
FORMAL DESCRIPTION OF WEB USER INTERFACES FOR
AUTOMATIC GENERATION
Vincenzo Cannella, Daniele Peri, Roberto Pirrone and Edoardo Ardizzone
DINFO, Università degli Studi di Palermo, Viale delle Scienze, 90128 Palermo, Italy
Keywords: SDL, interface design, declarative programming, model-view-control paradigm, Prolog, AJAX, Web.
Abstract: In this work we present an extension of a paradigm for abstract description of user interfaces using data
structures described in the Set Description Language (SDL). An experimental software system for the
automatic design and generation of web client interfaces has been developed too, which makes use of the
Extended SDL (ESDL). At first, an interface is described at the highest level of abstraction through the data
it operates on, and it is generated in a way that enforces data correctness. Generation of interfaces is
executed by an expert system on the basis of a set of rules expressed in first order logic. The development of
the system relies on AJAX technology, which makes the developing process adaptive and allows the
feasibility of dynamic web interfaces.
1 INTRODUCTION
Specification languages allows to describe properly
the development of a software project or the
description of a program. High precision can be
gained using a notation defined in a rigorous way
both syntactically and semantically. Specifications
can be expressed in a descriptive language in a very
abstract manner. An application can be described
defining a state space, whose properties and
constraints can be expressed using either logical or
algebraic formalisms. In this field, languages
founded on the first order logic have proven to be
useful to express program specifications as
relationships between the input and the output data.
This is a case of declarative programming. The
statements in a formal specification language can be
automatically analyzed to put in effect the
specification themselves. Many systems have been
presented in the literature for automatic GUI
generation. In (Zanden et al., 1990) the tool Jade is
presented. It is able to automatically create and lay
out GUIs. The specification of interfaces doesn’t
depend on the data model of the application. The
user defines directly the structure and the
components of the interface. ITS (Wiecha et al.,
1989) exhibits similar capabilities to Jade. One of
the most significant systems proposed is Mastermind
(Browne et al., 1997). It supports the automatic
construction of user interfaces from declarative
models describing the components of the GUI or
their behaviours. No attention is reserved to the data
structure. Other systems are based mainly on the
analysis of the data model. In (Dennis et al., 1992)
an object oriented data modelling is proposed. Data
are structured as objects, which have attributes and
methods, mapped by some rules to widgets. Object
oriented modelling has inspired the Taellach system
(Griffiths et al, 1999) too. Recently, GUI generation
tools based on mark-up languages are gaining in
interest. Such tools make use of the languages used
in web applications, like XML and XSLT. An
example of using XSLT to convert an XML data file
into a GUI implemented with Java Swing is reported
in (Lay et al., 2004). Another example is offered by
XUL (Gooder et al., 2006), a cross-platform mark-
up language allowing to describe the components
and the structure of an interface. As in Jade, the
specification of the interface does not depend on the
data model. XIML (Puerta and Eisenstein, 2002) is
also a XML-based language, but it allows to enables
a programmer to describe either GUI elements and
data structure. In this work we propose a paradigm
for the automatic generation of a web GUI on the
basis of its formal description. We describe our
interfaces using an original extension of the Set
Description Language (SDL) (Ardizzone et al.,
2001), (Ardizzone et al., 2002), (Ardizzone et al.,
2004). GUI generation is performed by means of a
425
Cannella V., Peri D., Pirrone R. and Ardizzone E. (2007).
FORMAL DESCRIPTION OF WEB USER INTERFACES FOR AUTOMATIC GENERATION.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Web Interfaces and Applications, pages 425-428
DOI: 10.5220/0001281804250428
Copyright
c
SciTePress
set of rules expressed in first order logic. We present
an experimental software system for the automatic
design and generation of web client interfaces too.
At first, an GUI is described at the highest level of
abstraction through the data it operates on, and it is
generated in a way that enforces data correctness.
The rest of the paper is arranged as follows. Section
2 reports some brief remarks on the Model-View-
Control (MVC) software design paradigm, which
inspired the design of our interface architectures. In
section 3 the technique we used to describe the
interface models is presented. Section 4 deals with
the interface generation phase. In section 5 a case
study with some real examples is detailed. Finally,
in section 6 some conclusions are reported.
2 THE MODEL-VIEW-CONTROL
PARADIGM
One of the most used assumptions in designing
graphical user interface is the model-view-control
(MVC) paradigm (Krasner and Pope, 1988).
According to it, elements of an interface are
classified as controls, views or models. A model
encapsulates data and functions managing them. It
modifies its state accordingly to the orders received
from a controller, and replies to the requests for
information regarding its state. A view presents data
to the user using often a mixture of text and
graphics. It updates itself when a change happens in
the model, in order to reflect this change. Finally,
the controller receives the input from the user and
passes it to the model. In this way the model is
instructed about the need to carry out the actions
based on the input.
3 INTERFACE DESCRIPTION
In our system, the abstract description of an interface
is produced according to the MVC paradigm. We
will define our interface model by means of a
suitable logical structure that has been called
“context”. It is a collection of interface controllers
and views. We will use an original extension of the
SDL, called ESDL, to define contexts. An ESDL
interpreter has been implemented in Prolog so that
the actual interface can be generated using a suitable
rule based system. A context is defined as a logical
structure made up by controllers and views. Each of
them manages a variable defined by means of a set
of constraints and conditions. Each context can
optionally contain other contexts. The state space of
a context is composed by its own variables and by
the state spaces of the contexts contained by it. Each
controlled variable in a context is independent from
the other ones; there is no hierarchy between them.
This kind of structure is very simple, but not error-
safe. Variables definitions can produce loops. In
fact, a programmer can create erroneously two
mutually dependent control variables while defining
a context. Such a control loop would make no sense
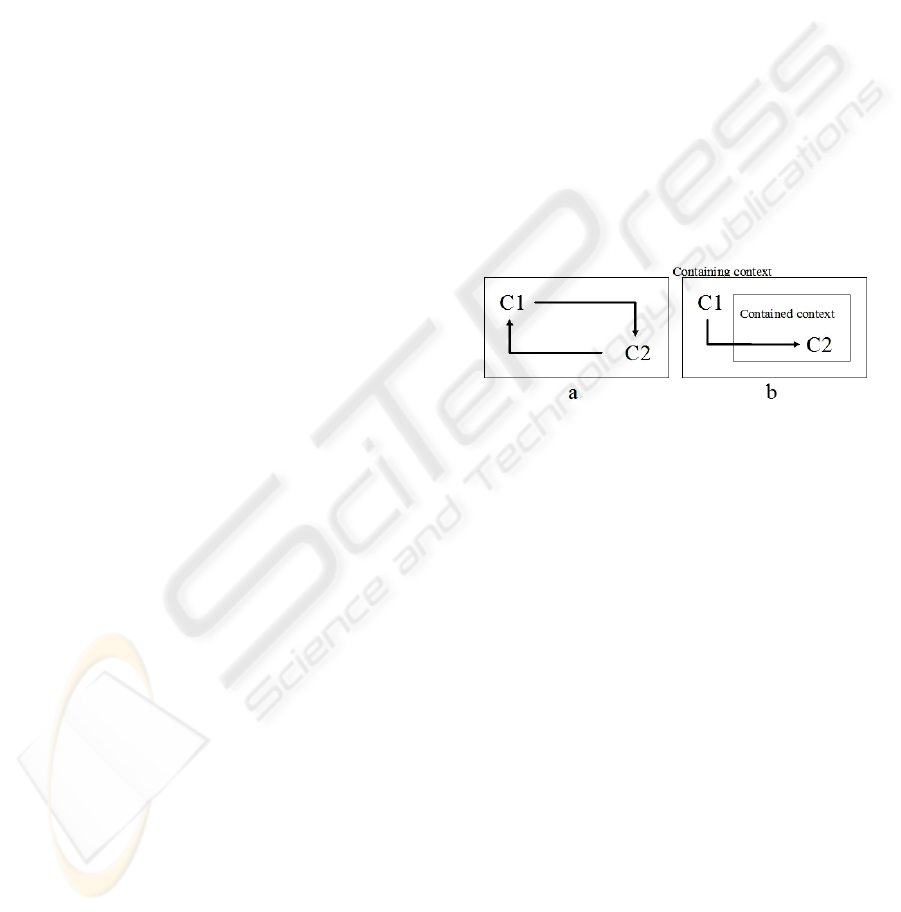
(figure 1,a). A good context design needs that a
variable C2 controlling another one C1 is defined in
a context that is external with respect to the one
containing C1 (figure 1,b). Similar considerations
hold for the view variables. On the contrary, view
variables depend on control ones. Each controlled
variable can be influenced only by the variables in
the ancestors of the context. Similarly, such a
variable can influence only the view variables in the
same context or in the descendants.
Figure 1: a) developer should avoid logical loops in
defining control variables of the same context; b) if C2 is
influenced by C1, it should be placed in a context
contained by the context that holds C1.
Defining a context needs a suitable formal language.
To this purpose SDL has been designed. Here we
present a new extended version of SDL that we
called ESDL, enabling new configurations for
contexts structures. Here is an example of code in
ESDL:
context ContextName(ParametersList) :=
controls := ControlsList,
views := ViewsList,
contains context
ContainedContext1(Lp_cont_context1) if
IfCond1:
contains context
ContainedContext2(Lp_cont_context2) if
IfCond2:
contains context
ContainedContext3(Lp_cont_context3) if
IfCond3: …
(Conditions_on_controlled or viewed
variables).
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
426
The name of the elements of the code is self-
explanatory, with reference to the roles of these
elements. Not all the previously defined terms must
be present in a context: a context can contain only
controls or only views, and it can even contain no
contexts. One of innovations introduced in the
ESDL language is the if statement. It allows a
context to be optionally present inside another one.
Another important innovation introduced in ESDL is
the possibility to include more than one context in a
context. This allows to build a tree-like structure of
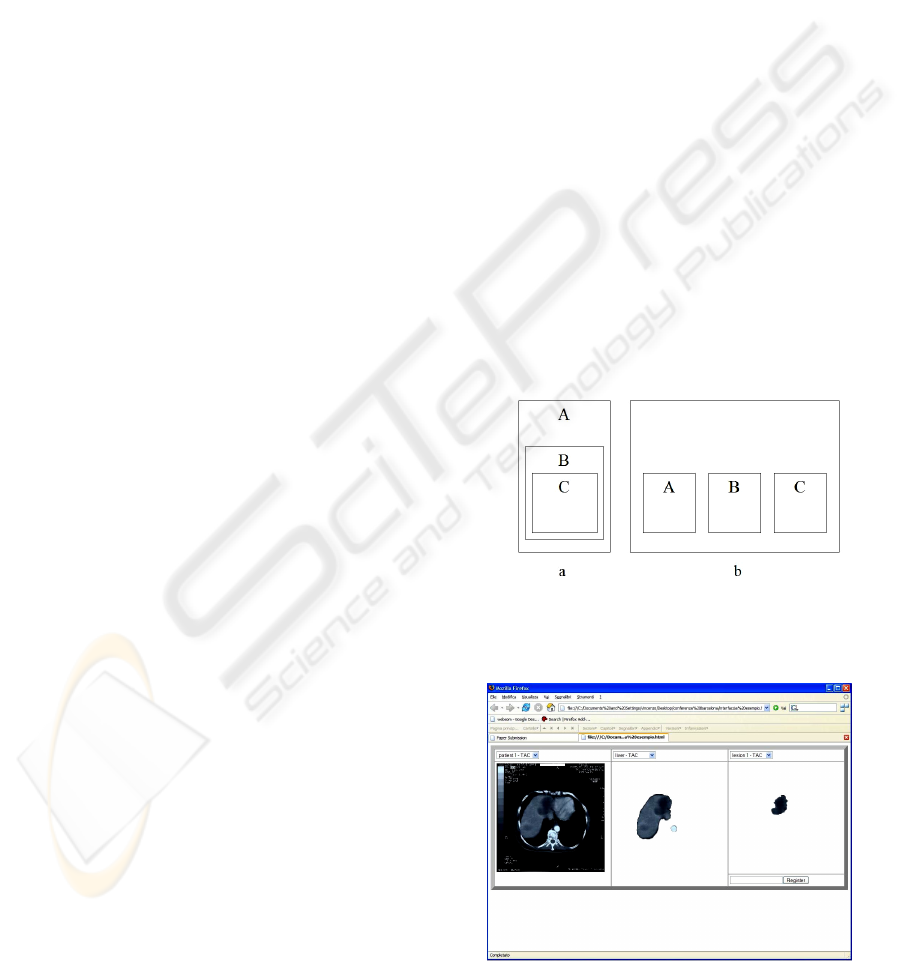
contexts. When using SDL language, the developer
who wants to define a context bringing together the
contexts A, B and C, has to insert C inside B, and B
inside A (figure 2,a). This is due to the linear
structure of contexts. There is no chance to solve the
problem differently, even if B and C are not related
to each other. ESDL allows the developer to put A,
B and C inside a more general container, without
creating relations between them (figure 2,b). This
makes the code modularization and re-using simpler.
ESDL lets the developer to define the domain of a
set of variables and the interaction modality of the
GUI with the user. Variables domains are declared
using conditions statements at the end of the context.
The direction of interaction is established assigning
a variable to a control or a view. The choice of the
widgets and their placement in the window are
delegated to the expert system. This separation
between data model and interface presentation
makes the developer free from low-level aspects of
programming interfaces, letting him take care of
high level aspects.
4 INTERFACE GENERATION
The whole system has been implemented using a
modified version of the GNU Prolog implemented in
Javascript. This choice has been inspired by the
AJAX technology (Asynchronous JavaScript and
XML), in order to create an interactive web
application. The GUI is generated by an ESDL
engine, which interprets Prolog rules implementing
ESDL statements. From a computational point of
view, the task at hand is not so heavy. The obtained
interface is a DHTML and Javascript web page.
Each element of the interface is able to manage
autonomously one of the variables in the context.
Each control of the interface interacts directly with
the user, but also propagates the information of this
interaction to the other view widgets of its context.
Each context gives the contained ones the
information too. Each widget reacts to events and
responds by posting further events to successor
widgets. The system establishes the type of each
variable of the context and choices the
corresponding widgets, considering if a variable acts
as a control or a view. The system is able to manage
many different types of GUI components, and
selects a widget on the basis of a set of rules
expressed in first order logic. These rules has been
inspired to the most spread user interface style
guides (OSF, 1990), (Apple Computer, 1986), (IBM
Corporation, 1987), (Sun Microsystems, 1990).
Finally, the ESDL engine has to enrich widgets with
the ability of rejecting erroneous values.
Arrangement of widgets must reflect the dependency
between them. Widgets of the same context should
be placed next to each other. Similarly, if a context
is contained in another one, then its graphical
implementation should be inside the layout of the
container. Widgets are arranged in rows or in
columns, for each widget at first controls, and then
views. Each widget has its own horizontal and
vertical weights, on the basis of its type or its
content. The total weight of every row or column is
the sum of the weights of the widgets it contains.
The stacking of widgets must produce stacks whose
height or width is almost equal.
Figure 2: a) SDL allows the user to insert only a context
inside another context; b) ESDL allows the user to insert
more contexts inside a context.
Figure 3: an example if interface generated by the system.
FORMAL DESCRIPTION OF WEB USER INTERFACES FOR AUTOMATIC GENERATION
427

5 A CASE STUDY
The ESDL engine has been used to produce
automatically the interface for a simple medical
image viewer (figure 3). Using this application, the
user can insert or choose an image file name and
specify a numeric value. In this case, the system has
used only two types of widgets as controls: menus
and text-entries. When the variable dealt is
alphanumeric, the system chooses a menu. The text-
entry is preferred when the user has to insert a
numeric value. The view has been rendered as an
image. To decide the arrangement of widgets inside
the interface, the system has set height weights
equals to 1 for text-entries and menus, and to 4 for
images. A common value has been given to the
width weights.
6 CONCLUSIONS
An original web interface generation paradigm has
been presented, which allows the user to formally
define the GUI with a suitable description language
that is an extension of the Set Description Language,
called ESDL. A working system has been realized,
which implements an ESDL interpreter using a Java
Prolog implementation and embeds it in a DHTML
page as Javascript code along with the rules to build
the interface. The GUI generation procedure relies
on the definition of context as a data structure
containing a description of a part of the interface
according to the MVC paradigm. The presented
paradigm offers new functionalities with respect to
the former one through a minimal modification of
the context definition language. Therefore, it has
been extended for web applications. We are
currently investigating other extensions of the
paradigm including a description of the user model,
or the use of fuzzy rules. In this way more
customizable and effective interaction modalities
can enrich the system.
REFERENCES
Apple Computer, Inc., 1986. Human Interface Guidelines:
The apple Desktop Interface. Apple Programmers and
developer’s Association. Renton, WA.
Ardizzone, E., Cannella, V., Peri, D., Pirrone, R. , 2004.
Automatic Generation of User Interfaces using the Set
Description Language, WSCG(Poster)
Ardizzone, E., Peri, D., and Pirrone, R., 2002. User
Interfaces for SDL Applications, KES2002,
Knowledge based Information Engineering System &
Allied Technologie, Podere di Ombriano
Ardizzone, E., Peri, D., Pirrone, R., Palma, A., Peri, G.,
2001. A Knowledge based Approach to Intelligent
Data Analysis of Medical Images, IDAMAP, London,
September 4th
Browne, T. P. et al., 1997. Using declarative descriptions
to model user interfaces with MASTERMIND, In F.
Paterno and P. Palanque, editors, Formal Methods in
Human Computer Interaction. Springer-Verlag
Dennis J. M. J. de Baar , James D. Foley , Kevin E.
Mullet, 1992. Coupling application design and user
interface design, Proceedings of the SIGCHI
conference on Human factors in computing systems,
p.259-266, May 03-07, Monterey, California, United
States
Gooder, B., Hickson, I., Hyatt, D., Waterson, C., XML
User Interface Language (XUL) 1.0, 2006, URL:
http://www.mozilla.org/projects/xul/xul.html
Griffiths, T., Barclay, P. J., McKirdy, J., Paton, N. W.,
Gray, P. D., Kennedy J., Cooper, R., Goble, C. A.,
West, A., and Smyth, M., 1999. Teallach: A Model-
Based User Interface Development Environment for
Object Databases, in Proc. User Interfaces to Data
Intensive Systems (UIDIS), IEEE Press. pp. 86-96.
IBM Corporation., 1987. System Application
Architecture, Common Access Panel Design and User
Interaction. SC26-4351-0. December.
Krasner, G.E. and Pope, S.T., 1988. A Description of the
Model-View-Controller User Interface Paradigm in
the Smalltalk-80 system, Journal of Object Oriented
Programming, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 26-49
Lay, P. and Luttringhaus-Kappel, S., 2004. Transforming
XML Schemas into Java {S}wing GUIs, GI
Jahrestagung (1), INFORMATIK 2004 - Informatik
verbindet, Band 1, Beitrage der 34. Jahrestagung der
Gesellschaft fur Informatik e.V. (GI), 20. September -
24. September 2004 in Ulm, p. 271-276, Peter Dadam
and Manfred Reichert, ISBN 3-88579-379-2
OSF. OSF/Motif Style Guide, 1990. Revision 1.0, OSF 11
Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142, ISBN 0-
13-640491-X.
Puerta, A., Eisenstein, J., 2002, XIML: a common
representation for interaction data, IUI 2002
Sun Microsystems, Inc. and AT&T OPEN LOOK, 1990.
Graphical User Interface Application Style Guidelines.
Addision-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 0-
201-52364-7.
Wiecha, C., W. Bennett, S. Boies, and J. Gould, 1989.
Generating Highly Interactive User Interfaces, CHI’89
Proceedings, Austin, Texas, may pp. 277-282
Zanden, V. B., and Myers, B. A. , 1990. Automatic, look-
and-feel independent dialog creation for graphical user
interfaces. In Proc. ACM CHI'90 Conf. on Human
Factors in Comp. Sys., pages 27--34
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
428
