
THE DATA COLLECTION MODULE
OF THE AGENT BASED SEARCH SYSTEM (ABSS)
R. Baran, A. Zeja, T. Orzechowski, A. Dziech and M.Lutwin
Department of Telecommunications,AGH University of Science and Technology
al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Krakow, Poland
Keywords: JADE and JADE-LEAP platform, FIPA, OAI-PMH protocol.
Abstract: The main purpose of this paper is analysis and description of the Data Collection Module (DCM) that is the
main unit of the ABSS system. The aim of the DCM module is to process the metadata for the learning
resources and preparing them for the search algorithms. The components of the DCM module are analysed
with respect to technologies and standards used to their implementation. Advantages of proposed solutions
are also discussed. The subject of the paper is related to the Calibrate (Calibrating eLearning in Schools)
project.
1 INTRODUCTION
Subject of this paper is related to the CALIBRATE
project (Calibrate). The CALIBRATE (Calibrating
eLearning in Schools) is co-ordinated by European
Schoolnet (EUN) and supported by the European
Commission’s Information Society Technologies
Programme(IST). The key aim of this project is to
build the system to support the collaborative use and
exchange of learning resources in schools by
allowing teachers to access resources in a federation
of learning repositories. The ABSS system creates
e-learning platform for collaborative searching. The
Data Collection Module is one of the most important
parts of the ABSS system.
2 THE ABSS SYSTEM
The Agent Based Search System has advantages of
the JADE platform which comply with the latest
FIPA 2000 standard (FIPA). Implementation of the
JADE multi-agent platform is fully based on JAVA
technology and is distributed in Open Source under
LPGL license. The latest version of JADE has been
released on 14th March 2006 (JADE 3.4) (JADE).
The JADE platform interconnects hosts of the
federation - Learning Management Systems (LMSs)
and particular elements of the ABSS system
(especially, the main ABSS server) into the one
virtual machine. Each LMS creates a peripheral
container. Peripheral containers are then joined with
the main container of the Agent Platform. The host
of the main container is the ABSS server.
Containers of the JADE platform across the
ABSS system are illustrated in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: The JADE platform of the ABSS system.
The JADE platform creates an environment for
a group of various software agents, dedicated to
perform tasks for effective search. Tasks of the
ABSS agents can be divided into three main
functional categories:
Metadata harvesting, analysis and storing;
Management of user profiles;
Search.
451
Baran R., Dziech A., Orzechowski T., Dziech A. and Lutwin M. (2007).
THE DATA COLLECTION MODULE OF THE AGENT BASED SEARCH SYSTEM (ABSS).
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Internet Technology, pages 451-454
DOI: 10.5220/0001290604510454
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Search services implemented by agents must be
provided to users. There are two types of users
expected:
End users, searching by a web browser;
Developers, that use a search service API.
Web Services (WebS) and the Enterprise Java
Beans with JBoss Application Server (JBoss) were
used to implement search services. The JBoss
Application Server is considered as the best open-
source implementation of the Java 2 Enterprise
Edition technology. Web Services are dedicated to
support machine-to-machine interactions over
a network. They provide interoperability between
various software applications running on different
platforms.
Information processed by the Data Collection
Module is stored in databases under control of the
MySQL DBMS system. Two groups of databases
were used:
Metadata - designated to hold metadata
collected from the LMSs;
Users accounts - prepared for information
about profiles of registered users.
3 DATA COLLECTION MODULE
The Data Collection Module (DCM) is a set of the
following agents:
Collector Agent (CA) – a mobile agent
(multiple implementations);
Content Management Agent (CMA) – a static
agent (one implementation).
The Content Management Agent resides on the
main container and maintains information of all
connected LMSs. The CMA is responsible for
processing, arranging and storing the metadata that
describe the Learning Objects (LOs) - learning
resources provided by the federation. The Collector
Agent is used to gather metadata from the
repositories.
The Collector Agent migrates to the LMS when
registration process of peripheral container is
succeeded. Peripheral containers are established as
results of specialised services of ABSS-LMS
Component. Services of ABSS-LMS element can be
added and supported by the Spark-Core libraries.
Metadata repositories are accessed via the Open
Archive Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting
(OAI-PMH).
Architecture of the Data Collection Module is
depicted in Fig. 2.
Figure 2: Architecture of the Data Collection Module.
4 ABSS-LMS COMPONENT
Connection between the peripheral and the main
containers and communication between CA and
CMA agents are based on the modified JICP
protocol of the JADE-LEAP platform (JadeLEAP).
Communication must be secure and stable. The
SSL Java protocol and mutual authentication are
used to ensure security of the system. In addition, a
set of complex guard threads is used to perform
control of data flow between peripheral and main
containers.
The ABSS-LMS Component includes:
JadeLeap – the JADE-LEAP implementation;
Modified JICP protocol:
JICPSConnectionABSS;
JICPSPeerABSS;
LEAPIMTPManagerABSS;
Set of specialised procedures (including guard
threads)
Main configuration file with parameters of
ABSS-LMS Component (lms.properties).
There are two simple and recommended ways of
starting the ABSS-LMS component and reading the
lms.properties file:
As java applet;
As java servlet.
Parameters of the lms.properties file are divided into
six categories. The most important are
communication parameters:
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
452
Connection parameters – giving numbers of
ports used to communicate CA and CMA;
lms.abss_host;
lms.abss_port;
lms.local_server_port;
lms.local_client_port;
SSL/TLS parameters – indicating paths to the
digital certificates and giving a password:
lms.keystore_file;
lms.truststore_file;
lms.authentication_phrase
NAT parameters – giving IP address of the
NAT box:
lms.public_nat_ip.
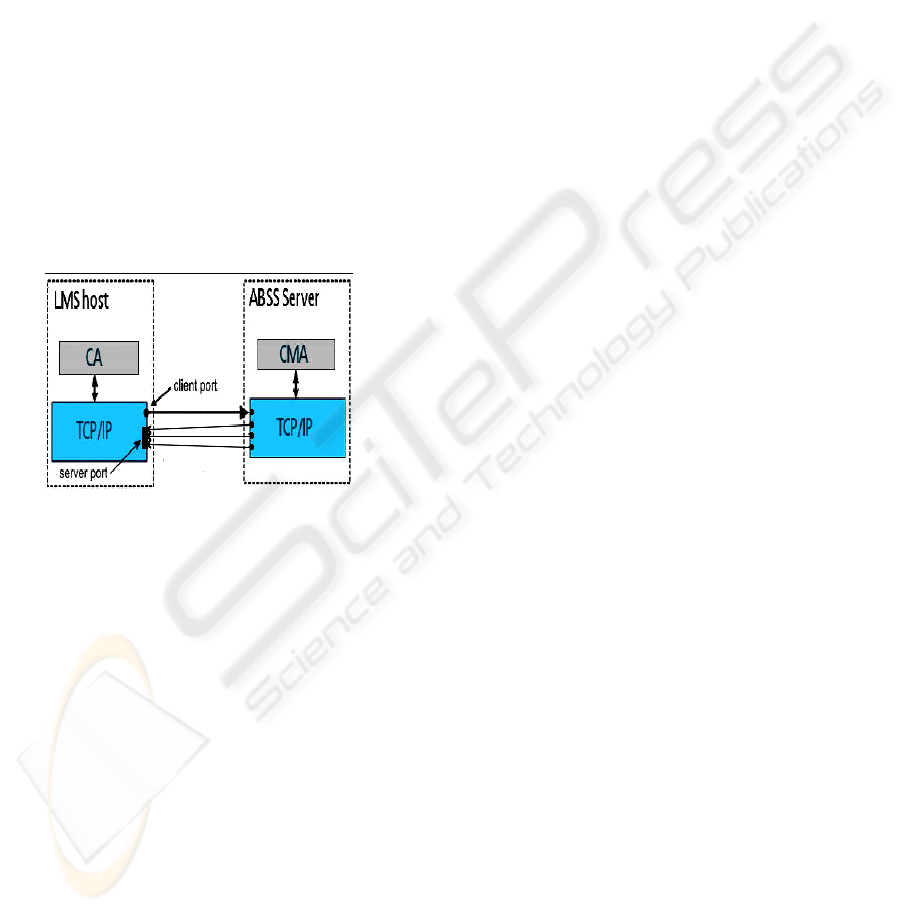
Communication between the peripheral and the main
containers requires two open ports on the LMS
hosts:
One public server port;
One client port.
Connections between the containers, during and
after the registration process, are depicted in Fig. 3.
Figure 3: Connections between the containers.
5 COLLECTOR AGENT
The Collector Agent is a mobile agent designed to
monitor metadata repositories of LMSs.
The Collector Agent is designated to:
Report a complete information about new,
registered LMS and their repository;
Monitor content of the repository and report
changes – new item was added, item was modified
or deleted;
Take a detailed information about added,
modified or deleted items;
Initially process gathered metadata.
Metadata are gathered using the Open Archive
Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-
PMH). The Collector Agent getting an instance of
local (LMS) implementation of OAI-PMH protocol.
The ListRecords method is used to harvest the
metadata. Responses of the ListRecords method,
given in a XML format, are conveyed to the parsing
module. The DOMparser from Xerces2 Java Parser
2.8.1 (Xerces2) has been chosen as a default parser
class of the Collector Agent.
The DOM models of each single record are
filtered and processed to select the required
information. These models are also used to check the
profile of harvested records. The profile should
match arrangements
of Celebrate Application
Profile.
The Collector Agent provides a special class,
called the MetaLOM, which properties refer to the
particular categories of required data. The
MetaLOM object is serialized and transmitted to the
CMA.
6 CONTENT MANAGEMENT
AGENT
The Content Manager Agent is a supervisor of the
data collection process. The main tasks of the CMA
agent are as follows:
Secure registration of the peripheral container;
Creation and transfer of the Collector Agent;
Management of the CA behaviour;
Receiving the MetaLOM objects;
Processing the harvested metadata and storing
them in especially designed database, called the
DB_LOMS database.
The CMA co-operates with three other agents of
the main container:
AMS – Agent Management System;
DF – Directory Facilitator;
Converter Agent.
The AMS agent of the ABSS system holds the
parameters of all registered peripheral containers
and working Collector Agents.
The Directory Facilitator agent of the ABSS
system indicates registered Converter Agents and
their services. This way, it gives possibility of
calling the appropriate service of selected Converter
Agent.
The Converter Agents are designed to prepare
the metadata for a particular search method. These
agents are specialized to operate in one selected
language.
THE DATA COLLECTION MODULE OF THE AGENT BASED SEARCH SYSTEM (ABSS)
453

7 CA-CMA CO-OPERATION
Messages between agents of the Data Collection
Module are exchanged in asynchronous mode. Every
message transferred in the CA-CMA system is
signed by the appropriate ontology. A set of valid
ontologies is defined by the LMSOntology class.
When migration of the CA is successfully done,
the “MOVE_COMPLETED” message is received by
the CMA. Next, the “START_COLLECT”
command is send to force the CA to start the
initialisation process - the ListRecords method is
used to collect
a complete content of the repository. Obtained
records are parsed and the appropriate MetaLOM
objects are signed by the “LOM_ADDED”
ontology name. Collection of transferred MetaLOMs
is followed by the “END_COLLECT” message.
From this moment, the CA agent is used to harvest
only these records which have been added, modified
or deleted.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The Data Collection Module plays a major role in
the ABSS system. The DCM module is based on the
JADE platform. The JADE platform, according to
the FIPA specifications, makes interoperability and
interconnections between particular elements of the
Data Collection Module easy and secure.
The mobile Collector Agents can be also treated as
significant advantage of the proposed solution. The
Data Collection Module and the other components
of the ABSS system, are implemented in JAVA
language, what makes the system open for the
different platforms.
The ABSS system described in this paper is in
the realization stage. The DCM module is working
with two test repositories. However, the ABSS-LMS
Component is ready to be used to connect next
machines to the federation. Specialized services
guarantee that communication is stable. Metadata
harvested from the repositories are parsed and stored
in DB_LOMS database. Stored information is
processed by the Converter Agents. Actually, the
search algorithms are developed. Algorithms are
implemented as new, dedicated to this purpose,
agents.
The main advantage of the ABSS system is an
open, agent-based and distributed architecture.
Provided researches show that such a system can be
efficient. More comprehensive conclusions can be
formulated when the ABSS system start to work
with federation of authentic repositories.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work presented in this paper is supported by the
European Commission under the Information
Society Technologies (IST) program – as part of the
CALIBRATE project, contract IST-28025.
REFERENCES
Calibrate:http://calibrate.eun.org/ww/en/pub/calibrate_proj
ect/home_page.htm
EUN. http://www.eun.org/portal/index.htm
IST:http://europa.eu.int/information_society/index_en.htm
ABSS. http://shalom.kt.agh.edu.pl
FIPA. http://www.fipa.org
JADE. http://jade.tilab.com
LMSs. http://www.eun.org/ww/en/pub/celebrate_help/
glossary.htm
Jboss AS. http://www.jboss.com/products/jbossas
WebS. http://www.w3c.org
LOs.:http://www.uwm.edu/Dept/CIE/AOP/learningobjects
.html
OAI-PMH:http://www.openarchives.org/OAI/openarchive
sprotocol.html
JadeLEAP.:http://jade.tilab.com/doc/LEAPUserGuide.pdf
Spark: http://minor.sourceforge.net/
Xerces2: http://xerces.apache.org/xerces2-j/
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
454
