
INTERFACING TASK SCHEDULING FOR
A B-LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
Roberto F. Arroyo
1
, José L. Garrido
1
, Miguel Gea
1
, Pablo A. Haya
2
and Rosa M. Carro
2
1
E.T.S.I. Informática y de Telecomunicación, Universidad de Granada, Granada, Spain
2
Escuela Politécnica Superior, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid,Madrid, Spain
Keywords: Task scheduling, b-learning, mobility, multi-view interfaces, ubiquity.
Abstract: Computer aided learning envir
onments is one of the main interests for computer scientists. Ambient
Intelligence represents a novel and promising paradigm to be applied to blended-learning systems. These
systems handle very dynamic contextual information that can be used in task scheduling to increase the
benefits of proactiveness and context-aware characteristics. This paper proposes the use of the calendar
metaphor to solve the scheduling of contextualised tasks in b-learning systems. In particular, the proposal is
centred on building of calendars on the basis of multi-view interfaces. The aim is to provide direct and more
suitable access to structured contextual information according to specific requirements. The proposal is
applied to a particular b-learning case study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ambient intelligence (AmI) systems are taking
relevance in the user-centred approach of computer
applications (Weiser, 1991, Ducatel, 2001). These
systems incorporate technology into an omnipresent
and transparent infrastructure for the implementation
of smart environments emphasizing on user-
friendliness, more efficient services, and support for
human and group interaction (Hess, 2003).
Important requirements for achieving a successful
AmI scenario are: context-awareness (Dey, 2000),
natural user interfaces (Montoro, 2004),
collaborative and dynamic spaces (Aldunate, 2002),
proactiveness (Oliver, 2000), shared knowledge
(Tazari, 2003), and usefulness (Pascoe, 1999).
The field of computer-aided environments is one
o
f the main areas of interest for computer scientists.
Since most learning activities are structured, the use
of a task-based approach for modelling the
environment, roles, responsibilities, rules, etc., can
be useful (Garrido, 2005). Context awareness means
that we are interested in identities, their location and
other related concepts such as tasks, roles and
artefacts. For example, relevant issues in an on-site
teaching activity are who the teacher is (i.e. Mairi),
where the classroom is (location), which students are
taking part, and what materials are being used
(adapted to artefacts). Additionally, blended learning
uses both virtual resources (course structures and
communication systems) and physical resources
(projectors, electronic whiteboards, notebooks,
lighting systems, etc.).
Although there is a great deal of interest in this
k
ind of system (since much effort is devoted to its
design and implementation), various problems arise
due to its expensiveness, technological difficulties
and lack of real support for human activity. For
example, one important activity in a traditional
learning model is resource management and scholar
time scheduling due to limitations of space, artefacts
and teachers. A usual method before courses start is
to plan a course calendar where resources are
assigned to each classroom and teacher. However,
unpredictable dynamic changes in this plan (a new
seminar, need for multimedia support, etc.) give rise
to new demands that must be solved in real time.
These changes sometimes involve the participation
of a new actor (playing the academic manager role)
who is responsible for solving these needs. Thus,
blended learning systems require efficient classroom
management and needs to be adapted to student
timetables dynamically. Usually, however, as the
flexibility in classroom scheduling increases, so do
the number of difficulties when managing
497
F. Arroyo R., L. Garrido J., Gea M., A. Haya P. and M. Carro R. (2007).
INTERFACING TASK SCHEDULING FOR A B-LEARNING ENVIRONMENT.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 497-504
DOI: 10.5220/0001292204970504
Copyright
c
SciTePress

classrooms and resources. When we think about task
scheduling, calendars immediately spring to mind,
whereby people make a note of tasks to be carried
out on either digital or traditional calendars. Due to
proactiveness, we must therefore manage strongly
contextualised tasks and let the system know as
much as possible about both the task and its context.
A reinforcement of task context in the scheduling
process will increase the system’s proactive
capacity.
This research work proposes the use of the
calendar metaphor under the ambient intelligence
paradigm in order to schedule contextualised tasks in
b-learning systems. In particular, the proposal
addresses the design and implementation of
calendars that provide a multi-view interface for
homogeneous data access; the system can create
queries for solving scheduling restrictions or
providing specific information to the users while
planning the task. The advantages of such an
approach is the additional flexibility which is
obtained since certain routine tasks (such as
checking when each actor and resource is free) are
dynamically solved in real time depending on
changing constraints.
The second section of this paper analyses general
technological methods for learning. After that,
Section 3 introduces a general description of the
case study, i.e. AmI system for b-learning, as well as
the concrete problem to be treated with, i.e. task
scheduling. Section 4 proposes the use of the
calendar metaphor for context-aware activity
scheduling. Section 5 shows the design and
implementation scheme carried out on the basis of
the previously described case study. Finally, Section
6 presents the main contributions and outlines future
work.
2 COMPUTER-BASED
LEARNING
Although asynchronous e-learning emphasizes a
one-to-one style of communication which has many
educational advantages, it is not without its
disadvantages: online students often experience
feelings of isolation and insecurity which can only
be overcome by frequent support from the instructor
or other students. Synchronous (meeting and
collaborative) tools, however, can help to improve
group awareness by increasing the feeling of a
virtual meeting.
Nevertheless, although this model is currently
useful for many students, the real situation is far
from initial expectations. The reasons for this gap
between hopes and realities are probably technical
(e.g. Internet bandwidth, cost, pedagogical
methodologies, standards), cultural (e.g. relevance of
colleges and institutions), and sociological (e.g. the
importance of personal relationships in any human
activity, including learning). Efforts to integrate
collaboration capabilities in Web-based courses have
already been done. For example, in (Carro, 2003),
adaptation methods and techniques have been used
for the personalization of the course contents, the
navigational options and also different collaboration
aspects. It consists not just of putting adaptive
courses and collaborative tools together, but of
integrating adaptation and collaboration in a
seamless way. A new emerging paradigm has in fact
been proposed, which merges the benefits of each
learning model, and blended learning has now
become the following step, mixing on-site classes
with on-line activities.
Importance of ubiquitous information access and
management is increasing due to the creation and
implantation of Wireless Local Area Network on
Campus and Centres. The ActiveCampus (Sohn,
2006) project is an example of using location-based
services for educational networks enabling
collaboration and services between students and
teacher.
3 LEARNING SCENARIOS
Active spaces are physical places part of the Spanish
Research U-CAT Project (Ubiquitous Collaborative
Adaptive Training). The intended goal is the user
and group’s support for: situated activities,
understanding context and the available resources to
carry out these learning objectives. Some relevant
objectives are the following (Haya, 2004): the
framework to be provided in order to support a
seamless integration among pervasive components
that use heterogeneous technologies (physical
devices and TCP/IP network); use of adapted
interaction mechanism such as natural spoken
interfaces (Montoro, 2004); application of
adaptation techniques to recommend activities to
users according to the users' context (Martín, 2006);
development of authoring tools to facilitate the
creation of adaptive hypermedia (Carro, 2004); and
task support and intelligent behaviour using agents.
As ubiquitous systems, Ambient Intelligent
environments are composed by a great number of
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
498
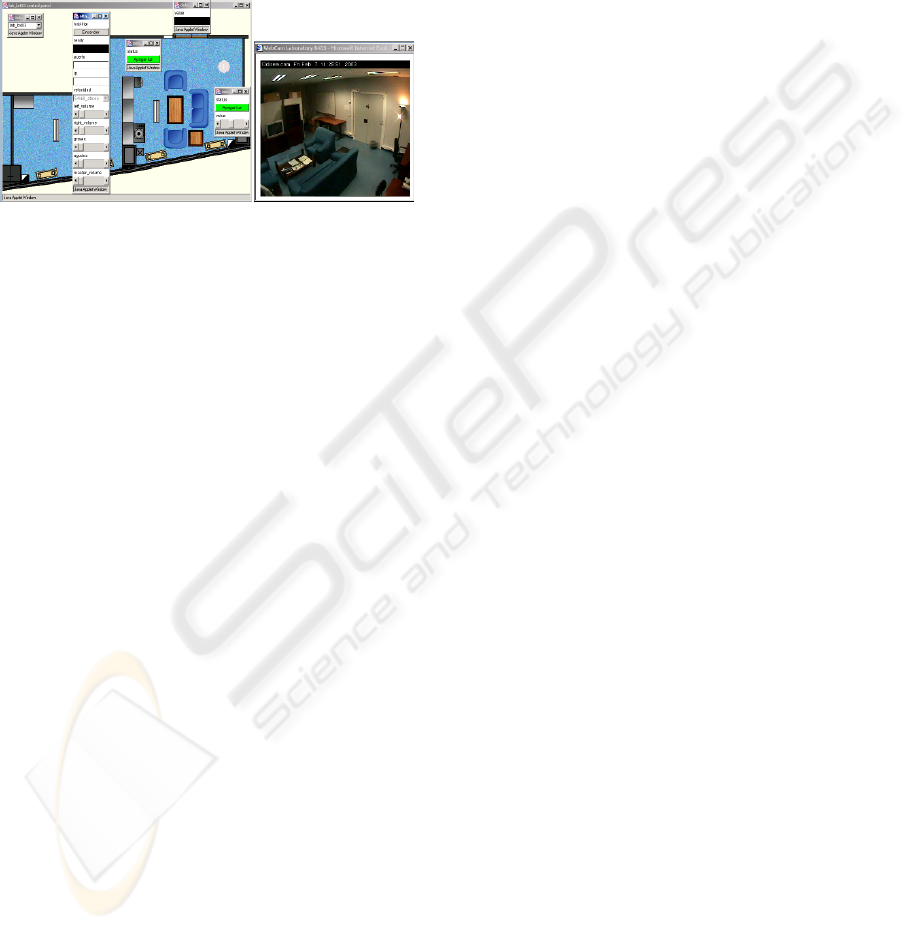
sensors and actors. To separate data processing of
sensors at a low-level from the high-level
applications, we need to introduce a middleware
layer to fetch sensor's data and convert them into a
format comprehensible by the application, and
distribute it among the interested applications. Labs,
as shown in Figure 1, can be controlled using web
interfaces or natural spoken language.
Figure 1: The U-CAT laboratory.
The framework proposed is a context layer based
on the blackboard metaphor (Haya, 2004), which
stores a global data structure representing a world
model. This model stores all the relevant
information. This layer is used for the asynchronous
information querying mechanism too.
This approach has two advantages: it is a light
coupling between producer and consumer (the
interpretation is dependent of consumer, and a client
is not aware of the rest), and the model is easily
extensible. This blackboard receives and returns
XML information using HTTP protocol. The
blackboard is able to store generic entities and theirs
relations using a basic information mechanism of
insertion/querying.
3.1 Task Scheduling
The aim is to provide context aware scheduling of
collaborative tasks. In the AmI scenario, presence
classes have similar behaviour as tutoring where
lecturer and students organize meetings for problem
solving. Therefore, the expected intelligence
behaviour have to been done by software agents
identifying current state and restrictions. This task is
context dependent and it can be solved knowing
current tasks, locations and state of actors and
physical devices involved in these activities.
For example, the teacher Mairi decides that next
week, the presential Programming course will be
held in a laboratory instead of the usual classroom to
solve practical problems. The system should have a
decision support mechanism to help her in the
following way: When is Mairi free? When are the
students free? Which laboratories are free? Do these
laboratories have the required features?
These questions should at least be solved (with
or without the aid of involved users) so that these
situations can be managed dynamically. It should be
noted that these resources are shared by different
users, and so once these classes have been fixed, the
other users should be able to see the result.
Therefore, the users involved (teacher and students)
should be notified about the date and the location of
the class. Scheduling and planning bearing in mind
preferences or restrictions have been widely studied
(Brzozowski, 2006) with a range of different
techniques. Scheduling refers to allocation and
cancellation tasks. Since scheduling tasks (i.e.
classes) may change according to a new scenario, it
is therefore important to obtain an efficient
notification mechanism and to know the context of
users in order to understand the current state and
future availability.
Usability on computer-mediated scenarios means
that different goals must be achieved: continuous
notification, due to the fact that the availability of
resources can change constantly and the actors must
know the variations which have occurred according
to their preferences; hierarchical planning, social
support demands that priorities be identified in order
to achieve the best solution (precedence of teacher
restriction rather than student restrictions); usability
issue, although the information managed is complex,
it should be easy to use and understand, and adapted
to each available device (PDA, phone, etc.) and user
preferences; and variable granularity, temporal
planning means that time should be dealt with at
different levels of perception (Ning, 2002) since
planning can cover days, weeks or even semesters,
and so the proper level of detail is needed in each
case (hiding irrelevant information from the user).
The fuzzy nature of human time (Payne, 1993),
however, must be considered due to human
interaction. Kutar (2002) addressed the difficult task
of managing statements with both contextual and
fuzzy semantics, such as “on the same day” might
be.
Scheduling multiple activities is a complex task
requiring the collaboration of system users and a
great degree of resource management by the system.
This system (like many others with a large number
of users attempting to carry out collaborative
activities) generates a series of widely studied
inherent problems (Dix, 1998). Since the users we
deal with have different needs and abilities, we need
a system which is easy to use but which has
powerful scheduling capacities due to the
INTERFACING TASK SCHEDULING FOR A B-LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
499

enormously complex system we are working with.
In the following section, we will study a traditional
scheduling mechanism which can be used to solve
both problems.
4 CALENDAR AS AN
INTERFACING MECHANISM
FOR TASK SCHEDULING
A calendar has traditionally been considered as a
tool for noting down and remembering events and
meetings on a temporal dimension (viewed by
day/week/month/year). Various types of calendars
are available and these are used for planning
individual and also collaborative events (Tullio,
2002, Palen, 1999). This is a well-known paper
metaphor for representing activities on a temporal
axis. Nowadays, computer technology can transfer
these calendars to any artefact (PC, mobile phone,
PDA) or applications (mail system, Web based), and
important effort has been focused on
synchronisation mechanisms (i.e. Evolution, Mozilla
Sunbird). This synchronisation could be present in
two forms: synchronisation between the same user’s
various calendars, and synchronisation between
different users’ calendars. Both these cases reflect
the fact that one person may have different calendars
or schedules for noting down events according to
their nature (job, personal, leisure, etc.) or their
location at that moment (office, home, meeting,
etc.), and they reflect the need for global calendar
coherence between system users in order to enable
the capability of semi or fully automated scheduling.
An interesting example is the digital family
calendar (Neustaedter, 2006) (as an alternative to a
traditional one) has received good results as a
planning tool. An academic planning calendar shares
four similar features with a family calendar: Firstly,
it has been designed as a basic context-aware
mechanism: the simplicity and intuitiveness of the
calendar is an advantage to the user (since it is easy
to use and recall). The complexity and error rate can
be reduced if the calendar is designed to perform
specific tasks (Norman, 1998). Secondly, it should
be flexible enough to support different kinds of tasks:
planning involves capturing, organizing, and
integrating different types of information (to do lists,
stick notes, paper reminders) using the calendar. The
digital model should allow these combinations to
include different organisational schemes and
visualizations. Thirdly, it should offer coordination
support: task planning involves a group (e.g. a
family, department, school) where decisions should
be reached by general consensus. Deliberation is
carried out by phone, in person, or using other
technological instruments (email, instant-
messenging), and negotiation is the basis for this
agreement. And fourthly, it should consider location
awareness: in the case of the family calendar, the
digital calendar has a physical placement and each
occupant knows where it is.
However, some additional features should also
be present in ubiquitous academic systems. These
are scalability: a b-learning system can contain
more than a hundred participants. Since task
allocation for each user is huge, the system must
therefore manage only relevant information
(Mackinlay, 1994) with an expected time response
which is independent of the number of users;
privacy (Boyle, 2003): information should follow a
restriction policy, and must also administer time
intervals for private use (users can decide whether to
make tasks visible to others); and remote
notification: information may be obtained anywhere
at any time. The system should notify users of when
the relevant tasks are due to start and end. In order to
prevent annoying situations (Werle, 2002) the
notification mechanism should be defined by the
user.
4.1 Calendar Definition
When people use calendars to schedule tasks or
other kinds of appointments, they unconsciously
perform different operations on the calendars. For
example, when two people are trying to arrange a
meeting in a given week, they try to find a common
free slot in both calendars. Unconsciously, what they
do is to combine both calendars for that week, and
search for free slots. Similarly, we can outline two
additional operations (Harris, 1998) intersection and
difference. The first is useful to see the common
events between calendars, and the second is used to
exclude certain kinds of events from a calendar.
The On-line Cambridge Dictionary defines a
calendar as “a list of events and dates within a
particular year that are important for an
organization or for the people involved in a
particular activity”. While this is the most general
intuitive meaning for the word calendar, we will
expand this concept to a more general definition
which is useful for our needs in our environments.
We therefore define calendar as a list of entities and
dates that are important for scheduling other
entities.
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
500

This new calendar definition is useful for
understanding what the calendar is for and what kind
of elements are being recorded. As we mentioned
previously, traditional calendars trace a person’s
tasks, but we are not only limited to this: we can also
have calendars for objects as well as humans.
We denote the calendars as C
i
, where C
represents the calendar and the subscript symbolizes
an instance. We define three operations over them:
union (
∗), intersection ()) and difference (\). Figure 2
shows examples of these operations on personal
calendars with noted down tasks. Therefore, C
a
is
Mairi’s calendar and C
b
is Pádrig’s, and tasks have
been noted down on both. Letters are used to
symbolize the different tasks: e.g. task A may
correspond to the task GiveClass.
This system also has collaborative tasks which
are shared between several people. It must be
remembered that these tasks are common to more
than one personal calendar yet refer to the same task
element, and this is important for a correct
understanding of calendar operation within the
system.
Figure 2: Calendar operations (letters show individual
4.2 Case Study: A b-Learning
We need the system to be capable of managing the
recorded in the system.
l as the system needs more
con
mework (Garrido, 2005), we have
defi
t use all the
sem
f AmI environments provide to
imp
tasks, and question marks symbolize tasks which have
been marked as private).
Environment
available system resources and to represent the
activities performed by each user in a given time
stamp. Due to the problem domains which we aim to
solve, we can use time slots lasting an hour and so
we can divide a day into 24 equal time slots. Any
entity can be noted down with a precision of an hour
although it can conclude at any time after it starts.
For example, a planned class lasting two hours may
finish after an hour and a half, and so it must be
The entities recorded on the calendar cannot be
restricted to a text labe
cise knowledge about what will happen and what
will be needed. As a proactive system, it must be
able to infer future events and for this, it needs to be
as aware as possible about their environment. For
these reasons, each record must be associated with a
semantic related to specific system elements, with
the possibility of navigating, interconnecting, linking
and tracing them.
Based on the AMENITIES conceptual and
methodological fra
ned a design model (Arroyo, 2006) that includes
the structured semantic of the task modelling as the
primary class context on AmI systems.
In order to correctly integrate a scheduling
system within a task model, we mus
antic capacity we have available. We are able to
provide the necessary flexibility in the calendar’s
tools and to reduce the intrusive proactivity with
increased knowledge about the activities occurring
in the system. Figure 3 shows the established link
between calendar scheduling and system modelling,
and the correspondence between this and the
modelled real world. This figure also shows Mairi’s
calendar and the planning of a future class has been
highlighted. As this is a relation between the task
and the time slot (and not only a label), we have
increased semantic information about it so that we
know who is involved in it, which roles or resources
are needed, etc.
We must emphasize the benefits that the
semantic web o
licit scheduling, simplifying the overhead cost of
users in planning tasks. Since our AmI model
establishes a semantic network which merges
ubiquitous and task-driven elements, when a task is
defined, we can explore this network by navigating
through the links and extracting the information that
we consider to be important, whether ubiquitous or
related to the task model. For example, if we plan a
class in classroom 3-A on Wednesday with Mairi as
a teacher, even though Mairi notes down that she
will have this classroom, we can create a calendar
for classroom 3-A by showing the people who will
be in it, using the information provided by all the
system users to complete new calendars. We should
not forget that the system is dynamic and that, for
example, users move around the system. The
ubiquitous location of users can be traced using
these calendars since they store not only future but
also past and present events.
INTERFACING TASK SCHEDULING FOR A B-LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
501
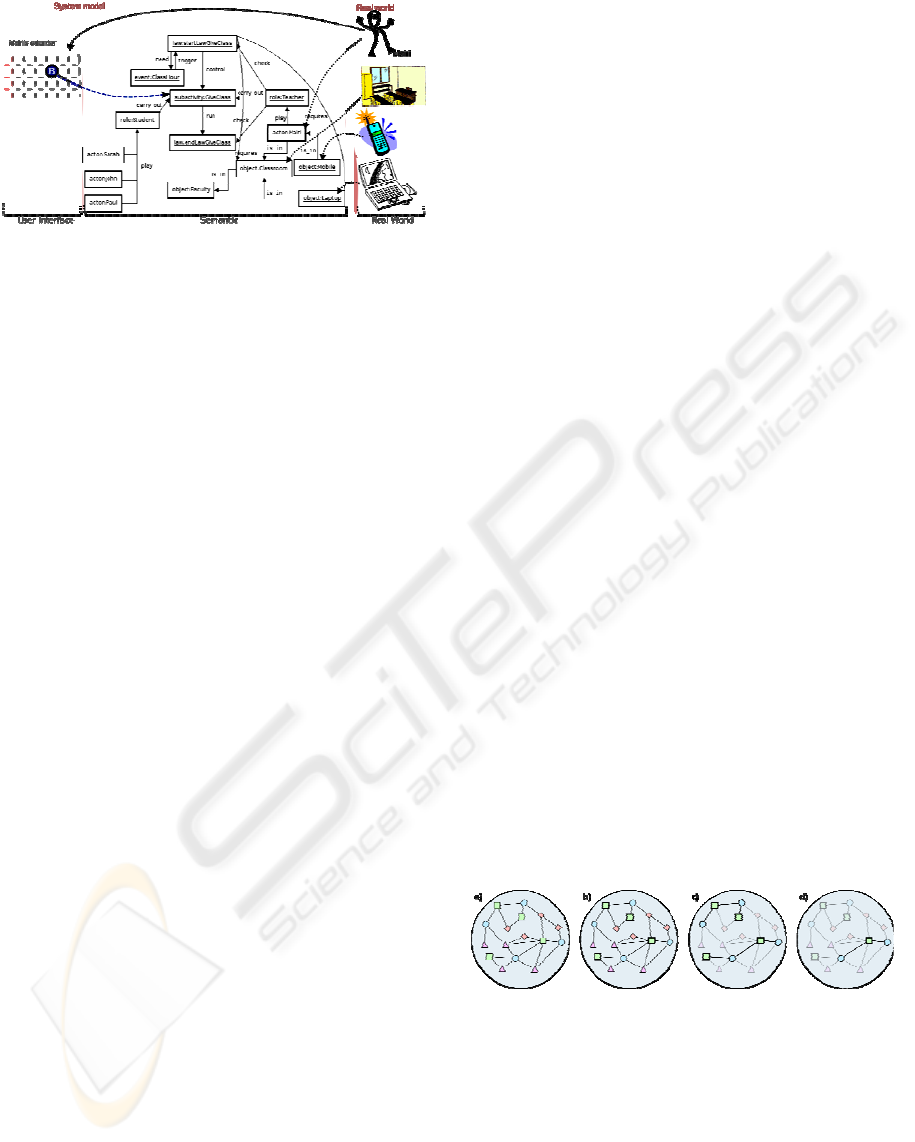
Figure 3: The calendar annotates semantic information
about task.
contextual information, we can show how
the di
source
other words,
Fig the
mantic net associated to calendar queries. The
pe
) and
2.
be the
This de
which is ab define multip ws of the system
as
a
cal
Now that we have presented our conceptual
model for
fferent calendars can be constructed from the
semantic network. As we defined in Section 4.1, a
calendar is not only useful for people as we define
the calendar for any entity. We consider the entire
semantic network to be a set S and any calendar C is
a subset of S. We define the following two attributes
for any calendar C:
Source: we define source as the entity
interested in the calendar. We denote the
source with
superscript (C ). For
example, we can write Cactors to define
those people (actors) who will be the entities
interested in the calendar. We can assign
attribute-value pairs to the source list and so
we can write C
actors
t
{name=Mairi}
to define a
calendar where Mairi is the interested entity.
We can use equal to, different from or a list
of values for the attribute. A source must be
defined to create a calendar.
Target: we define target as the entities that
are important for the source. In
the entities we aim to be recorded in the
calendar’s time slots. We denote the target
with subscript (C
target
). If the target is not
present, then all the entities are of interest to
the source. For example, C
actors
tasks
will
construct a calendar for the actors where their
associated tasks comprise the entities to be
noted down on it. We can specify attribute-
value pairs as we did for the source. For
example, if we want to construct a calendar
for the actors containing any task except the
task PlanClass, we define the calendar C
actors
tasks→{name≠ PlanClass}
.
ure 4 represents the construction of
se
o
rations defined in Section 3.1 are implicit in the
notation introduced here. We can establish the
following equivalences between this notation and
the previously used algebraic notation:
1. If we have a calendar containing Mairi’s
tasks (C
a
or C
actors
t
{name=Mairi}
tasks
another containing Pádrig’s tasks (C
b
or
C
actors
t
{name=Pádrig}
), we can define C
a
∗
C
b
as C
actors
t
{name=(Mairi,Pádrig)
tasks
}
.
If we have a calendar containing Mairi’s
tasks, we can consider it to
intersection of the calendar containing
all the actors’ tasks (C
a
or C
actors
tasks
) and
the calendar containing Mairi as an actor
(C
b
or C
actors
t
{name=Mairi}
), and therefore
C
a
) C
b
= C
actors
t
{name=Mairi}
tasks
. Similary,
if we want the task of all actors except
Mairi, we can define the result as C
a
\ C
b
= C
actors
t
{name⎯Mairi}
tasks
.
finition presents a degree of freedom
le to le vie
different calendars, covering different needs by
relying on the same information in a homogeneous
way. For example, if we want to check on where
Mairi will be, we can generate a calendar such as
C
actors→{name=Mairi}
locations
. This sentence will create a
calendar where Mairi is the actor we are interested in
(source) and the locations are the entities (target).
We can therefore conclude that by using this
calendar definition, we expand the uses which
endar has traditionally had. By abstracting
interested entities from people to any other kind of
element, we can specify a wider range of calendars,
and use different conceptions for them, generating
multiple homogeneous views of the global
annotation system. In this way, we increase calendar
flexibility, and are able to define which entity is
interested in representing which by means of a timed
tabular view.
Figure 4: Construction of a calendar as a series of queries:
a) the full semantic network; b) the semantic network with
squares as the source entities (for example, if the squares
correspond to actors, we can denote them as C
actors
); c) the
target established as the circles entities (for example, if the
circles correspond to the tasks, we can notate them as
C
actors
tasks
); and d) an individual specific square chosen as
the source (for example, if the chosen square is Mairi, we
can notate it as C
actors
t
{name=Mairi}
tasks
).
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
502

5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
In this paper, we have presented the definition and
address
que
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is partially supported by a Spanish
Weiser, M. (1991). The computer for the 21st Century.
Du Ambient
He cation of a
De bowd, G.D., Brown, P.J., Davies, N., Smith,
WORKS
implementation of a calendar as an interfacing
mechanism to be applied to b-learning systems. This
mechanism is able to benefit from an enriched
context by adding entities of the task model
paradigm as the primary context. We conclude that
calendars are useful for scheduling activities on
these complex environments, and which fulfil the
requirements that a scheduling system must provide.
This calendar model solves the main drawbacks of
traditional models, such as synchronisation issues,
non-flexible records and ubiquitous locations. In
addition, we have describe the implementation of a
real system so that the calendar retains all its
functionality at an appropriate abstraction level,
without modifying the existing lower layers.
By way of future work, we intend to
stions related to adaptive and user-friendly
interfaces as soon as the system has been provided
with a scheduling-driven proactiveness to help the
end user by notifying and resolving conflicts. Our
aim is to implement the task re-planning and the
notification caused by the cancellation of other
planned tasks. We also aim to include the
elimination of the time sampling on the user’s side
in an attempt to eliminate the fixed time slots,
thereby providing a greater scheduling flexibility.
R&D Project TIN2004-03140, Ubiquitous
Collaborative Adaptive Training (U-CAT).
REFERENCES
Scientific American. 94-110.
catel, K. et al. (2001). Scenarios for
Intelligence in 2010, tech. report, Information Society
Technologies Advisory Group (ISTAG), Inst. of
Prospective Technological Studies (IPTS).
ss, C.K., & Campbell R.H. (2003). An appli
context-aware file system. Pers Ubiquit Comput 7:
339-352
y, A.K., A
M., & Steegels, P. (2000). Towards a better
understanding of context and context-awareness.
Workshop of Context-Awareness (CHI-2000).
Montoro, G., Haya, P.A., & Alamán, X. (2004). Context
adaptive interaction with an automatically created
spoken interface for intelligent environments.
INTELLCOMM 04. LNCS-3283.
Aldunate, R., Nussbaum, M., & González, R. (2002) An
Agent-Based Middleware for Supporting Spontaneous
Collaboration among Co-Located, Mobile, and not
necessarily Known People. Workshop on "Ad-hoc
Communications and Collaboration in Ubiquitous
Computing Environments" ACM CSCW.
Oliver, N. (200). Towards Perceptual Intelligence:
Statistical Modeling of Human Individual and
Interactive Behaviors. PHD Thesis. MIT Media Lab.
Tazari, M.R., Grimm, M., & Finke, M. (2003). Modeling
user context. 10th International Conference on
Human-Computer Interaction (HCII).
Pascoe, J., Ryan, N., & Morse D. (1999). Issues in
Developing Context-Aware Computing. HUC'99,
LNCS 1707, pp. 208-221.
Garrido, J.L., Gea, M., & Rodríguez, M.L. (2005).
Requirements Engineering in Cooperative Systems.
Requirements Engineering for Socio-Technical
Systems. Chapter XIV. IDEA GROUP INC. (USA),
226-244.
Garrido, J.L., Paderewski, P., Rodríguez, M.L., Hornos,
M.J. & Noguera, M. (2005). A Software Architecture
Intended to Design High Quality Groupware
Applications. 4th International Workshop on
System/Software Architectures (IWSSA'05) -
Proceedings of SERP'05. Las Vegas (USA), 59-65.
Arroyo, R.F., Gea, M., Garrido, J.L., & Haya, P.A. (2006).
A Task-Driven Design Model for Collaborative AmI
Systems. In Thibaud Latour and Michaël Petit, editors,
Proceedings of the CAiSE'06 Workshops and Doctoral
Consortium, 969-983. Presses Universitaires de
Namur. Workshop: UMICS'06.
U-CAT project web page. http://orestes.ii.uam.es/ucat/
Haya, P.A., Montoro, G., & Alamán, X. (2004). A
prototype of a context-based architecture for
intelligent home environments. International
Conference on Cooperative Information Systems
(CoopIS 2004), Larnaca, Cyprus. October 25-29,
2004. LNCS 3290.
Montoro, G., Alamán, X. & Haya, P.A. (2004). Spoken
interaction in intelligent environments: a working
system. Advances in Pervasive Computing. Alois
Ferscha, Horst Hoertner and Gabriele Kotsis, Eds.
Austrian Computer Society (OCG).
Carro, R.M., Ortigosa, A., Martín, E., Schlichter, J.
(2003): Dynamic Generation of Adaptive Web-based
Collaborative Courses. En: Groupware: Design,
Implementation and Use. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science 2806. Eds: Decouchant, D. and Favela, J.
(Springer-Verlag), 191-198.
Martín, E., Carro, R.M., Rodríguez, P. (2006): A
Mechanism to Support Context-based Adaptation in
M-Learning. En: Innovative Approaches for Learning
and Knowledge Sharing. LNCS 4227. Eds: Nejdl, W.
and Tochtermann, K.(Springer-Verlag), 302-315.
INTERFACING TASK SCHEDULING FOR A B-LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
503

Carro, R.M., Freire, M., Martín, E., Ortigosa, A., Paredes,
P., Rodríguez, P., & Schlichter, J. (2004). Authoring
and Dynamic Generation of Adaptive E-Courses. En:
Web Engineering. Lecture Notes in Computer Science
3140. Eds: Koch, N., Fraternali, P. and Wirsing, M.
(Springer-Verlag), 619-620.
Brzozowski, M., Carattini, K., Klemmer, S.R., Mihelich,
P., Hu, J., & Andrew Y. Ng. (2006). GroupTime:
preference based group scheduling”. SIGCHI
conference on Human Factors in computing systems
CHI '06.
Ning, P., Wang, X. S., & Jajodia, S. (2002). An Algebraic
Representation of Calendars. Annals of Mathematics
and Artificial Intelligence 36, 1-2, 5-38.
S. Payne (1993). Understanding Calendar Use. Human-
Computer Interaction, 8(2):83-100
Kutar M., Britton C. & Nehaniv C. L. (2000). Specifying
Multiple Time Granularities in Interactive Systems.
Proceedings DSV-IS 2000, LNCS Springer Verlag,
Limerick, Ireland, 51-63.
Dix, A., Ramduny, D., & Wilkinson, J. (1998). Interaction
in the Large. In Interacting with Computers,11(1) p.9-
32
Tullio, J., Goecks, J., Mynatt, E. D., & Nguyen, D. H.
(2002). Augmenting shared personal calendars. In
Proceedings of the 15th Annual ACM Symposium on
User interface Software and Technology (Paris,
France). UIST '02. ACM Press, New York, 11-20
Palen, L. (1999). Social, individual and technological
issues for groupware calendar systems. In Proceedings
of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in
Computing Systems: the CHI Is the Limit (Pittsburgh,
Pennsylvania, United States). CHI '99. ACM Press,
New York, NY, 17-24
Beard, D., Palaniappan, M., Humm, A., Banks, D., Nair,
A., & Shan, Y. (1990). A visual calendar for
scheduling group meetings. In Proceedings of the
1990 ACM Conference on Computer-Supported
Cooperative Work (Los Angeles, California, United
States, October 07 -10, 1990). CSCW '90. ACM Press,
New York, NY, 279-290.
Neustaedter, C. & Bernheim Brush, A. J. (2006). "LINC-
ing" the family: the participatory design of an inkable
family calendar. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
(Montréal, Québec, Canada). R. Grinter, T. Rodden, P.
Aoki, E. Cutrell, R. Jeffries, and G. Olson, Eds.
CHI'06. ACM Press, New York, NY, 141-150.
Norman, D. (1998). The Invisible Computer, Cambridge,
MA, MIT Press, 51-68.
Mackinlay, J. D., Robertson, G. G., & DeLine, R. (1994).
Developing calendar visualizers for the information
visualizer. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual ACM
Symposium on User interface Software and
Technology (Marina del Rey, California, United
States, November 02 - 04, 1994). UIST '94. ACM
Press, New York, NY, 109-118
Boyle, M. (2003). A Shared Vocabulary for Privacy. In
Workshop on Ubicomp Communities: Privacy as
Boundary Negotiation. Held as part of the
UBICOMP'2003 5th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Computing, Seattle, October 12.
Werle, P., & Jansson C. G. (2002). Achieving Non-
intrusive Notifications in a Ubiquitous Service
Environment. In Proceedings of RadioVetenskap och
Kommunikation, RVK 02. Stockholm, Sweden.
Harris, J.W., & Stocker, H. (1998). Handbook of
Mathematics and Computational Science. New York:
Springer-Verlag.
On-line Cambridge Dictionary.
http://dictionary.cambridge.org/
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
504
