
A GEOGRAPHICAL QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM
Ehsan Behrangi, Hamed Ghasemzadeh
Iran University of ´Science and Technology, Farjam, Tehran, Iran
Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili, Behrouz Minaei Bidgoli
Semantic lab., Sharif University, Iran University of Science and Technology Tehran, Iran
Keywords: Question answering system, fuzzy methods, geographical questions.
Abstract: Question Answering systems are one of the hot topics in context of information retrieval. In this paper, we
develop an open-domain Question Answering system for spatial queries. We use Google for gathering raw
data from the Web and then in a few iterations density of potential answers will be increased, finally based
on a couple of evaluators the best answers are selected to be returned to user. Our proposed algorithm uses
fuzzy methods to be more precise. Some experiments have been designed in order to evaluate the
performance of our algorithm and results are totally promising.
We will describe that how this algorithm
can be applied to other type of questions as well.
1 INTRODUCTION
The base scenario of most current web search
engines is receiving user’s query and extracting its
keywords and returning documents that contain
more keywords with higher frequency. But this type
of answering forces users to change their keywords
till receive exact answers. In fact, system doesn’t
answer to client’s questions. System just returns
popular documents that contain more keywords.
Question answering (QA) systems try to reply
original client’s questions with an exact expression
instead of a big document.
We have two types of Question answering (QA)
systems. First systems that answer to questions that
selected from specific corpora and second systems
that answer to questions on the web (open domain
QA systems).In this paper we explain our open
domain QA system. Similar systems usually use
NLP
1
methods beside a KB
2
(like Wikipedia
3
) or an
anthology (like WordNet
4
) for finding the relation of
keywords and answering to questions. Our System
uses new approach for finding exact answers. It uses
higher density of correct answers in the web (against
noise) and finds overlap of probable answers in an
iterative manner. In each iteration we try to refine
set of probable answers with fuzzy methods and give
a score to each probable answer. Unfortunately
because huge scale of work we implement our
algorithm just for “where-is” questions and achieve
good results.
In remain of paper we explain related works, our
QA algorithm, detail of implementation and testing.
2 RELATED WORKS
We can categorize current algorithms for QA to
these groups:
NLP based algorithms: These algorithms
usually restrict QA systems to a specific
language but Radev (Radev,2002) and
(Agichtein,2004) offer unrestricted domain
QA systems. NLP is optional In Radev
(Radev,2002) and (Agichtein,2004) uses
learning methods beside NLP for question
answering.
Heuristic algorithms: Mulder (Kwok, 2001) is a
good heuristic question answering system and
divide questions into three types: nominal,
numerical and temporal. The rules of each
question dictates the type of queries sends to
search engine. The way it determines question
types is by consulting an NLP and a database
that classifies words to certain types.
308
Behrangi E., Ghasemzadeh H., Sheykh Esmaili K. and Minaei Bidgoli B. (2007).
A GEOGRAPHICAL QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Web Interfaces and Applications, pages 308-314
DOI: 10.5220/0001287203080314
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Learning: In FADA (Yang, 2004), a learning
algorithm is used to split web pages into three
groups: topic pages, collection pages, and
everything else. Given a training set of the two
types of pages allows for FADA to compare
them and create a list of common attributes so
that later it can refer to these common
attributes and give more weight to pages
identified to be on a specific topic or
collections of facts. Tritus (Agichtein, 2004)
uses a learning algorithm to find probable
patterns for answering to a specific question
and search for these patterns in corpora and
find answers that satisfy this patterns. Falcon
(Ramakrishnan, 2004) searches FAQ web
pages and extracts question and answer pairs
and use them to answer user queries.
Clustering and Ranking: these algorithms rank
words with stochastic methods and calculate
the score of each sentence. Neumann
(Neumann, 2004) and Lin et al(Lin, 2003) use
an annotated database for ranking. Roussinov
(Roussinov, 2004) train it’s pattern matcher
algorithm with stochastic methods and uses it
for ranking candidate answers. Our algorithm
use stochastic and density for ranking and may
belong to this group.
You can find a survey about challenges of Web
QA and it’s techniques in (Richard, 2005).
3 OUR APPROACH
At first we try to explain the logic behind of our
method and then involve implementation. Suppose
we want to correct exam’s papers but we don’t know
correct answers and just have background
knowledge about probable answers. Deleting
digressive answers and finding overlaps between
other answers seems wisely. Using this method
evolutionary may finally guide us to correct answer.
In web QA we have same problem but in web we
can’t trust to many answers. At first more relevant
answers should be filtered then we calculate
candidate answers membership in final result set
with Fuzzy logic. Now we reassemble more accurate
query with high rank results and send new query for
search engine and search engine return more
accurate snippets with fewer noise. Increasing input
accuracy leads fewer chances for incorrect answers
membership in final result set.
This density based approach omits dependency
of algorithm to NLP methods. NLP methods are
time consuming, depending on a specific language
and may contain ambiguity. Other advantage is
reducing use of knowledgebase and Encyclopedias.
Totally Encyclopedias help us finding exact answers
but there is not any Encyclopedia that contains
answer to all questions so Encyclopedia based
method defeats in this situation.
One popular and effective method for QA is
pattern matching, it means finding all possible reply
patterns to a specific question. These methods
belong to NLP approach and have same problems.
For example the system receives this question:
“where is Iran university of science and
technology?” and have these snippets:
Ans1) Iran university is located in Hengam
street near Farjam street in Narmak, Tehran, Iran.
Ans2)Iran university, Tehran, Iran.
Ans3)ZamZam industrial company located in
Tehran, near Iran university.
Ans4)ZamZam in front of iran university, Farjam
street,Tehran.
Unfortunately pattern matcher algorithms search
for patterns like : X is located in…, X is in … and
… so they can find correct answer in Ans1 but they
can’t find correct answers in other scenarios.
Someone may suggest adding Ans2, Ans3 and …
patterns to our pattern finder database, but this trick
causes system finds incorrect answers in other
snippets that may have same pattern with irrelevant
information. But density based algorithms will
success in these scenarios.
Briefly our system first extract keywords of user
query and omit stop words and send first query to
search engine (Google) like this:
First Search Query="MKW1" <Space>
“MKW2” <Space> “MKW3” <Space> ... <Space>
“MKWN” OR “KW1” OR “KW2” OR “KW3” OR
… OR “KWM”.
In above MK means main keywords and contain
keywords that refer to a specific location or begin
with capital letter like: USA, Iran … and KW
contains other keywords like: park, street and….
After receiving result we extract name of query’s
country and abbreviation of this country with a
specific method And refine our next query like this:
Search Query=First Search
Query<Space>”Recognized Country” OR
“Abbreviation of the Country”
GEOGRAPHICAL QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM
309

Figure 1: Architecture of our system.
At next stage we obtain query’s province and
concatenate it to end of previous query with OR
operator. At each stage we receive 30(stage one), 10
(stage two) and 10 (stage three) first snippets of our
search engine. Finally we return most probable
result to user. Our system use some ranker that we
will introduce them at end, if the place doesn’t
belongs to a country for example: “where is
pancreas?” Other rankers will try to answer it, but
our focus is on open domain geographical questions.
4 IMPLEMENTATION DETAILS
Figure1 describes our System architecture and
dataflow. We divide our architecture to three
subsections.
4.1 Data Preparing
In this section we prepare data for next stages. We
omit stop words, extract abbreviations and try to
recognize correct destination of each abbreviation
with using fuzzy sets.
We calculate
])::([ YXXX
μ
that means the
probability that abbreviation XXX is equal with
place Y:
Figure 2: Probability distribution graph.
||)deg(
2
1
1])::([
YrYnY
YXXX
++
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−=
μ
(1)
deg(Y) means degree of vertex Y, n|Y| means
frequency of place Y in raw data and r|Y| means
number of related places with Y in raw data (so r|Y|
differs from deg(Y)), for example if Y be name of a
country r|Y| will mean number of all provinces of
this country that appear in input raw data and if Y
be a province r|Y| will be number of province that
locate in same country and appear in raw data.
For example we find United States in a text and
then we find AL so best choice for AL is Alabama,
this algorithm acts like this scenario.
Input Question
Ranking Place
Classification
Names of
Sentence
Ranking Frequent
Keywords for
Addressing of
Sentence
Ranking States
and Countries of
Sentence
Ranking D ensity
of C ountries and
States of
Sentence
Ranking
Abbreviations of
Sentence by an
Usual M ethod
Ranking D ensity
of First C apital
L e tte rs o f T h e
words of Sentence
Place
Classifications
Keywords of
Addressing
Countries -
States
Collecting
W eights- Values
and Generating
Final Score of
Sentence
Static Sensors
Recognized
Country Ranker
Recognized State
Ranker
Recognized
State
Recognized
Country
Dynamic Sensors
Creating D ynam ic
Country Sensor
D a ta S e le c tio n
Module
Question
Processing &
Classification
W here
Extracting
Question
Keywords
W hat
...
When
Do
Who
Which
Splitting
Sentences by
Garbage Char.
D elim ite rs
C om b in in g
Related Parts of
Com bined- W ords
Recognizing
Abbreviations by
Fuzzy M ethod
F ilte rin g
Sentrences
Stop W ords
Filtering G arbage Noises
Countries -
States
Data Preparation
Module
Google
Query Creation by
Keywords and
Recognized Data
Snippets
Snippets
Snippets
Appending to
Search Space
Extracting
Sentences From
HTM L Tags and
Delim iters
D a ta E xtra ctio n
Module
Recognizing State
of Question by
Fuzzy M ethod
R ec o g n iz in g
Country of
Question by Fuzzy
M ethod
First
Itera tio n
Second
Itera tio n
Creating Dynam ic
State Sensor
Third
Iteration
Top Answers
Dynamic Knowlage Static Knowlage
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
310
4.2 Data Extraction
The main goal of this phase is finding country and
province parts of the final answer.
Let V(G) be an empty set. If we find name of a
country we add this country location to V(G)
(notice: names are ambiguous and one name may be
representative of many provinces but locations are
unique for example Montana is a name but
[Bulgaria, Montana] represent the location of
Montana ).
Then we build a graph with V(G) members. Two
vertexes are adjacent if one located in another. Now
we have some stars (star is a graph that don’t have
more than a vertex with degree>1) that main vertex
of each star is name of a country. Now we initialize
weight of each vertex with it’s repetition in raw data
and weight of main vertex.
∑
=
i
i
k
k
Cw
Cw
CP
)(
)(
)(
(2)
P(C) is probability of main vertexes of different
stars (we have more than one suspect country so we
have more than one star) and W(C) is weight of that
main vertex.
Now we calculate probability of other vertexes
(provinces) with (3):
∑∑∑
∈∈
×
×
=
×
=
i
i
CS
i
kk
CS
i
k
k
CwSw
CwSw
Sw
CPSw
SP
ii
)()(
)()(
)(
)()(
)(
**
*
(3)
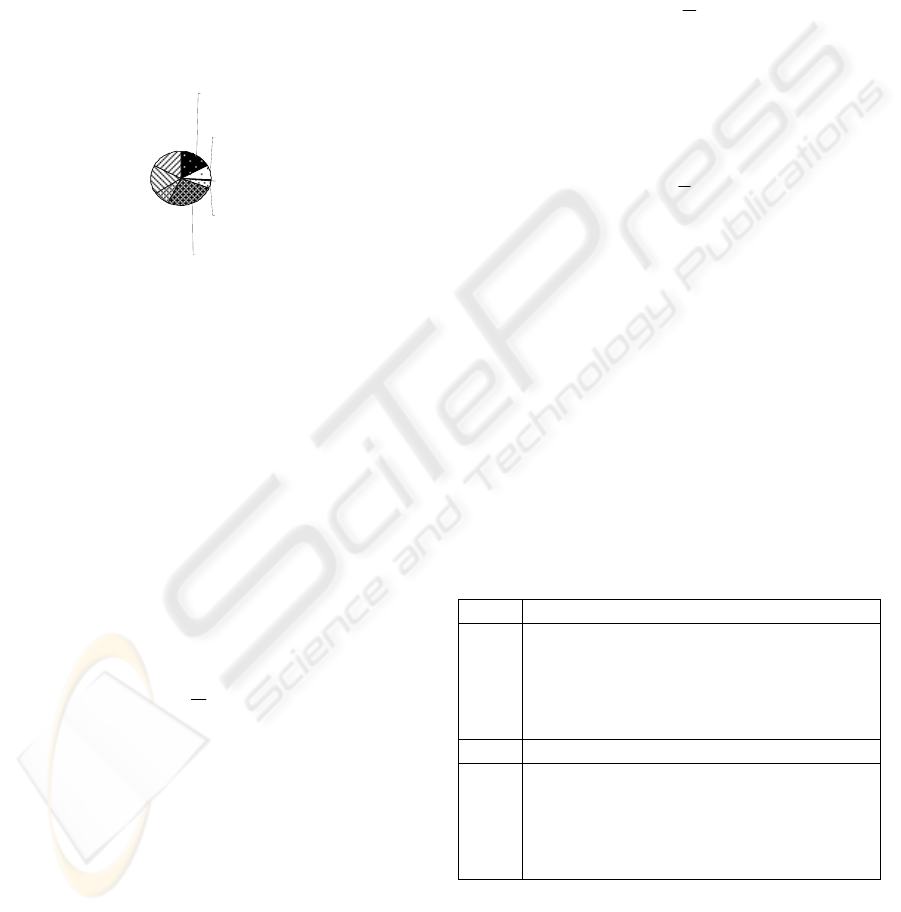
For example, suppose that in our search space
(after filtering the input sentences), we have these
names and frequencies: Argentina -> 3, Santa Cruz -
> 1, Corrientes,-> 1, Tarijia -> 1, Rio Negro -> 3.
According to our databases, we know that
Corrientes belongs to Argentina, Tarijia belongs to
Bolivia, Santa Cruz belongs to both of them, and Rio
Negro belongs both of Argentina and Uruguay.
Based on this information, we can draw following
graph (Fig3)
Figure 3: Graph for above example
So, we can say that Argentina (Rio-Negro) is
related country (province) of input query with
confidence of 0.6 (0.36).
Considering what we told, we have:
1
)(
)(
)( ==
∑
∑
∑
i
i
k
k
k
k
Cw
Cw
CP
(4)
In addition:
1)()()(
)(
)(
)()(
)(
*
*
*
*
*
*
===
⇒=
×
=
∑∑∑∑
∑
∑
∑
∈
∈
∈
jj
j
CS
k
i
i
S
CS
i
k
CS
k
CPSPSP
CP
Sw
CPSw
SP
jk
k
i
k
(5)
and it shows that sum of probability distribution
of provinces is 1. Again it agrees with our another
initial assumption that tells finding province name –
if any- is guaranteed.
If we define:
∑
∈
=
*
)(
)(
)|(
*
CS
i
k
k
i
Sw
Sw
CSP
(6)
Then:
*
*
**
() ()
(|) () ()
()
i
k
kk
i
SC
wS PC
pS C PC PS
wS
∈
×
×= =
∑
(7)
Based on conditional probability principles, these
expressions(6,7) show that assigned probability to
each province, completely agrees with selection
process. In other words, assigned probability to a
province is multiplication of country detection
probability and province independent detection
probability. Our sensor weights recognize from this
rule that we will discus it later.
4.3 Data Selection
We select best sentences for final answer using a
ranking module. This module contains 8 small
evaluator functions that we refer to them as sensors.
Six of these sensors use predefined information
sources so we name them static sensors. In contrast,
outputs of two remaining sensors depend on
information gained in data extraction phase –
detected country and province names- and they are
dynamic sensors. Each sensor evaluates input
sentences and returns a value ( v(i) ) as output. Final
[State:Bolivia->Tarij]
w(S)=1 P(S)=0.076
[State:Bolivia->Santa Cruz]
w(S)=2 P(S)=0.153
[State:Argentina->Corrientes]
w(S)=1 P(S)=0.122
[State:Argentina->Santa Cruz]
w(S)=1 P(S)=0.122
[Country:Bolivia]
w(C)=0 P(C)=0.23
[Counry:Argentina]
w(C)=3 P(C)=0.61
[Counry:Uruguay]
w(C)=0 P(C)=0.15
[State:Uruguay->Rio Negro]
w(S)=2 P(S)=0.153
[State:Argentina->Rio Negro]
w(S)=3 P(S)=0.366
GEOGRAPHICAL QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM
311
point for each of input sentences is calculated as
follow:
∑
=
sensors
iviwR )().(
(8)
Which w(i) is assigned weight to each sensor.
Considering their priorities, these weights are not
equal and they have been chosen manually in a trail
and error process. For static sensors these weights
are constant, but in dynamic sensors they are subject
to change based on previous steps results. Our
weighing scheme has been summarized in figure 4.
Figure 4: Sensor weights.
Sensor of addressing-words: usually, answers to
”where” questions contain some specific words used
for addressing. Therefore, a collection of these
words can help us in order to resolve final sentences
more precisely. For constructing such collection, we
crawled a number of Yellow Pages on the web and
extrated most common words.
At first, we extract this type of words and their
frequencies from input sentences. Then according to
following formula, a value will be assigned to each
sentence. In this formula,
j
n
is frequency of jth
word.
∑∑
=
−
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
j
n
i
i
j
v
1
1
2
1
(9)
Sensor of geographical divisions: functionality of
this sensor is like to previous one but here we use a
list of famous geographical divisions like: Airport,
Arch, Area …
Sensor of country and province names: similarly,
it works like our first sensor, but it’s benefited from
the database of countries and provinces which has
been described in section 4-1.
Sensor of word initiated with a capital letter:
simply we return ratio of these words to all of words
in each sentence.
Sensor of distance between country name and
province name in a sentence: output of this sensor
has an inverse relation with distance between
country and province names in sentence
Sensor of definitive names: by preparing a list of
all words started with a capital letter, this sensor
operates similar to first sensor.
Sensor of detected province: output of this sensor
is calculated as follow:
∑
=
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
×=
n
i
i
spv
1
2
1
)(
(10)
P(s) is probability of detected province in
probability distribution graph and n is its frequency
in sentence.
Sensor of detected country: like previous sensor
but uses P(c) instead of P(s).
∑
=
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
×=
n
i
i
cpv
1
2
1
)(
(11)
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
We have applied our proposed algorithm on two
different test cases and results are reported
separately.
5.1 Trec
We select 400 “where-is” questions, between years
1999 and 2005 then answer them online. we don’t
use Trec corpora for finding results and find results
from web and check them manually.
Table 1: Sample of our system output.
Where was Pythagoras born? Q:
Pythagoras was born on the island of
Samos, migrated to southern Italy, and
established a school at Croton.
Pythagoras taught that the order of the
world
Top
A:
Where are the British Crown jewels kept?Q:
British Crown Jewels , England. The
Crown Jewels are kept in the Tower of
London, guarded by special guards called
Yeoman Warders. Among the jewels are
the
Top
A:
During evaluation, considering two top-ranked
answers returned by system, following results
gained:
Classification
Names Sensor
17%
Frequent
Keyw ords for
Addressing
Sensor
9%
Abbreviations
Sensor
1%
First Capital
Letters Sensor
4%
States and
Countries
Sensor
26%
Density of
Countries and
States Sensor
9%
Dynamic
Country Sensor
17%
Dynamic State
Sensor
17%
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
312

Table 2: Our TREC experimental result.
False Partially True True
124 29 254
30.46% 7.12% 62.40%
5.2 GeoNet
5
In order to have more practical evaluation, we
decided to design a specific test collection for
evaluating web-based question answering systems.
Therefore, we selected GeoNet -a web site
containing millions records of various locations
around the world with their geographical
characteristics like altitude, latitudes, respective
province and country, an so on- to forming such
collection.
We gathered near 5000 records from this web
site using a special crawler and then converted them
to a ready-to-use XML format for further
applications.
In table3 AMD1 means (capital of provices), AMD2
(big cities), AMD3 (small cities), and AMD4
(villages and other small places).
To have a fair evaluation, during construction of
this test case, before selection of queries, we divided
all countries in the world to three categories from
their internet access facilities point of view: 1)
developed countries like Canada and China, 2)
developing countries like Argentina, Australia,
Belgium, 3) undeveloped countries: Angola,
Bahrain, Bhutan, Bolivia, Brazil, Burma, Chad, and
Congo.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
Because of high complexity and low efficiency of
NLP-based methods in question answering systems,
we tried to propose a density-based algorithm which
uses fuzzy logic to provide high-quality answers.
Our algorithm shows promising results even in a
noisy, open-domain environment like web.
Because of difficulty of construction of other
question types’ databases, we have implemented this
algorithm just for spatial queries, but it can be
applied to other types of questions easily. Currently,
we are extending our system to include “when” and
“who” questions.
REFERENCES
D.Radev, K.Libner, and W. Fan, ”Getting answers to
natural language questions on the web ” American
Society for information Science and Technology, vol.
53, pp. 359-364, January 2002.
D. Radev, W. Fan, H.Qi, H. Wu, and A. Grewal,
“probabilistic question answering on the web,” in
WWW ’02: Proceedings of the eleventh international
conference on World Wide Web, (Honolulu, Hawaii,
USA), ACM Press, 2002.
E. Agichtein, S. Lawrence, and L. Gravano, “Learning to
find answers to questions on the web,” 2004.
C. C. T. Kwok, O. Etzioni, and D. S.Weld, “Scaling
question answering to the web,” in WWW ’01:
Proceedings of the tenth international conference on
World Wide Web, (Hong Kong, Hong Kong), pp. 150-
161, ACM Press, 2001.
H. Yang and T .-S. Chua, “Fada: find all distinct answers,”
in WWW Alt. ’04: Proceedings of the 13
th
international World Wide Web conference on
Alternate track papers & posters, (New York, NY,
USA), pp. 304-305, ACM Press, 2004.
G. Ramakrishnan, S. Chakrabarti, D. Paranjpe, and P.
Bhattacharya, “Is question answering an acquired
skill?,” in WWW ’04: Proceedings of the 13
th
international conference on World Wide Web, (New
York, NY, USA), pp. 111-120, ACM Press, 2004.
G. Neumann and F. Xu, “Mining natural language answers
from the web” Web Intelligence and Agent Systems,
vol. 2, pp. 123-135, January 2004.
D. Roussinov and J. Robles, “Learning patterns to answer
open domain questions on the web,” in SIGIR ’04:
Proceedings of the 27
th
annual international
conference on Research and development in
information retrieval, (Sheffield, United Kingdem),
pp. 500-501, ACM Press, 2004.
J. Lin and B. Katz, “Question answering from the web
using knowledge annotation and knowledge mining
techniques,” in CIKM ’03: Proceedings of the twelfth
international conference on information knowledge
management, (New Orleans, LA, USA), pp. 116-123,
ACM Press, 2003.
Richard T. Carback III ,” A Survey of Algorithms for
Question Answering on the Web”
http://trw.umbc.edu:16080/~rick/QAsurvey.pdf,
March 2005.
APPENDIX
1
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
2
Knowledge base (KB)
3
http://www.wikipedia.com
4
http://wordnet.princeton.edu
5
http://earth-info.nga.mil/gns/html/index.html
GEOGRAPHICAL QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM
313

Table 3: GeoNet Results.
Country
Total
ADM1
Total
ADM2
Total
ADM3
Total
ADM4
Total
Country
Recognized
State
Recognitized
Average
Recognizing
Value(ARV)
Angola 0 0 276 2 278 52.15 23.74 37.94
Argentina 0 0 608 9 617 63.2 48.62 55.91
Australia 0 0 15 0 15 80 80 80
Bahrain 32 0 0 0 32 28.12 18.75 23.43
Belgium 24 0 0 11 35 82.85 74.28 78.56
Bhutan 38 0 0 0 38 94.73 94.73 94.73
Bolivia 23 0 272 6 301 68.77 58.13 63.45
Brazil 52 0 193 2 247 51.41 24.29 37.85
Burma 33 0 0 0 33 36.36 30.3 33.33
Canada 28 0 281 9 318 76.1 68.55 72.32
Chad 28 0 0 0 28 60.71 50 55.35
China 80 2 364 1740 2186 68.57 41.12 54.84
Congo 23 0 0 0 23 95.65 78.26 86.95
All Cases 361 2 2009 1779 4151 66.176 44.326 55.251
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
314
