
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON
THE INTERNET
∗
Javier Balladini, Leandro Souza and Remo Suppi
Computer Architecture & Operating System Department
Universitat Autonoma of Barcelona, Spain
Keywords:
VoD, media streaming, internet congestion control protocol, network traffic scheduler.
Abstract:
Most of the Video on Demand (VoD) systems were designed to work in dedicated networks. However, there
are some approaches that provide VoD service in nondedicated and best effort networks, but they adapt the me-
dia’s quality according to the available network bandwidth. Our research activities focus on VoD systems with
high quality service on nondedicated networks. Currently, we have designed and developed, to integrate in the
VoD server, a network manager that provides: total network control, network state information, and adapta-
tion of the transmission rate in a TCP-Friendly way. The present work describes this network manager, named
Network Traffic Scheduler (NTS), which incorporates a congestion control algorithm named "Enhanced Rate
Adaptation Protocol" (ERAP). ERAP is an optimization of the well-known protocol denominated "Rate Adap-
tation Protocol" (RAP). Maintaining the basic behavior of RAP, ERAP increases the efficiency of the NTS by
reducing the resources usage (of the server and the network). These components has been extensively evalua-
ted by simulations and real tests in which the resource consumption and the performance were measured. This
paper presents the advantages of using ERAP instead of RAP in a VoD server, and its viability to be integrated
within the NTS in a VoD server on nondedicated networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Our research group have designed a distributed Video
on Demand (VoD) system architecture for dedica-
ted networks (Qazzaz et al., 2003). This platform
works very well in Local Area Network (LAN) en-
vironments, but many problems appear that need to
be solved whilst trying to provide a service in nonde-
dicated Wide Area Network (WAN) environments.
Therefore, our investigation must be lead to solve
other kinds of problems that arise when the VoD sys-
tem works in a nondedicated network such as the In-
ternet. It is necessary to adapt the main component of
the platform, the Video Proxy Server (VPS), to a set
of restrictions imposed by the type of communication
that is possible to make on this type of networks.
Since at the moment the Internet does not offer a
multicast service (in a general form), the first change
that must be made is that the VoD service will be
made solely on unicast channels (instead of a com-
bination of multicast and unicast).
∗
This research is supported by the MEyC-Spain under
contract TIN 2004-03388.
Another problem is that on the Internet all the
packets are treated in the same way, without dis-
crimination or explicit delivery guarantees, known as
the “best-effort service model”. The quality of ser-
vice and the resources are not guarantees in terms
of bandwidth, transfer delay, delay variation (jitter),
and packet losses. The packet losses can be due to
physical reasons and droppings. In the first case, the
noise that affects the transmission of the signals or
the putting out of service of active communication de-
vices (links, routers, etc.) are included. The dropping
of packets is due to the congestion that takes place
because the network is overloaded by the demand of
network resources and this demand is close or exceeds
the network capacity (Tanenbaum, 2002).
When the transmission is made within the network
capacity, the packets arrive at their destination (except
for a few that are affected by noise in general) and
the number of received packets is proportional to the
number of sent packets. However, when increasing
the traffic, the network cannot handle it, and begins to
lose packets. The result is a state of congestion which
continues to build up and get worse. When a packet
loss exists (for example if any router has dropped it),
260
Balladini J., Souza L. and Suppi R. (2006).
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON THE INTERNET.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 260-268
DOI: 10.5220/0001569602600268
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the retransmission timer will expire and the sender
will possibly retransmit the packet. More packets in
the network make the situation worse, and as the ca-
pacity of delivery of the network continues to be the
same, the proportion of received packets against the
sent packets declines even more. (Kurose and Ross,
2004; Tanenbaum, 2002)
The optical fiber is being used in long distance
communication of the backbones so the loss of pack-
ets by transmission errors is relatively low. Conse-
quently, in the Internet communication, the most of
the expired packets are due to the network congestion,
rather the transmission errors. Therefore, all Trans-
port Control Protocol (TCP) algorithms assumes that
packets expire is consequence of the network conges-
tion.
In order to adapt to congestion states, the VoD
server must decreases the traffic sent by the network,
allowing the possibility to identify two types of strate-
gies for this aim: Dynamic Rate Control and Antici-
pation.
The Dynamic Rate Control strategy, allows the
transmission rate to adapt dynamically according to
the network conditions, but to reduce the transmission
rate, the media quality must be lowered (Wang and
Schulzrinne, 1999). The solutions based on Antici-
pation are applicable only to prerecorded continuous
media, that is to say, the whole multimedia file that
can be sent to the client already exists. This strategy,
takes advantage of the periods of low use of the server
and the network bandwidth, to send media in advance
that the client will consume later. In this way, it is
possible to tolerate moments in which the network or
the server are overloaded.
The algorithm developed in our VPS is named
Credit Based Media Delivery Algorithm (Cb-Mda),
and belongs to the Anticipation category. This type
of algorithm, from a general point of view, is a Lo-
gical Channel Scheduler (LCS), or is also known as
Streams Scheduler.
The main function of the LCS is to plan the diffe-
rent streams in order to make use of the server exit
bandwidth. However, the LCS does not have the
capacity to manage the communications at the net-
work level. This capacity, necessary to guarantee the
QoS, is assigned to a new module that we named Net-
work Traffic Scheduler (NTS). The NTS works to-
gether with the LCS (Cb-Mda in our case), and a feed-
back from NTS to LCS is provided to inform of the
communication state between the server and clients.
When the NTS detects congestion, in the path of com-
munication with a client, it must warn the LCS so that
it takes the suitable measures to reduce the transmis-
sion rate of the logical channel or stream. For that
reason, it is necessary that the NTS and the LCS work
coordinately and cooperatively to obtain the best so-
lution to the problem raised. Without information of
the real transmissions and the state of the network, the
LCS will not be able to work accordingly.
The investigation has been centered in the deve-
lopment of a NTS based on User Datagram Protocol
(UDP) packets and with congestion management so
that the VPS can be used on the Internet with total
guarantees and quality of service. The use of UDP,
instead of TCP, has significant advantages with res-
pect to the overload that implies TCP in the transmis-
sion. Furthermore, TCP does not give any of the in-
formation required by the LCS, and it does not allow
that this capacity can be added to it.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: in
section 2 the related works to this article are des-
cribed. In section 3, the NTS and its interaction
with the rest of the components of the VPS are ex-
plained. Furthermore, the characteristics that must
have their algorithm of congestion control in order to
adapt it to the new necessities of the VPS are indi-
cated. The “Rate Adaptation Protocol” (RAP) (Rejaie
et al., 1999; Rejaie et al., 1998), a well-known con-
gestion control protocol, whose basic characteristics
are suitable in order to adapt to the NTS, is described
in section 4. This protocol is optimized to be intro-
duced in the NTS, giving origin to the new protocol
"Enhanced Rate Adaptation Protocol" (ERAP), which
is presented in section 5. In section 6, the RAP and
ERAP behaviours are compared, and the advantages
to using ERAP instead of RAP as congestion control
algorithm of the NTS are analyzed. Finally, in section
7 the conclusions and future works are described.
2 RELATED WORKS
Congestion control has been studied for many years,
nevertheless, the existing protocols are not many if we
are restricted to TCP-Friendly protocols for multime-
dia transmission on the Internet.
Jacob et al. (Jacobs and Eleftheriadis, 1997)
presents a congestion control algorithm similar to
TCP except that this one does not make retransmis-
sions.
Cen et al. (Cen et al., 1997) proposes the “Strea-
ming Control Protocol” (SCP) for real-time strea-
ming of continuous multimedia data across the In-
ternet. Dorgham Sisalem et al. presents the “Loss-
Delay Adjustment Algorithm” (LDA) in (Sisalem
and Schulzrinne, 1998) and their variant “LDA+”
in (Sisalem and Wolisz, 2000). Sally Floyd et al.
exposes the protocol “TCP-Friendly Rate Control”
(TFRC) in (Floyd et al., 2000), and later M. Handley
et al. describes this protocol in the RFC 3448 (Hand-
ley et al., 2003).
Reza Rejaie et al. presents the “Rate Adaptation
Protocol” (RAP), and a mechanism of layered quality
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON THE INTERNET
261
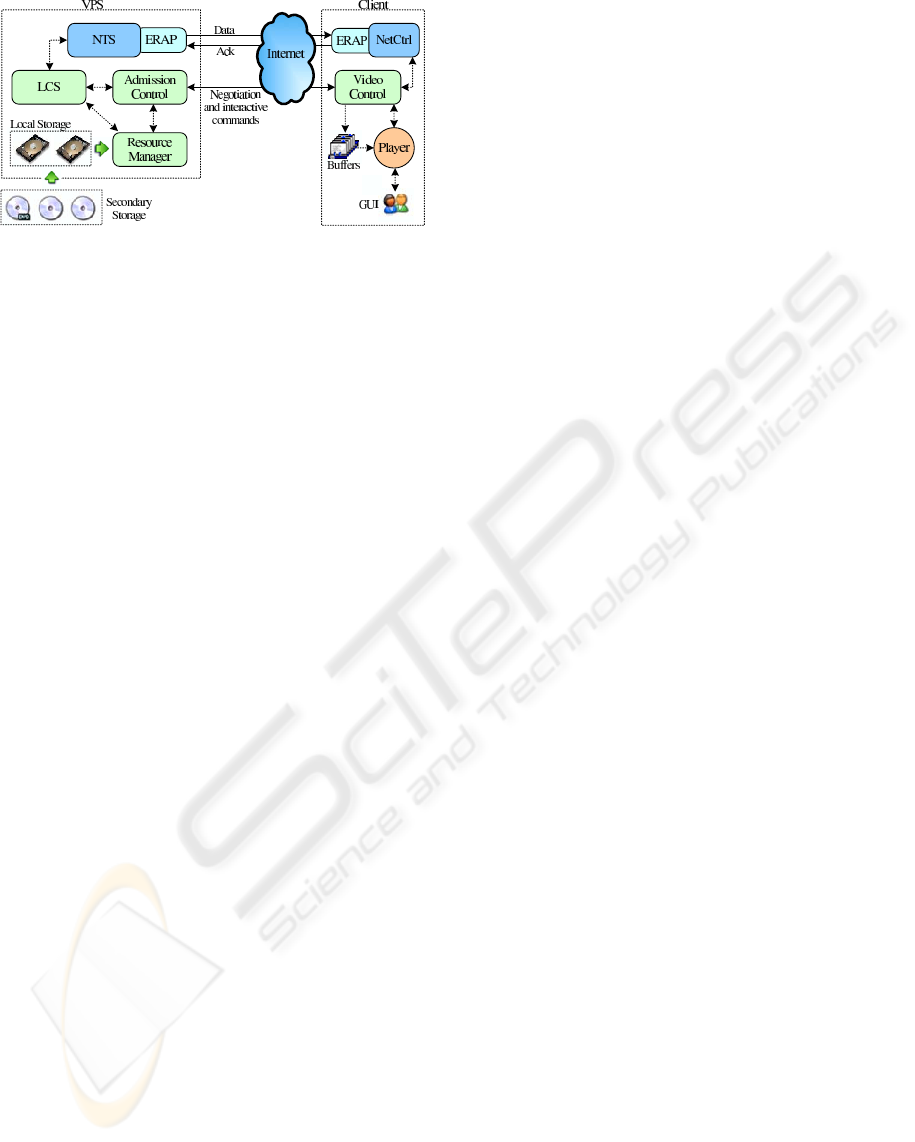
Figure 1: VPS and Client architectures.
adaptation for Internet video streaming in the context
of unicast congestion control are described in (Rejaie
et al., 2000).
Between the commercial players of video strea-
ming on the Internet we can include: RealPlayer,
Windows Media Player, and QuickTime. Although
their algorithms of congestion control have not been
revealed, there exists publications ((Hessler and
Welzl, 2005) and (Chung et al., 2002) among oth-
ers) that show studies on the performance and its
behaviours with respect to if they are or not TCP-
Friendly according to the answers that they offer in
congestion cases in real networks.
3 NETWORK TRAFFIC
SCHEDULER
The NTS is the component of the VPS in charge
to manage the communications at the network level
guaranteeing a transport with QoS to the LCS. The
new architecture of the VPS is presented in figure 1.
The NTS will inform the LCS about the state of
communication with each client, in such a way that
the LCS can carry out their tasks with real and up-
dated information of the network. If the NTS finds
that the communication of a certain connection has
improved, then the LCS will be able to increase the
transmission rate of that channel. In case the commu-
nication gets worse, the LCS will have to reduce the
transmission rate immediately.
The NTS must be equipped with a congestion con-
trol algorithm to fulfill their responsibilities. All con-
gestion control algorithm that is used on the Internet
must have the property of being TCP-Friendly, that
is to say, the use of bandwidth (in a stable state) does
not have to be greater than that required by TCP under
similar circumstances (Floyd and Fall, 1999). If irre-
sponsible users capture more bandwidth than corres-
ponds to them, the delivery service of the users that
cooperate for the good operation of the network could
be degraded. Furthermore, the stability and opera-
tion of the whole system would be threatened (Gevros
et al., 2001).
Different strategies for the congestion control exist,
but the NTS must make use of a strategy of type
Black-Box (this scheme sees the network as a black
or closed box) since there is no feedback from the
interconnection devices (routers) and the feedback
from the receiver is the only one available. The
streaming applications generally have better behavi-
our (and therefore they require it) when the traffic
flows in continuous forms and with few throughput
variations in the time. This property is known as
Smooth Sending Rate. Although it is a characteristic
that our LCS does not use, it is good that the conges-
tion control protocol of the NTS includes it for versa-
tility purposes.
Furthermore, it has been decided for a line of work
of rate-based protocols (instead of window-based)
because they have the advantage of not transmitting
packets in bursts. If a sender has the transmission ca-
pacity of b packets/second, is better to send a packet
each 1/b seconds and not a sequence of b packets
every second. A sequence of b packets could be un-
acceptable for an interconnection device that does not
have the sufficient amount of memory to store it tem-
porarily. On the other hand, if it does have the suffi-
cient amount of memory, long queues in routers will
increase the end-to-end delay. This can cause retrans-
missions (when expiring the time of the packets) that
produces an increase of the congestion state.
Several rate-based congestion control protocols
exist in the literature, between which are LDA, RAP,
TFRC, and SCP (see section 2). Many of the exist-
ing protocols are proposed by investigators, and in
many cases a real implementation does not exist, or
this does not adapt to the NTS. Thus, our investiga-
tion has been oriented in taking the specifications of
the most open of them, and the most suitable to our
objectives.
We have chosen the RAP specification because this
has the expected properties of black-box, rate-based,
and smooth sending rate, and also because it is sim-
ple, well documented, and well known as the Network
Simulator - NS2 (McCanne and Floyd, 2005; Bres-
lau et al., 2000) includes an implementation of them.
Nevertheless, in the official site of RAP no real im-
plementation of this protocol is provided.
The RAP protocol was adapted and optimized to
fulfill the requirements of the NTS, giving origin to a
new RAP version named Enhanced Rate Adaptation
Protocol (ERAP).
The NTS and the NetCtrl (see figure 1) use the
ERAP protocol for media stream transmission, and
the rest of the communications between the VPS and
the Client (negotiations and interactive commands)
are performed by a TCP connection.
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
262
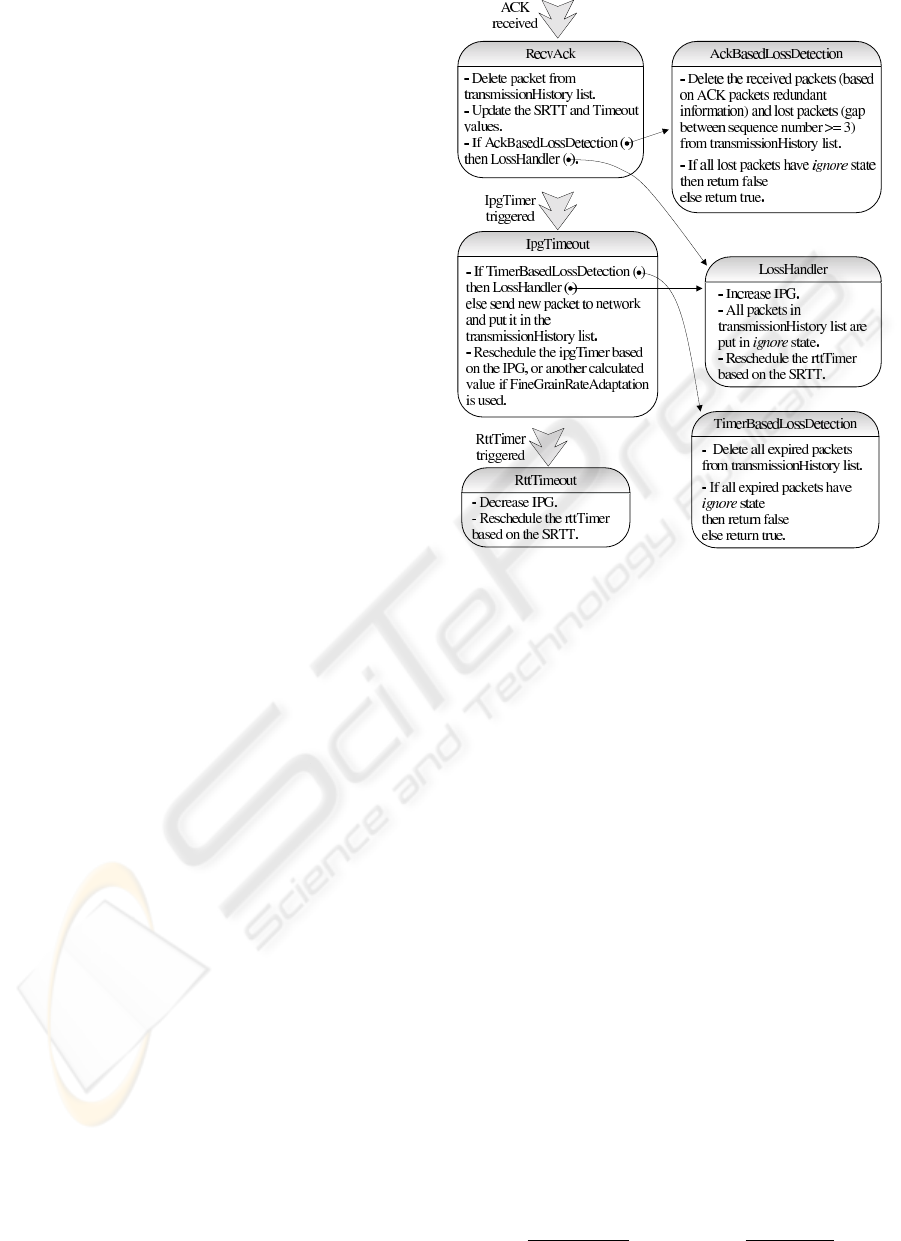
4 THE RAP PROTOCOL
As their authors explain in (Rejaie et al., 1999; Re-
jaie et al., 1998), the RAP is an end-to-end rate-based
congestion control mechanism that utilizes an Addi-
tive Increase Multiplicative Decrease (AIMD) algo-
rithm for rate adaptation to achieve TCP-friendliness.
The AIMD rate adaptation algorithm can have non
TCP-friendly behaviour when a heavy load produces
the reduction of TCP’s performance. Therefore, a
fine-grain rate-adaptation mechanism is added to as-
sist RAP in becoming more stable and reacting to
temporary congestion while realizing the AIMD algo-
rithm at a coarser granularity. Basic RAP has a TCP-
Friendly behaviour in many situations, and the fine-
grain rate-adaptation mechanism expands this beha-
viour to more circumstances.
The RAP protocol is mainly implemented in the
sender. A RAP sender sends data packets with a
sequence number, and a RAP receiver sends an ac-
knowledgment (ACK) for each packet. Using this
feedback, the RAP sender can detect losses and sam-
ple the round-trip-time (RTT). Timeouts and gaps in
the sequence space are used to detect packet losses.
This protocol only considers the packet losses as a
congestion symptom. Unlike TCP, a RAP sender may
send many packets before receiving a new ACK.
In principle, an ACK packet includes the sequence
number of the delivered data packet, but in order to
provide robustness against single ACKs losses, the
following redundant information is added to them:
• lastRecv: the sequence number of the last received
packet
• lastMiss: the sequence number of the last missed
packet previous to lastRecv, or 0 if no packet was
missing
• prevRecv: the sequence number of the received
packet previous to lastMiss, or 0 if lastRecv was
the first packet
For example, if the pattern of packet losses was
“1 _ _ 4 _ _ 7”, the values are: lastRecv =
7, lastMiss = 6, and prevRecv = 4. A packet
with sequence number Seq
i
will be considered
received if ((lastRecv ≥ Seq
i
)and(Seq
i
>
lastM iss))or (Seq
i
= prevRecv ).
Basically, the algorithm is conformed to by two
timers, the ipgTimer and the rttTimer, that along with
the reception of ACKs are the triggers of the three
events that direct the algorithm.
Furthermore, the following important variables are
included: IPG (inter packet gap, used to control the
transmission rate), SRTT (smoothed - or estimated -
round trip time, defines the periodicity of the trans-
mission rate increment), and Timeout (defines the
time to live or expiration of the packet); and a list
Figure 2: The RAP algorithm.
named transmissionHistory. This list stores the sent
packets but not the acknowledged packets, which
change to the ignored state when the loss of a packet
is detected. Thus, the algorithm only reacts once, at
the most, when a burst of packet losses occurs, related
to the same congestion case. The SRTT and Timeout
variables are updated based on the last sample RTT
using the Jacobson/Karels algorithm (Jacobson and
Karels, 1988).
The diagram of the figure 2 describes the operation
of the RAP, where the arrows represent the events that
direct it, and the boxes represent their main proce-
dures. To start the algorithm, initially, the IpgTimeout
and the RttTimeout procedures are invoked.
The algorithm uses an adaptation scheme (AIMD)
so that if does not detect congestion, the transmission
rate is periodically and additively increased, and if it
detects congestion, the transmission rate is immedi-
ately and multiplicatively decreased.
When no packet losses are detected, the transmis-
sion rate, S
i
, is increased by a certain value α (i.e.
S
i+1
= S
i
+ α) updating the value of the IP G (inter
packet gap) based on equation (1).
S
i
=
P acketSize
IP G
i
IP G
i
=
IP G
i
∗ C
IP G
i
+ C
(1)
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON THE INTERNET
263

100
80
60
40
20
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
network bandwidth utilization (%)
simulation time (seconds)
sample interval=0.05s
Figure 3: Characteristic RAP behaviour.
In this equation, C has the dimension of time and
determines the value of α. RAP assigns to C the
value of SRTT to emulate the TCP window adjust-
ment mechanism in the steady state. At any rate, α
represents the increment of one packet in each adjust-
ing point. When packet losses are detected, the trans-
mission rate is multiplicatively decreased by a certain
value β (i.e. S
i+1
= β ∗ S
i
), updating the value of the
IP G based on equation (2).
IP G
i+1
= IP G
i
/β β = 0.5 (2)
RAP gives a value of β = 0.5 in order to follow the
behaviour adopted by TCP.
The expected behaviour would be of a progressive
increase of the transmission rate in absence of conges-
tion and a abrupt decrement of this upon congestion
(tooth of mountain range) as can be observed in the
figure 3.
5 THE ERAP PROTOCOL
The Enhanced Rate Adaptation Protocol (ERAP) is
an adaptation and optimization of the RAP protocol to
be introduced in the NTS. The NTS must work with
a lot of connections in order to utilize the maximum
possible of the available bandwidth and to serve the
greater amount of possible requests.
With the purpose of diminishing the use of re-
sources and increasing the efficiency of the NTS, the
ERAP protocol was designed with the following par-
ticular characteristics:
1. Encapsulation: A ERAP packet is encapsulated
within a UDP packet to be transmitted by the Inter-
net.
2. Reliability: as our system does not analyze streams
of video, making a separation in frames, it is im-
possible to determine if certain packets contain data
of low or high relevance. Therefore, all lost packets
must be retransmitted. Is not possible to retransmit
a lost packet with its initial sequence number, be-
cause of the fact that a packet with an old sequence
number (smaller or equal to the last sequence num-
ber less than 3) immediately will be considered as
lost and retransmitted.
In order to solve this problem, the packets that need
to be retransmitted, are transmitted as if they were
new packets (i.e. with a sequence number equal
to the last, plus one). However, a new sequence
number is added to each packet, named applica-
tion_sequence_number, that the receiver uses to
maintain the real sequence of packets, and to iden-
tify the duplicated packets.
3. Centralized ACKs’ reception: The decentralized
ACKs’ reception does not work well when it is used
in a server with many active sessions. According
to the model proposed by RAP, each Sender must
handle his own packets’ reception. In this manner,
in a real implementation that uses sockets (to trans-
mit the packets), each Sender would have a thread
in charge of packets’ reception. Therefore, by each
active video or established session a thread would
be used.
However, ERAP centralizes the reception of ACKs
from multiple destinations, and in this way, only
a single thread is necessary instead of so many
threads as connections as the server has. Thus,
when a packet arrives at the server, it is received
by a central module named RapManager and later
it is given to the corresponding ErapSender.
The RAP and ERAP architectures are showed in
the figure 4 (a) and the figure 4 (b), respectively,
where RS is a RapSender agent, RM is a RapMana-
ger agent, RR is a RapReceiver agent, and AR is a
Acks Reception Thread.
4. Header Size Reduction: so that the protocol is
versatile and it does not overload the network, a
minimum set of information has been defined to
the data and ACK packets. RAP has only one
header used for data packets and ACKs packets,
that contain the following integer data: seqno, size,
rap_flags, lastRecv, lastMiss, and prevRecv. Seqno
is the sequence number, size is the packet size,
rap_flags identify the type (ACK or DATA) of
packet, and the rest of the fields are only used when
the packet is of ACK type.
On the other hand, ERAP determines two types
of headers, the data header and the ACK header,
avoiding the unnecessary data transport in the hea-
ders. The data header has only two integer data:
seqno, and appSeq. The first field is the sequence
number, and the second field is the application se-
quence number added to manage the retransmis-
sions. As the packets are received by different
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
264
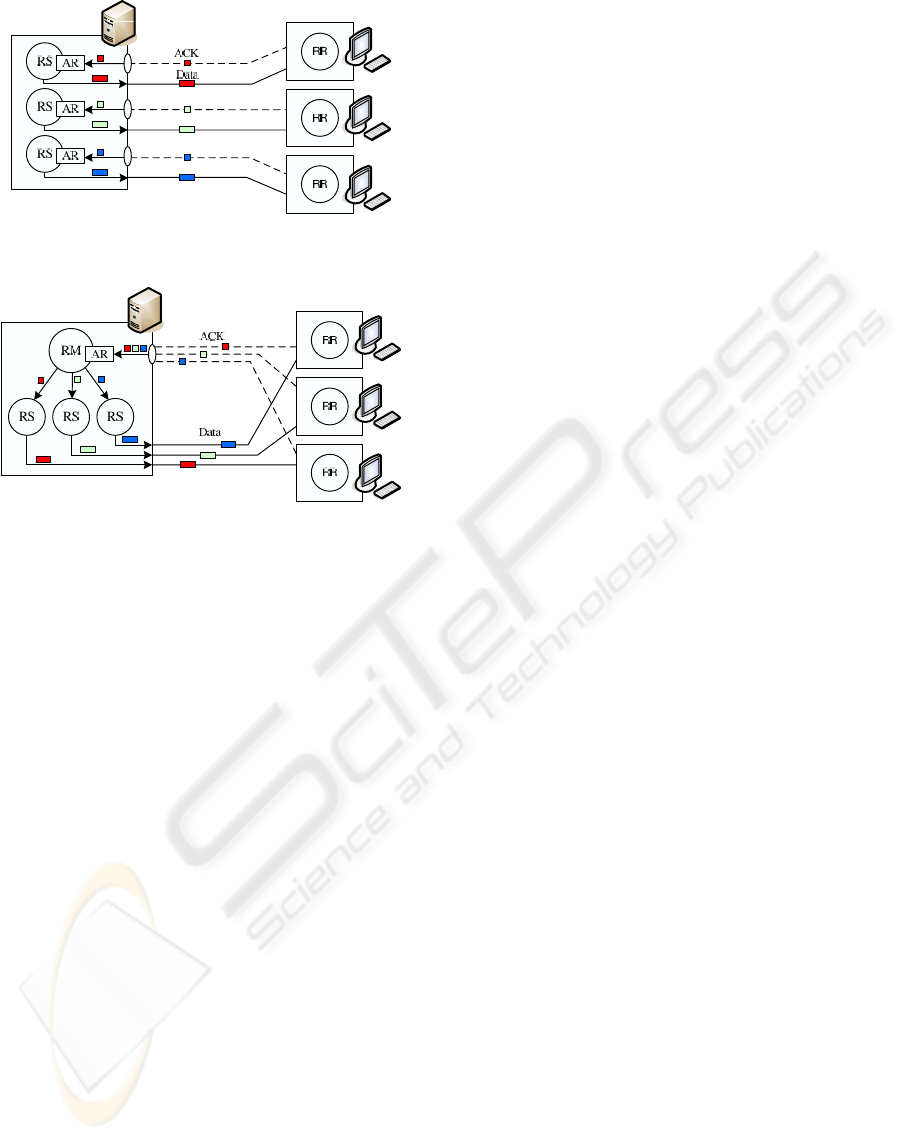
(a) RAP architecture with decentralized ACKs’ re-
ception
(b) ERAP architecture with centralized ACKs’ recep-
tion
Figure 4: RAP and ERAP architectures.
ports, ERAP automatically identifies the type of
them (ACK or DATA) and, therefore, the rap_flags
field is not used. The rest of the fields (lastRecv,
lastMiss, and prevRecv) are specifics of the ACK
header. The size field is not necessary because
each ERAP packet is encapsulated in only one UDP
packet.
The ACK header has the following fields of integer
type: port, seq, lastRecv, lastMiss, and prevRecv.
The port field is added so that the centralized
ACKs’ reception module (RapManager) can distin-
guish to what connection the ACK belongs. If the
Receiver wants to send ACK packets to the Sender
with a source IP (Internet Protocol) address diffe-
rent to the IP address by which receives the data
packets, then the ACK header will contain an ex-
tra field named IP that will have the IP address of
the Receiver by which it receives the data packets,
allowing it to identify the session correctly.
5. Optimized events management: When in a ses-
sion, the transmission of packets is suspended tem-
porarily, and later this is re-initiated, the protocol
would have to continue the transmission suppos-
ing that the network state has not changed. In this
way, the network state information, learnt during
the previous course (of use of connection) would
be wasted. At this moment of inactivity (i.e. when
there are no more packets to send) it does not make
sense to continue shooting events of the protocol
for that session. Then, ERAP deactivates the timers
and maintains the state of the session so that when
the transmission is resumed, the timers will be reac-
tivated and the transmission rate will be continued
from the previous point.
On the other hand, RAP stops only the ipgTimer
and the rttTimmer continues being triggered, that
will invoke the RttTimeout procedure repeatedly,
with the consequent CPU cost. This procedure will
only decrease the IPG if during the past SRTT time,
a certain percentage (modifiable) of the SRTT/IPG
packets were sent. If RAP sent less than that, the
rate is not increased.
6. Generation of information required by the LCS:
as it were explained in section 1, it is necessary that
the NTS and the LCS work coordinately and co-
operatively in order to optimize the transmission.
The information that the NTS must give to the LCS
and that ERAP must generate is: total server exit
bandwidth (Mbps), available bandwidth (Mbps) for
each connection at each moment, and the number
of enqueued Mbits in the queue of the NTS that
waits to be transmitted (considering all the packets
of all the connections). All these measures only
include the length of the Application Data Unit
(ADU) without counting the overhead of the pro-
tocols, that is to say, the bits corresponding to the
headers of the own ERAP or any used protocol of
the Internet protocol stack (link, network, trans-
port). RapManager is the central module in charge
of collecting information from all ERAP connec-
tions and the network to generate this data.
6 RAP VS. ERAP
The NTS-ERAP and the RAP have been extensively
evaluated by simulations and real tests in which the
consumption of resources and the performance are
measured. The simulator used is the NS2 version 2.29
released on October 19, 2005. This version of the
NS2 includes the implementation of the RAP proto-
col that we used to compare with ERAP. The results
presented in this section show the advantages of using
ERAP instead of RAP in a VoD server.
Figure 5 shows the topology used for the simu-
lations, where R1 and R2 are routers, C1...Cn are
clients, and S1 is the VPS.
The link R1-R2 is the bottleneck and R1 is the bot-
tleneck point. The routers are simulated as elements
with FIFO scheduling and drop-tail queuing. When
the NTS-ERAP is simulated, S1 is composed of a
RapManager and n RapSender, whereas, when the
RAP is simulated, S1 only has n RapSender.
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON THE INTERNET
265

Table 1: Simulation parameters.
Packet Size 100, 512, 1024 bytes
Data Header Size RAP: 24 bytes ERAP: 8 bytes
ACK Size RAP: 24 bytes ERAP: 20 bytes
Links Bandwidth R1-R2: 1 MB/s Others: 2 MB/s
Links Delay 10 ms
Queue Size R1-R2 10 packets
Figure 5: Simulated topology.
The simulation parameters used are shown in
table 1.
Because of the fact that ERAP does not try to mo-
dify the basic behaviour presented by the RAP pro-
tocol, one of the objectives of the simulations was to
show that both protocols act in a similar way reducing
or increasing the transmission rate, upon detection of
congestion or in absence of it, respectively.
RAP and ERAP have presented almost the same
performance as far as the use of network bandwidth,
the small difference that is observed is because RAP
uses greater ACK packets (4 bytes) than ERAP.
Figure 6 (a) shows the percentage of network band-
width usage for a total simulation time of 120 se-
conds, with a data packet size of 100 bytes, and with
a continuous data sending by only one active connec-
tion.
The transmission rate is increased until the maxi-
mum transmission capacity (100%) of the R1-R2 link
is used, so that the router R1 begins to drop packets,
and, upon detection of packet losses, the transmis-
sion rate is decreased immediately. These two phases,
the increase and decrease of the transmission rate, are
continuously repeated.
As described in item 5 of section 5, ERAP and
RAP solve the inactivity problem in different ways.
Nevertheless, for our specific environment, in which
the packets will be given in a form of burst by the
LCS, behaviour differences practically do not exist.
This can be observed in the figure 6 (b), correspond-
ing to a simulation with an inactivity period between
time 4 and 6, and a data packet size of 100 bytes.
Also, the deactivation of both timers at inactivity mo-
100
80
60
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
network bandwidth utilization (%)
simulation time (seconds)
sample interval=0.05s
erap
rap
(a) Continuous trasmission for 120 seconds
100
80
60
40
20
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
network bandwidth utilization (%)
simulation time (seconds)
sample interval=0.05s
erap
rap
(b) Inactivity times behaviour
Figure 6: RAP and ERAP network utilization.
ments that ERAP carries out has two advantages, the
saving of CPU and memory resources. The queue
of event scheduler will be much smaller. Instead of
having X + N timers, N being the total number of
connections, and X the number of connections that
have been selected by the LCS to be served at cer-
tain moment or slot of time, will only have X ∗ 2
timers. In this way, when reducing the events queue,
the used memory is reduced and the useless triggering
of timers is avoided saving CPU cycles.
ERAP makes better use of the resources when the
ACKs’ reception is centralized (item 3 of section 5).
In this approach, a single thread is necessary in or-
der to receive the ACK packets corresponding to all
connections. In this way, a great amount of mem-
ory and CPU resources are saved. Each empty thread
(i.e. without data and code) occupies approximately
10 MB of memory. If a decentralized ACK packet re-
ception is used, N active sessions (therefore, with N
threads) will require N ∗ 10 MB of memory, and the
system will quickly begin to start swapping.
With respect to the CPU usage, when having many
threads, the scheduling and context changes will be
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
266
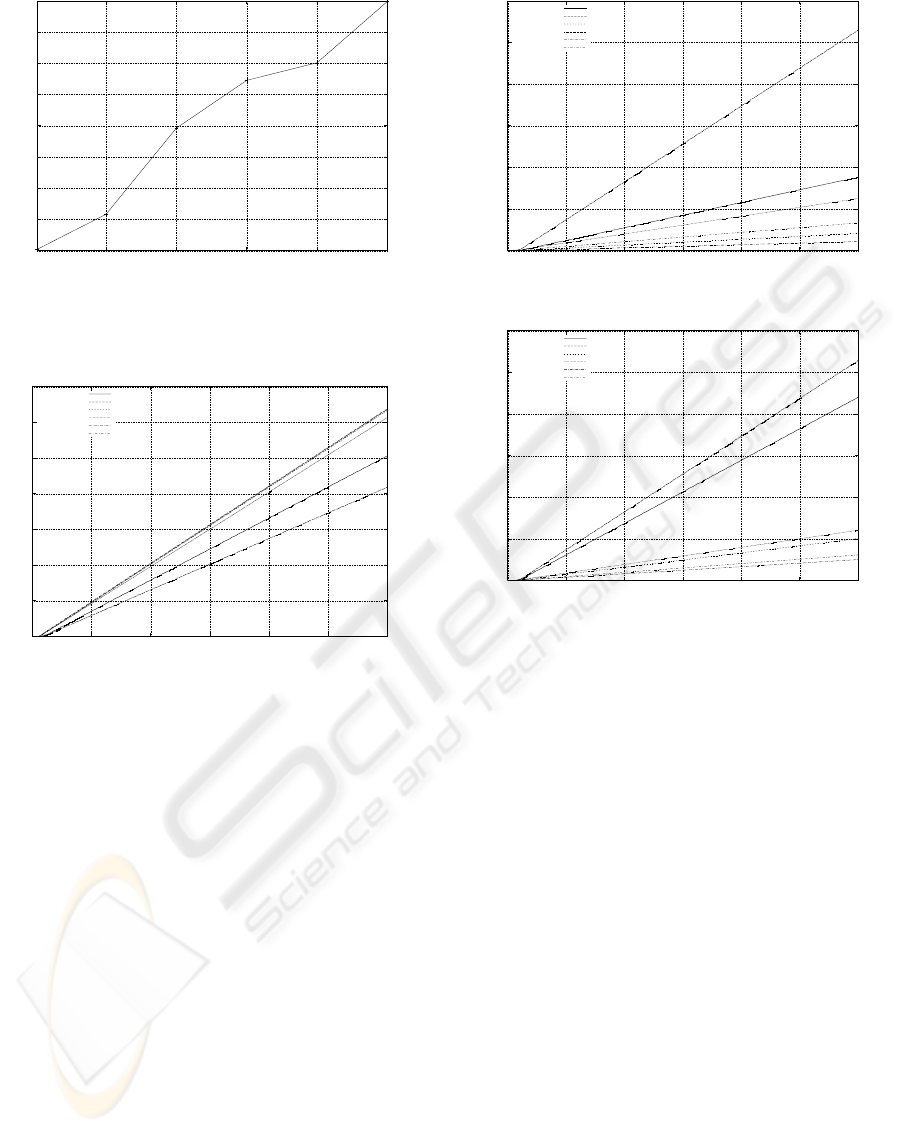
4.4
4.6
4.8
5
5.2
5.4
5.6
5.8
6
250 200 150 100 50 1
CPU time (seconds)
number of threads
Figure 7: CPU usage according to the number of packets
receiving threads.
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
received data (megabytes)
simulation time (seconds)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(1)
(2)
(4)
(3, 5, 6)
erap 100B
rap 100B
erap 512B
rap 512B
erap 1024B
rap 1024B
Figure 8: Amount of application data received by the client
in the time.
more expensive. In order to verify this affirmation,
tests were made in which a sender application sends
an UDP traffic load, equitably distributed between N
destination ports of another computer. And, in this
other computer, N threads (one by port) were waiting
to receive the corresponding packets.
The graph in figure 7 shows the sum of the
times consumed in user and system mode for each
set of receiving threads (1, 50, 100, 150, 200,
and 250 threads), with a load of 10
6
packets uni-
formly distributed between participants threads (i.e.
1 thread: 10
6
packets/thread, 200 threads: 5000 pack-
ets/thread). A clear increase of the consumption of
CPU time is observed when the number of threads
are increased. Another disadvantage, is that the num-
ber of threads that each process can have is limited
by the operating system, therefore the number of ses-
sions that the server can support will be restricted.
The header size reduction (item 4 of section 5), us-
ing different headers to data and ACK packets, im-
proves the performance of the protocol. Simulations
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
data overhead (megabytes)
simulation time (seconds)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
erap 100B
rap 100B
erap 512B
rap 512B
erap 1024B
rap 1024B
(a) Data overhead in the time
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
ACKs overhead (megabytes)
simulation time (seconds)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
erap 100B
rap 100B
erap 512B
rap 512B
erap 1024B
rap 1024B
(b) ACKs overhead in the time
Figure 9: RAP and ERAP protocols overheads.
were made of 120 seconds in length with continuous
transmission through only one active connection and
sizes of data packet of 100, 512, and 1024 bytes.
In figure 8 it is observed that when the ERAP pro-
tocol is used, the amount of application data received
by the client is increased, because of that, ERAP has
a smaller data header.
The overhead decrease in the network, that presents
the ERAP protocol as opposed to RAP, can be ob-
served in figure 9, where the bandwidth consumption
caused by data and ACK headers at each moment of
the simulation time, are presented in the figure 9 (a)
and 9 (b), respectively.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
This paper is part of an innovative investigation line
focus on VoD systems that guarantee a high quality of
service in the Internet domain, or another nondedica-
ted and best effort network. We present a Network
A NETWORK TRAFFIC SCHEDULER FOR A VOD SERVER ON THE INTERNET
267

Traffic Scheduler (NTS) to be included in a Video
Proxy Server (VPS). The VPS must support a high
workload, therefore, the NTS was designed to maxi-
mize the performance and minimize the resource con-
sumption.
To achieve the better system perform of the VPS,
the NTS must cooperate with it, and also must co-
operate with the Internet’s operation. Therefore, the
NTS must include a congestion control protocol that
is TCP-Friendly. Based on the specification of the
RAP congestion control protocol, the ERAP has been
developed to be included in the NTS module. The
results presented in this paper show that ERAP im-
proves the RAP protocol, not from the point of view
of the behaviour in the adjustment of the transmission
rate (that is practically the same), but from the point
of view of the resource usage as much of the server
as of the network. This improvement also allow to
conclude that the ERAP protocol avoid the limitant
factors arising on RAP protocol, giving to the video
server more flexibility and opportunity to attend the
client’s petitions. The optimized events management,
the header size reduction, and the centralized ACKs’
reception, were the strategies to obtain such resource
usage diminution.
The NTS has been developed and evaluated exten-
sively by means of simulations. The future works are
centered mainly in the integration of the NTS module
with the rest of the VPS architecture. The benefits of
this new platform, in contrast to the pre-existing plat-
form that does not include the NTS, will be evaluated.
REFERENCES
Breslau, L. et al. (2000). Advances in network simulation.
IEEE Computer, 33(5):59–67.
Cen, S., Pu, C., and Walpole, J. (1997). Flow and conges-
tion control for internet media streaming applications.
Technical Report CSE-97-003.
Chung, J., Zhu, Y., and Claypool, M. (2002). FairPlayer
or FoulPlayer? - Head to Head Performance of Re-
alPlayer Streaming Video Over UDP versus TCP.
Floyd, S. and Fall, K. (1999). Promoting the use of end-
to-end congestion control in the Internet. IEEE/ACM
Transactions on Networking, 7(4):458–472.
Floyd, S., Handley, M., Padhye, J., and Widmer, J. (2000).
Equation-based congestion control for unicast appli-
cations. In SIGCOMM 2000, pages 43–56, Stock-
holm, Sweden.
Gevros, P., Crowcroft, J., Kirstein, P., and Bhatti, S. (2001).
Congestion control mechanisms and the best effort
service model. IEEE Network, 15(3):16–25.
Handley, M., Pahdye, J., Floyd, S., and Widmer, J. (2003).
TCP Friendly Rate Control (TFRC): Protocol specifi-
cation, RFC 3448.
Hessler, S. and Welzl, M. (2005). An empirical study of
the congestion response of realplayer, windows medi-
aplayer and quicktime.
Jacobs, S. and Eleftheriadis, A. (1997). Real-time dynamic
rate shaping and control for internet video applica-
tions.
Jacobson, V. and Karels, M. J. (1988). Congestion avoid-
ance and control. ACM Computer Communication Re-
view; Proceedings of the Sigcomm ’88 Symposium in
Stanford, CA, August, 1988, 18, 4:314–329.
Kurose, J. F. and Ross, K. W. (2004). Computer Net-
working: A top down approach featuring the Internet.
Addison-Wesley, third edition.
McCanne, S. and Floyd, S. (2005). Ns - Network Simulator.
http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/.
Qazzaz, B., Suppi, R., Cores, F., Ripoll, A., Hernandez, P.,
and Luque, E. (2003). Providing interactive video on
demand services in distributed architecture. Proceed-
ings 29th Euromicro Conference, ISBN: 1089-6503-
03, CL - I:215–222.
Rejaie, R., Handley, M., and Estrin, D. (1998). RAP:
An end-to-end rate-based congestion control mech-
anism for realtime streams in the internet. In
Technical report 98-681, CS-USC, august 1998,
http://netweb.usc.edu/reza/papers/rap.html.
Rejaie, R., Handley, M., and Estrin, D. (1999). RAP: An
end-to-end rate-based congestion control mechanism
for realtime streams in the internet. In INFOCOM (3),
pages 1337–1345.
Rejaie, R., Handley, M., and Estrin, D. (2000). Layered
quality adaptation for internet video streaming.
Sisalem, D. and Schulzrinne, H. (1998). The loss-delay
based adjustment algorithm: A TCP-friendly adap-
tation scheme. In Proceedings of NOSSDAV, Cam-
bridge, UK.
Sisalem, D. and Wolisz, A. (2000). LDA+: A TCP-friendly
adaptation scheme for multimedia communication. In
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and
Expo (III), pages 1619–1622.
Tanenbaum, A. (2002). Computer Networks. Prentice Hall
PTR, fourth edition.
Wang, X. and Schulzrinne, H. (1999). Comparison of adap-
tive internet multimedia applications. IEEE TRANS.
COMMUN., VOL.E82-B, NO.6 JUNE 1999.
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
268
