system model.
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING
ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS
313

environment. Also, it provides actions the players
can take and control in order to achieve what they
expected. They do not have these capabilities in the
real world;
And Fantasy: a game can provide graphic
animation, music and sound, and actions with
response. These make a fantasy feel like real.
When Lepper and Malone (1981) studied
computer games, most computer games are only
single user games. Therefore, the factors considered
in what make computer games fun are related to
intrinsic motivation. However, in a multi-user game,
extrinsic motivation factors should be included. The
extrinsic includes
Competition: players in a multi-user game can
see the scores, level of other players. Besides, they
can compete or fight with other players;
Collaboration: a multi-user game can arrange
missions that are to be accomplished by group of
players. It can also provide an environment for
players to make friends;
And recognition: if a player got high score or
promote to higher level, other players can know
from the game. Thus, a multi-user game provides
chances for players to be recognized by other
people.
3.2 Activity Theory
Activity theory originates from Vygotsky’s idea
that explicit description of activity (Leont’ev 1978).
His student, Leont’ve, develops hierarchical levels
style from Vygotsky’s and Yrjö Engeström extended
Vygotsky’s to the activity theory (figure 1). Lucia
Rohrer-Murphy (1999) thinks that activity theory
provides a unique lens for analyzing learning
processes and outcome and activity theory is an
important precursor to good instructional
design.(figure 1)
3.3 Learning Stage (Gagne’s 1970)
The purpose of instruction is to assist learning
process (Robert M. Gagne, Leslie J.Briggs, and
Walter W. Wager 1988). The learning processes are
included in cognitive learning theory (Anderson,
1985; Estes, 1975; Klatzky 1980). They are
Attention, Expectancy, Retrieval of Relevant
Information to Working Memory, Selective
Perception, Encoding: Entry of Information into
Long-Term Storage ,Responding ,Feedback ,and
Cueing Retrieval.
3.4 Events of Instruction (Gagne’s
1970)
They deduce the event’s of instruction from learning
processes. They are Gaining attention, Activating
motivation: Informing the learner of the objective
,Stimulating recall of prerequisite learning,
Presenting stimulus material, Providing learning
guidance, Eliciting the performance, Providing
feedback ,Assessing the learner's performance,
Promoting retention and transfer.
3.5 Machine Learning
Technique-Decision tree
Decision tree: Decision Tree (Jiawei Han,
Micheline Kamber, 2001; Tom M. Mitchell, 1997) is
a tree structure similar to flow char structure. The
internal node represent the testing on attribute with
condition an branch represent the result of testing.
The leaf nodes represent the last result of
classification.
A typical example of Decision Tree (figure 2) is
that decision tree judge a customer whether buy the
car or not. The rectangle is equal to the node and the
ellipse is equal to the leaves. To judge one man
whether could buy the car or not, we have to get
some attributes of the man and use the attributes
tested by decision tree. The test is begun from the
root of the tree and test along to leaf. The leaf
represent the result of predict. For example: some
attributes of a man description below:
Table 1: Decision tree could easy transfer to these rules of
classifying (age=30, city=no, background=master).
Figure 2: Example of Decision tree.
If salary<=20 AND city=no
If salary<=20
AND city=yes
If salary =20…30
If salary =>30
AND background=master
If salary =>30
AND background=bachelor
THEN buys_car=no
THEN buys_car=yes
THEN buys_car=no
THEN buys_car=no
THEN buys_car=yes
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
314
Now, There are some decision support systems
of commercial use Decision tree to predict the
market of stock ,evaluate the risk of economic,.. and
so on.
3.6 A MUD Game
Many ideas of our multi-user game come from
Multi-User Dungeon MUD games. A MUD game is
a text base game. In a MUD game, there are (1)
levels of players and (2) communication tool such as
talk and chat room. Each level in MUD has different
privileges. Thus, it forms a players community.
Because it is a text base game, it provides users
imagination possibilities. However, it is not suitable
for elementary school students. We adopt its ideas to
form a community of practice.
3.7 Study of Westrom and Shaban
Westrom and Shaban (1992) investigated the effect
difference between a game and an instructional
game. They showed an instructional game is not so
fun as a pure game. In this paper, we investigate the
degree of effect for motivation factors proposed by
Lepper and Malone. We compare the difference
between a pure tutorial course and an instructinal
game.
Figure 3: Arranging the game script according to the learning hierarchy.
Consecutive
M
uZa county
subtraction
Consecutive zon-
s
han
multi
p
lication count
y
Consecutive Na-kan counity
addition
Mix of Chen-Der county
addition and su
b
traction
Prepare
M
ain scene
Using parenthesis Da-
A
n county
Consecutive Da-Ton
g
division count
y
Mix of yan
g
-ming cave
consecutive multiplication,
consecutive division and parenthesis
Mix of addition, su
b
traction, Da-Tuen cave
multiplication, division, and
parenthesis
Token A and, score>=200
T
oken D and score>=2000
Token E and score>=3000
Token F, G and score>=4000
Token H and score
>=5000
Token B, C and score >=1000
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING
ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS
315

3.8 WebQuest
Web Quest (CoDa96) is a web based instructional
game. The students ramble about in the game to find
related information to pass a scene. When facing
with problems, the students can invoke a web
browser to find the answer. The students can design
their own game. Experiment shows that the students
more like to design a game than to play the game.
They did not try to build a community of practice in
the game.
4 GAME SCRIPT AND
LEARNING MATERIALS
4.1 Selection of the Style of the
Game
The first thing of developing a instructional game is
to design a game script and put learning materials
into the game. Since a learning material always has a
learning hierarchy (Gagn68), the game script should
follows the learning hierarchy. Therefore, we decide
to implement our game as a role playing for the
following reasons.
First, role playing games are the most popular
games in Taiwan and this style of games allows
player to explore and think. A player is required to
figure out the structure of the game and learn the
strategies to overcome the problems in order to
accomplish the missions given in the game script
and to get score.
Second, a role playing game always has a
hierarchical script structure. Thus, it is easy to
design the game script according to the learning
hierarchy. When the learners try to accomplish the
script’s mission, they will learn and practice the
learning material according to the learning
hierarchy.
Third, a multi-user role playing game can forms
an environment to serve as a community of practice.
We can design different roles in the game. Each role
has different privileges. A role can invoke an action
only if it has the privilege to take the action. Thus,
the game scenery forms a community of practice if
every role is using the learning topics to solve
problems in order tp accomplish missions. However,
there should be missions assigned for roles to
cooperate or collaborate.
4.2 Arranging the Game Script
According To the Learning
Hierarchy
Gagne (Gagn68) proposed that a learning material
can be decomposed into elements and learning
should follow a procedure from simple to complex.
Thus, learning material should organized as a
learning hierarchy with a learning flow embedded in
it. This structure can be perfectly fit into a role
R
ule
Rule of game
Learning condition
Division of labour
(Role)
Master, sheik, and
ordinary people
Sub
j
ects
Player / NPC
Out Come
(To spend more time in
learning and **Curiosity,
**Challenge,
*Competition,*Cooperation,
*Cognition)
Communit
y
TOOL
MSEOG ( **querying and displaying of NPC and **learning
companion, **help me,**teaching, **questions, **chat room, **peer
talk, **note book, *represent of role,*shout), pen, paper, calculator
of computer, CAI
Figure 4: MSEOG based activity theory.
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
316

playing game script. Figure-1 is a learning hierarchy
for arithmetic skills. Each box represents a subskill.
The arrow line represent the legal learning flow. The
bar line represents a and join. A student should learn
all the subskills connected to the bar line.(figure 3)
We can design a hierarchy of script scenery
based on the learning hierarchy as shown in Figure-
1. The text in italic form are of the game script. Each
learning element or box is a scene or an act. In the
scene, the background is a place in Taipei city with
roles in it which give hints, asking question, and
lecturing through page in world wide web. The
player is trying to get scores and the token by
studying courseware or practicing exercises.
Players should get enough score or token in order
to get into another act or scene. The condition of
passing is stored in the bar line in the above figure.
The players are free to go to any scene if they hold
enough tokens and scores. Since the game script is
designed based on the learning hierarchy and flows,
the players will learn and practice accordingly.
5 ACTIVITY THEORY
ANALYSIS-ONLY CAI AND
MSEOG WITH CAI IN
INSTRUCTION OF
CLASSROOM
We used the factor of motivation of learning and
server log to serve as evidences to analyze activity
of MSEOG in previous study. We found some
questions of questionnaire related to the factors and
decided some tools involved in the activity from the
cue in the questions. We choose the most high score
one of questions. They are listed below then tools
and rules decided by the cue of question:
Curiosity: I want to know another player when I
played the MSEOG. From this question, querying
and displaying of the NPC and learning
companion were the tools to do that.
Challenge: I continue to play next stage of game
when I passed the condition of learning. From this
question, question in the game is the tool. The
challenge comes from two ways. One is the NPC
and the other is learning companion. A player need
help when answers the question. He could use “help
me” function by clicking animation of learning
companion. The challenge is to teach. In order to
teach, we provide discussion and synchronize
action function to reach “let me do it show you”.
Discussion function includes peer talk, chat room.
A player could challenge another play via
“challenge you” function with notebook to choice
question when another higher degree role player use
the “shout” function to show this position in the
learning community designed by considering the
Cognition of motivation (ML87).
Competition: I feel very happy when I passed the
condition of learning. From this question, condition
of learning is the rule.
Cooperation: I want to discuss with classmates
after playing game and discuss seriously for
answering question in the future to reach the
condition of learning to go next stage of game. From
this question, language, paper and pen are the
tools.
Cognition: I feel exciting when I got the higher
degree of role. From this question, the role
representation and “shout” function are the tools.
To support the decision, we analyze the server
log. We found the coincidence between curiosity to
comparison for self and another and challenge to
question answering by T-test significant degree and
percent order.
In the server log, the communication by text
supported the peer talk and chat room tool using and
teach mode support the synchronize action.
The purpose of the previous study is focus on
motivation supported by game, so the CAI
presentation served as the same environment. But
there is a problem generated from previous study
about CAI presentation, e.g. how to identify the
meaningful learning of frequency of CAI presenting.
Play Action Count Percent (%)
Communication by Text 558 14.11
4
Teach mode 61 1.54
6
Ask question to another 100 2.53
5
Choice style question
answer
1037 26.24
2
Comparison for self &
another
1401 35.45
1
CAI presentation 36 0.91
7
Virtual people hint 759 19.21
3
6 GUIDLINE OF APPLING
EDUCATION ONLINE GAME
IN CLASSROOM
By result, there are some guidelines to apply
education online game in classroom in first stage by
considering learner feeling.
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING
ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS
317

1. “Learning condition” is the most important
rule of game. It mediates the subjects in the
community to use tool to let mathematic learning
transform to outcome-Competition increasing.
2. “Querying and displaying of NPC and learning
companion” are the most important tools to let
subjects to transform mathematic learning to
outcome-curiosity enhancing.
3. “Learning companion, help me, teaching,
questions, chat room, peer talk, note book” are the
same as important tools to let subjects to transform
mathematic learning to outcome- Challenge.
4. “Represent of role, shout”- are the second
important tools to let subjects to transform
mathematic learning to outcome- Challenge
enhancing.
5.”shout” is the same as the second important
tool to let subjects to transform mathematic learning
to outcome- Cognition enhancing.
6. Above 5 points based on students’ feeling
about intra-game situation, we also found student
paper, pen, and calculator in PC to assist the solving
question by using observation based on extra-game
situation.
7 POTENTIAL RULES
GENERATION BY MACHINE
LEARNING TECHNIQUE
There are two kinds about generating potential:
1. one activity :Using learning action of Server log
to predict motivation/achievement, for example:
(simulation data)
34 question answering > 72:
: 11 CAI > 47:
: :...14 peer to talk <= 26: 49 (7/5)
: 14 peer to talk > 26:
: :...29 challenge you <= 28:
: :...10 teach mode <= 36:
: : :...35 notebook <= 60: 78 (3/1)
: : : 35 notebook > 60: 40 (2)
: : 10 teach mode > 36:
: : :...4 decide to PK <= 65: 67 (2)
: : 4 decide to PK > 65: 62 (2)
: 29 challenge you > 28:
: :...18 roam(thinking or idle) <= 33: 92 (4/2)
: 18 roam(thinking or idle) > 33:
34 question answering <= 72:
:...5help me > 58:
:...25shout <= 24:
: :...15 express emotion <= 38:
: : :...15 peer to talk <= 16: 89 (3/1)
: : : 15 peer to talk > 16: 44 (2/1)
: : 15xpress emotion > 38:
: : :...6 notebook <= 52: 24 (3/2)
: : 6 notebook > 52: 11 (3/2)
: 25shout > 24:
: :...9 peer to talk > 63:
: :...21 express emotion <= 45:
: : :...34 let me do it show you <= 46: 63 (3/1)
From this perspective, we found a problem in
using server. The frequency of learning action was
not explained the learning meaning related to
achievement. For explain: peep to talk so many
times why achievement is higher? So, we have to so
some strategy to prove the learning action meaning
quality in learning.
2. between two activities: Using factors of
motivations to predict achievement.
8 RESEARCH LIMITATION
There are two limitations in previous research.
First, because it is difficulty of measuring
motivation, using the same questionnaire in only
CAI and online game with CAI is the limitation.
Second, chidden whether the ability of expression
the motivation has or not. Finally, it is difficulty to
find the relation between with intrinsic motivation
and learning achievement in first stage of education
online game learning.
9 CONCLUSTION
This study based on previous study to analyze the
Multi-user educational online game applying in
instruction of classroom. the motivation as a
outcome, we backward to find the cues in the
questions of questionnaire. Then, we also analyze
the server log. There are some decision about
activity theory: learning condition is a potential rule.
MSEOG ( querying and displaying of NPC and
learning companion, questions, chat room, peer talk,
note book, represent of role), pen, paper, calculator
of computer, CAI are tools.
In order to reduce the obstacle of MSEOG
applying in instructional activity in classroom, first,
we adopt the factors of motivation as outcome and
decided the tools and rule by found the cue in the
questionnaires and server log. Second, we consider
events of instruction and learning phrases (Gagne)
and using Machine Learning Technique to get the
WEBIST 2006 - E-LEARNING
318

potential rule (activity theory). From these, we want
to develop a methodology to get stability of guiding
online game applying in instruction of classroom.
There are six guide found in the first stage
describing before.
Finally, there are two advantages of constructing
the education online game community practice. One
is the teacher has opportunity to conduct the social
learning in the gaming environment so as to avoid
the frustration or incorrect action in social
interaction. Other is the environment will extend the
learning in classroom to out of school and to
facilitate student continue learning about knowledge
in classroom.
REFERENCES
Amory, A., Naicker, K., Vincent, J. & Claudia, A. (1998).
Computer Games as a Learning Resource.
Proceedings of ED-MEDIA, ED-TELECOM 98,
World Conference on Education Multimedia and
Educational Telecommunications, Vol. 1, pp. 50-55.
Alexander E. Voiskounsky, Olga V. Mitina, Anastasiya A.
Avetisova Playing Online Games: Flow Experience
PsychNology Journal, 2004 Volume 2, Number 3, 259
- 281
Chan, T. S., & Ahern, T. C. (1999). Targeting Motivation
- Adapting Flow Theory toInstructional Design.
Journal of Educational Computing Research, 21(2),
151-163.
Gwo-Dong Chen, Gee Yu Shen, Yuan-Jen Tai & Alf Lai
(1997) A Multi-User Situated Learning Games on
Internet ICCE.
Gagné, R., Briggs, L., & Wager, W. W. (1988). Principles
of instructional design (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Holt,
Rinehart and Winston, Inc.
Jiawei Han, Micheline Kamber, Data Mining : Concepts
and Techniques, MORGAN KAUFMANN
PUBLISHERS , 2001
Kirriemuir, JK, McFarlane, A, (2003) Use of Computer
and Video Games in the Classroom. Proceedings of
the Level Up Digital Games Research Conference,
Universiteit Utrecht, Netherlands. Available from:
http://www.silversprite.com/
LEONT’EV, A. N. Activity, Consciousness, and
Personality. Prentice Hall, 1978. Available online at
http://www.marxists.org/archive/leontev/works/1978/.
Lucia Rohere-Murphy (1999) Activity theory
LAWRENCE ERLBAUM ASSOCIATES, Publishers
Mahwah, New Jersey p.159
Maria M. Klawe: Computer Games, Education and
Interfaces: The E-GEMS Project. Graphics Interface
1999: 36-39
Malone,T.W.&Lepper, M.R.(1987) ”Making Learning
Fun: A Taxonomy of Intrinsic Motivations for
Learning,” In R.Snow and M.Farr (Eds.)﹐ Aptitude,
learning, and instruction ﹐ vol.3 ﹐ Cognitive and
affective process analysis﹐ Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence
Erlbaum Assoc.﹐ 1987﹐ ch.10﹐ pp.225-254
Malone, T.W. & Lepper, M.R. (1987).”What makes
computer games fun,” Byte,6(12),258-277.
Pippin Barr 2005 Play and Work:Investigating the Role of
Value in Human-Computer Interaction A proposal
submitted to the Victoria University of Wellington
RM Gagne70 The conditions of learning, New York, Holt,
Rinehart and Winston
Squire, K. (2002). Cultural framing of computer/video
games. The International Journal of Computer Game
Research, 2(1), Game Studies Available
online:http://www.gamestudies.org/0102/squire/
Retrieved 12-24-02
Rieber, L.P. (1996). Seriously considering play: Designing
interactive learningenvironments based on the
blending of microworlds, simulations, and games.
Educational Technology, Research and Development,
44, 43-58.
Westrom M. and Shaban A. ( 1992 ) “Intrinsic
Motivation in Microcomputer Games”Journal of
Research on Computing in Education﹐ vol.24
﹐ no.3
Summer 1992﹐ pp.433-445﹒
Quinn, C.N. (1994). Designing educational computer
games. In K. Beattie, C.McNaught, & S. Wills, (Eds.)
Interactive multimedia in university
education:Designing for change in teaching and
learning, pp. 45-57, Amsterdam:Elsevier.
A MULTI-USER EDUCATIONAL ONLINE GAME WITH WEB BASED MATHEMATIC LEARNING BY USING
ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS
319
