
RECOMMENDATION OF WEB RESOURCES FOR ACADEMICS
Architecture and Components
Pavel Cech and Vladmir Bures
Faculty of Informatics and Management, University of Hradec Kralove, Rokitanskeho 62, Hradec Kralvoe, Czech Republic
Keywords: Recommendation system, recommendation system architecture, web services, heterogeneous tools.
Abstract: Vast amount of resources in digital libraries and on the Internet makes the selection of relevant and
appropriate resources rather difficult especially for novices and less experienced academics such as
students. The article presents an architectural solution for personal recommendation system of web pages
targeted to the academic sphere. The solution aims to meet the objective of minimizing the overheads and
provide support for PDF documents. The solution is based on a set of heterogeneous components connected
via web services.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vast amount of resources in digital libraries and on
the Internet makes the selection of relevant and
appropriate resources rather difficult especially for
novices and less experienced academics such as
students. The article presents an architectural
solution for personal recommendation system of
web pages targeted to the academic sphere. For
inferring potentially interesting pages the content
filtering and collaborative filtering approaches were
used. There are many theoretical papers on how to
infer similar web pages and also many case studies
with particular implementations (Balabanovic 1997,
Balabanovic & Shoham 1997, Basu 1998, Sarwar
2000, Herlocker 2004). The goal in this article is to
show how one practical solution can be implemented
using various tools. The problem is that the tools
might often be fairly heterogeneous i.e. implemented
in different programming environments. Thus the
solution has to offer a way how to split the system.
The solution is also different in that it puts stress on
the usability of the system especially by academics.
The aim of the technological solution was to offer
user friendliness both for rating and also for
recommending (i.e. the overheads of doing the rating
has to be minimized) and to support also formats
other then simple HTML. In particular, the focus of
the project was first to integrate the recommendation
system into the internet browser so that user can rate
and be recommended while browsing the web pages;
second, to support PDF (Portable Document Format)
documents since the system is targeted for the
academic audience and PDF is de facto standard for
academic papers.
2 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The architecture of the system is guided by the need
for centralized store of user preferences on one hand
and on the other hand by the necessity to track the
users’ behaviour. Therefore, the whole system is
split into components. Splitting the whole system
into several components makes the system more
flexible and easier to develop. However, the main
reason for dividing the system to components rose
from the implementation tier in the form of a
constraint of available tools, especially for PDF
parsing and user tracking. To make the system use
various tools and technologies it was necessary to
implement corresponding parts in different
programming environments. Thus, the whole system
is divided into several components. Each component
has different role in the system and can be
programmed in different programming languages.
Since the individual components are programmed in
different programming languages the appropriate
communication infrastructure, with common
communication protocol had to be selected. Thus,
components are interconnected using the web
services infrastructure that enables the cooperation
437
Cech P. and Bures V. (2007).
RECOMMENDATION OF WEB RESOURCES FOR ACADEMICS - Architecture and Components.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Web Interfaces and Applications, pages 437-440
DOI: 10.5220/0001284304370440
Copyright
c
SciTePress
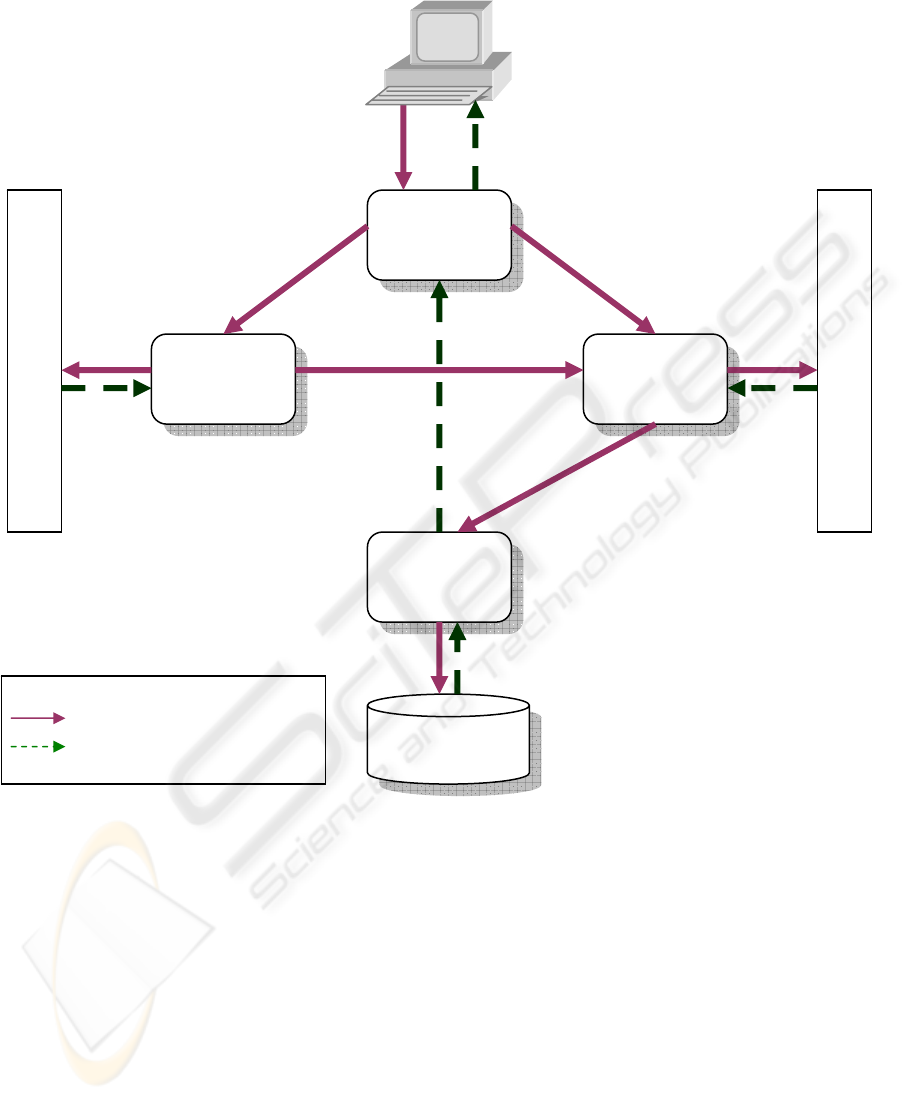
Figure 1: Architecture of the recommendation system.
of programs developed in different programming
languages. The overall architecture and the
communication lines between components are
illustrated in the figure 1.
2.1 User Component
The user component is responsible for monitoring
user behaviour and interacting with him. The user
component provides the interface to the system and
to the functions ensured. User component offers the
interface to search the web for resources. The system
is using the web services of various search engines
to perform the first search result. Those results
obtained from the search engine (if not specified
otherwise) are then refined based on the information
in the user profile.
The comfort offered by the user component to
the user is critical for the user acceptance of the
system. To minimize the overheads necessary while
rating resources the user component is integrated
directly into the web browser window. Thus, a part
of the user interface of the system is in the form of
an explorer window bar (placed vertically on the left
hand side) and explorer toolbar (placed horizontally)
– see figure 2.
However, there are features that cannot be placed
in the toolbar and the window bar of the browser
since the user probably wants to have the maximum
space for the opened resource. Therefore, some of
Legend:
request
response
User
Component
User Profile
Component
Collect
Component
Search
Component
S
E
A
R
C
H
S
E
R
V
I
C
I
E
S
Ratings
Use
r
results
displayed
D
I
G
I
T
A
L
L
I
B
R
A
R
Y
search
initiated
resources to
process
resources to
compute
similarity
search
specified
resources to
process
resources to
recommend
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
438

the details and reports that the system produces are
to be presented in the main window of the web
browser as a normal web page.
Since the most common browser is today MS
Internet Explorer, it had been selected for the user
interface layer. Hence, integrating the system user
interface directly to the MS Internet Explorer
window required the use of the COM (Component
Object Model) technology. However, the similar
user interface could be offered to Mozilla Firefox
users as well. This, however, was not covered in the
project.
The remote communication mainly between the
user component and the user profile component
required including the asynchronous processing of
requests and the display of the results. For this
reason the user component was developed as a
multithreaded application. The coordination of
individual requests as threads was provided by one
main thread that communicates with user interface
(which is usually not thread safe).
2.2 Search Component
Search component’s role is to query the search
engines and obtain result. Typically most of the
major search engines provide web services or other
interfaces to programmatically use the searching
capabilities. The search component waits for the
command of a user component to start the search.
The results from the search engine can then be
refined by computing the similarity and filtering out
those resources that do not correspond with the
preferences in the user profile. Before the similarity
can be computed the resources are processed in the
collect component.
2.3 Collect Component
Collect component is responsible for processing the
resources and for storing the resource information.
Typically the collect component obtains resource
from the search component or directly from the user
component, in case user gets the resource in other
ways than searching. The resources can also be
obtained from the digital libraries and, if appropriate
and the communication interfaces are specified, the
collect component can also supply some of the
resources into the digital library.
The obtained resource is first checked on the
type so that the particular parsing and extracting
engine can be used. Currently, only the resources in
the PDF (Portable Document Format) are supported.
The extension to Microsoft Word Documents and
the resources in XML or HTML pose only a minor
problem.
If the resources are parsed successfully, further
information is attempted to be extracted. The
information being extracted concerns title, authors,
keywords and an abstract. Optionally the publisher
and other information used for citations and
referencing can be included in the system. If
extraction does not succeed then it can be filled
manually using the user component interface in the
internet browser. The resource then is processed
against the terms identified and the normalized
frequencies are computed.
2.4 Recommendation Component
The recommendation component is the core of the
system. It has the role of the server providing
services for other components namely user
component. The main task of the recommendation
component is twofold: First, to obtain the necessary
resource information about a resource and rating
information of a particular user and store such data
in the database; Second, to infer the rank of searched
documents according to the preferences of users.
If request for recommending possibly interesting
resources is sent, then the recommendation
component computes the similarity between the user
preferences stored in the user profile and the
resources stored in the database or obtained from the
search engine. In this way the recommendation is
based on the content of the resources and the user
preferences i.e. content filtering (Herlocker 2004).
The weight of the recommended resources is given
by the similarity function.
The recommendation can also be based on the
computation of similarities between user preferences
in which the users with similar user preferences are
determined and the system then recommends the
resources that similar users have rated as interesting
i.e. collaborative filtering (Herlocker 2004).
2.5 User Interface
As stated above, the system was built with usability
in mind. The figure 2 shows window of the MS
Internet Explorer with recommendation system user
interface. First, the toolbar provides means for
documents rating. The rating can be done explicitly
or user can enable the implicit rating based on the
time spent on a page and other patterns (Herlocker
2004). The bar on a left hand side then serves for
recommendation or assisted search. The list of
recommended resources is displayed as hyperlinks
so that they can be used instantly.
RECOMMENDATION OF WEB RESOURCES FOR ACADEMICS - Architecture and Components
439

Figure 2: User interface of the recommendation system integrated to the internet browser window.
The user can select to open the resource or to see
additional information and metainformation about
the resource. In the figure 2 the abstract and rating
information is being displayed.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The future trends in the Internet tend to
personalization. The paper presented a solution of
recommendation system based on the user profile
and heterogeneous components connected via web
services. The prototype developed under the code
name Personal Recommendation (PRECO) is
located on the following website http://preco.uhk.cz.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is partially supported by AMIMADES,
the GACR project No. 402/06/1325.
REFERENCES
Balabanovic, M., 1997a. An adaptive web page
recommendation service, In Proceedings of the 1st
International Conference on Autonomous Agents,
California.
Balabanovic, M., Shoham, Y., 1997b. Fab: content-based,
collaborative recommendation, Communications of
the ACM, Volume 40 Issue 3.
Basu, C., et al., 1998. Recommendation as classification:
using social and content-based information in
recommendation, In: Proceedings of the 15th National
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, California.
Herlocker, J., L., et al., 2004 Evaluating collaborative
filtering recommender systems, ACM Transactions on
Information Systems, Volume 22 , Issue 1, January
2004, pp. 5 – 53
Sarwar, B., M., et al., 2000 Analysis of recommendation
algorithms for E-commerce, In Proceedings of the 2nd
ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, New
York.
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
440
