
WebELS E-LEARNING PLATFORM AND PROPOSAL FOR
AUTOMATIC VIDEO SUPPORT
Mahfuzur Rahman, Sato Hidoyuki, Vuthichai Ampornaramveth and Haruki Ueno
Principle of Informatics Division, National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2@Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda Ku
Tokyo 101-8430, Japan
Keywords: Video contents, web-based education, e-Learning and post-graduate education.
Abstract: This paper discusses video contents in WebELS e-learning platform for post-graduate education and
proposes ideas for automatic video support. WebELS provides a web-based, multi-platform tool, by which
traditional instructors can archive their learning materials on the web and students can do their personal
learning over the Internet. Uploaded contents can be used either in standalone or group learning in real-time
with discussion. WebELS supports contents with text, images, audio and video. However, VIDEO, because
of its nature and high volume of involved data causes series of problems regarding its capturing, uploading,
transmission, downloading, viewing, code conversion, compression and so on. The vision of this paper is to
discuss the WebELS editor and propose ideas to support PowerPoint presentation material with video
created by standard PowerPoint presentation editor, for example Microsoft PowerPoint with an explanation
of video pre-processing and video handling.
1 INTRODUCTION
THIS paper focuses on the pre-processing and
handling of video contents of the WebELS e-
learning platform and proposes ideas for automatic
support of presentation material with video clip
created by standard PowerPoint editor rather than
created by WebELS editor. Animations, video clips
etc. are widely used in presentation to depict any
scientific discovery, research result and so on. It is
very simple in the case of a stand-alone presentation.
But it could be very complicated if it needs to
support an Internet-based distance learning system
especially in the multi-platform environment. In the
postgraduate education environment, distance
learning through Internet is regarded as one of the
important ways to carry out education activities in a
global situation. In such environment education
activities are group discussions, presentations in the
conference etc. & VIDEO plays an important role of
making such discussion, presentation realistic. Web-
based learning prevails the opportunity for the
students to learn from anywhere, anytime, sitting on
their own place realizing the ultimate goal of
Internet i.e. virtual reality. Web-based learning
brings unprecedented level of accessibility to
courses in remote area, courses prohibited by budget
constraints, courses updated to recently discovered
knowledge, courses prepared by qualified
instructors, instructions given by qualified
instructors at any time etc. (Ueno, 2002).
But these opportunities come with bundle of
technological complexity. Hence, the creation of
quality material for web-based distance learning and
carrying out full-fledged multimedia supported
discussion or presentation through Internet yet
remains in the state-of-the-art of research. The
primary factor that prohibits the development of
web-based course materials is the enormous cost
associated with the tools and the number of person-
hours needed to produce a lesson (Lawhead et. al,
1997). So far a number of open and commercial
systems for web-based learning have been proposed.
WebCT (WebCT) provides integrated e-learning
systems for graduate education. Its contents can be
created by external applications that produce IMS-
compliant learning objects (IMS). It can produce
sophisticated on-line courses and requires
considerable amount of investment in software cost
and training. Macromedia Breeze delivers rich web
experiences for distance learning, professional
development and collaboration (Breeze). It is a rich
system that lets user reach their audience anytime
512
Rahman M., Hidoyuki S., Ampornaramveth V. and Ueno H. (2007).
WebELS E-LEARNING PLATFORM AND PROPOSAL FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO SUPPORT.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and e-Government /
e-Learning, pages 512-517
DOI: 10.5220/0001278105120517
Copyright
c
SciTePress

with multimedia content. The Virtuelles Informatik
Praktikum project’s main focus is to provide an
environment for virtual lab classes for computer
science students (VIP). TeleTeaching carried out by
the University of Mannheim (Tele-teaching)
supports three instructional settings i.e. RLR -
Remote Lecture Room, RIS -Remote Interactive
Seminars and IHL -Interactive Home Learning.
Realized by multimedia and telecom technology.
The WebELS system focuses on the on-line material
authoring, presentation, and management for
asynchronous learning (Kurtz et. al, 2002). It should
be noted that the uploaded contents on the WebELS
server are used for on-line Internet meeting
seamlessly as well. The system allows existing
learning materials to be reused again on the web.
These materials are stored on the server in a modern
and flexible XML format which can be delivered to
students in many different ways. Recently, MySQL
based storing system is under development, which is
supposed to enhance the quality and efficiency of
storage and management of the system a step ahead.
Unlike WebCT, WebELS is intended to provide
traditional instructors and easy way to create or store
their learning materials with all the required
authoring tools built-in as Java Applet and
automatically downloaded from the server. The
instructor needs to have only a Java-supported
browser. Java Media Framework based video-
module of WebELS system has been discussed and
with a real example it is shown how video
component are pre-processed and presented using
Internet-Based WebELS editor. Ideas are discussed
for automatic video support.
2 WebELS OVERVIEW
2.1 Background
Difference of characteristics in e-Learning is quite
obvious. Two main category of system is needed i.e.
e-Learning for under-graduate education and e-
Learning for graduate education. Both of the
systems have their own characteristics regarding
design issues, education contents and so on. e-
Learning for undergraduate education mainly deals
with management of course registration and
students, primitive education and automated
evaluation of students knowledge. Education
contents for undergraduate education are
standardized textbooks. Examples are Blackboard,
WebCT, Moodle etc.
On the other hand, e-Learning for post-graduate is
heterogeneous in nature. Issues are fusion of
education and research (lecture, research, meeting,
conference) ubiquitous of education contents
(journals, reports, video materials) meetings/
seminars, symposiums, conferences as well as
internationalization. Contents are not-standardized,
mostly personal contents. Design policy involves
fusion of asynchronous and synchronous features
with powerful authoring tools for self-learning and
Internet meeting Supporting distributed and
internationalized education in multi-language.
WebELS provides contents-shared e-Learning for
post-graduate education.
2.2 Design Concepts and Goal
e-Learning system designed to meet the
requests of postgraduate education: Ph.D
program is the main target of use
Supporting seamless service of
asynchronous and synchronous e-Learning:
Asynchronous self-learning and
synchronous Internet meeting using same
contents
Multi-OS system: Supports both Windows
users and Mac users at same quality
Powerful authoring features for end-users:
One-click uploading editor for Power Point,
pdf, audio/video contents
Multi-language interface to support
international use: Automatic selection of
English (standard), Japanese, Chinese, etc
“Anywhere, anytime & anybody” system:
Java- based system to support a variety of
usage
Open-source system
IBM
We b Se r ve r
Cont ent Se r ve r
Conversion: XML-to-PDF/HTML
Aut ogen of TOC, Index
Course Creator Students
Br owse i n HTML
Print in PDF
Content Editing via Java Applet
MS-Word Document Import
*Edit anywhere
Pr e vi ew
Figure1: WebELS network diagram.
WebELS E-LEARNING PLATFORM AND PROPOSAL FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO SUPPORT
513

2.3 Major Objectives
Major objectives of the system are as follows:
Povide a general purpose e-Learning
environment for distributed and
internationalized post-graduate education:
Distance learning, distance meeting, multi-
language, synchronous/asynchronous
Provide a variety of distance learning
functions such as Internet interview,
Internet conference, annotation system, on-
line whiteboard.
Provide a powerful authoring feature to
assist the lack of other e-Learning
platforms i.e Integration to such as
Moodle, Blackboard, NetCOMMONS,
WebCT etc.
2.4 System Configuration
The author client computer contacts the server and
downloads the necessary java tools for editing the
course materials. After the program is launched
locally on the author machine, the material data is
downloaded from the server and the author can edit
it on his local machine. This reduces the impact of
network delay on content editing. After editing is
completed, author uploads the updated data back to
the server. In building up the web server and
interfaces, the ease-of-use and ease-of-access are the
optimal goals. In designing the technical aspects of
the system, more attention is given in portability of
the system, and reusability of the learning materials.
In order to achieve minimal platform dependency,
many tools in WebELS have been developed from
ground up using Java programming language. This
allows to realize a portable foundation with rooms
for future expansion. The system attracts
international attention and in use at several sites
rather than NII such as NIG, Tsinhua University,
China, Dhaka University, Bangladesh and so on. As
the software is copyright free, every organization
download the core version and the related source
codes and develop depending on their own
requirement. Recently NII provides three versions of
the system i.e. WebELS Full version. The
conceptual network diagram of the system is shown
in Figure 1. The learning materials are kept and
managed by the server. Authors and students can
access via the Java-enhanced web-based interfaces.
2.5 Functions
WebELS system has three versions, i.e., WebELS
(full version), WebELSx (beginners version) and
WebELS Meeting (Internet meeting system). Full
version was developed first to provide a powerful e-
Learning platform for postgraduate education which
comprises of different modes of operation.
WebELSx is for beginners for further development
according to a real user’s request in a graduate
education at Sokendai, the Graduate University for
Advanced Studies (Vuthichai, 2006 & Gong, 2006).
WebELS Meeting is a software platform for
Internet-based distance meeting and interview, etc.
WebELS consists of two main modes, i.e., Learning
mode and Editing mode. These functions provide
following features. Note that WebELSx is designed
for novice users by means of simplified user
interface, where both functions are combined in a
unified manner.
Asynchronous mode in WebELS is for doing self –
learning by students. The users of learning mode are
classified into two types: guest and specific user.
Guest users can access public contents without
registration in the learning mode. Specific users can
access non-public contents after logging into
learning mode. In the learning mode, contents are
consisted of various types of courses. Each course is
indicated by the title, author, update time, category,
media type, etc. Each course can be displayed on the
computer screen or printed out. The courses in
WebELS can be one (or combination) of the
following primitive types: (1) Formatted text with
different typefaces, colors, languages; (2) Still image
in the following formats: JPG, GIF, and PNG; (3)
Animation such as GIF Animation; (4) Embedded
and On-Demand Streaming sound; (5) Embedded
and On-Demand Streaming Video Clips. There is a
searching function to locate the course quickly.
Usually on WebELS, contents can be presented to
the students using one or combination of the
following delivery modes: (1) A single HTML page;
(2) Multi-page HTML for slideshow presentation.
Each slide may correspond to a SECTION in the
content; (3) Video presentation; (4) Multi-Modal-
Synchronize video presentation with slides, side-by-
side; (5) PDF hardcopy; (6) On-line Internet
meeting. Multi-page HTML is used to divide a
lengthy content into smaller studying units, each can
be finished in a reasonable period of time. A
navigation bar is provided for the users to navigate
through the slides. For efficient content management
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
514

MySQL based database system is under
development. Figure 2 shows the example of a
course downloaded for Asynchronous self-learning.
It shows slide no. 40 of 61 slides and the bar on the
top shows the progress in sound by 16% that is
synchronized with cursor. If Auto playback mode is
checked, the slides will change automatically one
after another.
Using WebELS Meeting multi-sites on-line meeting
is available over the Internet by sharing Microsoft®
PowerPoint® content. It is shown in Figure 3.
Internet-based interview is available by using
WebELS Meeting as well. Microsoft® PowerPoint®
contents can be prepared using a usual Microsoft®
PowerPoint® system, and then can be uploaded to
the system by means of "Create a New Content for
Presentation" located under the Contents List.
Password could be attached to the contents if
needed. Changing of slides can be controlled by the
speaker by clicking "Speaker On" and control
bar.Speaker can be switched by clicking Speaker
icon at the next speaker's site. Voice line can be
chosen from usual telephone line, Skype™ and
VoiceLine of the system. Current VoiceLine is
available in a limited condition. Shared Whiteboard
system is available, to discuss and work on the
Internet. Finally, an advanced presentation mode is
provided in WebELS, called on-line Internet
meeting. It uses the function of client
synchronization. That is, it allows teacher to make
real-time presentation with group of students over
the Internet. As long as teacher and students open
the same course saved in WebELS, the teacher can
control slide which can be changed synchronized in
the student’s computer.
Teacher can also use a pointer to indicate the
contents in the slide. This pointer can be
synchronized appeared and moved in the student’s
slide. It is shown in Figure 4.
3 WEBELS VIDEO MODULE
3.1 Video Pre-Processing
To date, JMF (Java Media Framework) supports
limited video formats as described in (JMF). Also it
supports some specific Codecs. So, some pre-
processing may need to make it applicable to
WebELS video module. Currently, WebELS support
.avi video format in Windows/Linux or .mov video
format in Macintosh OS with cinepak codec by
radius. Once the video is pre-processed using any
OS, it becomes versatile i.e. it can be uploaded and
viewed in any Operating System. Here, an example
is given to pre-process video so that it could work
fine with WebELS video module. If the .avi file
doesn’t have cinepak codec by radius suitable for
WebELS editor, it can be done by VirtualDub what
is a freeware. It is available at:
http://www.virtualdub.org/ (VirtualDub)
Step1: Download and install VirtualDub
on your PC.
Figure 2: Self learning in asynchronous mode.
Figure 3: Meeting version.
Figure 4: Simultaneous cursor movement.
WebELS E-LEARNING PLATFORM AND PROPOSAL FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO SUPPORT
515

Step 2: Start VirtualDub, double clicking
on VirtualDub.exe file.
Step 3: Open video file and from pull
down menu of video select compression
(ctrl + P)
Step 4: There are many options of video
compression. Out of them select Cinepak
Codec by Radius and press OK as
shown in Figure 5.
Step 5: Save the file using save as avi
(F7) of the pull down menu of file with a
new name or it can be rewritten on the
same video file. Here original codec of
the file will be replaced with new one.
3.2 Video Handling
As WebELS is completely based on java platform,
JMF based media player plays an important role to
handle video contents. Media player is embedded in
the Applet and starts on a single click. For
experimental purpose we used the WebELSx version
of the system. To produce a presentation material
with video contents we have to follow the following
steps.
Step 1: Create new course: After log in
as a user in WebELSx version the
interface will come out. Different options
are here regarding a course. One can
view, edit, export, copy a course in the
list. To create a new course one has to
click on “create new course” button.
Step 2: Select a type of slide to add:
There are several options of adding a
slide such as PDF, IMAGE, PPT and
VIDEO. To create a video slide we
have to check VIDEO button.
Step 3: Template selection: There are
several built in templates for creating a
slide with video. As the user often needs
to add annotation or image to describe a
video, the template has a variety of
selections to add image and texts.
Step 4: Background selection: To choose
a suitable background, one can use
customised background colour from pop
up colour selection pad
Step 5: Adding video, annotation and
image: In the selected template upper left
corner is for image, upper right corner is
for image annotation, lower left corner is
for video and lower right corner
rectangle is for video annotation.
A complete video slide edited with WebELSx editor is
shown in Figure 6. It contains Video with sound, image
and text annotation. Video content uploading,
downloading, viewing etc. are tested in WinXP, Fedora
Core Linux and Macintosh OS. Format of the video file is
in .avi format with cinepak codec by radius. The size of
the file is 690KB. It uploads very fast on a single click and
playback on the Java Applet as shown in Figure 6. It is
tested with different web browsers such as Internet
Explorer in WinXP, Mozilla in Linux and Safari in
Macintosh.
3.3 Proposal for Auto Video Support
Video module of WebELS doesn’t support video
directly if the presentation file is created by standard
PPT editor, for example, Microsoft PowerPoint. The
limitation is due to the fact that the slides are opened
as PNG image file and the video portion appears as a
still image as shown in Figure 7. However, if the
presentation file is edited with WebELS editor in
that case it supports video with power point as
shown in Figure 6. WebELS users obviously want to
Figure 5: Codec selection.
Figure 6: WebELSx edited slide.
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
516
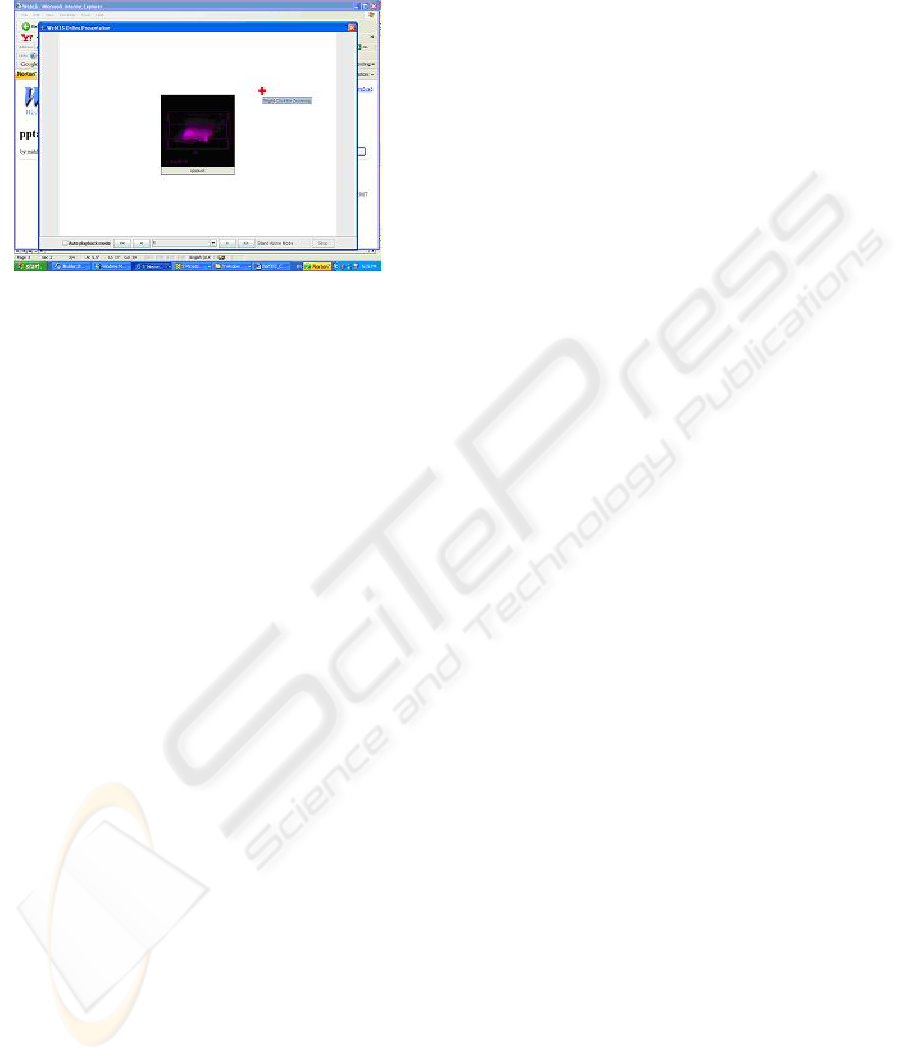
open and present PPT file that may contain video. In
this section ideas are discussed so that WEBELS
could supports PPT automation for video.
The proposed ideas can be summarized as follows:
Step 1: Open the specified PPT file and
insert video using the present module of
inserting video as shown in Figure 6.
Step2: Save as HTML so that the
elements of slide will have hyper link.
Step3: Check the slides whether any of
them is having link to video. HTML
format should also contain the size and
location of video.
Step 4: If there is a link to video, then
just put video on top of slide image.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This papers contribution is in detecting the limitation
and proposing probable solutions of video contents
with a discussion of video pre-processing and video
handling. The existing video model supports some
of the well know video formats but it has limitation
to directly support ASF i.e. Advanced Streaming
Format Media. With some format and coding
conversion, however, it is possible to apply the
existing module to a wide variety of video contents.
Further extension of the module is possible making
it applicable to ASF. Standard PPT edited embedded
video support system is under investigation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, special thanks goes to Open Source
developers who developed useful tools and authors
found useful for implementing this system. Authors
are highly delighted to acknowledge that the
research is supported by ROIS research fund,
SOKENDAI Taylor made education system project,
Science Research Foundation of JSPS and so on.
Finally, authors would like to thank Yiyuan Gong,
Prof. Nobuo Shimamoto and so on for their
contribution with many important comments.
REFERENCES
H. Ueno, 2002. Web-based distance learning for lifelong
engineering education – a personal view and issues,
Information and Systems in Education.
P.B. Lawhead, E. Alpert, and et all, 1997. The web and
distance learning: what is appropriate and what is now,
ITiCSE’97 Working Group Reports and Supplemental
Proceedings.
WebCT: http://www.webct.com/
IMS Global learning Consortium, Inc:
http://www.imsglobal.org/
Breeze: http://www.macromedia.com/software/breeze/
B. L. Kurtz, D. Parks & E. Nicholson, 2002. Effective
Internet education: a progress report, ACM SIGCSE
Bulletin, Proceedings of the 33
rd
SIGCSE technical
symposium on Computer Science Education, 34 -1.
XSLT: http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt
UTF-8 and Unicode standards: http://www.utf-8.com/
Extensible Style-sheet Language - XSL:
http://www.w3.org/Style/XSL/
FOP - Formatting Object Processor:
http://xml.apache.org/fop/
Skype: http://www.skype.com/
JMF: http://java.sun.com/products/java-media/jmf/
VIP:http://www-i4.informatik.rwth-
aachen.de/content/research/finished_projects/index.ht
ml
Tele-teaching:http://www.informatik.uni-
mannheim.de/pi4.data/content/projects/teleteaching/
VirtualDub: http://www.virtualdub.org/
Vuthichai Ampornaramveth, Tao Zhang, Ana Hadiana,
Nobuo Shimamoto, Haruki Ueno, 2006. A Web-Based
e-Learning Platform for Post-Graduate Education,
Proceedings of the Fifth IASTED International
Conference on Web-Based Education, pp. 388-393.
Y. Gong, H. Sato, Md. Mahfuzur Rahman & H. Ueno,
Nov., 2006. An Online Presentation Tool of A Web-
based E-learning System WebELS, Proceeding of the
technical meeting of Knowledge-based software
Engineering, Okinawa, Japan.
Figure 7: Slide containing video.
WebELS E-LEARNING PLATFORM AND PROPOSAL FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO SUPPORT
517
