
DATA QUALITY IN XML DATABASES
A Methodology for Semi-structured Database Design Supporting Data Quality
Issues
Eugenio Verbo, Ismael Caballero
Indra Sistemas
UCLM- Indra Research and Development Institute
Ronda de Toledo s/n – 13004 Ciudad Real, Spain
Eduardo Fernandez-Medina, Mario Piattini
ALARCOS Research Group
Information Systems and Technology Departament
UCLM- Indra Research and Development Institute
Paseo de la Universidad 4 s/n – 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain
Keywords: Data Quality, XML databases, design methodology, semi-structured data.
Abstract: As the use of XML as a technology for data exchange has widely spread, the need of a new technology to
store semi-structured data in a more efficient way has been emphasized. Consequently, XML DBs have
been created in order to store a great amount of XML documents. However, like in previous data models as
the relational model, data quality has been frequently left aside. Since data plays a key role in organization
efficiency management, its quality should be managed. With the intention of providing a base for data
quality management, our proposal address the adaptation of a XML DB development methodology focused
on data quality. To do that we have based on some key area processes of a Data Quality Maturity reference
model for information management process definition.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the World Wide Web Consortium (Bray et al.,
1998) approved the first edition of the XML
standard in 1998, its use has spread up to become the
standard de facto for data exchange due to the
flexibility and richness that XML provides to
capture semantic aspects of the application domain.
However, XML can also be used as a data
sto
rage technology. A good example of that kind of
use would be the OpenDocument standard (OASIS,
2006) for the specification of electronic documents.
Due to the great amount of data that are
tran
smitted in XML format, it is reasonable to think
that storing that data directly in DBMS adapted to
the characteristics of XML will improve the
performance of the retrieval and preparation of data
for its trasmission.
On the other hand, since data is one of the main
asset
s that organizations hold (Huang et al., 1999),
databases schemas should guarantee the quality of
the contained data because the proper working of the
information system (IS) could depend, in more or
lesser extent, on this feature.
A way to achieve that goal could be to enrich
d
ata items with metadata that would serve as a basis
to assess data quality according to the selected
quality criteria or quality dimension. Doing so, data
value quality, i.e. how adequately data values
represent real world objects or facts, could be
improved.
Although data quality is often associated to data
v
alue quality, even completely correct and valid data
could be faulty if they are supported by an invalid
data model (Levitin and Redman, 1995). Hence the
possible solution to those problems could go through
integrating quality aspects into the database design
process in order to get a resulting product that
satisfies the system quality requirements. Thus, data
model would be designed in a proper way so that the
117
Verbo E., Caballero I., Fernandez-Medina E. and Piattini M. (2007).
DATA QUALITY IN XML DATABASES - A Methodology for Semi-structured Database Design Supporting Data Quality Issues.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - Volume ISDM/WsEHST/DC, pages 117-122
DOI: 10.5220/0001337601170122
Copyright
c
SciTePress
number of defects propagated to the final
information product would not increase.
Our work comprises those concepts since we
propose data quality integration inside some
processes of CALDEA, a reference model defined in
(Caballero and Piattini, 2007), in order to create a
XML DB design methodology with data quality
support.
The remainder of the paper is structured as
follows: in section 2 the CALDEA reference model
is presented, in section 3 our proposal is shown, and,
lastly, in section 4 some conclusions are
summarized.
2 CALDEA
CALDEA is a Data and Information Quality
Management Maturity Model that can be used as a
reference for assessing and improving data quality
through the Information Management Process
concept, a specialization of the Software Process
(Fuggeta, 2000) for the Information and Data
Quality Management. This IMP is composed of two
kinds of subprocesses: a) data product fabrication
processes (MfP) and b) data quality management
processes (MnP), centered in data and information
quality.
CALDEA is the reference model for this
framework. It is structured in Key Area Processes
(KPA) in the same way as CMMI is. Each one of
these KPAs can belong to one or both of the two
kinds of subprocess previously defined.
Each KPA defines a set of activities which
identifies a collection of elements. For each activity,
these elements are: a) input and output products, b)
techniques and tools, c) workers and d) execution
time. The CALDEA KPAs used in the proposed
methodology and its corresponding acronyms can be
seen in
Table 1.
The URM KPA enumerates activities aimed to
compile, understand and document user require-
ments in order to drive the information management
process towards the user point of view.
The goal of the DSTM KPA is the identification,
definition and characterization of data sources and
destinations for the generated information products.
In the AIMPM KPA, it is done the management
of the databases and data warehouses of the
information system.
In the DIQM KPA, the information and data
quality management processes of the IMP are
implemented.
Table 1: CALDEA Definition level KPAs.
3 XML DATABASE DESIGN
METHODOLOGY WITH DATA
QUALITY SUPPORT
3.1 Methodology Steps
We have defined a semi-structured DB design
methodology divided in the following ten steps:
1. Define user requirements.
2. Define quality user requirements.
3. Design semi-structured DB schema.
4. Identify data quality dimensions of the DB
application domain.
5. According to the data quality dimensions
identified in the previous step, extend database
schema with quality data extension
mechanism.
6. Identify data sources.
7. Adapt data input format to the database
schema.
8. Define context dependant measures to
evaluate input data quality.
9. Establish a threshold for input data quality.
10. Apply quality measures to input data and only
store those whose measure results are above
the threshold previously defined.
These ten steps are the result of adapting
different activities of CALDEA KPAs. In the
following sections, we summarize tasks and
techniques to be used during the application of the
proposed methodology.
3.2 User Requirements Management
(URM)
This KPA covers points 1 and 2 of the proposed
methodology.
Acronym Meaning
URM User Requirements
Management
DSTM Data Sources and Data
Targets Management
AIMPM Database or Data
Warehouse Acquisition,
Development or
Maintenance Project
DIQM Data and Information
Quality Management in
IMP Components
ICSOFT 2007 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
118

It is composed of a set of activities aimed to
collect user requirements specification. Apart from
compile traditional user requirements, the definition
of user requirements related to data quality is also an
important task that should be done.
The importance of this KPA must be highlighted
because it is the basis on which the remainder of the
effort on data quality will be built in later phases.
3.3 Data Sources and Data Targets
Management (DSTM)
This KPA covers points 6 and 7 of the proposed
methodology.
If resulting XML DB must satisfy a quality
threshold, sources from which data is retrieved must
also satisfy that quality threshold. If data is
processed before storing it in the XML DB, proces-
ses in charge of that task must deal with data quality
either maintaining data quality already present in
data or improving it through an analysis of data.
If stored data is a product of another information
system, it would be recommendable that received
data were in a format that allows the integration of
the new data with data already stored in the DB and
that keeps quality data representation as, for
example, the one presented in (Verbo et al., 2007).
Following this approach, data sources could be
compared and only that ones according to the quality
requirements would be used.
3.4 Database Acquisition, Development
or Maintenance (DADM)
This KPA covers point 3 of the proposed
methodology.
DB development is done during this phase. One
of the main tasks is the XML DB conceptual
modeling. In the traditional approach, this task is
done using E/R and UML diagrams. However, this
is not the best choice for XML DBs modeling
because that kind of diagrams does not capture all
XML semantics like certain sorts of associations or
type creation. As a possible solution to this problem,
in (Marcos et al., 2001) an UML extension for XML
Schema (XSD) representation is proposed.
3.5 Data and Information Quality
Management (DIQM)
This KPA covers points 4, 5, 8, 9 and 10 of the
proposed methodology.
The goal of this KPA is to determine which
information and data quality aspects are involved in
the information management process components
and which are important to the context being
studied. Applying this concept to our discourse
domain, it means that after having created the XML
DB conceptual model it is necessary to integrate in it
all the elements that will help to guarantee the
quality for the given solution.
CALDEA define two activities for this process:
1. (DIQM.1) Identify information and data
quality dimensions starting from users data
quality requirements.
2. (DIQM.2) Identify measures for each
information and data quality dimension.
3.5.1 DIQM.1 Data Quality Dimensions
During this phase we must identify most important
data quality dimensions for the application domain.
Many authors like (Redman, 1996), (English, 1999)
and (Strong et al., 1997) have explained how to
identify these data quality dimensions and even how
to measure certain characteristic data quality aspects
in specific application domains and environments.
A major problem is that many of these proposals
for data quality dimension selection involve the
authors to define a set of dimensions that are valid as
a reference for a specific context. Further evaluation
of these frameworks reveals too much frequently
that they have been defined specifically for a
particular domain, which implies that they are highly
context dependent (Eppler, 2001).
A possibility could be to develop an universal
reference model valid for any context, but as (Lee et
al., 2006) affirm, this is highly unlikely due to the
fact that information and data quality are tightly
related to particular problems that organizations
have with their own information and data.
Due to this reason, instead of proposing a
concrete set of dimensions to be handled during this
KPA, the goal of our proposal is to define a structure
that allows to represent quality data in an uniform
way and with higher semantic meaning. To reach
this objective, we have based on the approach
proposed in (Wang et al., 1995), where it is shown
an extension of the relational model to represent
quality data. Its main contribution consists in using a
conceptual data model extended with data quality
attributes that store data related to data quality
dimensions to improve overall system data quality.
In order to get the highest detail as possible and
since the relational cell is the minimal storage unit in
the relational model, it is necessary to tag data
quality at cell level. Tag data quality means that
quality data is associated to a cell value.
DATA QUALITY IN XML DATABASES - A Methodology for Semi-structured Database Design Supporting Data Quality
Issues
119
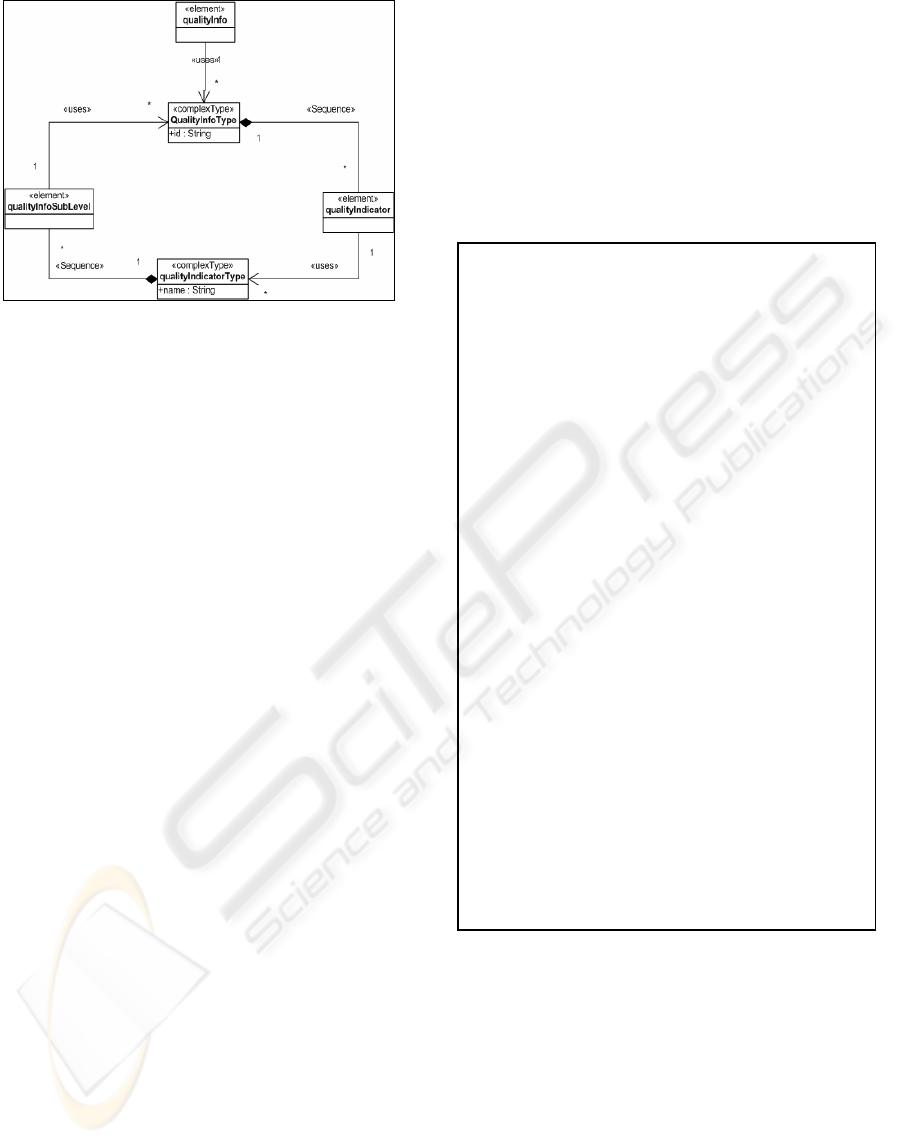
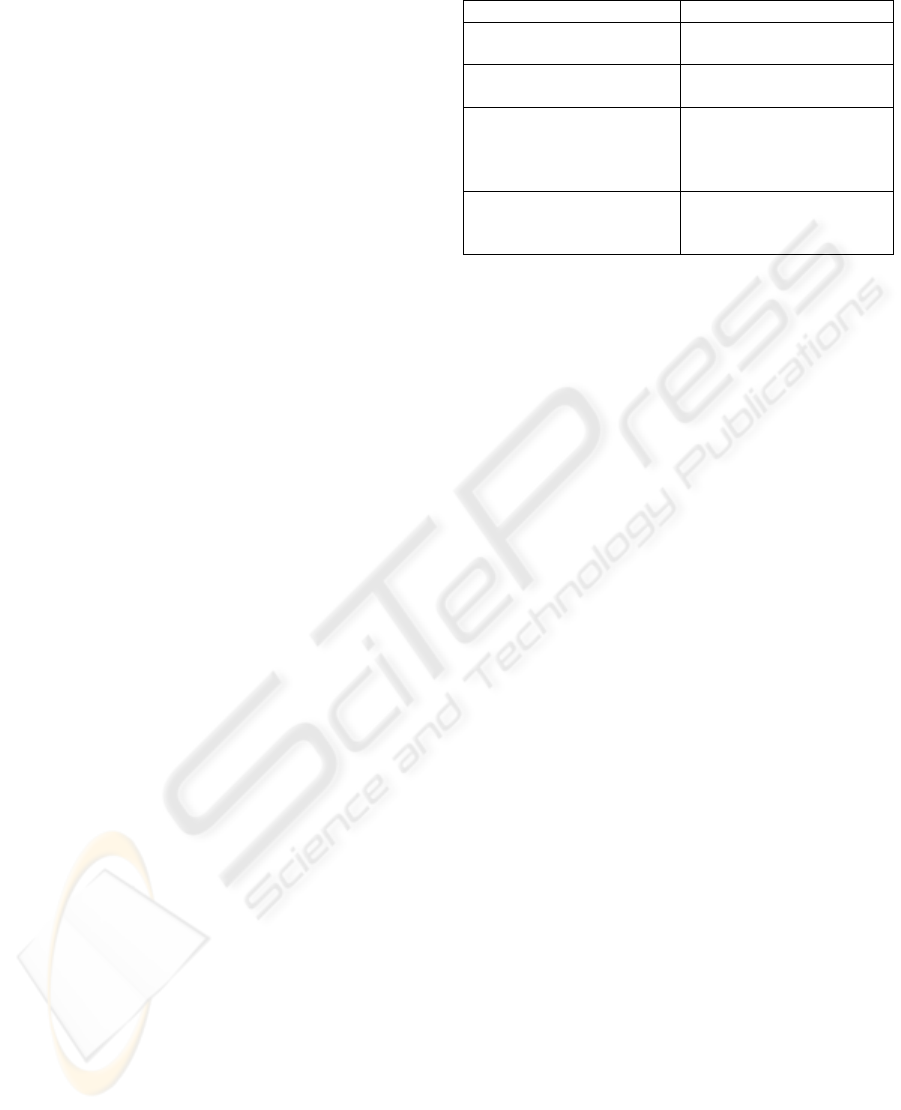
Figure 1: Data quality XSD extension diagram.
That proposal is based on the quality indicator
concept formerly explained. A quality indicator
gives objective information about certain data
characteristics and about its transformation process.
We have developed an extension mechanism to
represent quality data in XML DBs. To get that, we
have created an XML Schema (see Figure 1 for a
graphical representation and Figure 2 for the XSD
source code) that includes the following elements:
QualityInfo. This element acts as a grouping
section of quality data for an XML DB
component. It is optional since a component
may not have associated quality attributes.
QualityIndicator. This element contains
metadata about quality data. On the one hand,
it specifies the value assigned to that quality
indicator and, on the other hand, it may
contain “qualityInfo” elements, i.e., a quality
indicator can have associated quality
indicators. For example (see Figure 3), let us
suppose a newspaper includes a set of news.
Each piece of news has a source associated to
it. This source can be a news agency. This
would be the first level of quality indicators.
In turn, a news agency may have a set of news
sources that would correspond to the second
level of quality indicators.
This structure allows to enrich the model
obtained after the DB conceptual modeling to
represent quality data on it. In Figure 3 “qualityInfo”
elements are represented in bold font and
“qualityIndicator” elements are in italics.
3.5.2 DIQM.2 Measures
Information and data quality dimensions definition
represents an important step in the process of
deciding which quality aspects and quality criteria
are significant to the context of the problem to be
resolved. According to the ISO 9126 standard (ISO,
1991), it represents an answer to the problem of
identifying which data quality aspects must address
a specific component. But this is not enough as there
are other problems to solve like, for example, to
know how good the studied component with respect
to a concrete quality dimension is. To fulfill this
answer, it is necessary to define measures, i.e., sets
composed of a way of measure and a scale to obtain
a value on that dimension (García et al., 2005).
<xs:schema xmlns:xs=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element
name="qualityInfo"
type="qualityInfoType"
nillable="true"/>
<xs:complexType
name="qualityInfoType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="qualityIndicator"
type="qualityIndicatorType"
minOccurs="1"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute
name="id"
type="xs:string"
use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType
name="qualityIndicatorType"
mixed="true">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="qualityInfo"
type="qualityInfoType"
minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute
name="name"
type="xs:string"
use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
Figure 2: Data quality XSD extension.
As stated in previous section, data quality
dimension selection for a specific component may
be highly context dependent. Consequently,
quantitatively measure definition can also be highly
context dependent. However, this paper tries to give
a broad overview of XML DB development so the
set of measures we have defined are generic since
they can be applied to XML documents
independently of the application context in order to
optimize the schema design. Those measures try to
ICSOFT 2007 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
120
give a general understanding about the complexity
of the XML documents stored in the XML DB.
Figure 3: XML extended with DQ indicators.
To define measures we have followed the Goal-
Question-Metric (GQM) methodology. The steps
followed to get the resulting measures are shown in
Table 2 and Table 3.
Table 2: Measure definition for the first goal.
Table 3: Measure definition for the second goal
Resulting measures can be divided into several
groups according to their purpose:
1. Completeness measures. They give a notion
about the degree of completeness for an XML
document.
Number of elements (NE(D)). Defined as the
number of elements in an XML document D.
Number of attributes (NA(D)). Defined as the
number of attributes in an XML document D.
Number of Empty Elements (NEE(D)).
Defined as the number of elements in an
XML document D that has neither value of
any type nor child elements.
Number of Empty Attributes (NEA(D)).
Defined as the number of empty attributes in
elements of an XML document D.
2. Complexity measures. They give a notion
about the complexity of an XML document.
The more complex an XML document is, the
more difficult its processing will be.
Number of Nodes (NN(D)). Defined as the
number of nodes needed to represent the
XML document graph considering as a node
any element, attribute or element value.
Number of Arcs (NArc(D)). Defined as the
number of arcs needed to represent the XML
document graph, considering an arc as any
relation among parent and child elements,
element attributes and element values.
Structural Complexity (SCXML(D)).
Represents the structural complexity of an
XML document contained in a XML DB. It
is defined with the next formula:
SC
XML
= NArc -NN + 1 (1)
3. Associated quality data. They provide an
estimation of the amount of quality data is
associated to an XML document. As more
associated quality data it has, XML document
quality could be assessed more accurately.
Quality Data Volume (QDV(D)). Defined as
the total number of “qualityIndicator”
elements, in any nesting level, those
elements of an XML document contains. As
the result of this measure increases, more
quality data is stored in the XML DB so a
more precise data quality assessment could
be done.
Depth of the Data Quality Tree (DDQT(D)).
Defined as the maximum level of nested
“qualityInfo” elements in an XML
document. As data quality tree is deeper,
more detailed data quality will be stored in
the XML database.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Nowadays, information is one of the main assets that
organizations hold. Data is the raw material where
information is extracted from. It is logical to think
that the more quality data achieves, the more quality
could reach the resulting information improving
accordingly organizational processes quality.
Goal
Evaluate XML documents quality
Question
How does XML document complexity affects
when manipulating it?
Metrics
NE(D), Number of Elements
NA(D), Number of Attributes
NEE(D), Number of Empty Elements
NEA(D), Number of Empty Attributes
NN(D), Number of Nodes
NArc(D), Number of Arcs
SC
XML
(D), Structural Complexity
Goal
Evaluate quality of an XML document extended
with quality data.
Question
How does quality data complexity of an XML
document affects when manipulating it?
Metrics
QDV(D), Quality Data Volume
DDQT(D), Depth of the DQXML Tree
<news>
news_content
<qualityInfo id="news_qi2">
<qualityIndicator
name="news_source_l1">
Reuters
<qualityInfo id="news_qi2">
<qualityIndicator
name="news_source_l2">
John Smith
qualityIndicator> </
</qualityInfo>
qualityIndicator> </
</qualityInfo>
</news>
DATA QUALITY IN XML DATABASES - A Methodology for Semi-structured Database Design Supporting Data Quality
Issues
121

For many years the importance of data quality
has been ignored when designing and developing
databases in which organizations store their data.
Our proposal tries to integrate data quality notions
inside a DB development methodology in order to
open a new research work that fulfill this blank.
On the other hand, new technologies related to
XML have spread so widely due to the success of
Service Oriented Architectures that XML have
became the standard de facto to data exchange
among agents. This situation has provoked that new
approaches to semi-structured data storage optimiza-
tion have arisen. Inside this field, XML DBs have
been created with the goal of improving massive
storage of XML documents.
Our research work is centered in developing new
strategies for data quality treatment during XML
DBs development phase. To reach this target, we
have based on some Key Area Processes from the
CALDEA framework to define a methodology that
considers data quality as a basic aspect during the
creation of a XML DB.
The explained approach treats aspects related to
user quality requirements management, data source
quality assessment, data quality management during
the XML DB design phase and measure of different
characteristics of data stored in a XML DB.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is part of the FAMOSO and ESFINGE
projects supported by the Dirección General de
Investigación of the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y
Tecnología (Ministry of Science and
Technology)(TIC2003-07804-C05-03).
REFERENCES
Bray, T., Paoli, J. & Sperberg-McQueen, C. M., 1998.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0. W3C
Recommendation.
Caballero, I. & Piattini, M., 2007. Assessment and
Improvement of Data and Information Quality. IN AL-
HAKIM, L. (Ed.) Information Quality Management:
Theory and Applications. Hershey, PA, USA, Idea
Group Publishing.
English, L., 1999. Improving Data Warehouse and
Business Information Quality: Methods for reducing
costs and increasing Profits, New York, NY, USA,
Willey & Sons.
Eppler, M., 2001. A Generic Framework for Information
Quality in Knowledge-Intensive Processes. In
Proceeding of the Sixth International Conference on
Information Quality.
Fuggeta, A., 2000. Software Process: A Road Map. . In
FINKELSTEIN, A. (Ed.) In Twenty-Second
International Conference on Software Engineering
(ICSE'2000). Limerick, Ireland, ACM Press.
García, F., Bertoa, M. F., Calero, C., Vallecillo, A., Ruiz,
F., Piattini, M. & Genero, M., 2005. Toward a
consistent terminology for software measurement.
Information and Software Technology, 48, 631-644.
Huang, K. T., Lee, Y. W. & Wang, R. Y., 1999. Quality
Information and Knowledge, Upper Saddle River, NJ,
USA, Prentice-Hall.
Lee, Y. W., Pipino, L. L., Funk, J. D. & Wang, R. Y.,
2006. Journey to Data Quality, Cambridge, MA,
USA, Massachussets Institute of Technology.
Levitin, A. & Redman, T., 1995. Quality Dimensions of a
Conceptual View. Information Processing and
Management, 31(1), 81-88.
Marcos, E., Vela, B. & Cavero, J. M., 2001. Extending
UML for Object-Relational Database Design. In
Fourth Int. Conference on the Unified Modeling
Language, UML 2001. Toronto (Canada), Springer-
Verlag.
OASIS, 2006. ISO/IEC 26300:2006 Information
technology -- Open Document Format for Office
Applications (OpenDocument) v1.0. International
Organization for Standardization.
Redman, T. C., 1996. Data Quality for the Information
Age, Boston, MA, USA, Artech House Publishers.
Strong, D., Lee, Y. & Wang, R., 1997. Data Quality in
Context. Communications of the ACM, Vol. 40, Nº 5,
103 -110.
Verbo, E., Caballero, I. & Piattini, M., 2007. DQXSD: An
XML Schema for Data Quality. Paper accepted for the
9th International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems (ICEIS). Funchal, Madeira -
Portugal.
Wang, R. Y., Reddy, M. P. & Kon, H. B., 1995. Toward
quality data: An attribute-based approach. Decision
Support Systems.
ICSOFT 2007 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
122
