
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR
SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
Lamine Thiaw, Kurosh Madani
Laboratoire Image, Signal et Systmes Intelligents (LISSI / EA 3956) IUT de Snart, Universit Paris XII
Av. Pierre Point, F-77127 Lieusaint, France
Rachid Malti
Laboratoire Automatique Productique et Signal University Bordeaux 1 351, Cours de la Libration, 33405 Talence Cedex, France
Gustave Sow
LER, Ecole Suprieure Polytechnique de Dakar, Universit Cheikh Anta Diop, BP 5085, Dakar Fan, Senegal
Keywords:
System identification, non-linear systems, multi-model, recurrent models.
Abstract:
Multi-modeling is a recent tool proposed for modeling complex nonlinear systems by the use of a combination
of relatively simple set of local models. Due to their simplicity, linear local models are mainly used in such
structures. In this work, multi-models having polynomial local models are described and applied in system
identification. Estimation of model’s parameters is carried out using least squares algorithms which reduce
considerably computation time as compared to iterative algorithms. The proposed methodology is applied
to recurrent models implementation. NARMAX and NOE multi-models are implemented and compared to
their corresponding neural network implementations. Obtained results show that the proposed recurrent multi-
model architectures have many advantages over neural network models.
1 INTRODUCTION
Identification of nonlinear systems is an important
task for many real world applications such as process
behavior analysis, control, prediction, etc. In the last
years, several classes of models have been developed,
among which Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and
multi-models (also known as operating regime ap-
proach), for non linear system identification.
ANN are widely used for dynamical nonlinear
system modeling (Cheng et al., 1997; Konur and
Okatan, 2004; Vartak et al., 2005). Such implementa-
tions like Time Delay Neural Network (TDNN) (Cor-
radini and Cohen, 2002; Konur and Okatan, 2004),
Jordan Network (Jordan, 1986), Elman Network (El-
man, 1999) are very suitable for time series appli-
cations but they suffer of some limitations which re-
strict their use (Huang et al., 2005; Tomasz and Jacek,
1997). Several papers have been dedicated to the en-
hancement of neural networks for recurrent models
identification (Bielikova, 2005; Huang et al., 2006).
In (Huang et al., 2006) for example, a Multi-Context
Recurrent Neural Network (MCRN) is studied and its
performances are compared with those of the Elman
Network and Elman Tower Network. Even though
the proposed MCRN allows to achieve good perfor-
mances, the main drawback remains its complexity
due to the number of parameters induced by the con-
text layer (Huang et al., 2006) which has weighting
connections with both hidden and output layers.
The main difficulty encountered in recurrent neu-
ral networks is parameters estimation complexity.
The parameters estimation is mostly performed us-
ing the gradient descent method (Backpropagation
Through Time algorithm, Real Time Recurrent Learn-
ing algorithms, etc.) which cannot guarantee conver-
gence to global minimum. On the other hand, the re-
lated algorithm’s performance is very sensitive to the
learning rate parameter which determines the conver-
gence rate and the stability of the algorithm.
Multi-models have recently been proposed in nu-
merous papers (Boukhris et al., 2000; Vernieuwe
et al., 2004; Li et al., 2004) for modeling and con-
trol of nonlinear systems. For such systems, it is gen-
314
Thiaw L., Madani K., Malti R. and Sow G. (2007).
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 314-321
DOI: 10.5220/0001615503140321
Copyright
c
SciTePress

erally difficult to find a single analytical relationship
describing system’s behavior in its whole operating
range. The system’s complexity can be considerably
reduced if system’s operating range is divided into
different regions where local behavior could be de-
scribed with relatively simple models. The system’s
behavior is approximated by the weighted contribu-
tion of a set of local models. The difficulty encoun-
tered in this approach is the splitting of the system’s
operating range into convenient regions. For that pur-
pose, various techniques have been studied among
which grid partitioning, decision tree partitioning,
fuzzy clustering based partitioning (see (Vernieuwe
et al., 2004; Murray-Smith and Johansen, 1997)).
Fuzzy clustering based partitioning enables to gather
those data that may have some “similarities”, facilitat-
ing system’s local behavior handling. The main dif-
ficulty is the number of clusters needed to determine
the multi-model’s architecture. A method is presented
here to bypass this difficulty.
Parameter estimation of recurrent multi-models is
much simpler as compared to recurrent neural net-
works. We present in this work a multi-model imple-
mentation of recurrent models with polynomial local
models. The proposed structure is applied to NAR-
MAX and NOE models. The main advantage of such
structure is that it allows to adjust the complexity of
local models to the detriment of global one and vice-
versa. Parameters are estimated using least squares
algorithms, avoiding time consuming calculations and
local minima.
The paper is structured as follows: in section 2
an overview of models identification principle is pre-
sented. Section 3 describes the general principle of
multi-models using polynomial local models. The im-
plementation of recurrent multi-model is presented in
section 4. Results and discussions are presented in
section 5.
2 OVERVIEW OF NON LINEAR
MODELS
“Black box” models are very suited for complex sys-
tems representation (Sjoberg et al., 1995). Identifica-
tion of such models consists of determining the math-
ematical relationship linking system’s outputs (or its
states) to its inputs from experimental data. In gen-
eral, model describing system’s behavior
1
can be ex-
1
Multi-input and single-output (MISO) systems are con-
sidered here for ease of understanding. Results can be gen-
eralized to multi-input and multi-output systems.
pressed as:
y(t + h) = F
0
u(t), ˜y(t)
+ e(t + h) (1)
where :
y(t + h) is the unknown system output at time instant
t + h;
t is the current time instant and h is the prediction
step;
F
0
(·) is an unknown deterministic nonlinear function
describing the system (the true model);
u(t) is a column vector which components are sys-
tem’s inputs at time t and at previous time instants;
˜y(t) is a column vector which components are ob-
tained from system’s output at time t and at previous
time instants. It can be built from measured output
data, estimated output data, prediction errors, or
simulation errors;
e(t + h) is an error term at time t + h.
The identification task consists of determining the
function F(·) which is the best approximation of F
0
(·)
and estimating the system’s output ˆy:
ˆy(t + h) = F
u(t), ˜y(t),θ
= F
ϕ(t),θ
(2)
where :
ϕ(t) = [u(t)
T
, ˜y(t)
T
]
T
is the regression vector ob-
tained by the concatenation of the elements of vectors
u(t) and ˜y(t); and θ is a parameter vector to be esti-
mated.
If ˜y(t) in (2) depends on model’s output or model’s
states, then the model (2) is said to be recurrent. Re-
current models have the ability to take into account
system’s dynamics. On the other hand, data col-
lected from a process are usually noisy due to the
sensors or the influence of external factors. Recur-
rent models allow to obtain unbiased parameters esti-
mation. Various model classes have been established
for modeling dynamical systems in presence of vari-
ous noise configurations. Model classes differ by the
composition of their regression vector. Since the ex-
act model class is frequently unknown various classes
are usually tested and the best one is chosen. In this
work we focus on recurrent models called Nonlinear
AutoRegressive Moving Average with eXogenous in-
puts (NARMAX) and Nonlinear Output Error (NOE)
models. These classes of models are widely used be-
cause of their ability to capture nonlinear behaviors.
NARMAX model is a very powerful tool for mod-
eling and prediction of dynamical systems (Gao and
Foss, 2005; Johansen and Er, 1993; Yang et al., 2005).
It is well suited for modeling systems using noisy out-
puts and noisy states. It generalizes the Nonlinear Au-
toRegressive with eXogenous inputs (NARX) model.
Its regression vector is composed of the past inputs
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
315
u
k
, the past measured outputs y
s
, and the past pre-
diction errors (difference between measured and pre-
dicted outputs) e. The output of the NARMAX model
is given by:
y(t + 1) = F
u
1
(t − d
u
1
+ 1),.. .,
...
u
k
(t − d
u
k
+ 1),.. .,u
k
(t − d
u
k
− n
u
k
+ 2)
...
y
s
(t − d
y
s
+ 1).. .,y
s
(t − d
y
s
− n
y
s
+ 2),
e(t − d
e
+ 1),.. .,e(t − d
e
− n
e
+ 2)
+e(t + 1) (3)
where:
d
u
k
, d
y
s
and d
e
are inputs, output, and error delays re-
spectively;
n
u
k
, n
y
s
and n
e
are inputs, output, and error orders re-
spectively;
The prediction step in this representation corresponds
to:
h = min(d
u
k
,d
y
s
,d
e
) (4)
A NOE model is suited for system’s simulation
because it does not require measured outputs (Palma
and Magni, 2004). The corresponding regression vec-
tor is composed of past inputs u
k
and past simulated
outputs ˆy
u
. The output of the NOE model is given by:
y(t + 1) = F
u
1
(t − d
u
1
+ 1),.. .,
...
u
k
(t − d
u
k
+ 1),.. .,u
k
(t − d
u
k
− n
u
k
+ 2)
...
ˆy
u
(t − d
ˆy
u
+ 1),.. ., ˆy
u
(t − d
ˆy
u
− n
ˆy
u
+ 2)
+e(t + 1) (5)
Identification of recurrent models such as NAR-
MAX or NOE models is a difficult task because some
of the regressors have to be computed at each time
step. The parameter estimation must then be carried
out recursively.
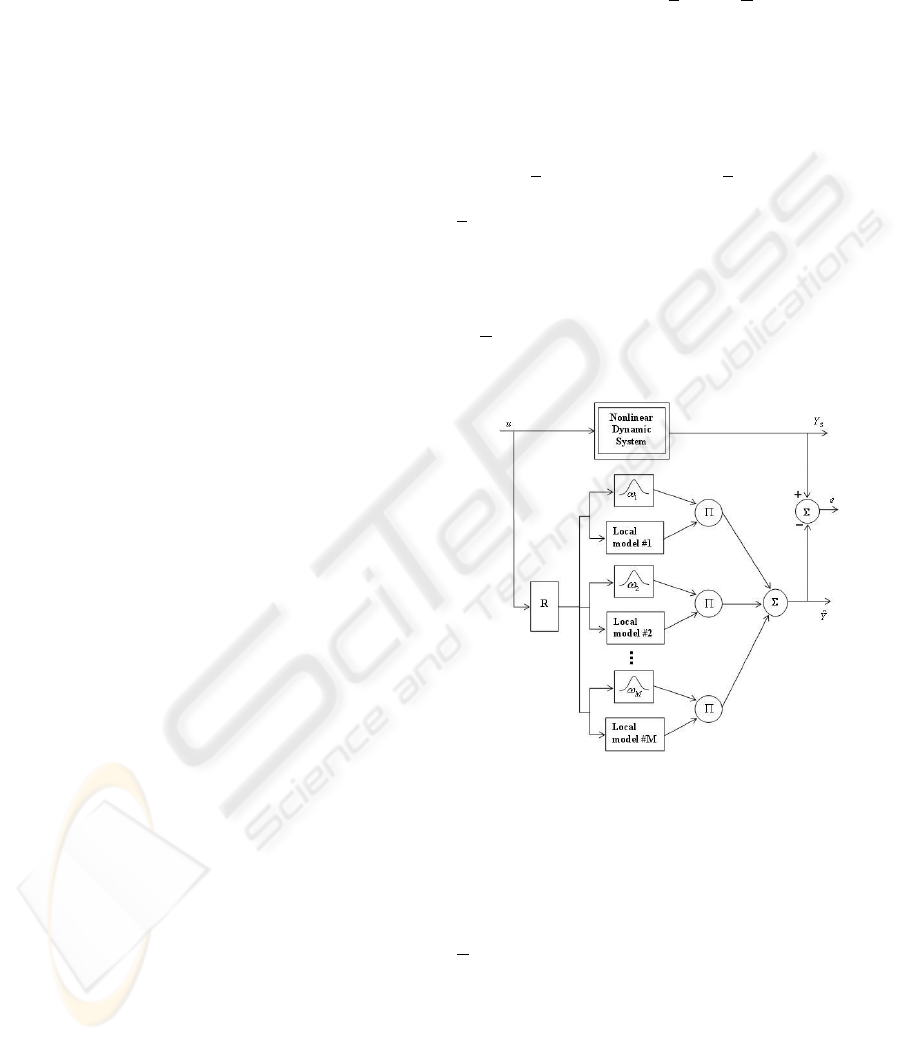
3 MULTI-MODEL’S PRINCIPLE
Multi-models were first proposed by Johansen and
Foss in 1992 (Johansen and Er, 1992). A multi-model
is a system representation composed by a set of local
models each of which is valid in a well defined fea-
ture space corresponding to a part of global system’s
behavior. The local validity of a model is specified by
an activation function which tends to 1 in the feature
space and tends to zero outside. The whole system’s
behavior can then be described by the combination of
all local models outputs. Figure 1 presents the basic
architecture of a multi-model. The relation (2) can
then be expressed as:
ˆy(t + h) =
M
∑
i=1
ω
i
ξ
(t)
f
i
ϕ(t),θ
i
(6)
where:
M is the number of local models;
ω
i
(·) is the activation degree of local model f
i
(·),
with :
ω
i
ξ(t)
∈ [0, 1] ,
M
∑
i=1
ω
i
ξ(t)
= 1 ∀t
ξ(t) is the vector of indexing variables (variables
whereby system’s feature space is divided into sub-
spaces (Orjuela et al., 2006));
θ
i
is a parameter vector characterizing the local model
f
i
(·);
f
i
ϕ(t),θ
i
= ˆy
i
(t + h) is the predicted output of the
ith local model.
In (6), the prediction step h may take any discrete
Figure 1: Basic architecture of a multi-model. Bloc R is a
set of time delay operators combined with a linear or nonlin-
ear transformation and used for the regression vector con-
struction; Y
s
is the measured system output.
value. It can also be specified by an appropriate
choice of the time delays d
u
, d
y
and d
e
of regressors in
ϕ(t) (see equation (4)). So without loss of generality,
we will assume that h = 1.
Activation degrees of local models can be de-
fined in a deterministic way using membership func-
tions like gaussian functions, sigmoidal functions,
etc. They can also be defined fuzzily using a fuzzy
clustering of the system’s feature space. This lat-
ter solution seems to be more natural as it allows to
gather data which may have some “similarities”. The
main difficulty is the determination of the number of
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
316

clusters. The proposed implementation combines ar-
chitectural (number of local models or clusters) and
parametrical identification. The number of clusters is
successively incremented and the parameters are esti-
mated at each step. The incrementation of the number
of clusters is stopped when Akaike Information Cri-
terion (see section §5) starts deteriorating.
The “fuzzy-c-means” algorithm (Bezdec, 1973)
is implemented here because of its simplicity. This
algorithm consists of maximizing the intra-cluster
similarities and minimizing the inter-cluster similari-
ties. The corresponding objective function is defined
as:
J(c
1
,c
2
,. ..,c
M
) =
M
∑
i=1
N
∑
t=1
µ
m
it
d
2
it
(7)
where:
d
it
= kϕ(t)− c
i
k denotes the distance between the ob-
servation ϕ(t) (t = 1,. .., N, N - number of observa-
tions) and the center c
i
of the ith cluster (i = 1,.. ., M,
M - number of clusters or local models);
µ
it
=
1
∑
M
k=1
(
d
it
d
kt
)
2/(m−1)
represents membership degree of
the observation ϕ(t) in the cluster i and stands for the
local model’s activation degree for that observation:
µ
it
= ω
i
ξ(t)
;
c
i
=
∑
N
t=1
µ
m
it
∑
N
t=1
µ
m
it
ϕ(t)
is the center of the ith cluster;
m ≥ 1 is the “fuzzy exponent” and represents the over-
lapping shape between clusters (generally, m = 2).
Local models may be of any structural type. As
suggested in (Johansen and Er, 1993), local mod-
els may be defined as the first p terms of the Tay-
lor’s series expansion of the true (unknown) model
F
0
(·) about a point located in the local model’s feature
space. Affine local models (p = 1) are mostly used
because of their simplicity. This multi-model struc-
ture is very close to Takagi-Sugeno one. For com-
plex systems, the number of linear local models may
be very important because of the simplicity of their
structure. We propose in this work polynomial local
models with p ≥ 1 which enable to enhance the han-
dling of local nonlinearities, reducing then the num-
ber of models. We use a nonlinear transformation of
the regression vector:
ϕ
p
(t) = g
p
ϕ(t)
where g
p
(·) is a nonlinear transformation producing
the new regression vector ϕ
p
(t) which components
are the products of elements of ϕ(t) at orders 1 to p.
ϕ
p
(t) can be easily obtained from the following pro-
cedure:
Let
ϕ(t) = [ϕ
1
ϕ
2
·· · ϕ
n
ϕ
]
T
(8)
where n
ϕ
is the dimension of ϕ(t).
Let us consider the following row vectors:
V
1,1
= [ϕ
1
ϕ
2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
]
V
1,2
= [ϕ
2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
]
...
V
1,n
ϕ
= [ϕ
n
ϕ
]
V
2,1
= [ϕ
1
V
1,1
ϕ
2
V
1,2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
V
1,n
ϕ
]
V
2,2
= [ϕ
2
V
1,2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
V
1,n
ϕ
]
...
V
2,n
ϕ
= [ϕ
n
ϕ
V
1,n
ϕ
]
...
V
p−1,1
= [ϕ
1
V
p−2,1
ϕ
2
V
p−2,2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
V
p−2,n
ϕ
]
V
p−1,2
= [ϕ
2
V
p−2,2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
V
p−2,n
ϕ
]
...
V
p−1,n
ϕ
= [ϕ
n
ϕ
V
p−2,n
ϕ
]
V
p,1
= [ϕ
1
V
p−1,1
ϕ
2
V
p−1,2
··· ϕ
n
ϕ
V
p−1,n
ϕ
]
ϕ
p
(t) is then obtained from the relation:
ϕ
p
(t) = [V
1,1
V
2,1
·· · V
p,1
]
T
(9)
For example if ϕ(t) = [ϕ
1
ϕ
2
ϕ
3
]
T
and p = 2, then
relation (9) gives:
ϕ
2
(t) = [ϕ
1
ϕ
2
ϕ
3
ϕ
2
1
ϕ
1
ϕ
2
ϕ
1
ϕ
3
ϕ
2
2
ϕ
2
ϕ
3
ϕ
2
3
]
T
The number of parameters n
ϕ
p
of ϕ
p
(t) may be very
important if the size of ϕ(t) is important or if the order
p is high.
For notation simplicity we will replace V
k,1
by V
k
.
Local models can then be expressed by the relation:
f
i
ϕ(t),θ
i
=
n
ϕ
p
∑
k=1
V
k
θ
i
k
+ θ
i
0
(10)
where:
θ
i
k
(k = 0 ·· ·n
ϕ
p
and i = 1 ···M) are real constants;
θ
i
= [θ
i
0
θ
i
1
·· · θ
i
n
ϕ
p
]
T
parameters vector of the
ith local model.
The main advantage of such a representation is that
local models are nonlinear whereas they are linear
with respect to parameters. This structure consider-
ably simplifies parameter estimation (see §4). Equa-
tion (6) can be rewritten as:
ˆy(t + 1) = Φ(t)
T
θ (11)
where:
Φ(t) =
h
ω
1
ξ(t)
φ
e
(t)
T
·· ·ω
M
ξ(t)
φ
e
(t)
T
i
T
is the
global weighted regression vector;
φ
e
(t) =
ϕ
p
(t)
T
1
T
is the extended regression vector;
θ =
θ
T
1
.. .θ
T
i
.. .θ
T
M
T
is a concatenation of all local
models parameters vectors;
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
317
Estimating θ can be carried out by using a global
learning criteria J which consists of minimizing the
error between system’s output and multi-model’s out-
put:
J =
1
2
N
∑
t=1
y
s
(t) − ˆy(t)
2
=
N
∑
t=1
ε(t)
2
(12)
For non-recurrent multi-models with polynomial
local models, J is linear with respect to the multi-
model’s parameters vector. J is minimized analyti-
cally using Least-Squares method. Multi-model pa-
rameters are then computed using the expression:
ˆ
θ = (Φ
T
g
Φ
g
)
−1
(Φ
T
g
Y
s
) (13)
where:
ˆ
θ is the estimation of θ;
Φ
g
=
Φ(t)
t=N
t=1
is global weighted regression matrix
of all observations;
Y
s
=
y
s
(t)
t=N
t=1
is the vector of output values of all
observations;
For recurrent multi-models, parameters are esti-
mated by a parametrical adaptation algorithm using
at each time step the values of Φ(t), y
s
(t) and ω
i
[ξ(t)]
as presented in the next section.
4 MULTI-MODEL’S
IMPLEMENTATION OF
RECURRENT MODELS
Parameter estimation in recurrent neural network
models is carried out iteratively using gradient based
algorithm. Convergence towards global minimum is
not guaranteed and convergence rate might be high.
As it will be stated here, for the proposed recurrent
multi-model (RMM), parameters are estimated using
recursive least squares. Hence, the criterion J in re-
lation (12) is computed up to time step k according
to:
J(k) =
1
2
k
∑
t=1
ε(t)
2
=
1
2
k
∑
t=1
y
s
(t) − Φ
T
(t − 1) θ
k
2
(14)
with θ
k
the value of θ evaluated up to time instant k.
The minimization of this criterion leads to:
θ
k
=
h
k
∑
t=1
Φ(t − 1) Φ
T
(t − 1)
i
−1
k
∑
t=1
y
s
(t)Φ(t − 1)
(15)
Relation (15) can be written in a recursive form.
Assuming
A
k
=
h
k
∑
t=1
Φ(t − 1) Φ
T
(t − 1)
i
−1
(16)
then
θ
k
= A
k
k
∑
t=1
y
s
(t)Φ(t − 1) (17)
θ
k+1
= A
k+1
k+1
∑
t=1
y
s
(t)Φ(t − 1) (18)
The sum in the right hand side of (18) can be trans-
formed after some manipulations to:
k+1
∑
t=1
y
s
(t)Φ(t − 1) = A
−1
k+1
θ
k
+ Φ(k)
e
ε(k + 1) (19)
where:
e
ε(k + 1) = y
s
(k + 1)− Φ
T
(k) θ
k
is the a priori predic-
tion error (the error at time instant k+1 evaluated with
parameters computed up to time instant k). Putting
(19) in (18) leeds to a recursive expression of θ:
θ
k+1
= θ
k
+ A
k+1
Φ(k)
e
ε(k + 1) (20)
A
k+1
can also be computed recursively. From (16)
one can write :
[A
k+1
]
−1
= [A
k
]
−1
+ Φ(k)Φ
T
(k) (21)
Applying matrix inversion lemma to relation (21),
A
k+1
is computed recursively:
A
k+1
= A
k
−
A
k
Φ(k) Φ
T
(k) A
k
1 + Φ
T
(k) A
k
Φ(k)
(22)
So, the parameters vector θ is updated recursively
at each time step using relations (22) and (20). This
learning algorithm is used for the identification of
NARMAX and NOE structures based on the RMM
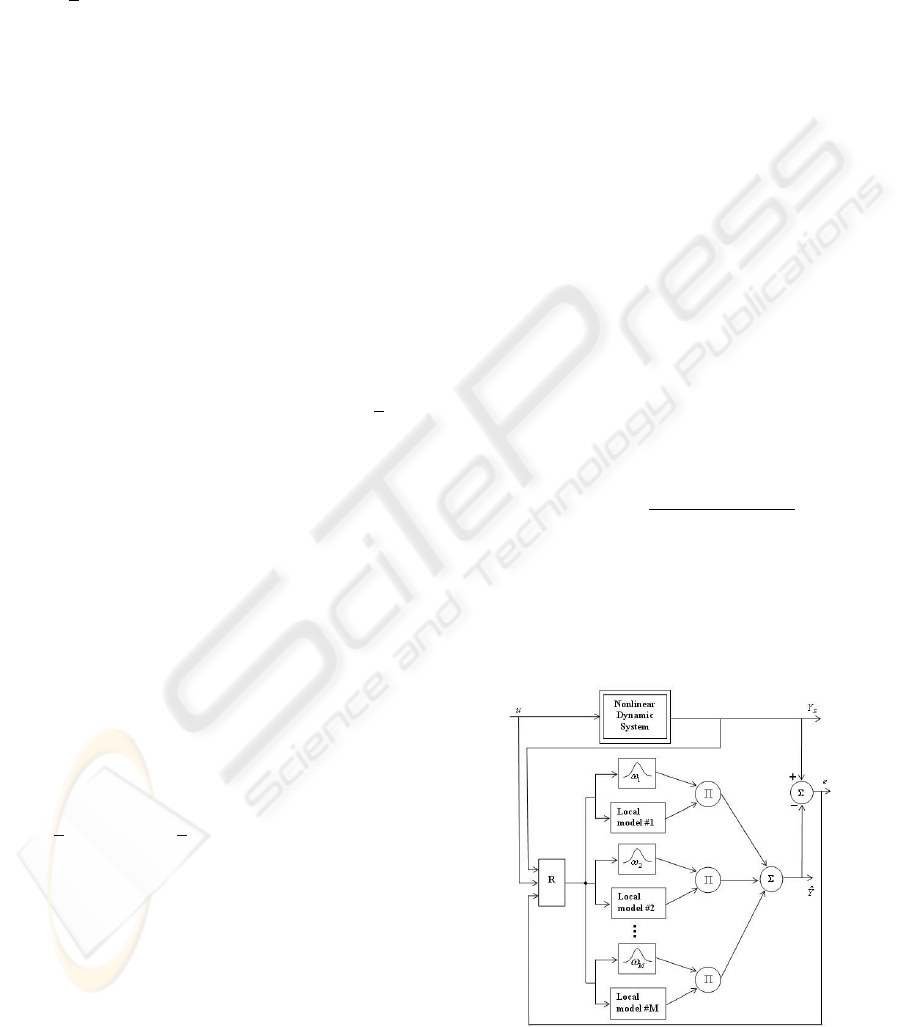
architectures (see figures 2 and 3).
Figure 2: Recurrent multi-model implementation of a NAR-
MAX model.
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
318
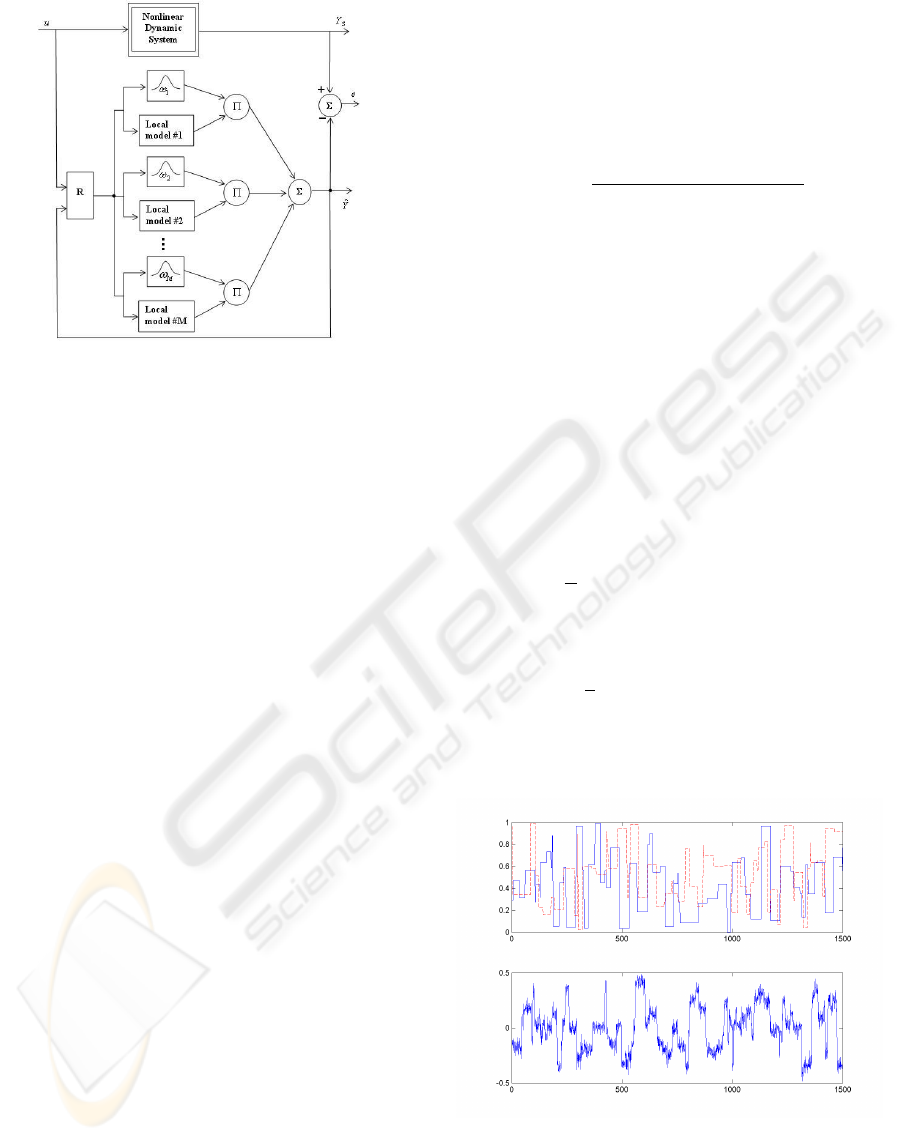
Figure 3: Recurrent multi-model implementation of a NOE
model.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To validate the proposed RMM architecture, two non
linear systems are used. The first one is a simulated
system which data are generated from a NARX model
(Gasso, 2000). The second one is Box-Jenkins gas
furnace benchmark (Box and Jenkins, 1970). For
comparison purposes, we have implemented recur-
rent Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) with one hidden
layer for NARMAX and NOE models, both trained
with the Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT) al-
gorithm (Werbos, 1990). To enhance the speed of
learning with the BBTT algorithm, the learning rate
is adapted so that it takes high values when the learn-
ing error decreases fastly and take small values when
it decreases slowly.
Performances of recurrent multi-models with
given order p of polynomial local models (RMM
p
)
are evaluated. Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)
is used for model’s parsimony estimation (least error
with minimum parameters):
AIC = N lnJ + 2 n
θ
(23)
where n
θ
denotes the number of model’s parameters.
Root Mean Square Error criterion (RMSE) is also
used for performance evaluation in learning (RMSE
L
)
and validation (RMSE
V
) phases. The architecture of
models (Arch) specifies the number of local models in
multi-models case or the number of hidden neurons
in MLP case. Computation time (CT) during which
models parameters are determined is used for algo-
rithms convergence speed evaluation.
5.1 Example 1: Narx Dynamic Process
The following system is simulated in a noisy context
and then identified using recurrent multi-model and
recurrent MLP.
y
s
(t) =
y
s
(t−1)
0.5u
1
(t−1)−0.3u
2
(t−1)
1+y
2
s
(t−1)
+0.3u
2
1
(t − 1) − 0.5u
2
2
(t − 1) (24)
Exogenous input signals u
1
(·) and u
2
(·) are cho-
sen to be pulses of random magnitude (in interval
[0,1]) and different widths; the output signal is then
corrupted by a white noise e issued from a normal dis-
tribution. The signal to noise ratio equals 14 dB. The
obtained noisy output y
s
n
(see figure 4) is expressed
by:
y
s
n
(t) = y
s
(t) + e(t) (25)
NOE model class is the most suitable one to iden-
tify this kind of system (Dreyfus, 2002). Both NOE
RMM and NOE MLP models are implemented. The
following regression vector is used:
ϕ(t) = [u(t − 1) ˆy(t − 1)]
T
where ˆy is the estimated model output. The vector of
indexing variables is:
ξ(t) =
u
1
(t) u
2
(t)
T
Table 1 shows obtained results for NOE RMMs and a
NOE MLP structures. System and NOE RMM
1
out-
puts are plot on validation data in figure 5. The ob-
Figure 4: Inputs and output indentification data.
tained results show that multi-model structures have
performances equivalent to MLP structures. How-
ever, their computation time is much lower.
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
319
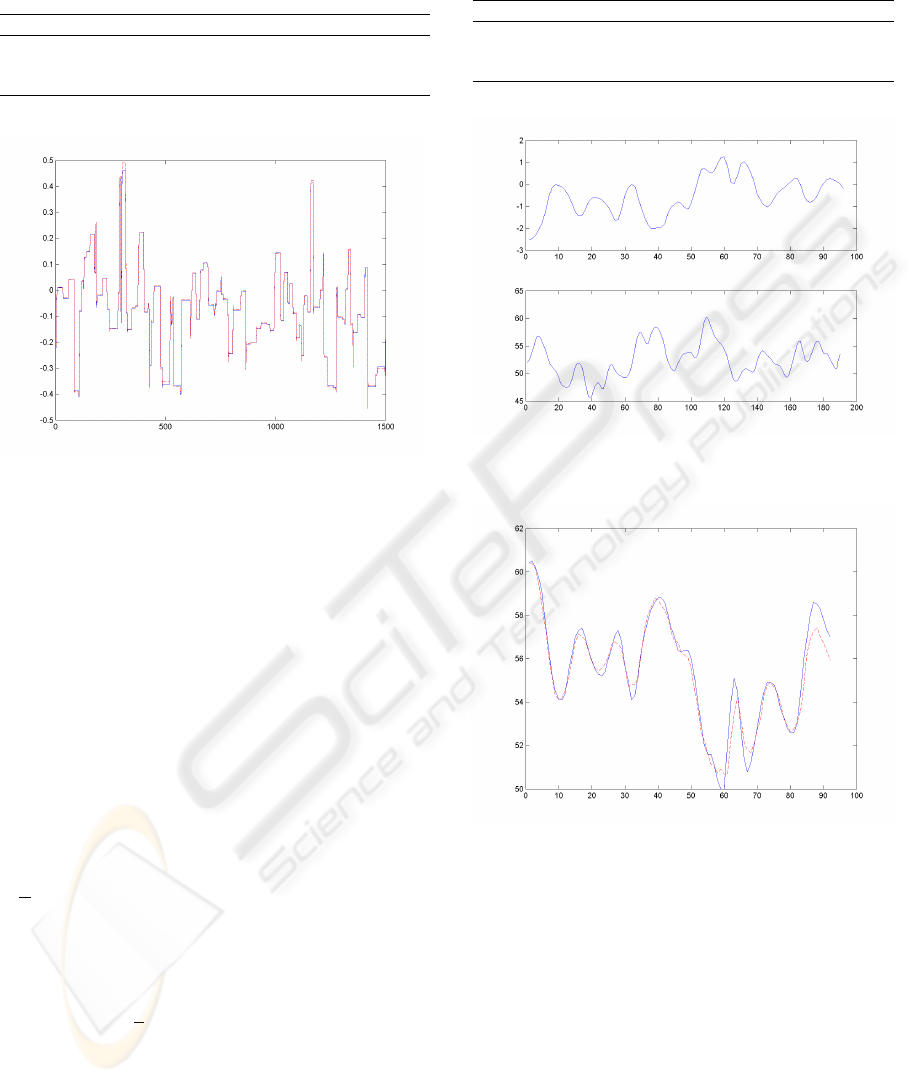
Table 1: NOE model for the nonlinear dynamic process:
results for NOE RMM and NOE MLP structures.
Model Arch. AIC CT(s) RMSE
L
RMSE
V
RMM
1
7 -9595 8 0.040 0.010
RMM
2
3 -9617 6 0.040 0.007
MLP 3 -9587 199 0.040 0.006
Figure 5: NOE RMM
1
output (dotted line) and noise free
system output on validation data.
5.2 Example 2: Box-Jenkins Gas
Furnace Benchmark
In this benchmark, data set are obtained from a com-
bustion process of methane-air mixture. The pro-
cess input is the methane gas flow into the furnace
and the output is CO
2
concentration in the outlet gas
(Box and Jenkins, 1970). System inputs and outputs
are presented in figure 6. We have implemented and
compared a NARMAX MLP and a NARMAX RMM
structures based on the described methodologies. The
following regression vector is used:
ϕ(t) = [u(t − 1) u(t − 2) u(t − 3)
y
s
(t − 1) y
s
(t − 2) y
s
(t − 3) e(t − 1)]
T
The vector of indexing variables is:
ξ(t) =
u(t) y
s
(t)
T
The results are presented in table 2. The NARMAX
RMM has the best parsimony and gives best perfor-
mances on validation data, with a very low computa-
tion time compared to the NARMAX MLP. It can be
seen that high polynomial orders reduces the number
of local models. Figure 7 shows process and NAR-
MAX RMM
1
outputs on validation data.
Table 2: NARMAX model for Box-Jenkins gas furnace
data: results for Multi-model and MLP structures.
Model Arch. AIC CT(s) RMSE
L
RMSE
V
RMM
1
6 -692 3 0.12 0.55
RMM
2
2 -637 2 0.13 0.63
MLP 3 -622 35 0.17 0.58
Figure 6: Process input and output on identification data.
Figure 7: Process and NARMAX RMM
1
(dotted line) out-
puts on validation data.
6 CONCLUSION
In this work, a new recurrent multi-model structure
with polynomial local models is proposed. The ad-
vantage of using polynomial local models is a better
handling of local nonlinearities and reducing hence-
forth the number of local models. The proposed struc-
ture is used to implement NARMAX and NOE mod-
els.
Identification task is carried out very simply and
obtained results show that the proposed recurrent
multi-model has many advantages over recurrent
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
320

MLP model, among which the reduction of compu-
tation time. This is due to the way the parameters are
estimated: least squares formula in the former model
and iterative algorithm in the latter.
The perspective of this study is the implementa-
tion of the proposed structures for model predictive
control in industrial processes.
REFERENCES
Bezdec, J. (1973). Fuzzy mathematics in pattern classifica-
tion. PhD thesis, Applied Math. Center, Cornell Uni-
versity Ithaca.
Bielikova, M. (2005). Recurrent neural network training
with the extended kalman filter. IIT. SRC, pages 57–
64.
Boukhris, A., Mourot, G., and Ragot, J. (2000). Nonlin-
ear dynamic system identification: a multiple-model
approach. Int. J. of control, 72(7/8):591–604.
Box, G. and Jenkins, G. (1970). Time series analysis,
forecasting and control. San Francisco, Holden Day,
pages 532–533.
Cheng, Y., Karjala, T., and Himmelblau, D. (1997). Closed
loop nonlinear process identification using internal re-
current nets. Neural Networks, 10(3):573–586.
Corradini, A. and Cohen, P. (2002). Multimodal speech-
gesture interface for hands-free painting on virtual pa-
per using partial recurrent neural networks for gesture
recognition. in Proc. of the Int’l Joint Conf. on Neural
Networks (IJCNN’02), 3:2293–2298.
Dreyfus, G. (2002). Rseaux de Neurones - Mthodologie et
applications. Eyrolles.
Elman, J. (1999). Finding structure in time. Cognitive Sci-
ence, 14(2):179–211.
Gao, Y. and Foss, A. (2005). Narmax time series model
prediction: feed forward and recurrent fuzzy neural
network approaches. Fuzzy Sets and Sytems, 150:331–
350.
Gasso, K. (2000). Identification de systmes dynamiques non
linaires: approche multi - modle. thse de doctorat de
l’INPL.
Huang, B., Rashid, T., and Kechadi, M.-T. (2005). A recur-
rent neural network recognizer for online recognition
of handwritten symbols. ICEIS, 2:27–34.
Huang, B., Rashid, T., and Kechadi, M.-T. (2006). Multi-
context recurrent neural network for time series appli-
cations. International Journal of Computational In-
telligence, 3(1):45–54.
Johansen, T. and Er, M. (1992). Nonlinear local model rep-
resentation for adaptive systems. In Proc. of the IEEE
Conf. on Intelligent Control and Instrumentation, vol-
ume 2, pages 677–682, Singapore.
Johansen, T. and Er, M. (1993). Constructing narmax using
armax. Int. Journal of Control, 58(5):1125–1153.
Jordan, M. (1986). Attractor dynamics and parallelism in
a connectionist sequential machine. In Proceedings
of IASTED International Conference of the Cognitive
Science Society. (Reprinted in IEEE Tutorials Series,
New York: IEEE Publishing Services, 1990), pages
531–546, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Erlbaum.
Konur, U. and Okatan, A. (2004). Time series prediction
using recurrent neural network architectures and time
delay neural networks. ENFORMATIKA, pages 1305–
1313.
Li, N., Li, S. Y., and Xi, Y. G. (2004). Multi-model predic-
tive control based on the takagi-sugeno fuzzy models:
a case study. Information Sciences, 165:247–263.
Murray-Smith, R. and Johansen, T. (1997). Multiple Model
Approaches to Modeling and Control. Taylor and
Francis Publishers.
Orjuela, R., Maquin, D., and Ragot, J. (2006). Identifica-
tion des systmes non linaires par une approche multi-
modle tats dcoupls. Journes Identification et Modli-
sation Exprimentale JIME’2006 - 16 et 17 novembre -
Poitiers.
Palma, F. D. and Magni, L. (2004). A multimodel struc-
ture for model predictive control. Annual Reviews in
Control, 28:47–52.
Sjoberg, J., Zhang, Q., Ljung, L., Benveniste, A., De-
lyon, B., Glorennec, P., Hjalmarsson, H., and Judit-
sky, A. (1995). Nonlinear black-box modeling in sys-
tem identification: a unified overview. Automatica 31,
31(12):1691–1724.
Tomasz, J. and Jacek, M. (1997). Neural networks tool for
stellar light prediction. In Proc. of the IEEE Aerospace
Conference, volume 3, pages 415–422, Snowmass,
Colorado, USA.
Vartak, A., Georgiopoulos, M., and Anagnostopoulos, G.
(2005). On-line gauss-newton-based learning for
fully recurrent neural networks. Nonlinear Analysis,
63:867–876.
Vernieuwe, H., Georgieva, O., Baets, B., Pauwels, V., Ver-
hoest, N., and Troch, F. (2004). Comparison of data-
driven takagi-sugeno models of rainfall-discharge dy-
namics. Journal of Hydrology, XX:1–14.
Werbos, P. (1990). Backpropagation through time: What
it does and how to do it. Proceedings of the IEEE,
78(10):1550–1560.
Yang, W. Z., L.H., Y., and L., C. (2005). Narmax model
representation and its application to damage detection
for multi-layer composites. Composite Structures,
68:109–117.
IMPLEMENTATION OF RECURRENT MULTI-MODELS FOR SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
321
