
COMPARISON OF TWO IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES:
THEORY AND APPLICATION
Pierre-Olivier Vandanjon
(1)
, Alexandre Janot
(2)
(1)
LCPC, Route de Bouaye BP 4129, 44341Bouguenais Cedex, France
(2)
CEA/LIST Interactive Robotic Unit, 18 route du Panorama, BP 6, 92265 Fontenay aux Roses, Cedex, France
Maxime Gautier
(3)
, Flavia Khatounian
(2)
(3)
IRCCyN, Robotic team, 1, rue de la Noë - BP 92 101 - 44321 Nantes Cedex 03, France
Keywords: Parameters identification, inverse model, least squares method, simple refined instrumental variable method.
Abstract: Parametric identification requires a good know-how and an accurate analysis. The most popular methods
consist in using simply the least squares techniques because of their simplicity. However, these techniques
are not intrinsically robust. An alternative consists in helping them with an appropriate data treatment.
Another choice consists in applying a robust identification method. This paper focuses on a comparison of
two techniques: a “helped” least squares technique and a robust method called “the simple refined
instrumental variable method”. These methods will be applied to a single degree of freedom haptic interface
developed by the CEA Interactive Robotics Unit.
1 INTRODUCTION
In most of cases, parametric identification is a hard
task and requires a good know-how. A popular
method consists in using the least squares technique
(LS) because of its simplicity. However, it has been
proven that the LS are sensitive to outliers, leverage
points and noise models (Hampel, 1971) and
(Hueber, 1981). In other words, the LS are not
intrinsically robust and we must “help” them in
order to obtain reliable results.
In the last decade, the IRCCyN robotic team has
designed a identification method based on LS
technique, inverse model, base parameters, exciting
trajectories and appropriate data treatment (Gautier
and Khalil, 1990), (Gautier and Khalil, 1991) and
(Gautier, 1997). This technique has been
successfully applied to identify inertial parameters
of industrial robots (Gautier, Khalil and Restrepo,
1995) and (Gautier, 1997). Recently, it was used for
identifying electrical parameters of a synchronous
machine (Khatounian et al, 2006), inertial
parameters of a haptic device (Janot et al, 2006) and
the parameters of a compactor (Lemaire et al, 2006).
The obtained results were interesting and reliable.
At the same time, robust methods have been
successfully used (Mili, Phaniraj and Rousseeuw,
1990), (Mili et al, 1996), (Young 2006) and (Gilson
et al, 2006). An interesting robust method is the
simple refined instrumental variable (SRIV) because
of its simplicity (Young 1979). Indeed, no noise
model identification is needed and this method is
consistent even in the coloured noise situation
(Gilson et al, 2006). This method is implemented in
the MATLAB CONTSID toolbox developed by the
CRAN team (Garnier, Gilson and Huselstein, 2003)
and (Garnier, Gilson and Cervellin, 2006). To our
knowledge, this method has not been used to
identify inertial parameters of robots.
Hence, it seems interesting to apply the SRIV
method to a single degree of freedom haptic
interface and to compare it with the LS method.
The paper is organized as follows: second
section presents the general inverse dynamic model
of robots, the LS technique and the SRIV method;
experimental results are presented in section 3;
finally, section 4 introduces a discussion.
341
Vandanjon P., Janot A., Gautier M. and Khatounian F. (2007).
COMPARISON OF TWO IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES: THEORY AND APPLICATION.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 341-347
DOI: 10.5220/0001621403410347
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 THEORY
2.1 General Inverse Dynamic Model
The inverse dynamic model (commonly called
dynamic model) calculates the joint torques as a
function of joint positions, velocities and
accelerations. It is usually represented by the
following equation:
)qsign(FqF)qH(q,qA(q)Γ
cv
+++=
(1)
Where, Γ is the torques vector, q, q
and q
are
respectively the joint positions, velocities and
accelerations vector, A(q) is the inertia matrix,
H(q,
q
) is the vector regrouping Coriolis, centrifugal
and gravity torques, F
v
and F
C
are respectively the
viscous and Coulomb friction matrices.
The classical parameters used in this model are the
components XX
j
, XY
j
, XZ
j
, YY
j
, YZ
j
, ZZ
j
of the
inertia tensor of link j denoted
j
J
j
, the mass of the
link j called M
j
, the first moments vector of link j
around the origin of frame j denoted
j
MS
j
=[M
Xj
M
Yj
M
Zj
]
T
, and the friction coefficients F
Vj
, F
Cj
.
The kinetic and potential energies being linear
with respect to the inertial parameters, so is the
dynamic model (Gautier and Khalil, 1990). It can
thus be written as:
()
χq,qq,DΓ
= (2)
Where D(q, q
, q
) is a linear regressor and χ is a
vector composed of the inertial parameters.
The set of base parameters represents the minimum
number of parameters from which the dynamic
model can be calculated. They can be deduced from
the classical parameters by eliminating those which
have no effect on the dynamic model and by
regrouping some others. In fact, they represent the
only identifiable parameters.
Two main methods have been designed for
calculating them: a direct and recursive method
based on calculation of the energy (Gautier and
Khalil, 1990) and a method based on QR numerical
decomposition (Gautier, 1991). The numerical
method is particularly useful for robots consisting of
closed loops.
By considering only the b base parameters, (2) can
be rewritten as follows:
()
b
χq,qq,WΓ
= (3)
Where W(q, q
, q
) is the linear regressor and χ
b
is
the vector composed of the base parameters.
2.2 LS Method
2.2.1 General Theory
Generally, ordinary LS technique is used to estimate
the base parameters solving an over-determined
linear system obtained from a sampling of the
dynamic model, along a given trajectory (q,
q
, q
),
(Gautier, Khalil and Restrepo, 1995), (Gautier,
1997). X being the b minimum parameters vector to
be identified, Y the measurements vector, W the
observation matrix and ρ the vector of errors, the
system is described as follows:
(
)
(
)
ρXq,qq,WΓY +
=
(4)
The L.S. solution
X
ˆ
minimizes the 2-norm of the
vector of errors ρ. W is a r×b full rank and well
conditioned matrix, obtained by tracking exciting
trajectories and by considering the base parameters,
r being the number of samplings along a trajectory.
Hence, there is only one solution
X
ˆ
(Gautier, 1997).
Standard deviations
i
X
ˆ
σ are estimated using
classical and simple results from statistics. The
matrix W is supposed deterministic, and ρ, a zero-
mean additive independent noise, with a standard
deviation such as:
(
)
rρ
T
ρ
IρρC
2
σE == (5)
where E is the expectation operator and I
r
, the r×r
identity matrix. An unbiased estimation of
ρ
σ
is:
()
br
ˆ
σ
2
2
−
−
=
XWY
ρ
(6)
The covariance matrix of the standard deviation is
calculated as follows:
(
)
1
T
ρ
XX
WWC
−
=
2
ˆˆ
σ (7)
ii
X
ˆ
X
ˆ
2
iX
ˆ
Cσ = is the i
th
diagonal coefficient of
XX
C
ˆˆ
.
The relative standard deviation
ri
X
ˆ
%σ is given by:
j
X
ˆ
X
ˆ
X
σ
100%σ
j
jr
= (8)
However, in practice, W is not deterministic. This
problem can be solved by filtering the measurement
matrix Y and the columns of the observation matrix
W.
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
342

2.2.2 Data Filtering
Vectors Y and q are samples measured during an
experimental test. We know that the LS method is
sensitive to outliers and leverage points. A median
filter is applied to Y and q in order to eliminate
them.
The derivatives
q
and q
are obtained without
phase shift using a centered finite difference of the
vector q. Knowing that q is perturbed by high
frequency noises, which will be amplified by the
numeric derivation, a lowpass filter, with an order
greater than 2 is used. The choice of the cut-off
frequency ω
f
is very sensitive because the filtered
data
()
fff
q,q,q
must be equal to the vector
()
q,qq,
in the range [0, ω
f
], in order to avoid
distortion in the dynamic regressor. The filter must
have a flat amplitude characteristic without phase
shift in the range [0, ω
f
], with the rule of thumb
ω
f
>10*ω
dyn
, where ω
dyn
represents the dynamic
frequency of the system. Considering an off-line
identification, it is easily achieved with a non-causal
zero-phase digital filter by processing the input data
through an IIR lowpass butterworth filter in both the
forward and reverse direction. The measurement
vector Y is also filtered, thus, a new filtered linear
system is obtained:
ffff
ρXWY += (9)
Because there is no more signal in the range [ω
f
,
ω
s
/2], where ω
s
is the sampling frequency, vector Y
f
and matrix W
f
are resampled at a lower rate after
lowpass filtering, keeping one sample over n
d
samples, in order to obtain the final system to be
identified:
fdfdfdfd
ρXWY += (10)
with:
fsd
/2ω0.8ωn = (11)
2.2.3 Exciting Trajectories
Knowing the base parameters, exciting trajectories
must be designed. In fact, they represent the
trajectories which excite well the parameters. If the
trajectories are enough exciting, then the
conditioning number of W, (denoted cond(W)) is
close to 1. However, in practice, this conditioning
number can reach 200 because of the high number of
base parameters. Design and calculations of these
trajectories can be found in (Gautier and Khalil,
1991).
If the trajectories are not enough exciting, then the
results have no sense because the system is ill
conditioned and some undesirable regroupings
occur.
2.3 SRIV Method
From a theoretical point of view, the LS assumptions
are violated in practical applications. In the equation
(4), the observation matrix W is built from the joint
positions q which are often measured and from
q
, q
which are often computed numerically from q.
Therefore the observation matrix is noisy. Moreover
identification process takes place when the robot is
controlled by feedback. It is well known that these
violations of assumption imply that the LS solution
is biased. Indeed, from (4), it comes:
ρWWXWYW
TTT
+=
(12)
As ρ includes noises from the observation matrix
(
)
0E
T
≠ρW .
The Refined Instrumental Variable approach deals
with this problem of noisy observation matrix and
can be statistically optimal (Young, 1979). It is the
reason why we propose to enrich our identification
methods by using concepts from this approach. In
the following, we describe the application of this
method in our field.
The Instrumental Variable Method proposes to
remove the bias on the solution by building the
instrument matrix V such as
(
)
0E
T
=ρV and V
T
W
is invertible.
The previous equation becomes:
ρVWXVYV
TTT
+= (13)
The instrumental variable solution is given by
(
)
YVWVX
T
1
T
V
ˆ
−
= (14)
The main problem is to find the instrument matrix
V. A classical solution is to build an observation
matrix from simulated data instead of measured
data. The following iterative algorithm describes this
solution:
Step 0: a first set of parameters is given by using
classical LS.
Step k: From a set of parameters
1V/k
ˆ
−
X given at
the previous step, the following ordinary differential
equation, describing the robot dynamic, is simulated:
(
)
f
1
Γ)qH(q,ΓAq ++=
−
(15)
COMPARISON OF TWO IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES: THEORY AND APPLICATION
343

Γ is the motor vector which is generally given
by a feedback built by comparison between the
desired and the real movement.
f
,, ΓHA
are respectively the inertia matrix, the
Coriolis-centrifugal vector and the friction
torques. They are computed with the parameters
identified at the step k-1:
1V/k
ˆ
−
X
By simulation of this differential equation,
kkk
q,q,q
are obtained. Then the Instrument Matrix
at the step k is computed:
)q,q,W(qV
kkkk
= . The
equation (14) gives the set of parameters
Vk
ˆ
X .
This iterative process is conducted until the
convergence of the parameters. Practically, 4 or 5
steps are enough to decrease dramatically the
correlation between the instrument matrix and the
noise on the system.
3 APPLICATION
3.1 Presentation and Modelling of the
Interface
The interface to be identified is presented Figure 1.
It consists of synchronous machine and a handle
actuated thanks to a cable transmission. This type of
transmission is a good comprise between friction,
slippage and losses. The modelling and the
identification are made under the rigid model
assumption. Naturally, the authors have checked that
this hypothesis is valid in the case of this study.
The modelling and the identification of the
synchronous machine are given in (Khatounian et al,
2006).
Figure 1: Presentation of the interface to be identified.
The frames defined to model the interface are
presented Figure 2. The inverse dynamic model is
given by the following equation:
fYX
gsin(q)Mgcos(q)MqJΓ Γ+
+
−
=
(16)
where q and
q
are respectively the joint position and
acceleration, J is the global inertia of the system.
The torque Γ is calculated through the current
measurement. We have verified that we have
Γ=NK
c
I, where N is the gear ratio, K
c
the torque
constant and I the measured current. More details
about the implemented control law can be found in
(Khatounian et al, 2006).
The friction torque Γ
f
was measured according to
the method developed by (Spetch and Isermann,
1988), which consists in measuring the torque at
different constant speeds and eliminating all
transient modes. Figure 3 shows that the friction
model can be considered at non-zero velocity as the
following, where
)qsign(
is the sign function of the
velocity
q
, and f
c
, f
v
denote the Coulomb and
viscous friction coefficients.
)qsign(fqfΓ
cvf
+
=
(17)
The dynamic model can be thus written as a
sampled linear form:
Γ = W X (18)
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
−
−
=
)qsign(q)gsin(q)gcos(qq
)qsign(q)gsin(q)gcos(qq
rrrrr
11111
#####
W
,
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
Γ
Γ
=
r
1
#Y and
[
]
T
cvYX
ffMMJ=X .
In this simple case, the parameters J, M
X
, M
Y
, f
v
and f
c
constitute the set of base parameters (QR
decomposition confirms that).
G
O
S
x
1
x
0
g
q
y
0
y
1
Figure 2: Notations and frames used for modelling the
interface.
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
344

-20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20
-0.2
-0.15
-0.1
-0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
Frictions torque measured
Velocity rads-1
Torque Nm
Figure 3: Friction torque measured.
3.2 Identification of the Base
Parameters
3.2.1 LS Method
Current I and joint position q were measured, with a
sampling period of 240μs. Exciting trajectory
consists of trapezoidal speed reference. This
trajectory was chosen because it is equivalent to a
rectangular trajectory for the joint acceleration. It
allows the estimation of the inertia term due to the
change of the acceleration sign, of the gravitational
and viscous friction terms because the velocity is
constant over a period and of the Coulomb term due
to the change of sign of the velocity. Vectors
q
and
q
were derived from the position vector q, and all
data were filtered as described in section 2.2.2.
Because of the friction model, the velocities close to
zero are eliminated.
The cut-off frequency of the butterworth filter and
of the decimate filter is close to 20Hz. This value
can be calculated thanks to a spectral analysis of the
data. In our case one has ω
dyn
close to 2Hz. Thus
with the rule of thumb ω
f
>10*ω
dyn
, we retrieve the
value given above.
The identified values of the mechanical parameters
are summed up in Table 1.
The conditioning number of W is close to 30.
Hence, the system is well conditioned and the
designed trajectories are enough exciting.
Direct comparisons have been performed. These
tests consist in comparing the measured and the
estimated torques just after the identification
procedure. An example is illustrated Figure 4.
Notice that the estimated torque follows the
measured torque closely.
Finally, we simulate the system by means of a
SIMULINK model. We use the same speed
references and the differential equation given by
(15) is solved with the Euler’s method (ODE 1). The
step time integrator is of 240μs. Figure 5 shows the
measured and the simulated states. They are close to
each others.
Table 1: Estimated mechanical parameter values.
Mechanical
parameters
Estimated
values
Relative
deviation %
J (kg.m²) 1,45.10
-3
0,5
M
X
(kg.m) 2,2.10
-3
5,0
M
Y
(kg.m) 0,9.10
-3
8,7
f
v
(Nm.s.rad
-1
)
2,4.10
-3
2,6
f
c
(Nm) 5,9.10
-2
0.8
Cond(W) = 30
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
Direct Validation
Nm
Mes ured
Estimated
Figure 4: Comparison between the measured and
estimated torque calculated through the LS technique.
1550 1600 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
-1
0
1
Measured and Si mulat ed Posi ti on
rad
1600 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
-10
0
10
Measured and Si mulat ed Velocity
rads-1
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
-100
0
100
Measured and Simulated Accelerat ion
rads-2
Figure 5: Comparison between the measured states (blue)
and the simulated states (green).
COMPARISON OF TWO IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES: THEORY AND APPLICATION
345
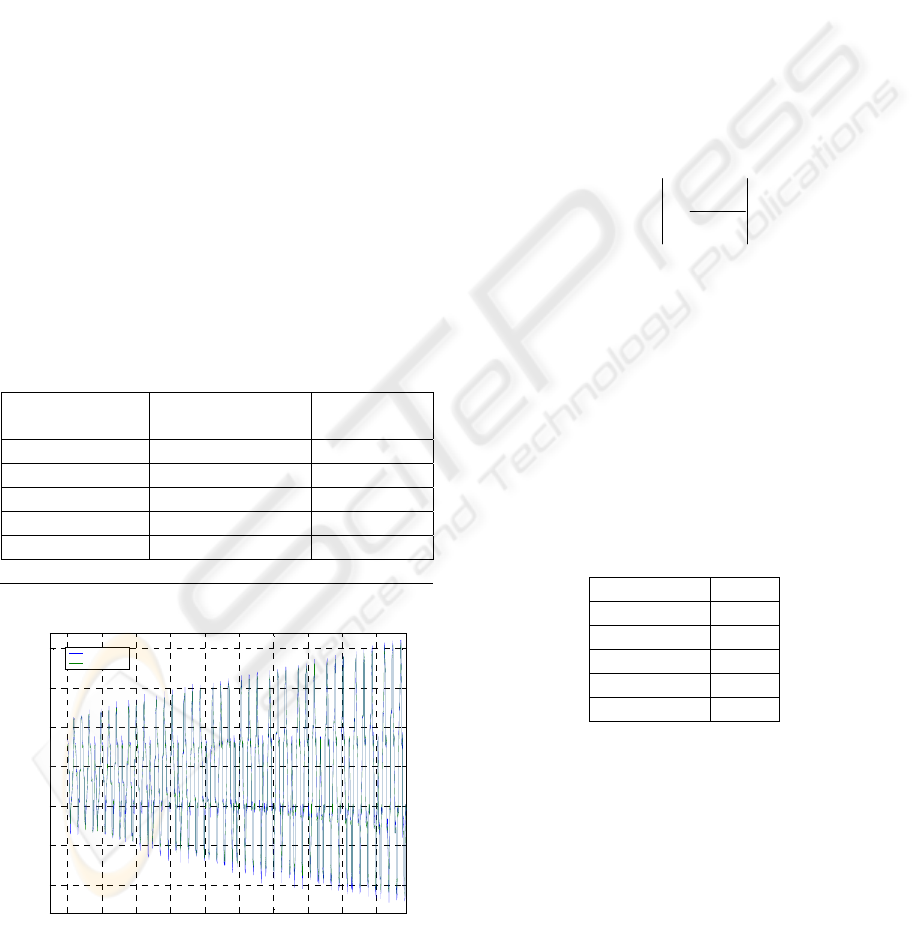
It comes that the LS technique identification gives
interesting and reliable results even if the
assumptions on the noise model are violated.
3.2.2 SRIV Method
As explained section 2.3, the instrument matrix is
built with the simulated states (see previous section
for the simulation parameters) and the algorithm is
initialized with the values given in Table 1. The
parameters are estimated thanks to (14). These
values do not vary consequently (only 2 steps are
enough to decrease the correlation between the
instrument matrix and the noise on the system). The
results are summed up in Table 2.
We have also performed direct comparison (Figure
6). Once again, the estimated torque follows the
measured torque closely. As an expected result, the
SRIV method gives reliable and interesting results
and can be used to identify inertial parameters of
robots. The results given Table 2 are close to those
exposed Table 1. That means that, in this case, the
LS method detailed section 2.2 is as efficient as the
SRIV technique detailed section 2.3.
Table 2: Estimated mechanical parameter values
calculated through the SRIV method after 5 steps.
Mechanical
parameters
Estimated values Relative
deviation %
J (kg.m²) 1,45.10
-3
0,4
M
X
(kg.m) 2,2.10
-3
5,0
M
Y
(kg.m) 0,9.10
-3
8,2
f
v
(Nm.s.rad
-1
)
1,9.10
-3
3,5
f
c
(Nm) 6,3.10
-2
0.8
Cond(W) = 30
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
Direct Validation
Nm
Mes ured
Estimated
Figure 6: Comparison between the measured and
estimated torque calculated through the SRIV.
4 DISCUSSION
In the case of this study, the experimental results
tend to prove that the identification technique
developed by the IRCCyN robotic team is as
efficient and consistent as the SRIV method. This
mainly due to the data treatment described section
2.2.2. Indeed, it helps the LS estimator: outliers and
leverage points are eliminated while the derivatives
of q are calculated without magnitude and phase
shift. In addition, the data filtering is well designed.
It is interesting to mix both methods. Indeed, with a
simple analysis, we can detect which parameters are
sensitive to noise measurement, noise modelling,
high frequency disturbances…
To do so, we introduce an estimation relative error
given by (19):
LSj
SRIVj
X
ˆ
X
ˆ
1100%e −=
(19)
Where
SRIVj
X
ˆ
is the j
th
parameter estimated by
means of the SRIV method and
LSj
X
ˆ
is the j
th
parameter estimated thanks to the LS technique. The
results are summed up in Table 3.
In our case, only the parameters of friction torque
are quite sensitive. This is mainly due to the fact that
they “see” all undesirable effects such as torque
ripple, cable wear and imperfect contacts which are
not modelled. Hence, that proves the interest of this
approach and the use of the SRIV method.
Table 3: Estimation relative error.
Parameter %e
J (kg.m²) 0,1 %
Mx (kg.m) 0,2 %
My (kg.m) 1,3 %
fv (Nm.s.rad
-1
) 20 %
fc (Nm) 7,3 %
During the experiments, it is appeared that the
SRIV could be helpful when we are not familiar
with the data filtering. We know that the LS
estimators are sensitive to noises filtering and if the
filtering is not well designed, the results could be
controversial. These results will be published in a
later publication.
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
346

5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, two identification methods have been
tested and compared: the first based on the ordinary
LS technique associated with an appropriate data
treatment and the second based on the SRIV method.
Both methods give interesting and reliable results.
Hence, we can choose these techniques for a
parametric identification.
In addition, the authors have introduced a simple
calculation which enables us to know the parameters
which are sensitive to noises and undesirable effects.
Future works concern the use of both techniques to
identify a 6 degrees of freedom robot.
REFERENCES
Garnier H., Gilson M. and Huselstein E., 2003.
“Developments for the MATLAB CONTSID
toolbox”, In: 13th IFAC Symposium on System
Identification, SYSID 2003, Rotterdam Netherlands,
August 2003, pp. 1007-1012
Garnier H., Gilson M. and Cervellin O., 2006. “Latest
developments for the MATLAB CONTSID toolbox”,
In: 14th IFAC Symposium on System Identification,
SYSID 2006, Newcastle Australia, March 2006, pp.
714-719
Gautier M. and Khalil W., 1990. "Direct calculation of
minimum set of inertial parameters of serial robots",
IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, Vol.
6(3), June 1990
Gautier M. and Khalil W., 1991. “Exciting trajectories for
the identification of base inertial parameters of
robots”, In: Proc. Of the 30
th
Conf. on Decision and
Control, Brigthon, England, December 1991, pp. 494-
499
Gautier M., 1997. “Dynamic identification of robots with
power model”, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and
Automation, Albuquerque, 1997, p. 1922-1927
Gautier M., Khalil W. and Restrepo P. P., 1995.
“Identification of the dynamic parameters of a closed
loop robot”, Proc. IEEE on Int. Conf. on Robotics and
Automation, Nagoya, may 1995, p. 3045-3050
Gilson M., Garnier H., Young P.C. and Van den Hof P.,
2006. “A refined IV method for closed loop system
identification”, In: 14th IFAC Symposium on System
Identification, SYSID 2006, Newcastle Australia,
March 2006, pp. 903-908
Hampel F.R., 1971. “A general qualitative definition of
robustness”, Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 42,
1887-1896, 1971
Huber P.J., 1981. “Robust statistics”, Wiley, New-York,
1981
Janot A., Bidard C., Gautier M., Keller D. and Perrot Y.,
2006. “Modélisation, Identification d’une Interface
Médicale”, Journées Identification et Modélisation
Expérimentale 2006, Poitiers, November 2006
Khatounian F., Moreau S., Monmasson E., Janot A. and
Louveau F., 2006. “Simultaneous Identification of the
Inertial Rotor Position and Electrical Parameters of a
PMSM for a Haptic Interface”, In: 12
th
EPE-PEMC
Conference, Portoroz, Slovenia, August September
2006, CD-ROM, ISBN 1-4244-0121-6
Lemaire Ch.E., Vandanjon P.O., Gautier M. and Lemaire
Ch., 2006. “Dynamic Identification of a Vibratory
Asphalt Compactor for Contact Efforts Estimation”,
In: 14th IFAC Symposium on System Identification,
SYSID 2006, Newcastle Australia, March 2006,pp.
973-978
Mili L., Phaniraj V. and Rousseeuw P.J., 1990. “Robust
estimation theory for bad data diagnostics in electrical
power systems”, In: C. T. Leondes editor, Control and
Dynamic Systems:Advances in Theory and
Applications, pp. 271-325, San Diego 1990, Academic
Press
Mili L., Cheniae M.G., Vichare N.S. and Rousseeuw P.J.,
1996. “Robust state estimation based on projection
statistics”, IEEE Trans. On Power Systems, 11(2),
1118-1127, 1996
Specht R., and Isermann R., 1988. “On-line identification
of inertia, friction and gravitational forces applied to
an industrial robot”, Proc. IFAC Symp. on Robot
Control, SYROCO’88, 1988, p. 88.1-88.6
Young P.C. and Jakeman A.J., 1979. Refined instrumental
variable methods of time-series analysis: Part 1, SISO
systems, International Journal of Control, 29:1-30,
1979
Young P.C., 2006. “An instrumental variable approach to
ARMA model identification and estimation”, In: 14th
IFAC Symposium on System Identification, SYSID
2006, Newcastle Australia, March 2006, pp. 410-415
COMPARISON OF TWO IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES: THEORY AND APPLICATION
347
