
A JOINT HIERARCHICAL FUZZY-MULTIAGENT MODEL
DEALING WITH ROUTE CHOICE PROBLEM
RoSFuzMAS
Habib M. Kammoun, Ilhem Kallel and Adel M. Alimi
Research Group on Intelligent Machines REGIM, University of Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords: Transportation Route Choice problem, Intelligent Transportation System, MultiAgent System, Fuzzy
Controller.
Abstract: Nowadays, multiagent architectures and traffic simulation agent-based are the most promising strategies for
intelligent transportation systems. This paper presents a road supervision model based on fuzzy-multiagent
system and simulation, called RoSFuzMAS. Thanks to agentification of all components of the transportation
system, dynamic agents interact to provide real time information and a preliminary choice of advised routes.
To ensure the model rationality, and to improve the route choice make decision, we propose to use a
hierarchical Fuzzy inference including some pertinent criteria handling the environment as well as the driver
behavior. A multiagent simulator with graphic interface has been achieved to visualize, test and discuss our
road supervision system. Experimental results demonstrate the capability of RoSFuzMAS to perform a
dynamic path choice minimizing traffic jam occurrences by combining multiagent technology and real time
fuzzy behaviors.
1 INTRODUCTION
In view of the enormous increase of vehicle number,
accidents and traffic jam situations become
widespread in all road networks in the world. A
solution for these problems is to develop and invest
in Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) which is
capable of managing in a better way the existing
capacity and encouraging more efficient vehicle
routing over time and space, in order to improve
safety, traffic efficiency, etc. Varied applications of
ITS currently under development represent a real
opportunity to advance toward a best future.
Furthermore, a number of ITS based on
multiagent approach came recently into being to
improve performances dynamic routing and traffic
management by employing collaborative driving
system (Hallé and Chaib-Draa, 2005) or by route
guidance system (Adler et al. 2005).
Since the nineties, the use of fuzzy logic in ITS is
marked. Research in soft computing field has been
exploring the application of fuzzy set theory as a
framework solving many transportation problems
(Teodorovic, 1999), as route choice problem, traffic
assignment problem, traffic control at the
intersection, accident analysis and prevention, and
traffic light controller. The majority of authors are
based on a comparison of fuzzy values representing
the routes’ costs. The corresponding rules are of the
type: “If times on route 1 and 2 are very high, I will
probably take route 3”.
In this sense, this paper presents a joint
hierarchical fuzzy-multiagent model dealing with
transportation route choice problem. Our model
called RoSFuzMAS, acronym for “Road Supervision
based on Fuzzy MultiAgent System” is poised
between two different philosophies: the distributed
and parallel ITS and the uncertain reasoning. To
ensure the model rationality, and to improve the
route choice make decision, we propose to use a
hierarchical Fuzzy inference including some
pertinent criteria handling the environment as well
as the driver behavior.
The paper is organized as follows: Next section
presents our road supervision system. The third
section describes the improvement of decision
making for route choice problem by adding other
decision criteria structured in a hierarchical fuzzy
controller. The simulation part detailed in the forth
section gives an idea about the environment and
discusses some results.
394
M. Kammoun H., Kallel I. and M. Alimi A. (2007).
A JOINT HIERARCHICAL FUZZY-MULTIAGENT MODEL DEALING WITH ROUTE CHOICE PROBLEM - RoSFuzMAS.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 394-397
DOI: 10.5220/0001629503940397
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 A ROAD SUPERVISION
DISTRIBUTED UNDER
MULTIAGENT APPROACH
Since some years ago, multiagent systems (MAS)
took hold data processing (Wooldridge, 2002).
Indeed, a cooperative interaction always leads to an
increase of quantitative and qualitative system
performances (Kallel et al., 2002), (Kammoun et al.,
2005), (Kallel and Alimi, 2006).
In this sense, our system has as objectives to
ensure an efficient network capacity allocation and
decrease the number of congestion situations.
Accordingly, the system proposes a best road choice
to help drivers’ vehicle to attempt their destinations.
We propose a model involving three kinds of
agents: City Agent (CA), Road Supervisor Agent
(RSA) and Intelligent Vehicle Agent (IVA). Figure 1
presents three levels of the proposed system as well
as the acquaintance links between CA, RSA and IVA.
Each agent use the organizational model AGRE
(Agent-Group-Role-Environment) (Ferber et al.,
2005) and lives according to a cycle bound to an
iterative process of reception / deliberation / action
detailed in (Kallel et al., 2006).
….
CA
Hierarchical
level of groups
RSA
IVA
Interaction link
….
Figure 1: Hierarchical organizational architecture.
The RSA computes the traffic index for road i
(RFI
i
) according to equation (1).
1
1
max max
*
*
1
with Average ( )
v
N
j
j
N
v
j
jj
v
i
vtvt
T
j
j
v
T
T
N
RFI
NTNT
TT
N
=
=
∑
==
==
∑
(1)
with N
v
is the number of vehicles in road i, N
vmax
is the maximum number of vehicles in this road, T
j
represents the time in jam state for vehicle j
calculating in T
t
period.
Equation 2 presents the Path Flux Index (PFI) as
a sum of RFI
i
average with the route length
pondered by a coefficient α.
1
nb
ii
i
PFI RFI l
α
+
=
=
∑
(2)
with nb is the number of road in the path, l
i
is the
length of road i and α is the length importance
coefficient.
3 HIERARCHICAL FUZZY
ROUTE CHOICE CONTROL
Modelling route choice behaviour is a complex
activity if we add other inputs. We try to improve
our route choice model by using fuzzy logic (Zadeh,
1965). Furthermore, the use of hierarchical fuzzy
controller in several applications’ areas showed a
real improvement in precision and interpretability
(Alimi, 1997), (Kallel et al., 2005) especially in
multi-choice problem.
As shown in figure 2, we select only the k first paths
as k alternatives for fuzzy choice, while fuzzifying
their PFI values. The hierarchical controller uses
other inputs fuzzy representations of route
characteristic depending on n criteria. It provides the
recommended route R to follow by the vehicle
driver.
Figure 2: Hierarchical fuzzy route choice model.
with FiPj is the fuzzy representation of path j corresponding
for criteria i and R is the
recommended route.
3.1 Fuzzy Criteria Controller FCC
Let suppose that k=3 and n=5, we will compare 3
alternative routes depending on 5 factors in urban
environment. These factors are the most important
FCC
k
.
.
.
FCC
1
F
1
P
1
F
n
P
1
.
.
.
P
1
FCC
2
P
2
P
k
R
FPFI
1
FPFI
2
FPFI
k
Arithmetic selection
F
1
P
2
F
n
P
2
.
.
.
F
1
P
k
F
n
P
k
.
.
.
FRCC
1
FRCC
2
FRCC
k
FP
1
FP
2
FP
k
A JOINT HIERARCHICAL FUZZY-MULTIAGENT MODEL DEALING WITH ROUTE CHOICE PROBLEM -
RoSFuzMAS
395

criteria, more used, and accessible from the vehicle
information system.
The FCC allows a better road evaluation
according to criteria concerning the vehicle state, the
driver behavior and the environment.
Inputs parameters: these criteria are presented
in descending order of their importance for
route choice makes decision.
o RWInformation (road work information, the
highest important criteria): NoRoadWork,
RoadWork
o TimeOfDay: Morning, Midday, Evening, Night
o Familiarity: Unfamiliar (with a route), Medium,
Familiar. This parameter takes in account the
driver’s experiences and will be updated in
each trip
o WeatherConditions: Bad, Medium, Good
o Speed: Slow, Medium, High
Output parameters:
o Preference: Weak, Strong
The figure 3 draws the membership function
used in this case.
Figure 3: Fuzzification of inputs and output used in FCC.
Rule base of FCC model: The rule base of
FCC model is built by combination of input and
output variables. This base is generated by experts in
the transportation area and formed initially by 216
rules. As an example of rule, we can cite: “if
RWInformation is NoRoadWork and TimeOfDay is
Night and Familiarity is Familiar and
WeatherConditions is Good and Speed is Medium
then Preference is Strong”.
Fuzzy Inference and defuzzification of the
FCC model: For the inference process, Mamdani
(max–min) inference method is used in FCC model.
The Center of Gravity (COG) method is used for
defuzzification of the FCC model.
In view of the fact that the number of rules is high,
we propose to model this controller by a hierarchical
fuzzy architecture in order to gain in interpretability
without decreasing efficiency. We regroup by pairs
the criteria having some correlation.
3.2 Fuzzy Route Choice Controller FRCC
The FRCC uses as inputs, the outputs of FCC and a
Fuzzy representation the PFI, called FPFI.
Input parameters:
o Preference: Weak, Strong
o FPFI: Low, Middle, High
Output parameters:
o FP: VeryUnrecommended, Unrecommended,
Undecided, Recommended, VeryRecommended
Rule base of FRCC model: The rule-base is
formed initially by 216 rules. As an example of rule,
we can cite: “if Preference is Strong and FPFI is
Low then FP is VeryRecommended”.
4 SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS
Figure 4 presents some virtual maps, created by
agent observer of TurtleKit tool (Michel et al.,
2005), in order to apply several tests varying
vehicles’ positions, environment conditions and
drivers’ behaviour factors.
Figure 4: Examples of simulation environments.
The simulator recognizes three kinds of vehicles
named classic vehicle, bad vehicle, and intelligent
vehicle. The first one is a vehicle without intelligent
module; the second one is a vehicle stopped in jam
situation; the third one is intelligent, that means it is
a part of RoSFuzMAS. With several tests, we try to
compare intelligent vehicle route choice behaviour
with a classic vehicle leaving from the same position
in the same time and having the same destination.
The first road network presented is a virtual map
holding eleven roads numbered from 1 to 11 in only
one city, and a variable number of cars circulating
with random and autonomous way. The network
state in defined time intervals is known as well as
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
396
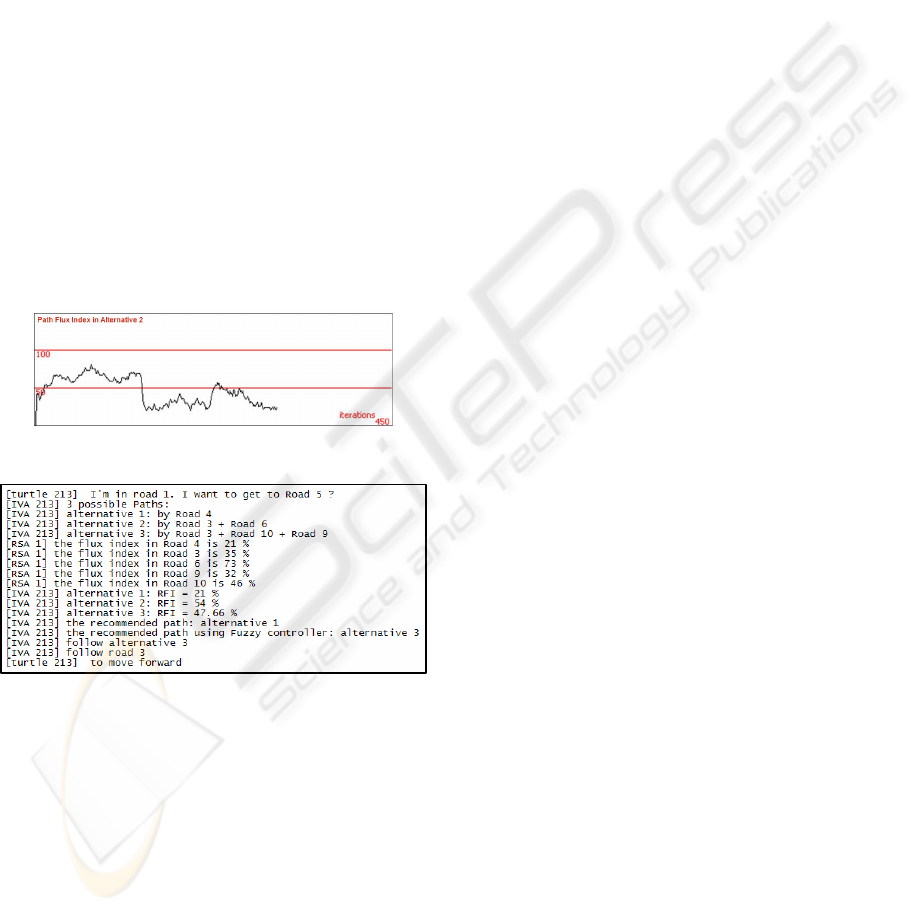
the traffic load intensity to be forwarded from road 1
to road 5. Figure 5 shows the road flux index in the
different alternatives from road number 1 to road
number 5. The IVA chooses the first alternative (by
road 4) because it has the smallest flux index
compared with second and third alternatives. The
flux index in the second alternative is high because
of jam situation in road 6. The flux index in the third
alternative is high because of the route length. The
RFI was from 0 to 100 %. The simulation has been
done every 450 seconds when updating the road flux
index table after every 60 seconds.
Second series of simulations was performed
using the fuzzy rule base with the same parameters
of the first simulation. Figure 6 confirms that after
the work information, bad weather condition, and
driver’s unfamiliarity of the road 4, the controller
proposes the third alternative to follow.
Various other simulations are applied with other
maps, other positions of clutters, and different
criteria. The results show that the fuzzy logic
application for route choosing gives a better
management of road network in all cases.
Figure 5: Viewer of Path Traffic Index.
Figure 6: Example of communication messages between
IVA and RSA.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we presented a hierarchical
architecture as well as a model and a simulation of
road supervision system based on joint fuzzy logic
and multiagent approach. The route choice algorithm
developed shows acceptable results, but it become
very complex if we add other criteria for route
choice make decision.
The originality of this model resides on:
A hierarchical fuzzy controller in the
multi-route choice problem.
Generic architecture, without limit for the
number of factors to use.
A hierarchical multiagent architecture handling
fuzzy inference for the route choice problem.
As perspectives, we intend in the near future to
add other options such as the factor of variant speed
for IAV, an advancement treatment of crossroads, an
environment with double way, and the change lane
problem. Applying learning methods such as (Kallel
et al., 2006) become a necessity in order to reduce
rule numbers and adjust membership functions.
Furthermore, paths learning and multiobjective
optimization of vehicle path planning can be added.
REFERENCES
Adler, J. L., Satapathy, G., Manikonda, V., Bowles, B., &
Blue, V. J., 2005. A multi-agent approach to
cooperative traffic management and route guidance.
Transportation Research Part B, 39(4), 297-318.
Alimi, A. M., 1997. A neuro-fuzzy approach to recognize
Arabic handwritten characters. In Proc. of the I. C. on
Neural Networks, vol. 3, 1397-1400.
Ferber, J., Michel, F. & Baez, J., 2005. AGRE: Integrating
environments with organizations. In Proc. of E4MAS,
Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, 3374, 48-56.
Hallé, S., Chaib-Draa, B., 2005. A collaborative driving
system based on multiagent modelling and simulations.
Transportation Research Part C, 13, 320-345.
Kallel, I., Jmaiel, M., & Alimi, A. M., 2002. A Multi-
Agent Approach for Genetic Algorithm
Implementation. In Proc. of IEEE SMC, Tunisia.
Kallel, I., Jelleli, T. & Alimi, A. M., 2005. Hierarchical
FLS Design Using Multi-Agent Genetic Approach. In
Proc. of GFS’2005, Granada, Spain, 142-147.
Kallel, I., Alimi, A. M., 2006. MAGAD-BFS: A Learning
Method for Beta Fuzzy Systems based on a Multi-Agent
Genetic Algorithm. I. J. of Soft Computing, 10(9), 757-772.
Kammoun, H. M., Kallel, I., Alimi, A. M., 2005.
RoSMAS²: Road Supervision based Multi-Agent
System Simulation. In Proc. of the I. C. on Machine
Intelligence ACIDCA-ICMI’2005, Tunisia, 203-210.
Michel, F., Beurier, G., & Ferber, J., 2005. The TurtleKit
Simulation Platform: Application to Complex
Systems. In Proc. of SITIS’05, 122-127.
Teodorovic, D., 1999. Fuzzy logic systems for
transportation engineering: the state of the art.
Transportation Research Part A, 33(5), 337-364.
Wooldridge, M., 2002. An introduction to multiagent
systems, John Wiley and Sons. February 2002.
Zadeh, L., 1965. Fuzzy sets, Information and Control 8,
338-353.
A JOINT HIERARCHICAL FUZZY-MULTIAGENT MODEL DEALING WITH ROUTE CHOICE PROBLEM -
RoSFuzMAS
397
