
AN ALGORITHM TO ENHANCE THE NETWORK SELECTION
PERFORMANCE IN IN AN INTEGRATED UMTS/WLAN
ENVIRONMENT
Abolfazl Nazari, Naser Yazdani, Naser Rezayi
ECE department- University of Tehran, Iran
Keywords: Heterogeneous networks, UMTS, WLAN, Network selection.
Abstract: Future wireless networks will be multi-access networks, and the users can benefit from the advantages of
any radio access technology. Then, network selection can play a critical role in overall network
functionalities. Interworking between UMTS and WLAN is considered as a feasible approach toward next
generation wireless networks. In this paper, we propose a method that uses statistical parameters of a
WLAN cell traffic load to measure its capabilities to ensure QoS for the requested service. A network
selection algorithm can use this measurement and user preference to select the best radio access technology.
We investigate the performance of this algorithm through simulation of transferring video traffic in WLAN.
The results show that the proposed algorithm has an acceptable performance and in about 95 percent of the
times, a user that opt WLAN as his access network will have the requested QoS.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wireless networks have emerged, evolved, and
experienced an extensive deployment. These
networks include cellular networks like GSM,
GPRS, UMTS, and CDMA 2000 for voice and data
transmission and wireless LAN for broadband
wireless Internet access. Each network has its own
merits and most likely the next generation wireless
networks will be multiple access networks
exploiting the advantages of all existing radio access
technologies (RAT).
Interworking between UMTS and WLAN is
considered as a feasible approach toward next
generation wireless networks (Salkintzis, 2005).
UMTS can provide data rates from 384 Kbps up to 2
Mbps for wireless Internet access over a wide
geographical area. In hot-spots, where user’s
mobility is limited, we can use WLAN to provide
users with higher data rates (up to 54 Mbps) and also
benefit from low deployment cost of this network
and its license free bandwidth.
Recently 3GPP has developed two UMTS-
WLAN interworking architectures for different
usage scenarios (3GPP, 2003), (3GPP, 2005a). A
common scenario is when a UMTS subscriber can
connect to a WLAN to use Internet and other
WLAN data services. This architecture, called
“WLAN direct access”, supports transferring
authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA)
signaling between two networks. The other
architecture which is named “WLAN 3GPP IP
access” enables UMTS subscribers to access UMTS
packet switching services through WLAN.
In heterogeneous networks, where the user can
select his access technology, the network selection
algorithm can have an important effect on the
overall network performance and the user’s
experience of received QoS. An efficient algorithm
for network selection should consider the network
condition like received radio signal strength (RSS)
and network traffic load to select the best RAT for
the user.
In this paper, we focus on network selection
issue in an integrated UMTS and WLAN
environment. We offer an algorithm that measures
WLAN cells capabilities in satisfying service
requirements and user preference. In this method
rather than using instant amount of the cell’s traffic
load, we use statistical parameters of the network
traffic load like mean and variance. These
parameters are calculated in Access Point (AP) and
are broadcast in the WLAN cell. We show that while
in some situation instant amount of the traffic load
can not be used, our method have an acceptable
performance even for highly stochastic traffics like
video.
45
Nazari A., Yazdani N. and Rezayi N. (2006).
AN ALGORITHM TO ENHANCE THE NETWORK SELECTION PERFORMANCE IN IN AN INTEGRATED UMTS/WLAN ENVIRONMENT.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems, pages 45-50
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The rest of the paper is organizes as follows. In
section II, we discuss the network selection issue in
heterogeneous networks and introduce the network
selection and advertisement scenario that 3GPP has
proposed for UMTS and WLAN interworking. In
section III, we introduce our algorithm. Simulation
results come in section IV. Finally, we conclude in
section V.
2 NETWORK SELECTION IN
HETEROGENEOUS
ENVIRONMENTS
In heterogeneous networks, where user can opt for
several access technologies, network selection
algorithm plays a vital role in insuring the quality of
the received service and efficient usage of the
network resources. An efficient network selection
technique which keeps the user Always Best
Connected (ABC) should consider user preference,
service requirement, and network condition
(Qingyang, 2005). The concept of ABC as defined
in (Gustafsson, 2003) is that the user is not only
connected but also connected through the best
device and access technology. In a network selection
procedure, the first step is collecting necessary
information about network condition, application
requirement, and user preference. Then, this
information is used for making decision.
For interworking between UMTS and WLAN,
3GPP considers the generic network advertisement
and selection scenario as been depicted in figure 1.
In this scenario, a user which is a subscriber of the
3GPP home network is located in an area which is
covered with several WLAN access networks. Using
information which is advertised by WLAN access
networks, the user decides which WLAN and which
3GPP visited network should be used.
The user can use periodic beacon frames sent by
WLAN access networks to gather the necessary
information. This method is called passive scanning.
The user can also use active scanning to collect this
information. In active scanning, by sending probe
request frame, the station asks the AP to send the
necessary information in the probe response frame.
In any WLAN access network, it is possible to
have cells with overlapping areas. In these areas the
user can opt for possible APs.
Therefore in an integrated UMTS and WLAN
environment, the network selection algorithm should
determine whether we must connect to UMTS or
WLAN access network, which WLAN should be
used and which AP in the WLAN should be
selected.
Most simple conventional network selection
algorithms use RSS for RAT selection. In (Yilmaz,
2005) the authors show that a simple ‘WLAN if
coverage’ strategy would lead to satisfactory results.
This is because when the hotspot is not congested,
WLAN with its low service cost and high bandwidth
can satisfy the user’s preference and the service
requirement. This simple strategy can also boost the
UMTS performance. Because by selecting WLAN
for wireless Internet access, UMTS channels become
free for voice traffic.
However, in this paper it is shown that when the
hotspot is congested, UMTS can offer higher
bandwidth. Hence considering only RSS is not
sufficient and the network traffic load should be
considered as an input parameter for network
selection algorithm, as the authors in (Hyun-woo,
2005) have used for AP selection. The authors show
that advertising the amount of traffic processed in
AP can lead to better network performance and
fairness among users.
Authors in (Qingyang, 2005) propose a general
decision method to take into account the other users
requirements like security, cost, and reliability.
In this paper, we propose a method for
evaluating WLAN capabilities in providing QoS for
real-time applications such as video and voice. We
show that for video services, the traffic load is
highly stochastic and instant amount of the traffic
load can not be used for network selection, as it is
used in (Hyun-woo, 2005) for AP selection.
Therefore in our algorithm, the statistical parameters
of the WLAN cell traffic load are estimated in the
AP and broadcasted in WLAN beacon frames. A
UMTS subscriber can use this information to
determine if this AP can ensure transferring data
frames in their due time or not.
Figure 1: Generic scenario for network advertisement and
selection.
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
46

Figure 2: Proposed IE for broadcasting traffic information.
3 THE PROPOSED SOLUTION
WLAN stations within a cell can use distributed
coordination function (DCF) and optional point
coordination function (PCF) for accessing the
medium. The former in which users compete with
each other to send their frames is not a feasible
option to support QoS for real-time application
(Rajavelsamy, 2005). Therefore, we have chosen the
latter method, PCF, to be used in WLAN cells.
In PCF, the AP periodically announces the
inception of a contention free period (CFP) with a
specified maximum duration. The period of the CFP
and its maximum duration is announced in a
standard information element (IE), which is included
in the beacon frame. In the CFP, the AP polls any
station on a polling list. During this period, stations
may transmit only if the AP solicits the transmission
with a CF-Poll frame. After elapsing the maximum
duration time or reaching the end of the polling list,
the CFP ends. After CFP, contention period (CP)
begins, in which users can access the medium using
DCF.
Depending on the traffic load, it is possible that
some station on the polling list can not be polled in
the CFP. Now the purpose of our algorithm is to
determine if a new user is added to the polling list,
can it be polled at least in the x percent of the CFPs
or not. The choice of x depends on the service
requirement and the user preference. If this AP is not
capable of polling the station, we conclude that the
WLAN cell is congested and we search for other
APs. If there is not any suitable AP, UMTS network
is selected. Our algorithm for assessing the WLAN
cell capabilities has the following stages: 1) The AP
measures the traffic transmission time (TTT) for
each CFP. TTT is the time spent for transmitting and
receiving data frames to and from polled stations. 2)
The AP estimates the mean and the variance of the
TTT. 3) These estimated parameters are broadcasted
using a non-standard IE which is included in the
beacon frame for passive scanning or in probe
response frame for active scanning. 4) By assuming
normal probability density function (pdf) for TTT,
and by considering the service requirements and the
user preference, any station is able to estimate the
upper bound so that, TTT in x percent of the CFPs is
bellow it. 5) By considering CFP maximum
duration, the estimated bound, the length of data
packets and the transmission rate, the station can
determine if this AP is capable to ensure the desired
QoS or not.
Before going into detail, we shortly discuss the
rationales behind our algorithm. For reasonable
handoff decision, we must consider cells traffic load.
However in the 802.11 standard, each station can
scale back its transmission rate, according to its
radio link condition. Considering only cell’s traffic
load, will lead to ignoring station’s transmission rate
which has a significant effect on the cell capacity.
For this reason, we have used traffic transmission
time to consider users rates in our WLAN capability
assessment.
Rather than using instant amount of the traffic
load, we use statistical parameters, mean and
variance. Even though VoIP flows usually have
constant bit rate, other real time services like video
generate data packets with vastly different packet
size. The interval between two successive packets
can also be very different. In this condition, the
amount of the traffic load in one CFP has little
information about successive CFPs. In the next
section we will show that the instant amount of the
traffic load is not a viable network selection criterion
for video flows.
When the number of the users associated with
the AP is large enough, the assumption of the
normal pdf for traffic transmission time is
reasonable. This condition usually occurs within
hotspots with high traffic load where the network
selection algorithm can play a pivotal role in overall
network functionalities.
Now we show how the mean and the variance
can be estimated and how the upper bound for TTT
is determined. A simple method for estimating mean
and variance is the moving average, which is shown
in bellow.
][]1[][ iTiavriavr ×
+
−
×
=
β
α
. (1)
.])[][(]1var[]var[
2
iavriTii −×+−×=
βα
(2)
Where:
10
<
<
α
and
1=+
β
α
In these formulas, T[i] is the traffic transmission
time in the i
th
CFP and α is called forgetting factor
and shows how much we pay attention to the past
data. The choice of α is a trade off between
algorithm precision and its delay. With greater α,
estimation of the mean and the variance would be
more prices, but the effect of the entrance of a new
user to the WLAN cell is detected with more delay.
The mean and the standard deviation of the TTT
can be broadcasted in WLAN cell by using a non-
standard IE. Figure 2 shows this IE. In the 802.11
standard each IE has a variable length and is
identified by ‘Element ID’ field. Many of the
AN ALGORITHM TO ENHANCE THE NETWORK SELECTION PERFORMANCE IN AN INTEGRATED
UMTS/WLAN ENVIRONMENT
47

Figure 3: CFP duration for all CFPs.
Element IDs are reserved for future uses. One of
them can be used for this non-standard IE.
If we assume the normal pdf for the TTT, we
easily can estimate an upper bound so that TTT in
the x percent of the CFPs is less than it.
1
() .
100
x
bound Q avr
σ
−
=×+
(3)
Where
1−
Q is the inverse of the standard normal
cumulative density function,
σ
and av
r
are the
standard deviation and the mean of the traffic
transmission time. But as a matter of fact, the normal
pdf is only an approximation for probability
distribution of TTT and the estimation of the mean
and variance is not very accurate. Therefore we
should use a little higher bound to ensure that the
estimated bound is equal or greater than actual
bound and our algorithm works well. Our simulation
results show that by using only 25% greater standard
deviation, the estimated bound has satisfactory
performance. So we use (4) to estimate the bound.
When the network has high traffic load, this bound
is not very different from what is estimated by
normal pdf.
1
1.25* ( ) .
100
x
bound Q avr
σ
−
=×+
(4)
By considering this bound, maximum packet size
and the transmission rate, if the station selects this
AP, it can be sure that x percent of the data packets
could be sent in their due time.
The choice of the x is a trade-off between service
requirements and user preference on the one hand,
and network performance on the other. Some
applications like VoIP can tolerate more frame loss.
But some applications like video are more sensitive
on frame loss. Users also have different preferences.
For example, rather than using an expensive UMTS
service, a user may prefer to pay less and use a
WLAN access network that guarantees to transfer
only 95% of the data frames. The network
performance is another issue. When transferring of
more data frames is required, fewer users can be
accepted and WLAN performance in most of the
time is bellow its maximum.
4 SIMULATION RESULTS
To study the performance of the proposed algorithm,
we have used a simulation scenario, in which 80
UMTS users get into a WLAN cell. The entrance
time of each user is randomly chosen from 1 second
to 1200 seconds. The entire simulation duration is
3000 seconds.
The AP of the WLAN cell supports 802.11a
standard. All UMTS users which want to connect to
WLAN should support WLAN radio interface as
they do in our simulation scenario. The transmission
rate of the users can be different according to their
radio link condition. We did not simulate the WLAN
physical layer. So we randomly chose 18 Mbps or
24 Mbps as the user’s transmission rate to imitate
the different radio link condition.
WLAN cell supports PCF for medium access.
The CFP maximum duration is 50 msec and CFP
announcement interval is 60 msec. Therefore,
stations can use DCF for remaining 10 msec. CP
was not explicitly simulated. We have used a
constant 10 msec period plus a random variable
chosen from [0, 1 msec] interval for CP to mimic the
real conditions in which CFP inception can be
delayed by CP.
All users have a bidirectional (up-link and down-
link) real-time video session. Video streams are
coded by H.263 standards with target rate of 64
Kbps. H.263, MPEG-4 and H.264 are three codecs
which 3GPP recommends for conversational video
services (3GPP, 2005b). For generating video traffic,
we have used trace files that publicly can be
accessed in http://trace.eas.asu.edu/trace /ltvt.html.
Figure 3 shows the traffic transmission time for
all CFPs. From this figure it is evident that since the
instant values of the TTT are vastly different, it is
not a viable criterion for network selection algorithm
as it is used in (Hyun-woo, 2005) for AP selection.
Figure 4 shows the cumulative density function
of the TTT, when there are 80 users in the WLAN
cell. In this figure 95% and 99% of the CFPs have
traffic transmission time less than 45 and 49.5 msec
respectively. Therefore the actual upper bound for x
= 95 and x = 99 is 45 and 49.5 msec respectively.
The CFP maximum duration is 50 msec. As a result,
if the maximum size of the packets generated by
application is 1500 bytes, for sending 99% of the
frames, more users can not be accepted. But for
sending 95% of the frames in CFP, still more users
can be accepted. So we can see that there is a trade
off between network performance and service
quality.
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
48
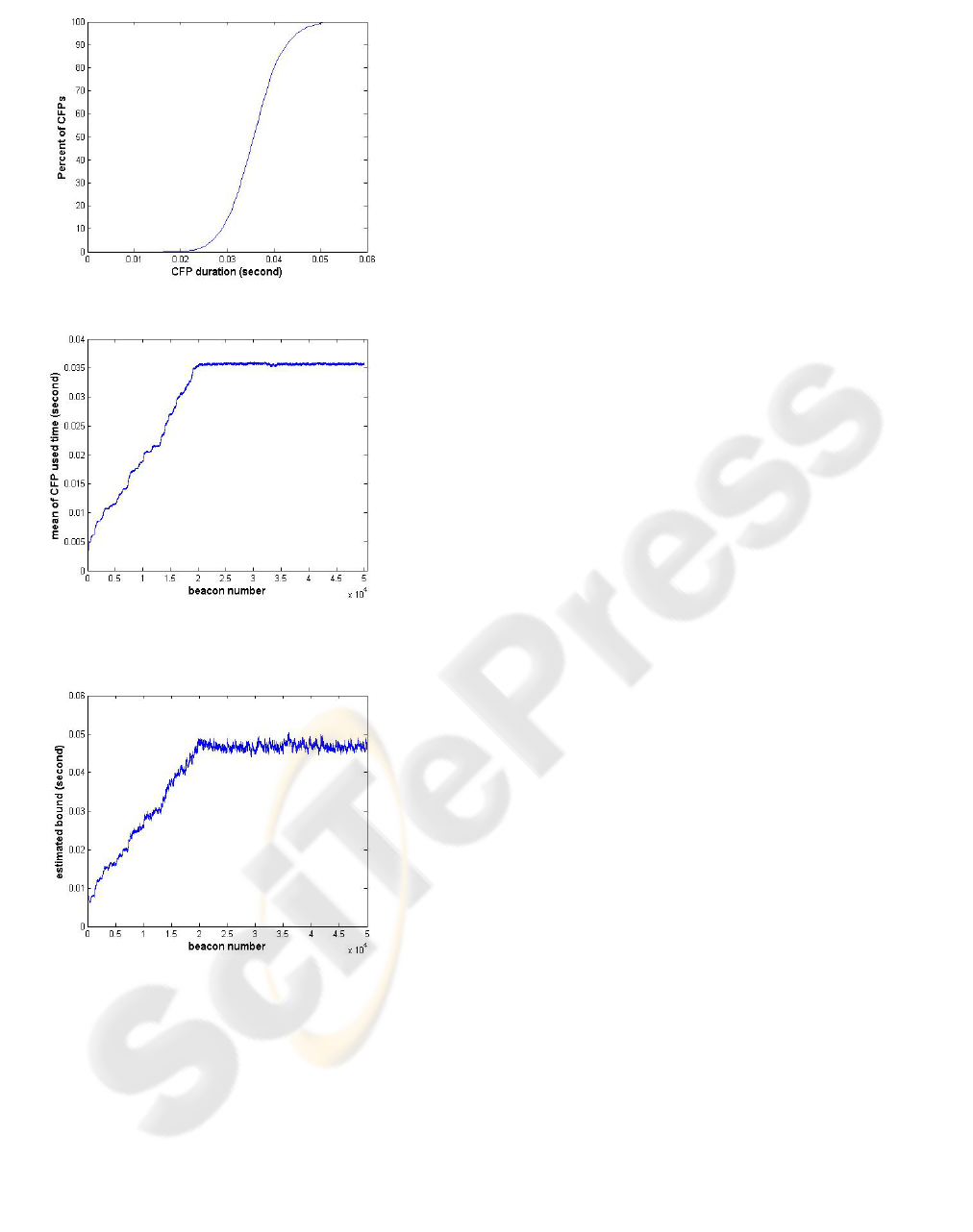
Figure 4: Cumulative density function of CFP durations.
Figure 5: Mean of the CFP duration.
Figure 6: Estimated bound for sending 95% of the frames.
For estimating the mean and the variance of the
traffic transmission time we have used (1) and (2)
with α = 0.01. Figure 5 shows the mean of the traffic
transmission time. The mean increases when more
users enter the WLAN cell and finally it reaches to
about 36 msec. As mentioned previously, to send
99% of the frames, no new user can be accepted.
Therefore the performance of the WLAN cell in
many times is below its maximum. The source of
this deficiency is the stochastic nature of video
traffic.
We have used (4) to estimate the upper bound for
traffic transmission time. As stated before, this
bound is a little greater than what is predicted by
normal pdf. In our simulated scenario, the standard
deviation is about 4 msec and the mean is 36 msec.
therefore the bound estimated by (4) is only 3%
greater.
This bound for x = 95 is depicted in figure 6. Our
simulation results show the estimated bound by a
new user in 98.5% of cases will be equal or greater
than its actual value, 45 msec. so in these cases, if
the user selects WLAN as its access technology, he
can transfer at least 95% of his frames. In only 4%
of the cases, the estimated bound is larger than 48.5
msec. In these cases a user with maximum packet
size of 1500 and transmission rate of 24 Mbps will
not choose WLAN as its access network. In these
cases our network selection algorithm has been
wrongly too skeptic. But as one can see in this 4% of
cases, only a small percent of the cell capacity
remains idle. Thus, our network selection algorithm
has an acceptable performance.
Figure 7 shows the estimated bound x = 99. Our
results show that in 6.3% of the cases, new users
wrongly estimate the bound less than its actual
value, which is 49.5 msec. This estimated bound
can be misleading for new users. For example in 2%
of the cases, a new user will estimate that the bound
is less than 49 msec. if the transmission rate of this
user is 24 Mbps and the maximum packet size is
1000 byte, the network selection algorithm wrongly
will choose the AP.
Our results show that the access delay is mainly
bellow the CFP announcement period. Access delay
is a function of network load, user’s place in the
polling list and the characteristics of the traffic load
generated by the user’s application. To demonstrate
this issue, in figure 8 we have shown the access
delay for three users which are placed in first, 50
th
and 80
th
row of the polling list.
From this figure we can see that the access delay
of the first user in the polling list is mainly affected
by his traffic load characteristics. Due to fact that
polling frame for this station is sent after CFP
inception. So network load can not affect the access
delay. On the other hand, access delay of the last
user in the polling list (user 80) is mainly affected by
CFP traffic transmission time. By comparing access
delay of this user with access delay of the 50
th
user
in the polling list, we can infer that being in the end
of the polling list does not mean that the station will
have greater access delay.
As a result of being the last one to be polled, the
last station has more chance to transfer its frame that
has been generated in this CFP interval. Therefore
AN ALGORITHM TO ENHANCE THE NETWORK SELECTION PERFORMANCE IN AN INTEGRATED
UMTS/WLAN ENVIRONMENT
49

Figure 7: Estimated bound for transferring 99% of frames.
Figure 8: Cumulative density functions of the access
delay.
the access delay for this station is less than CFP
period.
5 CONCLUSION
Next generation wireless networks will be multi-
access networks. In these networks, a subscriber can
use one of the access technologies to become always
best connected (ABC) according to his requested
service and network condition. Integration of UMTS
and WLAN is a viable solution toward the next
generation wireless networks. As we discussed in
this paper, the network selection algorithm has a
significant effect on the overall network
performance. In this paper we proposed a method for
measuring WLAN cell’s capabilities in such a way
that enables the network selection algorithm to
consider network condition, service requirement,
and user preference to keep the user ABC.
We have used video traffic in order to study the
performance of our proposed method. Simulation
results show that the proposed method has
acceptable performance in measuring WLAN cell
capabilities to accept the UMTS users.
REFERENCES
Salkintzis, A.K, Dimitriadis, G. et al., 2005. Seamless
continuity of real-time video across UMTS and
WLAN networks: challenges and performance
evaluation. In IEEE Wireless Communications. Vol
12, Issue 3, pp 8 – 18
3GPP TS 22.934 v6.2.0, 2003. Feasibility study on 3GPP
system to WLAN interworking (Release 6).
3GPP TS 23.234 v6.5.0, 2005a. 3GPP system to WLAN
interworking; System Description (Release 6).
3GPP TS 26.235 V6.4.0, 2005b. Packet switched
conversational multimedia applications; Default
codecs (Released 6).
Qingyang, S., Jamalipour, A., 2005. Network selection in
an integrated wireless LAN and UMTS environment
using mathematical modeling and computing
techniques. IEEE Wireless Communications. Vol 12,
Issue 3, pp 42 – 48
Gustafsson, E., Jonsson, A., 2003. Always best connected.
IEEE Wireless Communications. Vol 10, Issue 1pp 49
– 55
Yilmaz, O., Furuskar, A., Pettersson, J., Simonsson, A.,
2005. Access Selection in WCDMA and WLAN
Multi-Access Networks. IEEE Vehicular Technology
Conference. Vol 4, pp 2220 – 2224
Hyun-woo, L., Se-han Kim et al., 2005. Performance of an
efficient method for association admission control in
public wireless LAN systems. IEEE Vehicular
Technology Conference. Vol 7, pp 5049 – 5053
Rajavelsamy, R., Jeedigunta, V. et al., 2005.
Performance evaluation of VoIP over 3G-WLAN
interworking system. IEEE Wireless Communications
and Networking Conference. Vol 4 pp 2312 – 2317
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
50
