
Forming Neural Networks Design through Evolution
Eva Volná
University of Ostrava, 30ht dubna st. 22, 701 03 Ostrava, Czech Republic
Abstract. Neuroevolution techniques have been successful in many sequential
decision tasks such as robot control and game playing. This paper aims at
evolution in artificial neural networks (e.g. neuroevolution). Here is presented a
neuroevolution system evolving populations of neurons that are combined to
form the fully connected multilayer feedforward network with fixed
architecture. In this paper, the transfer function has been shown to be an
important part of architecture of the artificial neural network and have
significant impact on an artificial neural network’s performance. In order to test
the efficiency of described method, we applied it to the alphabet coding
problem.
1 Introduction to Neuroevolution
Evolutionary algorithms refer to a class of population-based stochastic search
algorithms that are developed from ideas and principles of natural evolution. They
include [1] evolution strategies, evolutionary programming, and genetic algorithms.
Evolutionary algorithms are particularly useful for dealing with large complex
problems which generate many local optima. They are less likely to be trapped in
local minima than traditional gradient-based search algorithms. They do not depend
on gradient information and thus are quite suitable for problems where such
information is unavailable or very costly to obtain or estimate. They can even deal
with problems, where no explicit and/or exact objective function is available. These
features make them much more robust than many other search algorithms. Fogel [2]
and Bäck et al. [3] give a good introduction to various evolutionary algorithms for
optimization. One important feature of all these algorithms is their population-based
search strategy. Individuals in a population compete and exchange information with
each other in order to perform certain tasks. A general framework of evolutionary
algorithms can be described as follows:
generate the initial population G(0) at random, set i=0
REPEAT
..Evaluate each individual in the population;
..Select parents from G(i) based on their fitness
in G(i);
..Apply search operators to parents and produce
offspring which form G(i+1);
..i = i+ 1;
UNTIL ‘termination criterion’ is satisfied
Volná E. (2007).
Forming Neural Networks Design through Evolution.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks and Intelligent Information Processing, pages 13-20
DOI: 10.5220/0001624700130020
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Neuroevolution represents a combination of neural networks and evolutionary
algorithms, where neural networks are the phenotype being evaluated. The genotype
is a compact representation that can be translated into an artificial neural network.
Evolution has been introduced into artificial neural networks at roughly three different
levels: connection weights, architectures, and learning rules. The evolution of
connection weights provides a global approach to connection weights training,
especially when gradient information of the error function is difficult or costly to
obtain. Due to the simplicity and generality of the evolution and the fact that gradient-
based training algorithms often have to be run multiple times in order to avoid being
trapped in a poor local optimum, the evolutionary approach is quite competitive. The
evolution of architectures enables artificial neural networks to adapt their topologies
to different tasks without human intervention and thus provides an approach to
automatic artificial neural network design. Simultaneous evolution of artificial neural
network architectures and connection weights generally produces better results. The
evolution of learning rules in artificial neural networks can be used to allow an
artificial neural network to adapt its learning rule to its environment. In a sense, the
evolution provides artificial neural network with the ability of learning to learn.
Global search procedures such as evolutionary algorithms are usually computationally
expensive. It would be better not to employ evolutionary algorithms at all three levels
of evolution in neural networks. It is, however, beneficial to introduce global search at
some levels of evolution, especially when there is little prior knowledge available at
that level and the performance of the artificial neural network is required to be high,
because the trial-and-error or heuristic methods are very ineffective in such
circumstances. With the increasing power of parallel computers, the evolution of large
artificial neural networks becomes feasible. Not only can such evolution discover
possible new artificial neural network architectures and learning rules, but it also
offers a way to model the creative process as a result of artificial neural network’s
adaptation to a dynamic environment.
2 Overview of the Evolution of Node Transfer Functions
The discussion on the evolution of architectures so far only deals with the topological
structure of architecture. The transfer function of each node in the architecture has
been usually assumed that is fixed and predefined by human experts, at least for all
the nodes in the same layer. Little work has been only done on the evolution of node
transfer function up to now. Mani proposed a modified backpropagation, which
performs gradient descent search in the weight space as well as the transfer function
space [4], but connectivity of artificial neural networks was fixed. Lovel and Tsoi
investigated the performance of Neocognitrons with various S-cell and C-cell transfer
functions, but did not adopt any adaptive procedure to search for an optimal transfer
function automatically [5]. Stork et al. [6] were, to our best knowledge, the first to
apply evolutionary algorithms to the evolution of both topological structures and node
transfer functions even though only simple artificial neural networks with seven nodes
were considered. The transfer function was specified in the structural genes in their
genotypic representation. It was much more complex than the usual sigmoid function
because authors in [6] tried to model biological neurons. White and Ligomenides [7]
14

adopted a simpler approach to the evolution of both topological structures and node
transfer functions. For each individual (i.e. artificial neural network) in the initial
population, 80% nodes in the artificial neural network used the sigmoid transfer
function and 20% nodes used the Gaussian transfer function. The evolution was used
to decide the optimal mixture between these two transfer functions automatically. The
sigmoid and Gaussian transfer function themselves were not evolvable. No
parameters of the two functions were evolved. Liu and Yao [1] used evolutionary
programming to evolve artificial neural networks with both sigmoidal and Gaussian
nodes. Rather than fixing the total number of nodes and evolve mixture of different
nodes, their algorithm allowed growth and shrinking of the whole artificial neural
network by adding or deleting a node (either sigmoidal or Gaussian). The type of
node added or deleted was determined at random. Hwang et al. [8] went one step
further. They evolved topology of artificial neural network, node transfer function, as
well as connection weights for projection neural networks. Sebald and Chellapilla [9]
used the evolution of node transfer function as an example to show the importance of
evolving representations. Representation and search are the two key issues in problem
solving. Co-evolving solutions and their representations may be an effective way to
tackle some difficult problems where little human expertise is available. In principle,
the difference in transfer functions could be as large as that in the function type, e.g.
that between a hard limiting threshold function and Gaussian function, or as small as
that in one of parameters of the same type of function, e.g. the slope parameter of the
sigmoid function. The decision on how to encode transfer functions in chromosomes
depends on how much prior knowledge and computation time is available. This
suggests some kind of indirect encoding method, which lets developmental rules to
specify function parameters if the function type can be obtained through evolution, so
that more compact chromosomal encoding and faster evolution can be achieved. One
point worth mentioning here is the evolution of both connectivity and transfer
functions at the same time [6] since they constitute a complete architecture. Encoding
connectivity and transfer functions into the same chromosome makes it easier to
explore nonlinear relations between them. Many techniques used in encoding and
evolving connectivity could equally be used here.
3 Evolution Design of Neural Networks With Fixed Topology
In the paper, the transfer function has been shown to be an important part of
architecture of the artificial neural network, one has significant impact on artificial
neural network’s performance. Here is presented a neuroevolution system evolving
populations of neurons that are combined to form the fully connected multilayer
feedforward network with fixed architecture. Neuroevolution evolves transfer
functions of each unit in hidden and output layers of the network. The system
maintains diversity in the population, because a dominant neural phenotype is likely
to end up in the same network more than once. As several different types of neurons
are usually necessary to solve a problem, networks with too many copies of the same
neuron are likely to fail. The dominant phenotype then loses fitness and becomes less
dominant. The system works well because it makes sure neurons get the credit they
deserve, unlike some other neuroevolution techniques, where bad neurons can share
15

in a good network or good neurons can be brought down by their network. It also
works by decomposing the task, breaking the search into smaller, more manageable
parts.
In the following is described a method of automatic searching the node transfer
function architecture in multilayer feedforward network: First, we must propose
neural network architecture before the main calculation. We get the number of input
(m) and output (o) units from the training set. Next, we have to define the number of
hidden units (h) that is very confounding issue, because it is generally more difficult
to optimize large networks than small ones. Thereafter the process of evolutionary
algorithms is applied. Chromosomes are generated for every individual from the
initial population as follows, see Fig. 1:
individual 1
individual 2
...
individual k
...
b
1
σ
1
. . .
b
h
σ
h
b
h+1
σ
h+1
. . .
b
h+o
σ
h+0
units in the hidden layer
units in the output layer
Fig. 1. Population of individuals and their chromosomes.
Symbols b
i
(i = 1, …,h+o) refers to varies types of activation functions [10]:
− b
i
= 1, if the activation function is a binary sigmoid function:
()
()
x
xf
σ
−+
=
exp1
1
.
(1)
where
σ
is the steepness parameter, which value is set in the initial population
randomly (e.g.
σ
i
∈ (0; 7>).
− b
i
= 2, if the activation function is a binary step function with threshold
θ
:
()
⎩
⎨
⎧
<
≥
=
θ
θ
xif
xif
xf
0
1
.
(2)
the steepness parameter
σ
i
is not define here thus we assigned value 0 to it.
− b
i
= 3 if the activation function is a Gaussian function:
(
)
(
)
2
exp xxf −= .
(3)
the steepness parameter
σ
i
is not define here thus we assigned value 0 to it.
16

− b
i
= 4, if the activation function is a saturated linear function:
()
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎨
⎧
>
≤≤
<
=
11
10
00
xif
xifx
xif
xf
.
(4)
the steepness parameter
σ
i
is not define here thus we assigned value 0 to it.
Next, we calculate an error value (E) between the desired and the real output after
defined partial training with genetic algorithms. Adaptation of each individual starts
with randomly generated weight values that are the same for each neural network in
the given population. On the basis of it is calculated a fitness function for every
individual as follows:
Fitness
i
= E
max
- E
i
. (5)
for i = 1, ...,N,
where E
i
is error for the i-th network after a partial adaptation;
E
max
is a maximal error for the given task,
E
max
= o
×
pattern
(o is number of output units and pattern is number of patterns);
N is the number of individuals in the population.
All of the calculated fitness function values of the two consecutive generations are
sorted descending and the neural network representation attached to the first half
creates the new generation. For each fitness function is calculated the probability of
reproduction its existing individual by standard method [11]. One-point crossover was
used to generate two offspring. If the input condition of mutation is fulfilled (e.g. if a
randomly number is generated, that is equal to the defined constant), one of the
individual is randomly chosen. There is randomly replaced one place in its genetic
representation by a random value from the set of permitted values. Our calculation
finishes, when the population is composed only from the same individuals.
4 Experiments
In order to test the efficiency of described method, we applied it to the alphabet
coding problem that exists in cryptography. Neural networks can be also used in
encryption or decryption algorithms, where parameters of adapted neural networks are
included to cipher keys [12]. Cipher keys must have several heavy attributes. The best
one is the singularity of encryption and cryptanalysis [13]. Encryption is a process in
which we transform the open text (e.g. news) to cipher text according to rules.
Cryptanalysis of the news is the inverse process, in which the receiver of the cipher
transforms it to the original text. The open text is composed from alphabet characters,
digits and punctuation marks. The cipher text has usually the same composition as the
open text.
17
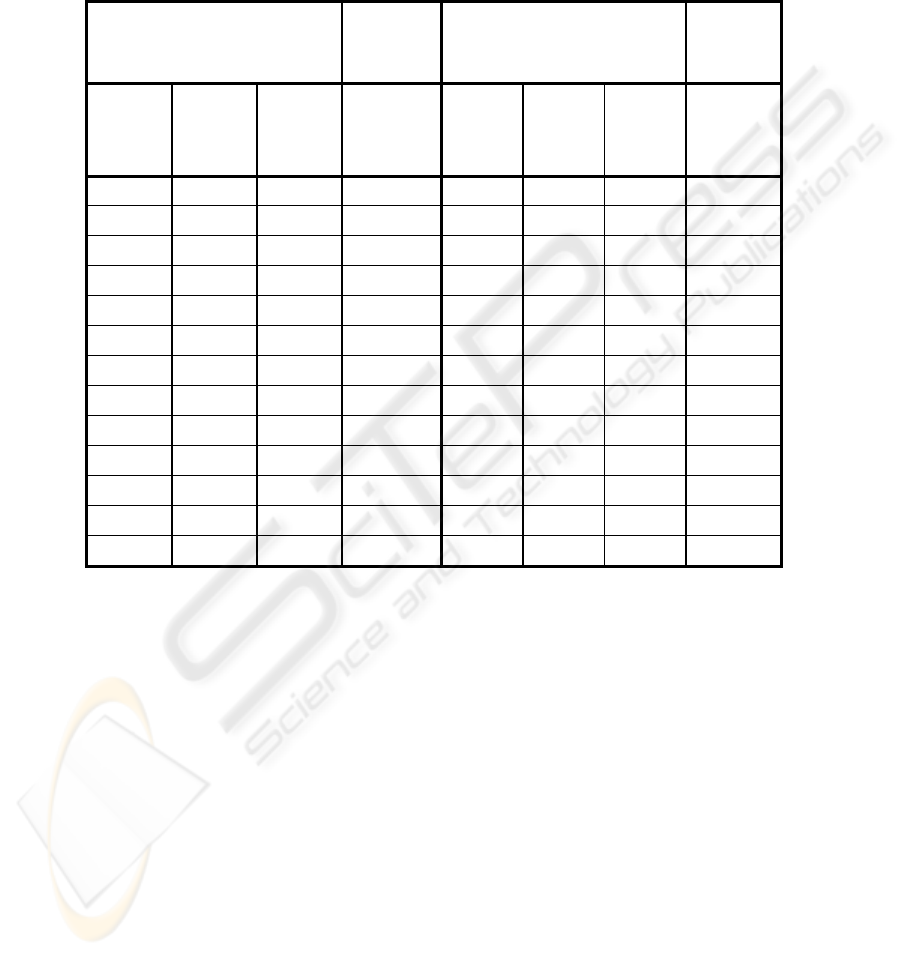
We worked with multilayer neural networks, which topologies were based on the
training set (see Table 1). The chain of chars of the plain text in a training set is
equivalent to a binary value that is 96 less than its ASCII code. The cipher text is then
a random chain of bits.
Table 1. The set of patterns (the training set).
THE PLAIN TEXT
THE
CIPHER
TEXT
THE PLAIN TEXT
THE
CIPHER
TEXT
Char ASCII
code
(DEC)
The
chain
of bits
The chain
of bits
Char ASCII
code
(DEC)
The
chain
of bits
The
chain
of bits
a 97 00001 000010 n 110 01110 011100
b 982 00010 100110 o 111 01111 101000
c 99 00011 001011 p 112 10000 001010
d 100 00100 011010 q 113 10001 010011
e 101 00101 100000 r 114 10010 010111
f 102 00110 001110 s 115 10011 100111
g 103 00111 100101 t 116 10100 001111
h 104 01000 010010 u 117 10101 010100
i 105 01001 001000 v 118 10110 001100
j 106 01010 011110 w 119 10111 100100
k 107 01011 001001 x 120 11000 011011
l 108 01100 010110 y 121 11001 010001
m 109 01101 011000 z 122 11010 001101
The initial population contains 30 three-layer feedforward neural networks. Each
network architecture is 5 - 5 - 6 (e.g. five units in the input layer, five units in the
hidden layer, and six units in the output layer), because the alphabet coding problem
is not linearly separable and therefore we cannot use neural network without hidden
units. The nets are fully connected. We use the genetic algorithm with the following
parameters: probability of mutation is 0.01 and probability of crossover is 0.5.
Adaptation of each neural network in given population starts with randomly generated
weight values that are the same for each neural network in the population. We also
used genetic algorithms with the same parameters for the partial neural network
adaptation, where number of generations for a partial adaptation was 500. Its
chromosome representation is described in [14].
History of the error function is shown in the figure 3. There are shown average
values of error functions in the given population. Other numerical simulations give
very similar results. The “binary sigmoid function” represents an average value after
adaptation with the binary sigmoid activation function consecutively with all
18

steepness parameters
σ
= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}. The “binary step function” represents an
adaptation with the binary step activation function (with the threshold
θ
), the
“saturated linear function” represents an adaptation with the saturated linear
activation function, and “Gaussian activation” represents an adaptation with the
Gaussian activation function. Each of these mentioned representations is associated
with all units in given neural network architecture. Opposite of this, the “best
individual” represents an adaptation of the best individual in population, which
chromosome is the following, see Fig. 2:
b
1
σ
i
b
2
σ
2
b
3
σ
3
b
4
σ
4
b
5
σ
5
b
6
σ
6
b
7
σ
7
b
8
σ
8
b
9
σ
9
b
10
σ
10
b
11
σ
11
1 5 1 7 1 1 3 0 1 5 3 0 1 7 3 0 1 5 1 6 1 2
units in the hidden layer units in the output layer
Fig. 2. The “best individual” chromosome in the last population.
5 Conclusions
All networks solve the alphabet coding task in our experiment, but artificial neural
network with evolving transfer functions of each unit works well, because several
different types of neurons are usually necessary to solve a problem. We can see that
the proposed technique is really efficient for the presented purpose, see the Fig. 3.
Networks with too many copies of the same neuron work usually worse.
0
5
10
15
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
number of generati on
E
binary sigmoid f unction
Gauss f unction
binary step f unction
saturated linear function
best individual
Fig. 3. The error function history.
Here, the transfer function is shown to be an important part of architecture of the
artificial neural network and have significant impact on artificial neural network’s
19

performance. Transfer functions of different units can be different and decided
automatically by an evolutionary process, instead of assigned by human experts. In
general, nodes within a group, like layer, in an artificial neural network tend to have
the same type of transfer function with possible difference in some parameters, while
different groups of nodes might have different types of transfer function.
References
1. Liu, Y. and Yao, X. “Evolutionary design of artificial neural networks with different
nodes”. In Proc. 1996 IEEE Int. Conf. Evolutionary Computation (ICEC’96), Nagoya,
Japan, pp. 670–675.
2. Fogel, D. B., Evolutionary Computation: Toward a New Philosophy of Machine
Intelligence. New York: IEEE Press, 1995.
3. Bäck, T. Hammel, U.and Schwefel, H.-P.“Evolutionary computation: Comments on the
history and current state,” IEEE Trans. Evolutionary Computation, vol. 1, pp. 3–17, Apr.
1997.
4. Mani, G. “Learning by gradient descent in function space”. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
System, Man, and Cybernetics, Los Angeles, CA, 1990, pp. 242–247.
5. Lovell D. R. and Tsoi, A. C. The Performance of the Neocognitron with Various S-Cell and
C-Cell Transfer Functions, Intell. Machines Lab., Dep. Elect. Eng., Univ. Queensland,
Tech. Rep., Apr. 1992.
6. Stork, D. G. Walker, S. Burns, M. and Jackson, B. “Preadaptation in neural circuits”. In
Proc. Int. Joint Conf. Neural Networks, vol. I, Washington, DC, 1990, pp. 202–205.
7. White D. and Ligomenides, P. “GANNet: A genetic algorithm for optimizing topology and
weights in neural network design”. In Proc. Int. Workshop Artificial Neural Networks
(IWANN’93), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 686. Berlin, Germany: Springer-
Verlag, 1993, pp. 322–327.
8. Hwang, M. W. Choi, J. Y. and Park, J. “Evolutionary projection neural networks”. In Proc.
1997 IEEE Int. Conf. Evolutionary Computation, ICEC’97, pp. 667–671.
9. Sebald, A. V. and Chellapilla, K. “On making problems evolutionarily friendly, part I:
Evolving the most convenient representations”. In Porto, V. W., Saravanan, N., Waagen, D.
and Eiben, A. E. (Eds.): Evolutionary Programming VII: Proc. 7th Annu Conf.
Evolutionary Programming, vol. 1447 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Berlin,
Germany: Springer-Verlag, 1998, pp. 271–280.
10. Volná E. “Evolution design of an artificial neural network with fixed topology”, In R.
Matoušek, P. Ošmera (eds.): Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Soft
Computing, Mendel'06, Brno, Czech Republic, 2006, pp. 1-6.
11. Lawrence, D. Handbook of genetic algorithms. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York 1991.
12. Volná, E. „Using Neural network in cryptography“. In P. Sinčák, J. Vaščák, V. Kvasnička,
R. Mesiar (eds.): The State of the Art in Computational Intelligence. Physica-Verlag
Heidelberg 2000. pp.262-267.
13.
Garfinger, S. PGP: Pretty Good Privanci. Computer Press, Praha 1998.
14. Volná, E. „Learning algorithm which learns both architectures and weights of feedforward
neural networks“. Neural Network World. Int. Journal on Neural & Mass-Parallel Comp.
and Inf. Systems. 8 (6): 653-664, 1998.
20
