
THE WEB BASED SYSTEM FOR RECORDING AND ANALYSING
DIFFERENT KINDS OF NEGOTIATIONS
Michal Piotrowski
Faculty of Electronics, Telecommunications and Informatics of Gdansk University of Technology
ul. Gabriela Narutowicza 11/12, 80-952 Gdansk Wrzeszcz, Poland
Beata Krawczyk-Brylka
Faculty of Management and Economics of Gdansk University of Technology
ul. Gabriela Narutowicza 11/12, 80-952 Gdansk Wrzeszcz, Poland
Keywords:
Internet technology, negotiations, team work, enterprises, web system.
Abstract:
Negotiations are a base of various human and electronic activities. The paper describes a web based system for
recording, analysing and supporting some steps of negotiations. It also discusses several, fundamental prob-
lems of implementation of the system. To show its usability, some experiments and outcomes of negotiation
processes are demonstrated. Two kinds of negotiations (f2f and cmn) where analysed and the essential drivers
are pointed out and discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays most of professional human enterprises
are performed by teams, where important activities
and decisions are taken by negotiations (Krawczyk-
Brylka and Piotrowski, 2004; Unsworth and West,
1999). Negotiation is a process that occurs between
at least two competing parties who discuss a certain
topic. The topic is an object of the real world that
parties have interest in. For the negotiation process to
take place, demands, connected with the topic, should
be formulated by both sides (negotiators). If the de-
mands are satisfying for both sides, an agreement of
negotiation has been reached.
We can distinguish two kinds of human negotia-
tions: natural (face to face) and executed in the Inter-
net environment (e.g. supported by chat). Moreover,
software agent technologies can be used to automate
some steps of the negotiation process. Understand-
ing of the face to face negotiations (f2f) and com-
puter mediated negotiations (cmn) is very important
to make various human enterprises more efficient and
effective (Phelps et al., 2004).
Let us consider a simple case of business negoti-
ations. The objects of negotiations are goods which
one partner (buyer) wants to buy and another part-
ner (seller) wants to sell. The demands are the suit-
able properties of the analysed goods such as prices of
goods, delivery terms, payment forms, etc. The final
step of the negotiation is the contract for the goods de-
scribing conditions for completion of buying/selling
transactions. The outcome of the negotiations repre-
sents the accepted values of contract demands.
There are many different possibilities to formulate
demand sets as well as to organize negotiation strate-
gies. Apart from the above mentioned aspects, the
compromise outcomes depend on many other factors:
negotiators’ personalities, their motivations and expe-
riences, available communication channels and meth-
ods, alternative possibilities of other contracts, qual-
ity of the negotiated goods, criteria of negotiation de-
mands and so on (Bazerman et al., 2000).
The paper presents a web based system for
recording and analysing negotiation enterprises called
GAJA. The system provides tools for examining
many different aspects of negotiation processes. In
Section 2 we describe functionality of the proposed
system. In Section 3 we present the GAJA architec-
ture and Section 4 shows the main implementation
problems. Section 5 gives some experiments and out-
comes which demonstrate system usability.
2 IDEA OF GAJA
GAJA is a web based system that enables studying
negotiations in a natural environment (f2f) and in ar-
tificial environment (cmn). The main features of the
GAJA system are as follows:
• possibility to monitor several types of negotiations.
Currently it is possible to consider:
82
Piotrowski M. and Krawczyk-Brylka B. (2006).
THE WEB BASED SYSTEM FOR RECORDING AND ANALYSING DIFFERENT KINDS OF NEGOTIATIONS.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and
e-Government / e-Learning, pages 82-87
DOI: 10.5220/0001253500820087
Copyright
c
SciTePress
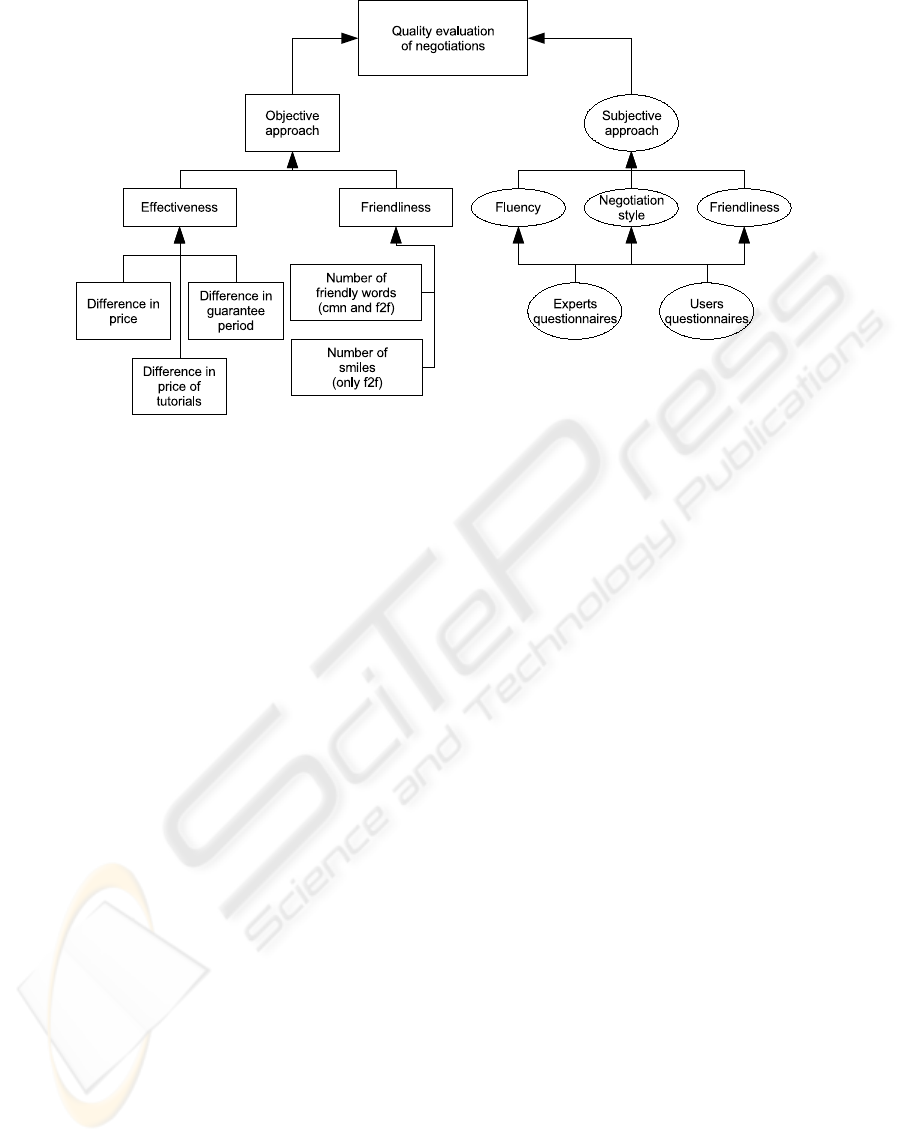
Figure 1: A fragment of the evaluation tree for sell/buy negotiations.
– sell/buy negotiations — a simple case of sell-
ing/buying a good by the participants;
– ranking negotiations — a group of people have
to collectively create a ranking of goods being
under consideration;
– enterprise negotiations oriented towards a design
of applications where small groups of students
are involved in designing of a simple web based
applications (using interactive incremental ap-
proach);
• possibility to define many versions (instances) of
experiments for each of the defined types of nego-
tiations, for instance:
– different communication channels used during
negotiations;
– different roles and positions (power) of negotia-
tors;
– different negotiators tasks and demands;
• possibility to support activities of different types of
users, which are as follows:
– experts — they can define negotiation experi-
ments, observe their executions and evaluate ne-
gotiation processes and obtained outcomes;
– negotiations’ participants — they participate ac-
tively in experiments and give their own opin-
ions about the expected results, negotiations out-
comes and moods;
– administrators — they have access to all the
available data and they configure the system for
concrete requirements;
• possibility of quality analysis of negotiators’ be-
haviour and negotiation processes:
– evaluation of personal characteristics of all ne-
gotiators using psychological tests;
– reviews of available chat logs and recorded video
media by experts to improve evaluation process;
– discovery of knowledge hidden in the collected
data and available questionnaires using profes-
sional analytical application suites.
For each type of negotiations we would define the
suitable model of evaluation. We use groupwork
model: contribution – processes – outcome (CPO)
described in (Unsworth and West, 1999; Bazerman
et al., 2000) and generalized by (Krawczyk-Brylka
and Piotrowski, 2004). Figure 1 shows a fragment of
the model (quality tree) used to evaluate wide aspects
of negotiation outcomes. The tree contains several
different factors divided into two main categories: ob-
jective (calculated from monitored data) and subjec-
tive (calculated from questionnaires). Each of these
categories have subcategories such as:
• effectiveness — describes how negotiation out-
come is close to BATNA (Best Alternative to a Ne-
gotiated Agreement) alternatives for each partici-
pant. Here, effectiveness means the difference be-
tween accepted and expected demands of goods;
• fluency — describes how fluent the negotiation pro-
cess was like. It takes into account sequences of
negotiation phases, interruptions, etc.;
• friendliness — shows if negotiations were handled
in a friendly way (negotiators used kind words, they
were smiling, etc.);
• negotiation style — could be aggressive or cooper-
ative.
THE WEB BASED SYSTEM FOR RECORDING AND ANALYSING DIFFERENT KINDS OF NEGOTIATIONS
83
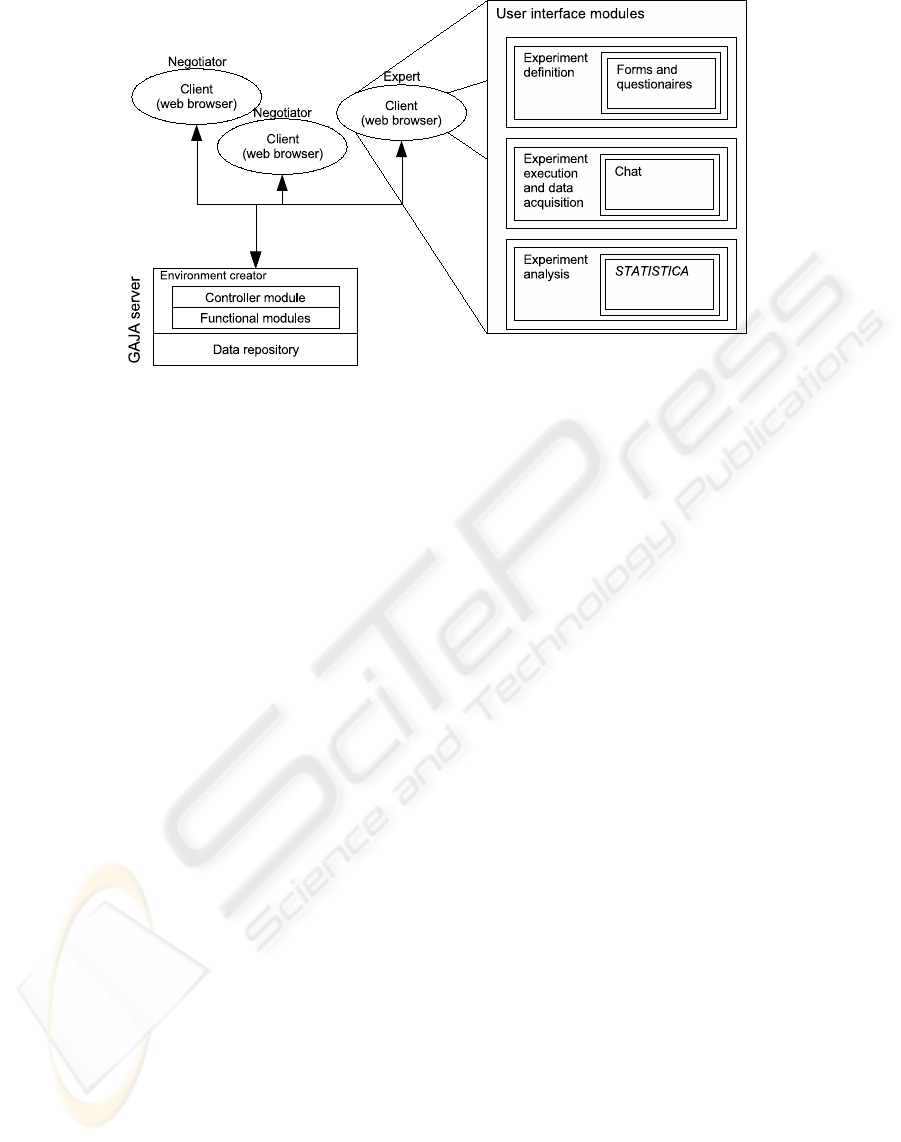
Figure 2: GAJA system architecture.
Some of the above factors can be evaluated in both
objective and subjective ways and some of them ei-
ther objectively or subjectively (see Figure 1). Some
quality metrics can be evaluated either by negotiators
or experts, or by both of them. Besides, we can regis-
ter the whole process of negotiations in the logs (chat,
video) and then analyse them many times for in depth
studies.
3 GAJA ARCHITECTURE AND
FUNCTIONALITY
In Figure 2 the GAJA system architecture is pre-
sented. It works in Internet infrastructure and its users
can connect to the system server using a web browser.
The available network environment is created by con-
troller module. The controller module has access to
repository where description of the system configura-
tion is stored. Also, all recorded data gathered from
experiments are registered in the data base. The con-
troller is responsible for creating user interface views
using appropriate functional modules. There are three
types of functional modules: experiment definition
modules, experiment execution modules and analysis
modules.
The experiment definition modules are available
only for experts and administrators. An expert selects
a type of negotiations and enters descriptions of an ex-
periment required by that type. Each negotiation ex-
periment consists of a task and contains background
information and precise instructions for each of the
negotiators. For example, an expert specifies what the
subject of the negotiations is, what the criteria which
can be negotiated are (good price, guarantee period,
tutorial course price etc.) and defines specific roles for
each participant. Moreover, a role of negotiator fol-
lows from real quality goods and their minimum and
maximum price. Knowing the contracts, the system
estimates the effectiveness of negotiation process as a
difference between the expected and achieved negoti-
ation outcomes. Besides, an expert define the evalua-
tion trees, suitable questionnaires, negotiation period
(lengths) and scales of ranking of possible outcomes
(see Figure 1).
All the data referring to the experiment definition
are prepared in advance. When negotiators log into
the system, the system presents the tasks suitable for
them and then they make experiments. This process is
controlled by the experiment execution modules. The
main steps executed by negotiators can be as follows:
• understand negotiation instructions (situation back-
ground, aim of negotiations, their roles),
• start, perform and finish the negotiation process,
• fulfill questionnaires: personal information, forms
about negotiation outcomes and about their opin-
ions and their feelings.
The negotiation processes are recorded as chat logs
or video logs. The analysis module allows to examine
outcomes by experts. All the recorded data are used
in post mortem analysis of given set of negotiations.
Some factors are calculated automatically on the ba-
sis of stored information and they are available im-
mediately after experiments. Some extra information
needed for further analysis is entered by experts, fol-
lowing observations of available logs. Experts, simi-
lar as negotiators, fulfill the questionnaires that eval-
uate both the whole negotiation processes and perfor-
mance of each participant (subjective evaluations). To
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
84
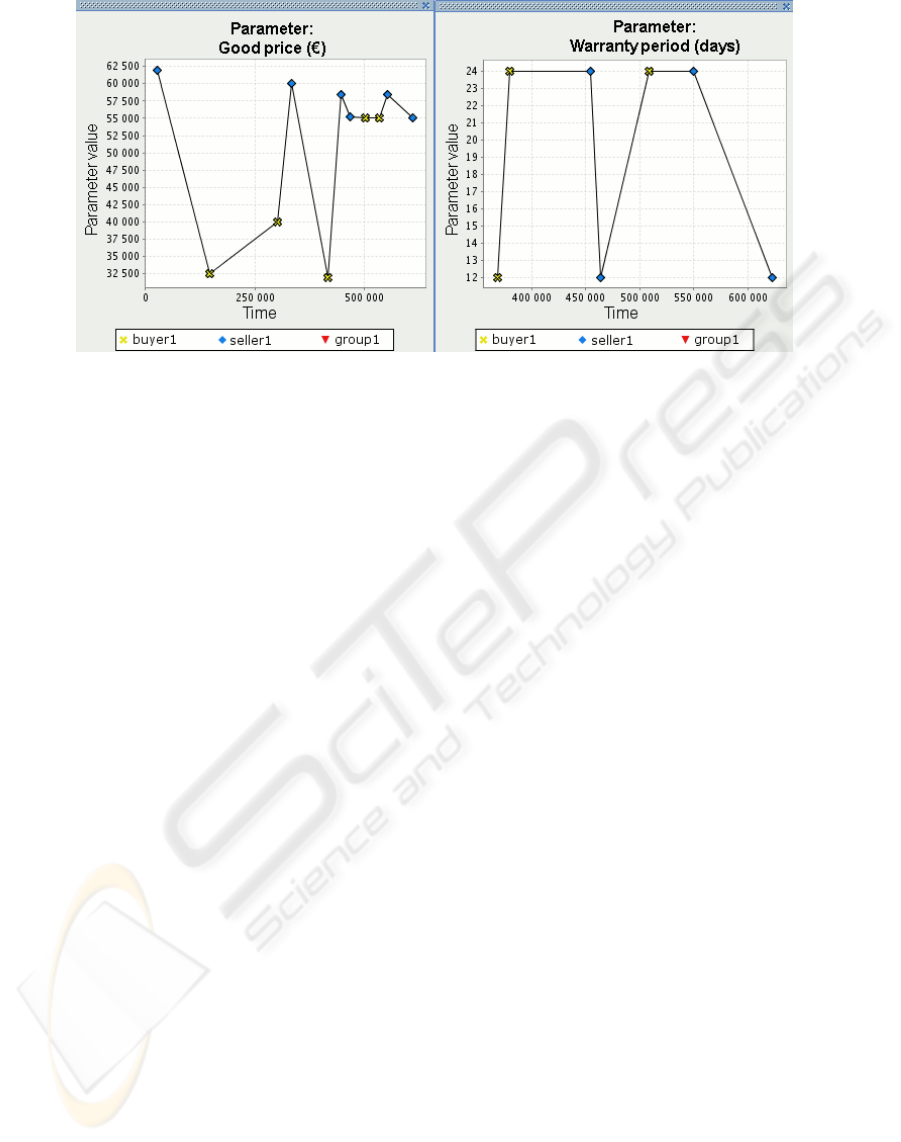
Figure 3: Negotiation dance graphs for two criteria of negotiations (good price and its guarantee period).
facilitate the log evaluation GAJA, offers new possi-
bilities. During observation of the logs experts can
push different buttons of the keyboard to automati-
cally point out some events and to provide some es-
sential values connected with the events. The GAJA
system counts such events and calculates as objective
factors.
One of the possibilities of GAJA analysis is to
display so called “negotiation dance” which shows
changes in time of the negotiated demands. Figure 3
presents the graphs for the price and warranty period.
The analysis modules allow us to display all gath-
ered data as tabular reports (see Figure 4). The tabular
reports show some parameters such as participant ex-
pectations for negotiation outcome, weight for each of
the negotiated demands and final values for negotia-
tion demands. The system enables exporting the table
to a CSV (comma separated values) file which can be
imported to any professional package e.g. STATIS-
TICA for more advanced statistical analysis.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
PROBLEMS
To achieve high system flexibility we decided to use a
web technology. We decided to use PHP technology
to implement the main modules of GAJA. We also
used Java Applets or Java applications when it was
necessary or more convenient. The choice of PHP
was motivated by facts that it is widely known, pop-
ular and open source technology and it is easy adapt-
able for typical hardware and software.
We used modular, component oriented approach to
develop the system. We use the Model View Con-
troller pattern (Buschmann et al., 1996). Its main
part is the controller module responsible for control-
ling access to modules and choosing which functional
module has to be executed for suitable user actions
(Figure 2). In a special configuration file it is set
which modules are activated and what types of users
can those modules use. Physically new modules are
just directories with code responsible for generating
appropriate views (Piotrowski and Krawczyk-Brylka,
2003; Krawczyk-Brylka and Piotrowski, 2004).
Each functional module is created with various
components (Gellersen et al., 1997). For main func-
tionality basic components were developed and added
to the GAJA system’s library. For the new function-
ality, the components were used to build new mod-
ules. Thanks to that approach, definition, execution
and analysis modules use common components and
objects, which simplifies the introduction of changes
into the system.
In the development of execution modules we intro-
duced the step based approach. Using the library of
components we define steps of activities required in
the experiments. Each step is supported by adequate
components which display appropriate instructions to
a user and require user interactions to enter other in-
formation. Moreover, we can rearrange steps accord-
ing to experiment requirements or reuse them in new
types of experiments. In many cases this requires the
change of the step’s number and the controller module
utilizes components in a modified, new configuration.
One of the big challenge in developing analysis
modules was to design a special user interface for
pointing out negotiation events that would be similar
for the video and chat logs. It is obvious that compari-
son of different media types is a difficult problem so it
is not easy to create user interface which will provide
a similar way to analyse both video and chat logs.
F2f and cmn negotiations are always performed in
THE WEB BASED SYSTEM FOR RECORDING AND ANALYSING DIFFERENT KINDS OF NEGOTIATIONS
85
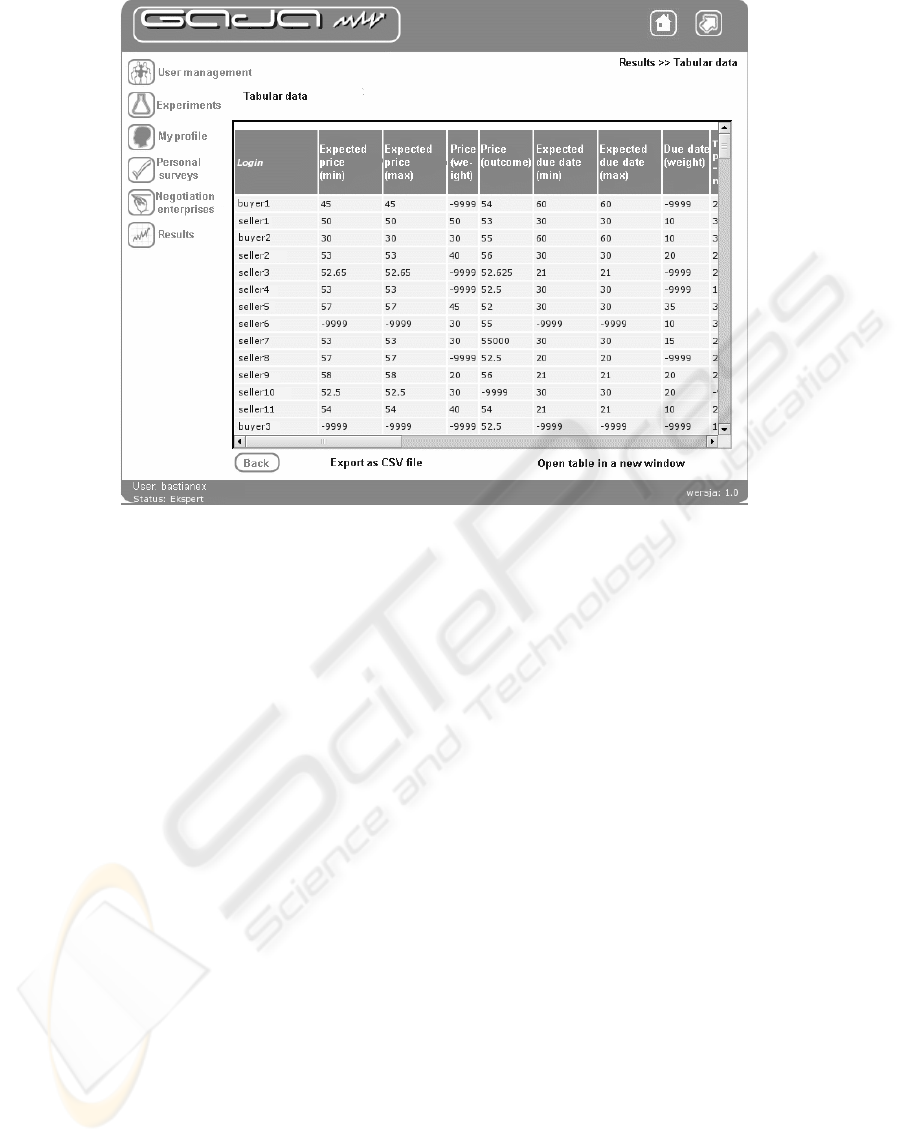
Figure 4: Screenshot of negotiation outcomes presented as tabular data (value of -9999 means lack of data).
a certain time frame. They take a period of time, start
in one point and end in another. As it was presented
the experts should point out some events (such as nice
gestures or friendly words) that occur in a certain mo-
ment in time. There arises problem how to synchro-
nize such events. Our proposition is the user interface
based on a logical timeline. For each negotiation ex-
periment we can define its own logical timeline. An
expert analysing the videos watches the records and
presses a key in the concrete moment of time when the
corresponding event is observed. Simultaneously the
event is marked on the timeline. Similarly an expert
analysing the chat logs marks a fragment of the suit-
able text which corresponds to a certain event. This
fact is registered on the logical timeline in the point
determined by the moment of sending the message by
the negotiator. In such way we obtain “negotiation
dances” (see Figure 3).
The approach allows us to analyse negotiation pro-
cesses in similar way regardless of what communica-
tion medium was used during the negotiations. More-
over, the system normalises the scale of times and var-
ious values of factors for all experiments.
5 EXPERIMENTS
To test GAJA system we arranged two main kinds of
experiments:
• sell/buy negotiations (f2f, cmn);
• enterprise negotiations oriented on a design of ap-
plications (development of blog, news site, wiki).
In the first kind of experiments the negotiators fo-
cused on selling/buying medical equipments. They
have to negotiate prices, delivery terms, payment
forms, guarantee period and tutorial course costs.
In the second kind of experiments a small group of
students has a list of typical functions that web based
system can provide. They have to choose exactly six
of them considering their priority and a period of time
needed to develop them.
Up to now we have performed more than 150 ex-
periments of that two kinds. Most of them (about
120) where cmn negotiations. The rest of them were
f2f negotiations recorded by a camera. We performed
more than ten chat experiments in parallel sessions
using two network computer laboratories simultane-
ously. The participants of our experiments were
students from several departments of our university.
The experiments allow us to deeply test the system.
Presently the system seems to be a mature tool for
recording and analysing different kinds of enterprises
including various negotiation strategies.
Figure 5 presents an example analysis which was
made using STATISTICA application. In this case the
experiments confirm the BATNA is not the most im-
portant factor in subjective assessment of negotiation
power. Other experiments show the choice of the
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
86
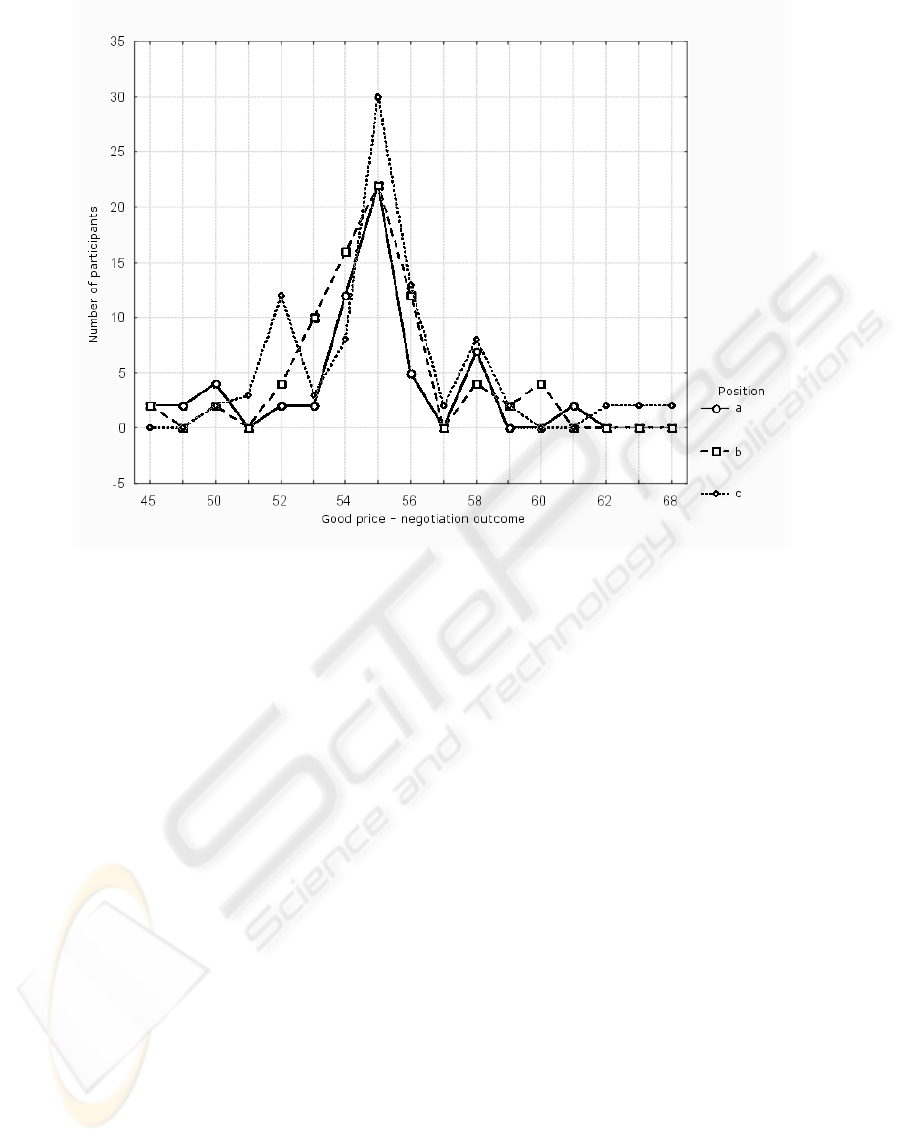
Figure 5: Distribution of negotiation outcomes for different negotiators power: a) equal for seller and buyer; b) buyer domi-
nance; c) seller dominance.
communication channel (chat or f2f) does not impact
on negotiation efficiency. Moreover, negotiation via
Internet leads to decrease of friendliness and fluency
what in consequences changes the negotiators satis-
faction. The personal features like extroversion and
consciousness play much more important role in the
chat negotiations that in f2f meetings, where for the
latter negotiation experiences are essential factors.
6 SUMMARY
GAJA system covers many aspects of analysing hu-
man negotiations. It consists of multiple modules
which can be reconfigured according to experiment
requirements. Distributed GAJA environment enables
performing many experiments in parallel. This en-
ables making a large number of experiments in short
time. It is very important for multidimensional anal-
ysis of negotiation processes and gives new possibili-
ties in discovering new rules hidden in various human
activities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported under KBN grant No
4T11C00525.
REFERENCES
Bazerman, M. H., Curhan, J. R., Moore, D. A., and Valley,
K. L. (2000). Negotiation. Annual Review of Psychol-
ogy, 51:279–314.
Buschmann, F., Meunier, R., and Rohnert, H. (1996).
Pattern-Oriented Software Architecture: A System of
Patterns. John Wiley & Sons, 1st edition.
Gellersen, H. W., Wicke, R., and Gaedke, M. (1997). We-
bComposition: An object-oriented support system for
the Web engineering lifecycle. Computer Networks
and ISDN Systems, 29(8–13):1429–1437.
Krawczyk-Brylka, B. and Piotrowski, M. (2004). Computer
based archivization of group activities processes (in
Polish). In National Conference on Information Tech-
nologies, pages 561–568, Gdansk, Poland.
Phelps, S., Tamma, V., Wooldridge, M., and Dickinson, I.
(2004). Toward open negotiation. IEEE Internet Com-
puting, 08(2):70–75.
Piotrowski, M. and Krawczyk-Brylka, B. (2003). Compo-
nent based design of internet system for evaluation
of communication-negotation enterprises (in Polish).
In National Conference on Information Technologies,
pages 553–561, Gdansk, Poland.
Unsworth, K. L. and West, M. A. (1999). Teams: the Chal-
lenges of Cooperative Work, chapter 14. Blackwell
Publishers.
THE WEB BASED SYSTEM FOR RECORDING AND ANALYSING DIFFERENT KINDS OF NEGOTIATIONS
87
