
CUSTOMISING E-LEARNING-PROCESSES
Towards a Decision Support System for the Individual Selection of E-Learning
Services in Academic Teaching Processes
Jan vom Brocke, Christian Buddendick, Nico Albrecht
ERCIS – European Research Center for Information Systems
Keywords: e-Learning, Service-oriented Architectures, Individualisation, E-Learning Management Systems.
Abstract: This paper presents a method supporting decisions for the selection of information systems in the context of
electronically supported teaching and learning. Existing approaches are supplemented by considering
individual context factors and teachers’ configuration desires. The supported selection process ranges from
the specification of situational characteristics of the teaching process to an individual selection of required e
learning services. Thanks to a process-oriented approach, functionalities of e-learning systems as well as
non-automated activities are identified. This comprehensive approach enables teachers to select an
information system appropriate for an individually planned learning scenario, which further consists of both
automated and non-automated parts.
1 E-LEARNING-SERVICES FOR
ACACEMIC TEACHING
PROCESSES
With e-learning, the design and application of
information systems is subject to research aiming at
the increase of both the effectiveness and efficiency
of learning processes (Curran 2004 p. 1; vom Brocke
2005). Recent learning products for example can
increase effectiveness, whereas efficiency can be
enhanced by special and temporal flexibility
(Wentling et al. 2000; Arnold et al 2004 p. 37). The
realization of these potentials can be achieved by a
large number of e-learning systems. (Lai-
kuen/Eastham 2002) Therefore users are confronted
with the necessity to choose a single or a
combination of systems that support their individual
teaching and learning scenario best (vom Brocke
2005; Westerkamp 2004).
Recent papers emphasize the impact of non-
technical aspects on the arrangement of teaching
scenarios (Dittler 2003 p. 14; Euler 2004; Albrecht
2003). The need for personnel giving technical
support, such as helping with setting up notebook
and beamer or handling the backing-up of online
learning material are examples for these aspects.
In order to ensure consideration of both technical
and non-technical aspects for the configuration of
teaching and learning scenarios, this paper utilizes
the term e-learning services. An e learning service
refers to an independent part of an information
system fulfilling a specific task in the context of e
learning. In general, information systems are
constituted of purposive socio-technical systems
dealing with the dissemination and the exchange of
information (Ferstl/Sinz 1998; Scheer 1994). The
systems are described socio-technical for the reason
that people as well as technical equipment are
involved in the dissemination and exchange
processes. In contrast, information systems with
entirely automatic execution are referred to as
application systems. Information systems are
purposive as they serve the accomplishment of a
specific task. E-learning services include services of
applications (e.g. chat or newsgroup) as well as
organizational services (e.g. the didactic concept).
The arrangement of computer-supported teaching
and learning processes demands determining which
which e-learning service is relevant in the specific
scenario (Adelsberger/Pawlowski 2002). From the
teachers’ perspective, this includes the choice of
services required for the realization of their
individual teaching scenario. From the university’s
point of view, the decision relates to the teacher-
supporting service to be provided. Due to the
definition of service in this paper, both applications
and organizational services are concerned, each of
215
vom Brocke J., Buddendick C. and Albrecht N. (2006).
CUSTOMISING E-LEARNING-PROCESSES - Towards a Decision Support System for the Individual Selection of E-Learning Services in Academic
Teaching Processes.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 215-221
DOI: 10.5220/0001427202150221
Copyright
c
SciTePress
them regarding specific context factors
(Lasonen/Finch 1995).
2 INTRODUCTION OF A
METHOD FOR THE CHOICE
OF E-LEARNING SERVICES
2.1 Preliminary Work
Preliminary papers concerning the choice of e
learning services focus on either the analysis of
application systems (Schulmeister 2001 p. 165ff.;
Baumgartner/Häfele/Maier-Häfele 2004 p. 153) or
the evaluation of software products using a list of
required features (Schulmeister 2000; Baumgartner/
Häfele/Maier-Häfele 2002 p. 65ff.). These papers
are constricted to the technical part of teaching and
learning processes, whereas non-technical parts of
information systems are largely missing.
Additionally, the principle of service-oriented design
of application systems is left unconsidered. In this
paper, a method based on a regulatory framework is
introduced, enabling teachers to identify individually
necessary e-learning services. Finally, the benefits of
this method are illustrated by means of a short
example.
2.2 General Framework
The method presented in this paper comprises three
levels: the context, the process and the service level.
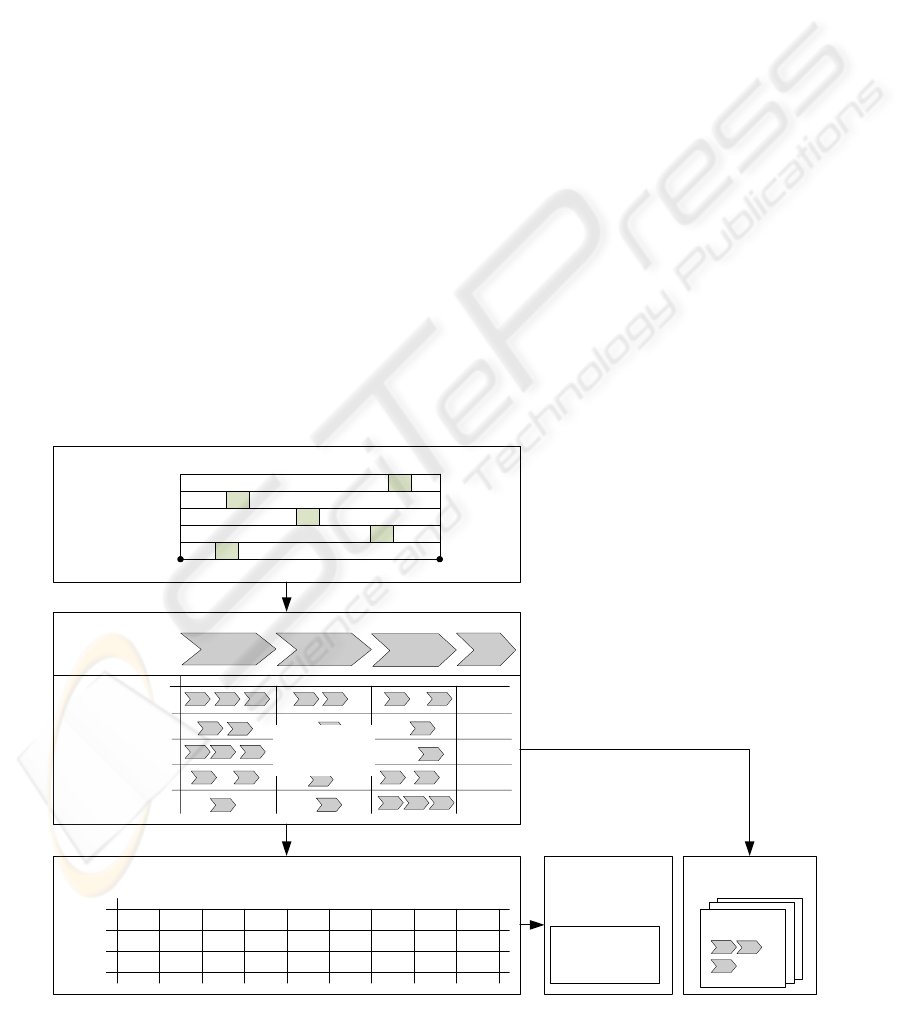
The regulatory framework shown in figure 1
illustrates the composition of the method.
In the following, these three levels are described in
detail.
Context level
The first level facilitates teachers describing their
individual teaching scenario with regards to their
context factors. These factors are based on papers by
Schulmeister and Arnold et al. (Schulmeister 2003 p.
175ff; Arnold et al. 2004 p. 9) enabling the
description of individual preferences and restrictions
(Baumgartner 2002 p. 9). Criteria for the selection of
the factors are independency and completeness.
Process level
Based on the teaching and learning scenario
described in the prior level, the processes required
for the preparation, accomplishment and post
processing of courses are considered.
The teaching processes identified by
Arentsen/Wieland as well as Gervedink Nijhuis
(Arentsen/Wieland 2001 p. 6; Gervedink Nijhuis
2005 p. 68) provided a basis for the processes
regarded in the method introduced in this paper.
Further activities (i.e. parts of a single service)
can be added easily in order to ensure the
Context
Processes
Services
to do lists
analog electronical
Knowledge dissemination
Planning and controlling
Administration
Communication
Collaboration
Information system or
combination of
information systems
Course
preparation
Handling
resources
Communi-
cation
…
...
...
...
...
...
Service requirements
System A
System B
...
...
...
...
Non-technical servicesTechnical services
Service
requirements
Knowledge dissemination
Planning and controlling
Administration
Communication
Collaboration
X
X
X
X
X
X
X X
X
X
Figure 1: Regulatory framework for the choice of e-learning services.
ICE-B 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-BUSINESS
216

upgradeability and adaptability of the method.
For each activity, the service requests required
for the accomplishment need to be identified.
Service level
Finally, adequate e-learning services are
identified on the basis of requirements derived from
the prior levels. Services concerning technical parts
of the information system can be utilized for the
choice of an application systems. Other services,
mainly consisting of organizational activities needed
for the accomplishment of a course, are merged in a
to do list.
The following chapter describes the proceeding
within the method and elaborates on the levels in
detail.
2.3 Levels of Configuration
2.3.1 Context Level
The first level enables the specification of context
factors for teaching and learning processes.
Technically, they can be described by the vector K:
{}
n
KKKK ,...,
21
∈
The motive of this selection is the bundling of
expectations towards the support of information
systems for teaching and learning processes on a
pragmatic level. The required services – technical as
well as non-technical – are not pre-specified, but are
selected by the method on a subsequent level.
For the standardized description of context
factors according to the vector K, a catalogue of
factors has been developed. In order to structure
these factors, they have been subdivided into
categories, created according to the proposed
description of teaching scenarios by
Baumgartner/Häfele/Maier-Häfele and Schulmeister.
(Baumgartner/Häfele/Maier-Häfele 2003 p. 8f.;
Schulmeister 2003 p. 175; Arnold et al. 2004 p. 91).
Figure 2 illustrates the categories and provides
examples of context factors for each of them.
Category Examples for context factors
Knowledge
dissemination
Presence lecture with
presentation software;
synchronous lecture with
spatially separated
participants communicating
by video; interactive elements
within self-study
Administration Provision of paper documents,
Transmission of electronic
materials by e-mail; Provision
of electronic materials on the
web.
Planning and
controlling
Presence examination; paper-
based evaluation; multiple-
choice evaluation on the web.
Communication Newsletter; information on a
website; discussion forum.
Collaboration Computer-based presence
seminar; synchronous editing
of documents by learners;
asynchronous editing of
documents by teachers.
Figure 2: Categories and examples of context factors.
For every context factor, the teachers can decide
whether and to what extent it should be supported by
technical systems. Thus, the teachers’ preferences
and possible restrictions can be specified for each
individual e-learning scenario. Within each category,
multiple context factors can be chosen. The
descriptions of the context factors are based on the
needs of teachers intending to keep usage barriers as
low as possible. In order to increase usability, pre-
defined combinations of context factors are
provided, enabling the selection of required
application systems and organizational services,
even without profound technical knowledge.
2.3.2 Process Level
Based on the context factors describing individual
preferences and restrictions, the required processes
are identified within the next level. These can be
described technically by the vector P:
{
}
n
PPPP ,...,
2,1
∈
The processes and activities proposed by
Arentsen/Wieland and Gervedink Nijhuis serve as a
basis for the processes used in the method described
in this paper. (Arentsen/Wieland 2001 p. 6;
Gervedink Nijhuis 2005 p. 68). Within the method,
11 processes containing 40 activities relevant for e
learning are pre-defined. A connection of the vectors
K and P produces a matrix, in which the cells
CUSTOMISING E-LEARNING-PROCESSES - Towards a Decision Support System for the Individual Selection of
E-Learning Services in Academic Teaching Processes
217
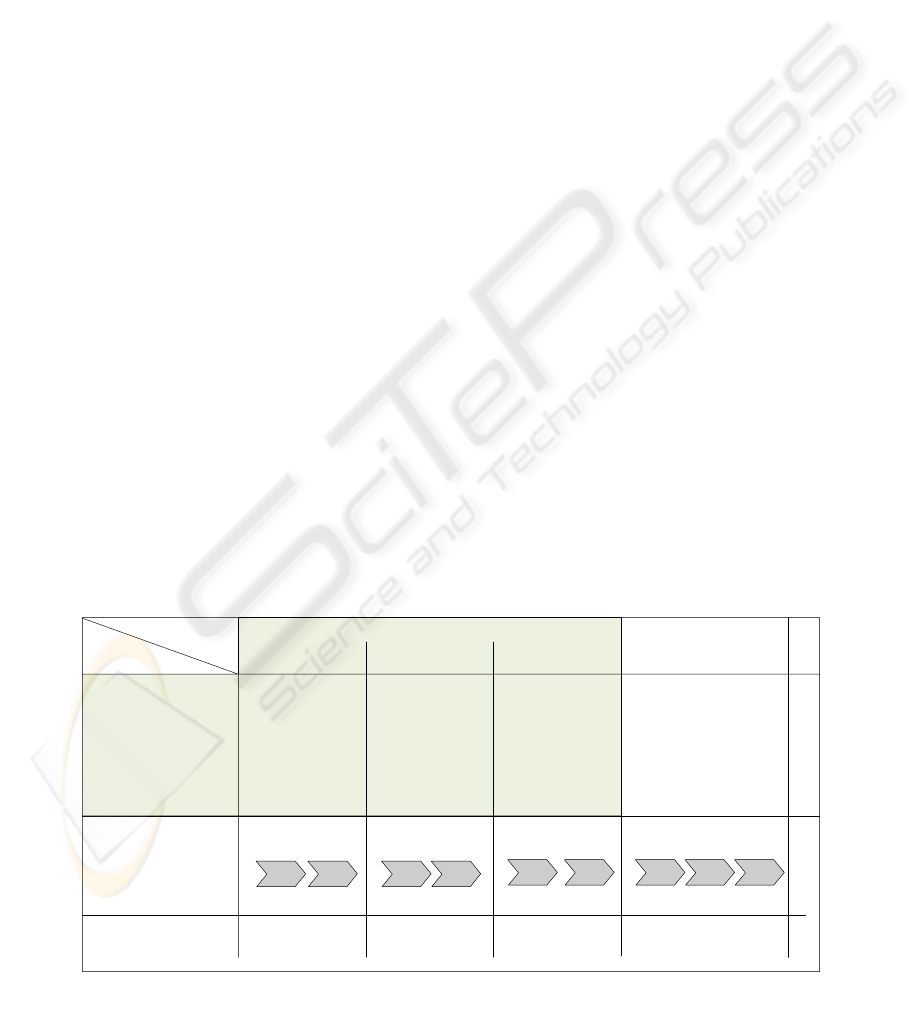
contain specific requirements for services in the
form of a vector S. This vector can be described
technically as follows:
{}
n
SSSS ,...,
21
∈
The vector includes the technical and non-
technical services required for a specific
combination of a context factor and an activity.
Figure 3 shows the matrix and the existing service
requirements in an extract.
In order to match all requirements of services, a
subsequent function of the method analyzes all
relevant cells. Cells not containing any data are not
considered.. The function determines the vector of
required services B
n,m
which can be described as
follows:
()
[]
nmnmn
SSSBPKf ,...,,,
21,
=
The vector of required services comprises all
relevant services required for the realization of an
individual scenario. Within this vector, technical as
well as non-technical service requirements are being
considered. Technical requirements form the basis
on which application systems are chosen. Non-
technical requirements serve the identification of
additional services required for the support of a
teaching scenario.
Further differentiation of the processes and
activities as well as the possibility of additional
activities being supplemented are offered within the
method by means of specific interfaces. Thus, the
capability of development and the future usability of
the method are ensured.
2.3.3 Service Level
The identified required services which can be
realized by application systems provide the input
parameters for the choice of a suitable information
system. (The papers of Baumgartner/Häfele/Maier-
Häfele and Schulmeister serve as a basis for the
identification of computer-supported services.
Baumgartner/Häfele/Maier-Häfele 2002;
Schulmeister 2000). Available information systems
require an analysis regarding their support of e
learning services in order to ensure an adequate
choice for teachers (refer to figure 4). For every
information system
{
}
n
ISISISIS ,...,,
21
∈
a vector
[
]
[
]
{
}
,...,...,,,,...,,
2121 nn
SSSSSSS
∈
needs to be defined, which includes all services
supported by the system. Therefore either a single or
a combination of information systems is proposed to
teachers − according to their individual scenario.
This proposition is the result of a best possible
overlapping of the vector
[
]
mn
BBBB
.2,11,1
,...,,
=
where a vector S represents a single information
system or a combination of several.
The service-oriented approach of information
systems is advantageous since the information
systems do not require categorization in advance.
Consequently teachers generally do not need to take
into consideration which application fits their
requirements best. Instead they determine the best
fitting system regarding their individual
requirements by means of the described decision
support process.
Processes
Context factors
Knowledge
dissemination
Administration
Course preparation Communication with
colleagues
Sub-factors [1, ...n]
...
S.1 S.2
S.3
S.4 S.5
S.6S.7 S.8 S.9
... ...
...
...
...
Research lecture
materials
Develop lecture
materials
Create excercises
and tasks
Use of presentation
software
...
...
... ... ...
---
Search former
presentations
Develop
presentations
...
Figure 3: Context-process-matrix
Figure 3: Contex-process-matrix.
ICE-B 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-BUSINESS
218

Services
Application
system
Clix Campus
WebCT
Development and administration of materials Communication
...
...
...
Search
featur e
Create
material
Administer
materials
...
Chat New sgroup ...
...
Up- and down -
load of m ater i al
...
Figure 4: Matrix of services and application systems.
3 APPLICATION OF THE
METHOD BY MEANS OF AN
EXAMPLE
This chapter presents a concrete example illustrating
the possibilities offered by the method discussed in
this paper: a university teacher for business
administration wants to conduct a presence lecture in
accounting. Important news such as room or
schedule changes should be transmitted to the
students by e-mail newsletter. In addition,
documents utilized in the lecture should be provided
electronically. It is assumed that the teacher has
already used presentation software and a beamer for
other lectures, wherefore lecture materials have
already been collected and transformed into the
format required for presentation and dissemination.
Finally, the teacher does not intend to spend
monetary resources for the purchase of software.
Thus, commercial software is excluded from the
consideration.
Initially, the teacher can chose the categories of
context factors required for the realization of a
specific course. For the purpose of this example, the
teacher selects Knowledge dissemination,
Administration and Communication. Presence
lecture with the use of presentation software,
provision of electronic data on the web and
newsletter are the relevant context factors for this
example.
Based on the inputs of the user, the system
generates a list of processes the teacher has to
accomplish. In the scenario described, a software
system has to ensure the processes Transmission of
lecture notes to learners and Provision of electronic
materials on the web. Further, the teacher wants to
make use of asynchronous and unidirectional
communication, wherefore only accordant systems
are eligible. The provision of material should be
web-based as well. In contrast to a transmission per
e-mail, this procedure enables the learners to access
the materials independent of access to their own
computer. Moreover, the teacher wants to use the
advantages of a document-management-software,
noticeably facilitating the administration compared
to editing an html-page.
The technical services form the basis of a
requirement catalogue based on which an
application system is chosen that fits the teacher’s
individual needs. Considering the scenario
described, for example, a software system is sought
combining functions for providing and updating
materials on the web on the one hand and
administration of e mail groups on the other hand.
The learning-management-platform OpenUSS is an
exemplary software fulfilling these criteria.
Additionally, the system provides a list of
processes requiring manual arrangement, such as
collecting the learners’ e-mail addresses. This sorted
list of non-technical services facilitates the
preparation and accomplishment of courses for
teachers. Moreover, an analysis of several of these
lists enhances the transparency of the demand for e-
learning services. Thus, university management is
assisted in the decision on providing manual or
semi-technical services for teachers.
Figure 5 shows a possible implementation of the
method. The user can select the relevant context
factors in the input window on the left. Upon
clicking the “Confirm selection” button, the right
window is displayed, showing the suggested
application systems and non-technical services.
Based on a J2EE framework, the implementation
of the method will be designed as a web-based open
source application. The context-process-matrix and
the matrix of services and application systems are
both stored by use of a relational database.
4 CONCLUSION
The heterogeneity of teaching at universities
requires individually designed e-learning services.
These services result from both specific restrictions
as well as demands of the teacher. In the course of
this paper, a method to tackle this problem has been
presented.
The method enables teachers to compose an
individual mix of services according to their
situation. Additionally, a basis for the identification
and comparison of the demands of several teachers
is provided. Thus, the university’s demand to
identify reasonable software systems requested by
several teachers is satisfied. Decisions regarding
which application systems (e.g. learning-
management software) to acquire or which
CUSTOMISING E-LEARNING-PROCESSES - Towards a Decision Support System for the Individual Selection of
E-Learning Services in Academic Teaching Processes
219

organizational departments (e.g. helpdesks) to set up
and change respectively can be facilitated.
The participation of teachers in the selection of
services seems promising in order to utilize the
teachers’ decentralised and detailed knowledge. On
the other hand, the acceptance of selection decisions
is enhanced. In order to increase efficiency of
coordination processes, pre-configured combinations
of context factors can be chosen and adapted in
accordance with individual needs. The simple and
transparent operation of the model reduce usage
barriers.
However, in this early stage of the method
conclusions are limited due to the lack of an
implemented application. Upon accomplishment of
the implementation, the tool will be deployed at the
University of Muenster. A subsequent evaluation by
both teachers and university management regarding
the usability and the extent of facilitation will be
initiated once the first usage data is available. In
order to apply this service-oriented procedure, future
e learning services have to be evaluated regarding
their requirements on the process level. Maintaining
and updating a pool of services seems to bear
promising possibilities, following the aim to share
good practices in e-learning.
REFERENCES
Adelsberger, H. H.; Pawlowski, J. M. 2002. Electronic
Business and Education. In: Handbook on Information
Technologies for Education & Training, International
Handbook on Information Systems. Berlin, pp. 653-
671.
Albrecht, R. 2003. E-Learning in Hochschulen : Die
Implementierung von E-Learning an
Präsenzhochschulen aus hochschuldidaktischer
Perspektive. dissertation.de - Verlag im Internet,
Berlin.
Arentsen, M.; Wieland, A. 2001. Tijdsbesteding van
docenten in het wetenschappelijk onderwijs [Time
expenditure of instructors in university education]. In
Proceedings van het symposium in het kader van het
vak Onderzoeksopdracht. Faculty of Educational
Science and Technology.
Arnold, P. et al. 2004. E-Learning : Handbuch für
Hochschulen und Bildungszentren. Didaktik -
Organisation - Qualität. Bildung und Wissen,
Nürnberg.
Baumgartner, P. 2002. Didaktische Anforderungen an
(multimediale) Lernsoftware. In Information und
Lernen mit Multimedia. Psychologie-Verl.-Union.
Baumgartner, P.; Häfele, H.; Maier-Häfele, K. 2002. E
Learning Praxishandbuch: Auswahl von
Lernplattformen. Marktübersicht - Funktionen -
Fachbegriffe. StudienVerlag, Innsbruck et al..
Baumgartner, P.; Häfele, H.; Maier-Häfele, K. 2003.
Evaluierung von Lernmanagement-Systemen (LMS):
Theorie - Durchführung - Ergebnisse. In Handbuch E-
Learning. Expertenwissen aus Wissenschaft und
Praxis. Fachverlag Deutscher Wirtschaftsdienst.
Baumgartner, P.; Häfele, H.; Maier-Häfele, K. 2004.
Content Management Systeme in e-Education :
Auswahl, Potenziale und Einsatzmöglichkeiten.
StudienVerlag, Innsbruck et al..
Curran, C. 2004. Strategies for E-Learning in Universities.
Center for Studies in Higher Education. CSHE-7-04.
Dittler, U. 2003. Einführung – E-Learning in der
betrieblichen Aus- und Weiterbildung. In E Learning:
Einsatzkonzepte und Erfolgsfaktoren des Lernens mit
interaktiven Medien. Oldenbourg.
Euler D. 2004. Einfach, aber nicht leicht –
Kompetenzentwicklung im Rahmen der
Implementierung von E-Learning an Hochschulen. In
Medienkompetenz für die Hochschullehre. Waxmann.
Output of e-learning services
Output of e-learning services
Input of context factors
Input of context factors
Suggested application sytems
Suggested
- OpenUSS
- PowerPoint/Impress
Optional/Alternatively
- ILIAS
- Stud.IP
To do-list
Manage preparing a course
- Search study material
- Develop study material
- Develop assignments
Handling resources
- Archive subject-matter and professional resources
Manage face-to-face sessions
- Develop overhead or presentation sheets
Administration
- Collect and administer student’s contact details
- Manage time and room planning
Selection of context factors
Presence lecture with overhead projector or blackboard
Presence lecture with presentation software
Presence lecture with presentation software and video
Knowledge dissemination
Lecture with asynchronous video transmission
Lecture with synchronous video transmission
Lecture with synchronous and interactive video transmission
Self-studies with advices for literature or copy samples
Self-studies with interactive software
Self-studies with non-interactive software
Transmission of electronic data by e-mail
Online-provision of electronic data
CancelHelpConfirm selection
Face-to face lecture, teacher and
learners are in the same room.
For the use of presentation software
(e.g. PowerPoint or Impress) a beamer
and a computer are needed.
Administration
Provision of paper documents
Provision of electronic data on storage mediums
CancelHelpPrint
Planning and control
Presence examination
ICE-B 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-BUSINESS
220

Ferstl O.K.; Sinz E.J.: 1998. Modeling of Business
Systems Using (SOM). In: Handbook on Architectures
of Information Systems. International Handbook on
Information Systems, Volume I, Springer, p. 339 –
358.
Gervedink Nijhuis, G. J. 2005. Academics in Control:
Supporting Personal Performance for Teaching-
Related Activities. Enschede.
Kubicek, H. et al. 2004. Organisatorische Einbettung von
E-Learning an deutschen Hochschulen. Institut für
Informationsmanagement, Bremen.
Lai-kuen, K.; Eastham, T. R. 2002. Network Services for
Education. In: Handbook on In-formation
Technologies for Education & Training, International
Handbook on Information Systems. Berlin, pp. 557-
576.
Lasonen, J., Finch, C. R. 1995. Evaluating an International
Vocational Education Research Linkages A Case
Study of Culture, Communication, and Collaboration.
In: International Journal of Vocational Education and
Training, Fall 1995, pp. 51-71.
Scheer, A.-W. 1994. Business Process Engineering –
Reference Models for Industrial Companies Springer-
Verlag, Berlin.
Schulmeister, R. 2000. Selektions- und
Entscheidungskriterien für die Auswahl von
Lernplattformen und Autorenwerkzeugen. Gutachten
für das BM:BWK, 2000. Available at:
http://www.izhd.uni-hamburg.de/pdfs/Plattformen.pdf.
Schulmeister, R. 2001. Virtuelle Universität - Virtuelles
Lernen. Mit einem Kapitel von Martin Wessner.
Oldenbourg, München, Wien.
Schulmeister, R. 2003. Lernplattformen für das virtuelle
Lernen : Evaluation und Didaktik. Oldenbourg,
München, Wien.
Schulmeister, R. 2005. Welche Qualifikationen brauchen
Lehrende für die „Neue Lehre“? Versuch einer
Eingrenzung von eCompetence und Lehrqualifikation.
In Hochschulen im digitalen Zeitalter.
Innovationspotenziale und Strukturwandel. Waxmann.
vom Brocke, J. 2005. Multi-Channel-Learning (MCL), Ein
Referenzmodell für Learning Content Systeme (LCS).
Journal for E-learning & Education (eleed), 2,
urn:nbn:de:0009-5-2344, 2005.
Wentling, T. et al. 2000. E-Learning – A review of
Literature. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign.
Westerkamp, P. 2004. E-learning as a Web Service. In:
Tagungsband zum 16. GI-Workshop Grundlagen von
Datenbanken, Monheim.
CUSTOMISING E-LEARNING-PROCESSES - Towards a Decision Support System for the Individual Selection of
E-Learning Services in Academic Teaching Processes
221
