
SURFACE REGISTRATION USING LOCAL SURFACE EXTENDED
POLAR MAP
Elsayed E. Hemayed
Cairo University
Computer Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Giza, Egypt
Keywords:
Surface Registration, Surface Signature, Surface Matching, 3D Object Representation.
Abstract:
In this paper, we are presenting a new surface signature-based representation that is orientation-independent
and can be used to match and align surfaces under rigid transformation. The proposed scheme represents
the surface patches in terms of their signatures. The surface signatures are formed as extended polar maps
using the neighbours of each surface patch. Correlation of the maps is used to establish point correspondences
between two views; from these correspondences a rigid transformation that aligns the views is calculated. The
effectiveness of the proposed scheme is demonstrated through several registration experiments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many applications require the construction of precise
3D object models of physical objects, preserving as
much information as possible (Bernardini et al., 2002;
Ikeuchi and Sato, 2001). It is usually necessary to
scan the scene from different viewpoints in order to
build a complete 3-D model of a complex scene. The
registration of the acquired data sets into a common
coordinate system has been a subject of much re-
search during the last 15 years.
Several of the proposed methods (Rusinliewicz and
Levoy, 2001; Zhang et al., 2004; Blais and Levine,
1995; Zhang, 1994; Eggert et al., 1997; Okatani and
Sugimoto, 2004; Sharp et al., 2002) can be seen as
extensions or improvements of the Iterative Closest
Point (ICP) algorithm (Besl and McKay, 1992). ICP
is an iterative procedure minimizing the mean squared
error (or the sum of the squared distances) between
points in one view and the respective closest points in
the other view. At each ICP iteration, the geometric
transformation that best aligns the two images with
respect to this criterion is calculated.
Another approach (Fan et al., 2002; Robertson and
Fisher, 2002; Silva et al., 2005) to registering two im-
ages is to find the geometric transformation through
a pose-space search, rather than the correspondence-
based search of ICP. The search space of geometric
transformations contains solutions that can be used to
align two views. In this case, the objective is to find,
in a huge search space, a solution acceptably close to
the global optimum, in a reasonable time.
Recently, researchers have developed and dis-
cussed different surface representations that are ef-
fective in finding point corresponding between the
two sets to be registered. In this case, the reg-
istration problem is addressed in two steps, where
the first step is to establish the point correspond-
ing between the surface sets then to use these points
to compute the transformation that aligns the two
surfaces. These surface representations are known
as surface signature-based representation. They in-
clude the splash representation (Stein and Medioni,
1992), the point signatures (Chua and Jarvis, 1997),
the spin image representation (Johnson and Hebert,
1999), the spherical spin image representation (Cor-
rea and Shapiro, 2001), the surface point signatures
(Yamany and Farag, 2002), the harmonic shape im-
ages (Zhang and Herbert, 1999), the local surface de-
scriptors (Chen and Bhanu, 2004) and the point fin-
gerprints (Sun et al., 2003). In this paper, we are
proposing an extension for these representations to
solve the registration problem.
The proposed representation technique, Local Sur-
face Extended Polar Map (L-SEPMap), transforms
the surface from the Cartesian coordinate system
where surface descriptions vary with transformation
to an extended polar coordinate system where sur-
face descriptions are invariant to rigid transformation.
In this artificial domain, every surface patch, its cen-
143
E. Hemayed E. (2006).
SURFACE REGISTRATION USING LOCAL SURFACE EXTENDED POLAR MAP.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 143-148
DOI: 10.5220/0001375601430148
Copyright
c
SciTePress

ter of gravity, is represented by one L-SEPMap. As
a surface signature-based representation, L-SEPMap
places few restrictions on object shape and topology
and can be used to match surfaces in the presence of
clutter and occlusion.
Our approach to solve the surface registration prob-
lem is based on establishing point correspondences
using the L-SEPMap scheme. Next, sets of geo-
metrically consistent point correspondences are used
to compute the transformation that aligns the views
(Williams and Bennamoun, 2001).
This paper is organized as follows: The L-SEPMap
scheme is described in Section 2. The alignment pro-
cess using L-SEPMap scheme is described in Section
3. Experimental results are presented and discussed
in Section 4. Finally, conclusion and future work are
presented in Section 5.
2 L-SEPMap SCHEME
In this paper, surfaces are defined by a dense col-
lection of 3D points and surface normals (Hemayed,
2003). In L-SEPMap, we are extending the surface
signature representation to calculate the signature of
neighbor points only. Our approach is to use three
parameters (θ, φ, r) to represent the positions and the
curvature of each point with respect to the basis of
other neighbor points on the surface. In this represen-
tation, (θ, φ) capture the relative curvature while ’r’
captures the relative displacement between the sur-
face points. The three parameters are transformation
(rotation and translation) invariant.
L-SEPMaps generated for two corresponding
points on different surfaces would be similar, so ori-
ented points can be matched based on a compari-
son of their L-SEPMaps. L-SEPMaps are descrip-
tive enough that correspondences between points can
be established based on a comparison of L-SEPMaps
alone. Since L-SEPMaps is based on the neighbor
locality of the surface’s points of an object, the pro-
posed algorithm will generate a representation that is
robust to clutter and occlusion, so segmentation of
scene data is not necessary for surface matching in
cluttered scenes. In addition, the locality nature of
the L-SEPMap representation speeds up the process
and save the system memory. The process of generat-
ing the L-SEPMaps are presented in this section along
with the object model representation.
2.1 Object Model Representation
The object model is defined by a set of triangles. Each
triangle composed of three-vertices defined by their
Cartesian coordinates in the object coordinate sys-
tems. In order to simplify the L-SEPMap generation
process, the triangle’s center-of-gravity and its normal
are used instead of the actual triangle. So the object
model can be seen as a set of oriented points (repre-
sent the triangle’s center-of-gravity) and the surface
normal at these points. Mathematically, the object
model is defined by Eq. 1.
G = {g
i
= (p, n
p
)
i
, i = 1..N } (1)
Where p = (x, y, z) is the Cartesian coordinate of the
triangle’s center of gravity and n
p
= (n
x
, n
y
, n
z
) is
the triangle’s surface normal. g is known as an ori-
ented point.
2.2 L-SEPMap Generation
In the L-SEPMap generation process, each surface
patch (triangle) in the model is represented by a map
that is independent of the object coordinate system.
The map is generated at each surface patch by record-
ing the relative curvature and displacement of that sur-
face patch and its neighbors surface patches in the
model. The following terms are helpful in explaining
the generation process.
Neighbor Degree: This term is used to indicate
how two oriented points are close to each other. For
example, if an oriented point p is adjacent to another
oriented point q, i.e., their triangle patches share one
side, then we say that p is a neighbor to q with degree
1. And if w is not adjacent to p but it is adjacent to
q, then w is a neighbor to p with degree 2 and so on.
Fig. 1(a-c) shows the neighbors of a triangle patch for
1-, 2-, and 3-degree.
L-Degree Neighbors P
L
(g): This is the set of
all points that are neighbors to point g with degree
1, 2, ..L. If a point has an L-degree neighbors then
it may have an L+1 degree neighbors. However, if a
point does not have L-degree neighbors then it will
not have neighbors of any degree higher than L. We’ll
say that a point does not have an L-degree neighbors
if any of its L-1 degree neighbors has any of its side at
the edge of the model and as such it is not shared with
any other patch in the model. Fig. 1(d) illustrates that
triangle patch 1 and 2 lie on the edge and as such the
shaded triangle patch does not have a 4-degree neigh-
bors.
Inner Points of L-Degree: This is the set of all
oriented points that have at least L-degree neighbors.
In the other side, those points who do not have an L-
degree neighbors, they will be known as outer points
of L-degree. Fig. 1(d) shows that the shaded trian-
gle patch (oriented point) can be considered an inner
patch (oriented point) of 3-degree but an outer point
in case of 4 or higher neighbor degree.
For an object model G defined by Eq. 1, the L-
SEPMap M of an oriented point g ∈ G, g = (p, n
p
)
is defined by Eq. 2 (where N
L
is the number of L-
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
144

(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 1: The neighbors of the shaded triangle patch of (a-
c) 1-, 2-, and 3-degree, respectively. (d) Patches 1 and 2 are
edge patches.
Degree neighbors P
L
(g)), and is generated as fol-
lows:
M
L
= {m
j
= (θ, φ, r)
j
, j = 1..N
L
} (2)
For each oriented point g
j
∈ P
L
(g), g
j
= (q, n
q
)
j
,
1. Define v = the vector
−→
pq,
2. Calculate (θ, φ, r) as follows, see Fig. 2.
(a) θ = the angle between n
p
and v
(b) φ = the angle between n
q
and v
(c) r = the length of v (the distance between p and
q)
3. Record m
j
= (θ, φ, r) in M
The L-SEPMap generation process is repeated for
all inner points of L-degree g
i
∈ G, each will pro-
duce an L-SEPMap, M
i
, i = 1..N . The set of L-
SEPMaps are used to represent the object model G.
So the model L-SEPMap representation G
L
is defined
as
G
L
= {M
i
, i = 1..N },
M
i
= {m
j
= (θ, φ, r)
j
, j = 1..N
i
}
(3)
where N is the number of inner points of L-degree
in the model G and N
i
is the number of L-Degree
neighbors of the point g
i
.
3 REGISTRATION PROCESS
USING L-SEPMaps
The problem of registering two different surfaces de-
fined by their L-SEPMaps is solved in a two-step
Figure 2: The calculation of an L-SEPMap tuple
m = (θ, φ, r) of two oriented points (p, n
p
) and (q, n
q
).
process, L-SEPMap matching and the transformation
matrix estimation. In the first step, the L-SEPMaps
of the two surfaces’s points are matched establish-
ing points corresponding between the two surfaces.
The matched points are then fed into the second step
where a modified ICP algorithm is used to estimate
the rotation and translation matrices to align the two
surfaces. The L-SEPMap matching and the transfor-
mation estimation are presented in this section.
3.1 L-SEPMap Matching
The idea of the L-SEPMap matching is to establish
point corresponding between the two surfaces that
maximize the similarity between them. In our case,
the two objects are represented by their L-SEPMaps.
Mathematically, the L-SEPMap matching problem is
defined as follows:
Given the L-SEPMap representation of two objects
G = {M
0
i
, i = 1...N
0
},
H = {M
00
i
, i = 1...N
00
}
(4)
where N
0
and N
00
are the number of oriented points in
G and H, respectively. Find the point correspondence
between the two objects that maximizes the similarity
between them.
Let’s define the term Candidate Match Pair. This
term is used to indicate that two map points m
0
i
=
(θ, φ, r)
0
i
and m
00
j
= (θ, φ, r)
00
j
form a possible match
pair. m
0
i
and m
00
j
are possible match pair if they have
similar relative curvature and displacement, that is
θ
0
i
≈ θ
00
j
, φ
0
i
≈ φ
00
j
and r
0
i
≈ r
00
j
.
In order to measure the similarity between two ob-
jects G and H, we first measure the similarity, P , be-
tween their pair-wise L-SEPMaps defined in Eq. 4.
The similarity, P , between two L-SEPMaps, M
0
and
M
00
, defined in Eq. 5, is measured by the percentage
of matching records between the two L-SEPMaps.
Given two L-SEPMaps
M
0
= {m
0
i
= (θ, φ, r)
0
i
, i = 1..N
0
},
M
00
= {m
00
j
= (θ, φ, r)
00
j
, j = 1..N
00
}
(5)
SURFACE REGISTRATION USING LOCAL SURFACE EXTENDED POLAR MAP
145

The matching process can be summarized in the
following steps:
1. ∀M
0
i
∈ G and M
00
j
∈ H, calculate the similarity
measure, P
ij
as follows:
(a) Count the number of candidate match pair be-
tween all m
0
k
∈ M
0
i
and m
00
l
∈ M
00
j
(b) The similarity measure between M
0
i
and M
00
j
,
P
ij
, is the maximum count recorded in the pre-
vious step.
(c) If P
ij
> ∆ then M
0
i
and M
00
j
are said to be a
matched pair. ∆ is used to account for sampling
noise.
2. The overall similarity measure, P , between G and
H, is determined by a simple counting approach.
First, we form matching pairs between each M
0
i
∈
G and M
00
j
∈ H such that each will appear only
once in all the matching pairs. Since M
0
i
can have
several match with M
00
j
, we keep only the match
that have higher similarity measure P
ij
. The num-
ber of matching pairs formed is considered to be
the overall similarity measure P .
The matching pairs formed during the matching
process is the corresponding list that is fed into the
second step where a modified ICP algorithm is used to
estimate the rotation and translation matrices to align
the two surfaces.
3.2 Transformation Matrix
Estimation
The aim of the registration process is to compute the
transformations, which, when applied to the points
in that view, it brings the two surfaces into align-
ment. The desired transformations are expressed by
the 3x3 rotation matrix R and 3x1 translation vectors
t. The registration procedure can be posed as the min-
imization of a cost function which measures the sum
of squared distances between the transformed corre-
sponding points.
E =
N
1
i=1
N
2
j=1
u
ij
p
0
i
− (Rp
00
j
+ t)
2
, (6)
u
ij
=
1 if (p
0
i
, p
00
j
) forms pairwise correspondence
0 otherwise
where N
1
and N
2
are the numbers of points in the
two surfaces. The Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algo-
rithm proposed by Besl and McKay (Besl and McKay,
1992) is a commonly used framework for solving this
surface registration problem. In our work, we used
an enhanced ICP algorithm, developed by Williams
and Bennamoun (Williams and Bennamoun, 2001) to
solve the registration problem.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The registration process using SEPMap scheme has
been applied to several object models. In this paper,
we present the results of experimenting with four ob-
ject models (from 3D CAFE website); a chess king,
rook, queen, and bishop as shown in Fig. 3.
In the first experiment, we applied rigid transfor-
mation (rotation, translation) to the four whole-sized
models to form our full-size object set. Fig. 4 shows
the model and the transformed object. Table 1 shows
the transformation parameters of the experimental ob-
jects. The transformation parameters shown are the
rotation axis, rotation angle and the translation vec-
tor.
In the second experiment, we simulate a form of
occlusion where the object does not have a complete
3D-model. In this experiment, we cut a piece of the
models and applied to it rigid transformation to form
our partial-size object set. Fig. 5 shows the model and
the transformed partial-sized object. The transforma-
tion paramters are shown in Table 2.
the registration process using L-SEPMap scheme
has been applied to the full-size object sets and their
corresponding model. Fig. 6 shows the object and
the model after registration. Models are shown in
light grey-level (gold color) while objects are shown
in dark grey-level (purple color).
Similarly, the registration process using L-SEPMap
scheme has been applied to the partial-size object sets
and their corresponding model. Fig. 7 shows the ob-
ject and the model after registration.
To verify the accuracy of the registration process,
we calculate the sum of the squared distance error, de-
fined in Eq. 6. Table 3 shows the registration errors of
the registration experiments. The results demonstrate
the effectiveness of the proposed technique visually
and analytically. and the ability of the technique in
handling the general registration problem of full and
partial objects.
All experiments were conducted in a laptop com-
puter with Pentium-M processor 1.8 GHz and 512
MB RAM and assuming 5-degree of neighbors. The
average L-SEPMap generation total time (user + I/O +
CPU) is less than 2 seconds in a model of 1000 orig-
inal triangles. The matching total time (registration
time is negligible) between a model and object with
1000 triangle patches is less than 10 seconds. The
computational and memory requirements are propor-
tional to the number of original triangle patches and
the neighbors degree selected in the generation pro-
cess and can be reduced by applying the L-SEPMap
scheme to selected surface patches instead of the com-
prehensive search applied in this paper.
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
146
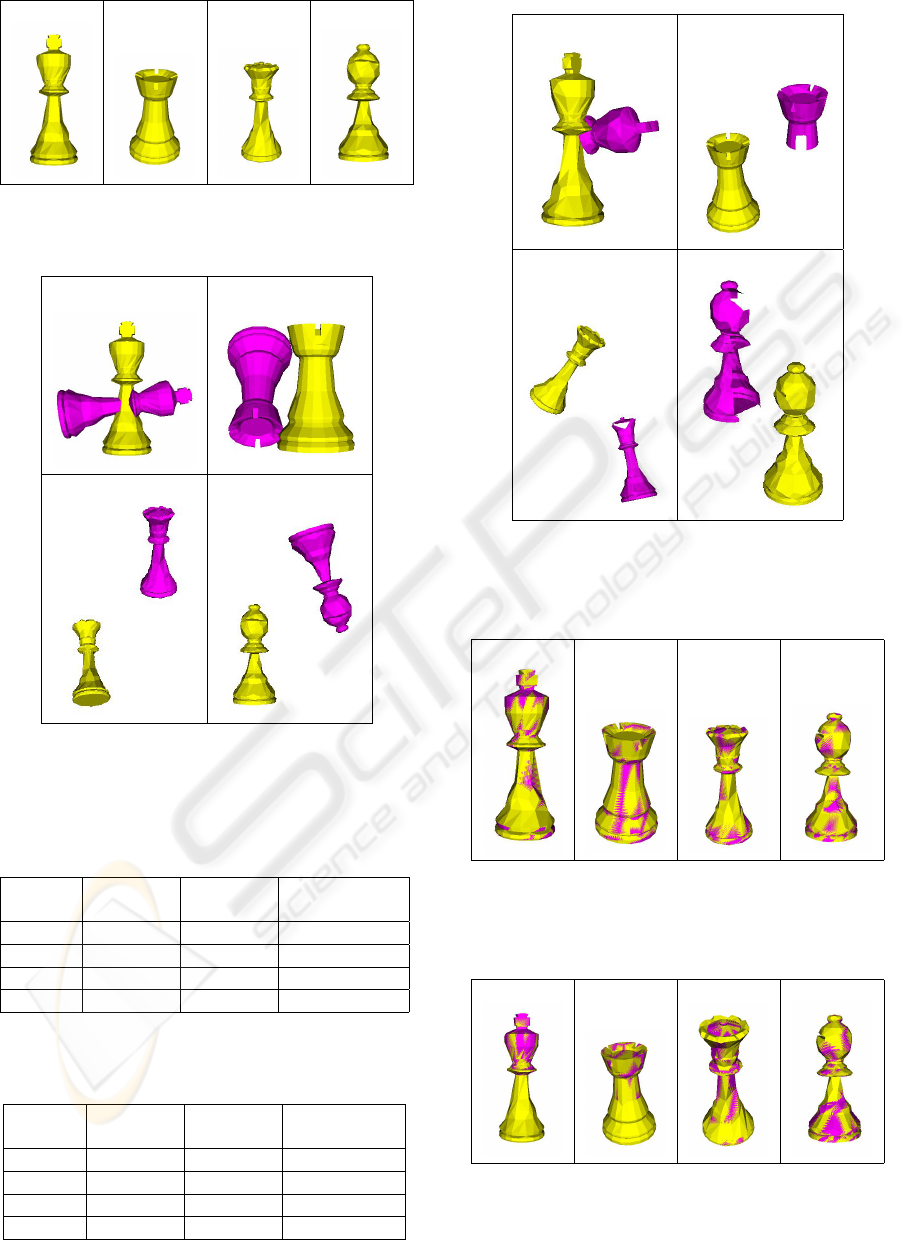
Figure 3: The models library, four chess pieces models,
from left to right, king, rook, queen, and bishop.
Figure 4: The models (yellow or light) and their trans-
formed objects (pink or dark).
Table 1: Transformation parameters for the full-size ob-
jects.
Rotation Rotation Translation
Axis Angle Vector
King z-axis 30 [00, -05, 00]
Rook y-axis 15 [-20, 00, -20]
Queen x-axis 45 [30, 30, 33]
Bishop z-axis 60 [30, 30, 20]
Table 2: Transformation parameters for the partial-size ob-
jects.
Rotation Rotation Translation
Axis Angle Vector
King x-axis -30 [04, 00, 00]
Rook y-axis -45 [30, 30, 20]
Queen x-axis -45 [30, -20, 30]
Bishop y-axis 60 [-15, 20, 20]
Figure 5: The models (yellow or light) and the transformed
partial objects (pink or dark).
Figure 6: The models (yellow or light) and the transformed
objects (pink or dark) after registration.
Figure 7: The models (yellow or light) and the transformed
partial objects (pink or dark) after registration.
SURFACE REGISTRATION USING LOCAL SURFACE EXTENDED POLAR MAP
147

Table 3: The registration errors.
Object Full Object Partial Object
King 0.2174 0.0001
Rook 0.0001 0.0844
Queen 0.0001 0.0001
Bishop 0.1011 0.0460
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
L-SEPMap is a surface signature-based representa-
tion scheme that is orientation-independent and can
be used to align surfaces under rigid transformation.
The experimental results demonstrate the effective-
ness of the proposed technique and the ability to han-
dle general registration problem of full and partial ob-
jects. Several items will be considered in future work.
Among those items are , studying the impact of noise
on the discrimination effectiveness of the L-SEPMap,
experimenting with clutter scenes and different trian-
gulation sampling, applying the L-SEPMap scheme
to the 3D segmentation problem, and extending the
matching algorithm to handle uniform scaling.
REFERENCES
Bernardini, F., Martin, I., Mittleman, J., Rushmeier, H.,
and Taubin, G. (2002). Building a digital model
of michelangelo’s florentine pieta. IEEE Computer
Graphics & Applications, 22(1):59–67.
Besl, P. and McKay, N. (1992). A method for registration
of 3-d shapes. IEEE Trans. on PAMI, 14(2):239–256.
Blais, G. and Levine, M. D. (1995). Registering multiview
range data to create 3d computer objects. IEEE Trans.
on PAMI, 17(8):820–824.
Chen, H. and Bhanu, B. (August 2004). 3d free-form ob-
ject recognition in range images using local surface
patches. In Proc. of the 17th Int. Conf. on Pattern
Recognition, pages 524–530, Cambridge, UK.
Chua, C. S. and Jarvis, R. (1997). Point signatures: A
new representation for 3-d object recognition. Inter-
national Journal of Computer Vision, 25(1):63–85.
Correa, S. and Shapiro, L. (2001). A new signature-based
method for efficient 3-d object recognition. In Proc.
IEEE CVPR, volume 1, pages 769–776.
Eggert, D. W., Lorusso, A., and Fisher, R. B. (1997). Es-
timating 3d rigid body transformations: a comparison
of four major algorithms. Machine Vision and Appli-
cations, 9:272–290.
Fan, Y., Jiang, T., and Evans, D. (2002). Medical image
registration using parallel genetic algorithms. LNCS
(Applications of Evolutionary Computing), 2279:304–
314.
Hemayed, E. (July 2003). A scalable approach for 3d
mesh generation. In Proc. of the 7th World Multi-
Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informat-
ics, Oralndo, FL.
Ikeuchi, K. and Sato, Y., editors (2001). Modeling From
Reality. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Johnson, J. and Hebert, M. (1999). Using spin images
for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3d scenes.
IEEE Trans. on PAMI, 21(5):433–449.
Okatani, I. and Sugimoto, A. (2004). Registration of
range images that preserves local surface structures
and color. In Proc. of the 2nd International Sym-
posium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and
Transmission (3DPVT’04), pages 789–796.
Robertson, C. and Fisher, R. (2002). Parallel evolutionary
registration of range data. Computer Vision and Image
Understanding, 87(1):39–50.
Rusinliewicz, S. and Levoy, M. (2001). Efficient variants
of the icp algorithm. In Proc. of the 3th Int. Conf. on
3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, volume 1, pages
145–152.
Sharp, G. C., Lee, S. W., and Wehe, D. K. (2002). ICP
registration using invariant features. IEEE Trans. on
PAMI, 24(1):90–102.
Silva, L., Bellon, O. R. P., and Boyer, K. L. (2005). Pre-
cision range image registration using a robust surface
interpenetration measure and enhanced genetic algo-
rithms. IEEE Trans. on PAMI, 27(5):762–776.
Stein, F. and Medioni, G. (1992). Structural indexing: ef-
ficient 3-d object recognition. IEEE Trans. on PAMI,
14(2):125–145.
Sun, Y., Paik, J., Koschan, A., Page, D. L., and Abidi, M. A.
(2003). Point fingerprint: A new 3-d object represen-
tation scheme. IEEE Trans. On Systems, Man and Cy-
bernetics - Part B: Cybernetics, 33(4):712–717.
Williams, J. and Bennamoun, M. (2001). Simultaneous reg-
istration of multiple corresponding point sets. Com-
puter Vision and Image Understanding, 81(1):117–
142.
Yamany, S. M. and Farag, A. A. (2002). Surface sig-
natures: An orientation independent free-form sur-
face representation scheme for the purpose of objects
registration and matching. IEEE Trans. on PAMI,
24(8):1105–1120.
Zhang, D. and Herbert, M. (1999). Harmonic maps and
their applications in surface matching. In Proc. IEEE
Conf. CVPR, volume 2, pages 524–530.
Zhang, H., Hall-Holt, O., and Kaufman, A. (June 2004).
Range image registration via probability field. In
Proc. of the Computer Graphics International, pages
546–552, Crete, Greece.
Zhang, Z. (1994). Iterative point matching for registra-
tion of freeform curves and surfaces. IEEE Trans. on
PAMI, 13(2):119–152.
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
148
