
INTEGRATED UNIVERSITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Thomas Kudrass
Dept. of Computer Science, Mathematics and Natural Science, HTWK Leipzig (University of Applied Sciences),
Gustav-Freytag-Str. 42 a, Leipzig, Germany
Keywords: Information System, Integration, Web Service, E-Learning.
Abstract: In this paper, we discuss the integration of heterogeneous databases with the example of a university
information system, based on previous experiences in the implementation of some components. The paper
stresses the new opportunities for universities resulting from database integration. We outline the target
architecture for an integrated information system whose principle is the coupling of existing systems and the
definition of global views on them. The services defined on those views can be used for high-level
information services in the web or for the definition of workflows in the university administration.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Motivation
The convergence of heterogeneous software and the
integration of legacy applications characterize the
development of today’s information systems, which
raises the question of interoperability. Examples are
health care information systems comprising many
components, convergence trends regarding ERP and
office applications (e.g., the Mendocino project of
SAP and Microsoft), enterprise content management
(ECM) systems that include functionality of
document and content management. The
development of highly integrated university infor-
mation systems (UIS) is the subject of this paper.
Related work can also be found in (Bischof, 2005).
A university information system has to provide
information about research and scientific
cooperation offers, education and further education
capabilities. The usage of information technology at
German universities is characterized by historically
grown system platforms, little integration and an
incomplete support of business processes in the
university administration. IT systems implement
mainly tasks that are specific to certain
organizations.
The ongoing reforms of higher education and the
adoption of bachelor/master degrees affect the
further development of university software. New
systems are introduced such as e-learning systems,
digital libraries, course evaluation software and
other proprietary developments. At the same time,
vendors of commercial university software enhance
the offered functionality to keep pace with the
requirements. The need for integration stems from
increasing requirements to combine data throughout
the whole university or department and to extract
information for the university management.
1.2 Example E-Learning
The usage of an e-learning platform causes more
integration problems. Without connections to the
administrative software, it implies additional costs as
an isolated application, particularly for manual
reconciliation of data. The acceptability decreases,
the long-term and sustainable usage of an e-learning
system is unlikely. Therefore, an e-learning platform
requires the integration with administrative software
without substituting it. The organization of the
education can profit from the introduction of self-
service functions.
The aim is an e-learning platform that resembles
a portal providing access to all relevant information
at a central point. The system must provide
ubiquitous services, e.g., checking the admission to
an examination or the publication of examination
results. A major problem is the existence of different
identities that are maintained in separated isolated
systems. The tighter integration of administration
and lectures is the base for a lot of innovations. The
assessment of education (course offerings, number
208
Kudrass T. (2006).
INTEGRATED UNIVERSITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterpr ise Information Systems - DISI, pages 208-214
DOI: 10.5220/0002466102080214
Copyright
c
SciTePress

of participants, evaluation results) can have an
impact on the allocation of resources. The
strengthening of extension studies requires the
inclusion of financial aspects in the systems. The
infrastructure has to be ready to provide new
services for the students, such as smartcards or
information services over the internet.
The potential for innovation in education regards
the publication and distribution of teaching material
that, in some cases, may be authored by students
themselves. The extension of the information
services may include theses and reports, e.g., from
internships abroad, which may replace the
conventional archiving of that material. The usage of
digital libraries and content management systems
requires the connection to administrative systems as
well. The electronic publication of the knowledge
assets sketched above may help fostering the
cooperation of universities.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 1 has
given a general introduction and a motivating
example. In section 2, we discuss requirements to
integrated systems from the perspective of the
university. Section 3 introduces the most important
components of a distributed information system as
they can be found in our university. Section 4
sketches the main concepts of system integration. In
section 5, we discuss architectural choices for inte-
grated systems and present the target system design.
Finally, section 6 summarizes with conclusions and
gives an outlook on the project HIM.
2 REQUIREMENTS ANALYSIS
The target architecture of IT applications follows the
concept of enterprise resource planning (ERP). It
tries to represent the business process flow in the
departments of a company by an integrated
approach. When considering a university as a
business, we can distinguish between two separate
areas: the production comprises research and
education, the administration addresses the office
and accompanying functionality.
Figure 1 represents the relevant user classes.
According to customer relationship management
(CRM), we use the term student relationship
management (SRM) or employee relationship mana-
gement (ERM) because of many similarities with
CRM. Besides, there are interfaces outside the
university, e.g., with cooperation partners, compa-
nies offering jobs and internships. In those cases the
exchange of services is bilateral. A management
information system (MIS) needs data in an
integrated and aggregated manner for decision
makers, university management and supervisory
authorities. Data are exchanged among all
components of such a system (Information Mana-
gement), which requires a suitable infrastructure.
Figure 1: Users and components of a university
information system (UIS).
2.1 Use Case: E-Learning
An e-learning platform mainly addresses the
education – not the research. The example of e-
learning proves the necessity of integrating all
subsystems. The integration comprises three aspects:
cooperation with information and administration
systems of the university
coupling to existing authoring systems
integration of digital libraries or content management
systems
Today’s e-learning systems include some admi-
nistrative functions as they are known from conven-
tional software, e.g., the enrollment in a course. Yet,
such a system is not capable to consider all the
examination regulations and additional restrictions.
Without connecting to administrative systems, the
online-registration is not failure-free and may result
in manual corrections of the enrollment lists.
An e-learning system will not evolve into a
platform that fully supports all business processes of
administration. The leading German system is HIS
customized to the needs of German university
administrations (HIS, 2005). There are other soft-
ware systems that implement important subtasks.
E-learning systems provide functions to edit
teaching material (mainly HTML), but do not
achieve the functionality of a general editor or
special editor tools. That causes a special need for
interoperability that encompasses the support of
INTEGRATED UNIVERSITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS
209

numerous formats and the treatment of metadata.
Besides describing the content of the course, the
metadata are related to data in other administration
systems for education. So there is a big potential for
the re-use of teaching material in digital libraries.
Data formats and protocols are already known, e.g.,
Z39.50 (Oldenettel, 2003).
2.2 Requirements to an Integrated
University Information System
Communication
An integrated university information system must
improve the communication between students and
teaching stuff. An added value results from the
definition of groups for different purposes, e.g., the
list of participants of a course. There are two
different communication mechanisms: active notifi-
cation (push) or the publication of information
(pull). Services are primarily provided via internet.
Self-Service Functionality
We have to define services that encapsulate the
implementation of administrative functions. An
example is the online-enrollment that can be
implemented in different ways: by using the HIS
module QIS-POS, by attaching to an e-learning
system, or by a proprietary development. Most
important is that the interface exhibits always the
same behavior with a syntactic definition that is
platform-independent (in an XML format).
Content Management and Publishing
The integration of a digital library or the coupling to
a document management system opens new ways to
provide more digital information. Among them are
theses or experience reports from internships.
An important part of the information services
offered to students is the presentation of the
university calendar beyond the class schedule. That
is required in many formats, e.g., in a brochure
(PDF) or embedded into an e-learning platform.
Indeed, current standard university software
provides the generation of HTML output from the
managed data but this is restricted to the underlying
data model, which excludes a further customization
to more individual requirements considering data
distributed on different systems.
Reporting and Statistics
The reporting can also benefit from the integration
of information, e.g., the education reports required
by the supervisory authority of the Saxon state
government, or the individual annual reports by the
professors on the teaching load. The role of report-
ing will increase by shifting competencies from the
ministry downwards to the universities in the mid-
term future. Thus, the envisioned reporting services
are the foundation of a management information
system (MIS) used by the university management.
The introduction of performance-oriented payment
of staff requires the inclusion of evaluation results
that has to be joined with other education data.
Information Extraction from
Heterogeneous Data Sources
The composition of a timetable individual for every
student is an example how new information can be
generated by combining two different systems. The
students that participate in a course are maintained
in the system HIS, the course schedules are managed
in another system, S-PLUS (Scientia, 2005). The
coexistence of both systems with some overlapping
data originates from historical reasons, since they
have been installed at different times. When joining
data of both systems, personalized schedules can be
created in a format flexible enough to support
different output channels.
Data Security and Privacy
The creation of a security infrastructure is a funda-
mental prerequisite to grant access to existing appli-
cation systems to the public. This includes following
tasks: a central user management, classification and
grouping of users to assign certain privileges. User
groups can be: faculty members, course participants,
professors, and alumni. The implementation may be
based on directory services such as LDAP. When
creating user groups we have to decide how far
additional categorization can be used in single
systems. For example, an e-learning system may
provide the classification of users according to their
proficiency level to personalize the content. Thus,
the definition of general user groups as they are
relevant in different business processes cannot cover
all aspects of single systems, which is obvious in e-
learning systems.
A crucial issue of authorization throughout all
applications is the introduction of an identity mana-
gement solution (e.g., IBM Tivoli Identity Mana-
gement). The purpose is the implementation of a
single-sign-on access to all services of the univer-
sity. An important identity management process is
the user provisioning, i.e., maintenance and mana-
gement of user information. The automation of the
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
210

user life cycle, the creation of accounts in separate
systems and the delegation of administrative tasks to
subsystems are parts of that process.
Much of the data (e.g., results of examinations or
evaluations) are private data and are, therefore, sub-
ject of the Data Protection Act. The design of a
university information system has to consider that
issue by the definition and enforcement of
appropriate access control rules. Some information
can be published in the internet without restrictions.
Maintenance of Partnerships
Besides students and employee of the university,
other partners such as research partners or coope-
rating companies have to be involved in the infor-
mation system. Therefore, the database has to be
enhanced by addresses and information for alumni.
3 IT SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT
AT THE SAMPLE UNIVERSITY
3.1 Administrative Systems
The sample university sketched below is the home
university of the author, the Leipzig University of
Applied Sciences (HTWK Leipzig). The main
administrative functionality is covered by HIS
(Hochschul Information System), a commercial
software system widespread at German universities
(HIS, 2005). HIS comprises several modules:
management of students (SOS), examinations
(POS), admission processes (ZUL), self-services
(QIS), reporting (LSF), and statistics (ISY). Besides
HIS, the system S-PLUS is applied for course
scheduling, which includes publication of class
schedules. Both systems manage overlapping data,
i.e., course data. The schedules managed by S-PLUS
apply only to whole classes of students. The infor-
mation about enrollments are not available in S-
PLUS. Individual timetables for students can only be
derived by global joins of the data of HIS and S-
PLUS. Both systems lack interfaces to the academic
part of the university.
Beyond that, there are various local systems at
some departments. For example, the system PLANet
(Planning via Net) manages data that are prepared
for the input into S-PLUS. PLANet is based on
XML database technology and supports the flexible
presentation of data in different formats. Another
enrollment system supports the organization of
general-education offerings.
3.2 New Applications
The e-learning system being developed is called
LIPS and is based on two platforms: the Zope Object
Database ZODB (Zope, 2005) manages course data
and implements some administrative functions such
as online-enrollment. A second component is an
authoring system on top of another database. Both
subsystems require data reconciliation.
The evaluation of courses is required by law.
Therefore, the system ELEVA has been purchased
in cooperation with other universities (CEC, 2005).
The web pages of the departments are often
manually maintained with no database support.
Another project aims at storing all graduation
theses in a digital library in order to exploit their
market potential. The chosen platform is the open
source system MyCoRe (Lützenkirchen, 2002).
The so-called Digiboard has been developed for
publishing news and announcements in the web,
comparable to a conventional blackboard.
The usage of smartcard technology is primarily
aimed at providing standard services of the admini-
stration office as self-service functions. Among them
are drawing up certificates or the return notifications
at the beginning of each term.
4 INTEGRATION OF
HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS
The use of an integration solution has several goals:
Maintenance of global data consistency facing
redundant data storages
One-time data input into the primary data source
Reduction of manual activities
Combination of data to implement new functions
(e.g., generation of education reports or individual
timetables)
In order to enable the cooperation of
heterogeneous applications an additional software
layer, called middleware, is needed. Messages or
events are exchanged among systems to integrate
data or functions. Those ideas are continued in the
enterprise application integration (EAI) approach
(Linthicum, 1999), i.e., independent applications are
loosely coupled via middleware. The middleware
layer establishes connections to existing applications
using adaptors or connectors, converts different data
formats, maps schemas and supports the data ex-
change among different applications (routing,
queuing, transaction management).
INTEGRATED UNIVERSITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS
211

Besides, the concept information integration is in
use. Unlike EAI, the basic idea of information
integration is the federation of data in a virtual
distributed database that can also include data of
commercial application systems such as SAP. That
development is driven by important vendors, e.g.,
IBM (Deßloch, 2003). Information integration fol-
lows the approach of multidatabases (Sheth, 1990).
Enterprise Information Integration (EII) is an
integration approach at enterprise level and provides
a basis for the implementation of portals or analy-
tical applications. Unlike EII, EAI uses an event-
driven data exchange mechanism without
dominating direction. Integration requires a common
understanding about the data shared by different
users. In that context, ontology-based products such
as the Enterprise Information Integrator of Software
AG are notable (Software AG, 2005).
Different integration levels can be defined: user
interface integration, data integration, function
integration, and process integration. The data
integration is very common because relational
databases are the platform of the systems to be
integrated.
When integrating heterogeneous systems, we can
distinguish between loosely and tightly coupling.
The loose integration presupposes the definition of
intervals for the data exchange among systems. The
transfer of data can be facilitated by defining appro-
priate data formats in XML, whereas the transfor-
mation can be performed using XSLT. The problem
of the loose coupling is that the modification of data
is propagated in a deferred way. This may result in
consistency problems when different systems try to
modify the same data.
Tight integration means that the systems are per-
manently coupled. Data are exchanged among com-
monly used database tables. The reconciliation effort
is only possible within systems of the same vendor.
5 SYSTEM DESIGN
5.1 EAI Architectures
The application-to-application integration (A2A) is
the traditional and simplest type of integration, a
point-to-point connection between two applications.
The single systems communicate directly and use a
large number of protocols and formats, which results
in a network with “spaghetti architecture” (Pezzini,
2003). Instead, two different EAI architectures
compete on the market: hub & spoke and bus
architecture. The systems do not interact directly but
they send messages via a bus or broker.
The bus architecture is based on the so-called
publish & subscribe principle: Information produced
in an application is sent to a central bus (publish)
and propagated to other applications connected to
the bus (subscribe). There is no central server that
coordinates the distribution of single messages. The
central bus merely forwards the messages to the
subscribers. The bus architecture is applied in
scenarios where a single system produces data for
lots of consumers or vice-versa. Thus, the main
emphasis is on the distribution of identical mass
data. Accordingly, the application potential is many-
sided, mainly in data-oriented integration.
The so-called hub & spoke architecture provides,
contrary to the bus architecture, a central informa-
tion hub that connects all applications and systems
the same way. This central information hub manages
the whole data traffic among several systems. The
underlying business rules are represented as
workflows managed by the hub, which favors a
process-oriented procedure. So the hub manages
both the business process and the technical
integration rules. Implementing hub & spoke
systems is easier because of a strict separation of
system-specific connectors and business-oriented
workflows. Therefore, such architectures are most
suitable in a dynamic infrastructure environment –
better than bus architectures. For that reason, they
are used in complex data dispatching scenarios, for
example in business processes that run over several
applications. The only weak point is the position of
the central hub as potential bottleneck.
From the point of view of university systems the
hub & spoke architecture appears more adequate for
different integration scenarios. An implementation
of that architecture is the Data Hub (Oracle, 2005).
5.2 Process Analysis
The analysis of business processes requires
identifying the primary data sources. These are the
information systems of the university administration
and the departments that are responsible for the
administrative processes. Data relevant for an e-
learning system, a web content management system
or metadata for digital libraries can be extracted
from those databases. The definition of business
processes presupposes the description of the
organization of the university in order to identify
roles (actors) that are primarily responsible for
dedicated data.
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
212
We choose the ARIS toolset (Davis, 2001) for
modeling. ARIS is well suited for the holistic
description of a company and can be applied for
universities as well. It classifies the overall system
into different views: organization, data, function,
process. Thus, the ARIS concept provides a general
framework for business process modeling that is
expressed by several methodologies. Among them
the event-driven process chain (EPC) is the most
popular method. It enables the modeling of the
process view that is also responsible for the inte-
gration of the other views. Data transfer processes
among heterogeneous systems can be modeled as
well.
5.3 Service-Oriented Architecture
The service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an archi-
tectural concept that describes the provision of
business services and functionality in terms of
services (Erl, 2004). A service is a system resource
that can be requested through a standard interface.
Complex business processes can be implemented by
combining service calls (orchestration). The
business logic is not located in a single program but
distributed among several autonomous services. A
SOA can be implemented with any service-based
technology based on SOAP, WSDL and UDDI. A
service can encapsulate the data access in a standard
manner. This reduces the redundancy and contri-
butes to a modular development of university
systems. Business logic in existing applications must
be re-implemented to services by the development of
appropriate adaptors.
A similar service approach has been used in the
CAMPUS information system (Bischof, 2005) to
integrate an e-learning system.
5.4 Architecture of the Target
System
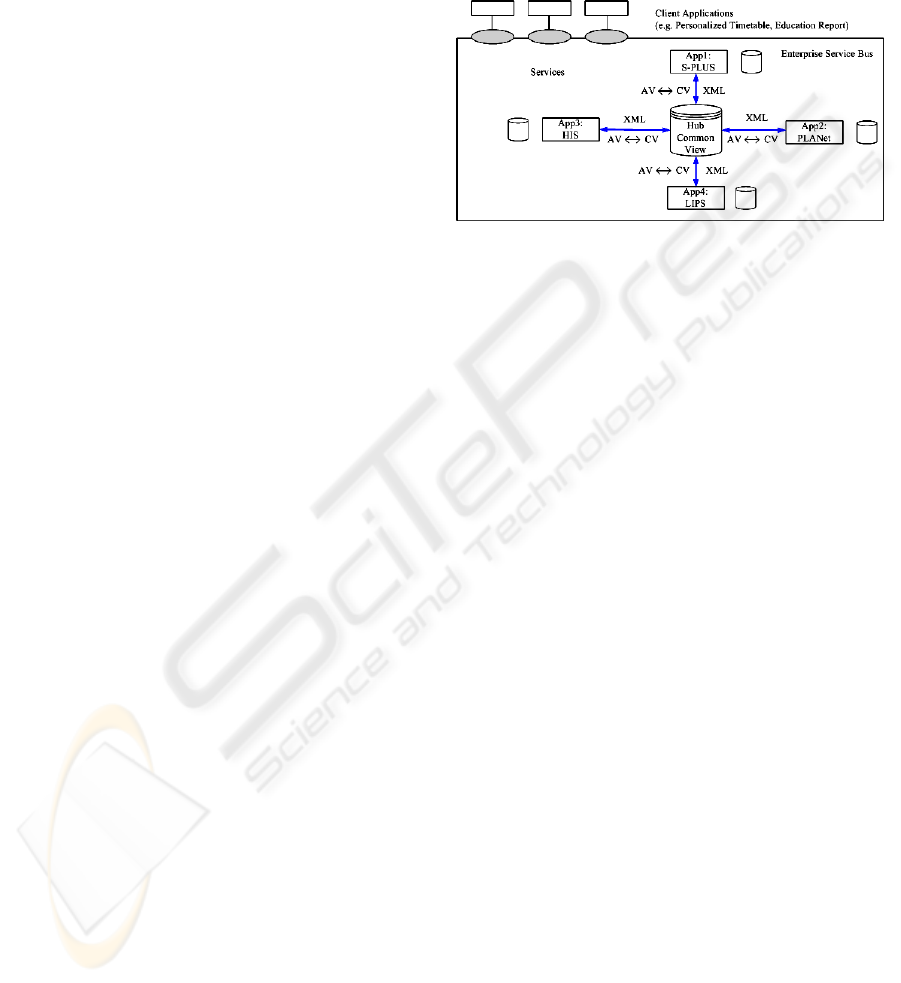
The future university information system appears as
an enterprise service bus (ESB) providing services to
different types of clients (Chappell, 2004). Those
services can be used in specific applications. The
physical location of the data is transparent to the
service users. Internally, several subsystems are
loosely coupled in a hub & spoke architecture. That
requires the definition of a so-called common view
(CV) on the hub. The spokes realize the mapping of
each local application view (AV) to the common
view. The data exchange between the hub and the
local applications is based on XML. Note that most
of the applications (e.g., HIS) do not provide a data
export in XML format. An important task of data
exchange is the definition of XML document
standards for the university administration, as they
have become quite common in many other e-
government applications.
Figure 2: Target system architecture.
Figure 2 exemplifies the envisioned integration
of four administrative systems of the university.
Other systems could be added in the near future, for
example the course evaluation tool. We recommend
an incremental integration approach, i.e. other
systems may join the federation later. The provided
content services can be used as building blocks for
the development of individual web applications.
Those applications may be customized to the needs
of specific departments. The use of the content
services ensures the consistent presentation and
utilization of data. Moreover, such services are the
basis for an improved reporting required by
university management. The services can also be
viewed as process steps in workflows specified in
BPEL.
6 CONCLUSIONS & OUTLOOK
The analysis of the current state of heterogeneous IT
systems of a university presented in this paper is the
starting point for a long-term development towards
an integrated system. Therefore, we started the
project HIM (Hochschul Information Management)
to deal with the overall information infrastructure of
the university. The avoidance of point-to-point
integration as it has been discussed in the previous
section is not contrary to the incremental approach
we strongly recommend.
We do a prototype implementation to validate
our ideas with the example of the “Virtual Internship
Office”. The task of the office is to support the
students to find internships in regional companies
and to supervise their successful completion. The
INTEGRATED UNIVERSITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS
213

“Virtual Internship Office” requires an overall view
on several databases that have to be integrated as
sketched above. The prototype system requires the
research of aspects of autonomy and semantic
heterogeneity. Besides, the implementation has to
prove the feasibility of the workflow technology in
an office environment.
An important task is the definition of document
standards as foundation of data exchange and for
service interface specifications. For that purpose we
aim at cooperation with other universities.
Future work to establish an IT infrastructure of
the university has also an impact on the education in
the information systems course, since the principles
of complex information systems and the integration
strategy can be demonstrated with a realistic
example. For that purpose, we have to face both
technical and interpersonal issues, since integration
of systems of different organization raises some
concerns that have to be alleviated.
REFERENCES
Bischof, C., Gebhardt, M., Steves, P., 2005. The
Integrated CAMPUS Information System: Bridging the
Gap between Administrative and E-Learning Proces-
ses. 11
th
EUNIS Conference.
CEC GmbH, 2005. www.eleva.de.
Chappell, D.A., 2004. Enterprise Service Bus, O’Reilly &
Associates.
Davis, R., 2001, Business Process Modelling with ARIS,
Springer Verlag UK.
Deßloch, S, Maier, A.; Mattos, N.; Wolfson, D.,
Information Integration – Goals and Challenges, 2003.
In Datenbank-Spektrum 6, (June 2003), dpunkt-Verlag.
Erl,T., 2004. Service-Oriented Architecture, Prentice Hall.
HIS GmbH, 2005. www.his.de..
Linthicum, D.S., 1999. Enterprise Application Integration,
Addison Wesley.
Lützenkirchen, F., 2002. MyCoRe – Ein Open Source
System zum Aufbau digitaler Bibliotheken (in Geman),
In Datenbank-Spektrum 4, (2002), dpunkt-Verlag.
Oldenettel, F., Malachinski, M., Reil, D., 2003. Integrating
Digital Libraries into Learning, In Proceedings of the
2003 Joint Conference on Digital Libraries Rice
University Houston, Tx.
Oracle 2005. www.oracle.com/data_hub..
Pezzini, M., 2003. Application Integration Scenario:
Making It All Work Together, Gartner European
Symposium ITxpo, Florence/Italy, March 2003.
Scientia GmbH, 2005. www.scientia.de.
Sheth, A.P. and Larson, J.A., 1990. Federated Database
Systems for Managing Distributed, Heterogeneous, and
Autonomous Systems. In ACM Comp. Surveys 22, 3
(1990).
Software AG, 2005. Enterprise Information Integrator,
Retrieved Nov. 2005 from www1.softwareag.com/
Corporate/Solutions/integration.
Zope, 2005. Website for the Zope Community,
www.zope.org.
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
214
