
A FUZZY SYSTEM FOR INTEREST VISUAL DETECTION BASED
ON SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
Eugenio Aguirre, Miguel Garc
´
ıa-Silvente, Rui Pa
´
ul
Department of Computer Science and A.I., E.T.S. Ingenier
´
ıa Inform
´
atica
University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain
Rafael Mu
˜
noz-Salinas
Deparment of Computing and Numerical Analysis, E.P.S.
University of Cordoba, Cordoba, Spain
Keywords:
Human-Robot Interaction, Interest Detection, Head Pose Estimation, Fuzzy Logic, Support Vector Machine.
Abstract:
Despite of the advances achieved in the past years in order to design more natural interfaces between intelligent
systems and humans, there is still a great effort to be done. Considering a robot as an intelligent system,
determining the interest of the surrounding people in interacting with it is an interesting ability to achieve.
That information can be used to establish a more natural communication with humans as well as to design
more sophisticated policies for resource assignment. This paper proposes a fuzzy system that establishes a
level of possibility about the degree of interest that people around the robot have in interacting with it. First, a
method to detect and track persons using stereo vision is briefly explained. Once the visible people is spotted,
their interest in interacting with the robot is computed by analyzing its position and its level of attention
towards the robot. These pieces of information are combined using fuzzy logic. The level of attention of a
person is calculated by analyzing th e pose of his head that is estimated in real-time by a view based approach
using Support Vector Machines (SVM). Although the proposed system is based only on visual information, its
modularity and the use of fuzzy logic make it easier to incorporate in the future other sources of information
to estimate with higher precision the interest of people. At the end of the paper, some experiments are shown
that validate the proposal and future work is addressed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The interaction between Intelligent Systems and hu-
man beings is a topic that is focusing a great research
effort nowadays. The development of natural and
multimodal interfaces is needed to enhance the inter-
action abilities of current Intelligent Systems. In par-
ticular, within the area of Robotics, the development
of successful robotic systems applied to service tasks
in home and office environments implies the genera-
tion of natural human-robot interfaces. In that sense,
important issues that must be taken into account are
how robots can detect the presence of persons around
them and how do they recognize when and how long
a person is interested in establishing an interaction.
In order to achieve this goal, it is necessary to solve
several problems. First, a robot must be able to de-
tect persons in its vicinity and track their movements
over time. People tracking is not an easy task since
several persons could be moving at the same time,
crossing their trajectories and occluding each others.
We can find many works in the literature on this topic
(Fritsch et al., 2003; Snidaro et al., 2005). The tech-
niques to perform the detection and tracking are fre-
quently based on the integration of different informa-
tion sources such as: skin color, face detectors, visual
analysis of the motion or laser range finder.
Once a robot is able to recognize and track the
persons in its vicinity, it should be able to detect their
interest in establishing an interaction with it. In that
task, several types of signals from the human can
be taken into account (both verbal and non-verbal).
Some authors (Bennewitz et al., 2005) use sound
source localization or speech recognition besides vi-
sual perception to detect which persons are the most
interested. In other cases, facial expressions (Song
181
Aguirre E., García-Silvente M., Paúl R. and Muñoz-Salinas R. (2007).
A FUZZY SYSTEM FOR INTEREST VISUAL DETECTION BASED ON SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 181-188
DOI: 10.5220/0001632601810188
Copyright
c
SciTePress

et al., 2001) or hand gestures (Ghidary et al., 2002)
are analyzed. Finally, other authors (Kulic and Croft,
2003) propose the use of non-verbal signals present
in physiological monitoring systems that include skin
conductance, heart rate, pupil dilation and brain and
muscle neural activity.
In regards to the role of the fuzzy logic in robotics,
an extensive catalogue of the uses of fuzzy logic in
autonomous robots can be found in (Saffiotti, 1997).
Fuzzy logic has been successfully applied to a multi-
tude of problems such as: design of controlling be-
haviors for navigation, behavior coordination, map
building, integration of deliberative and reactive lay-
ers, etc (Aguirre and Gonz
´
alez, 2000). Lately, fuzzy
logic has also been applied to the area of human-
robot interaction. In (Bien and Song, 2003) sev-
eral soft computing techniques are applied to service
robotic systems for comfortable interaction and safe
operation. Fuzzy logic is used for recognizing facial
emotional expression and for coordinating bio-signals
with robotic motions. In (Kulic and Croft, 2003) sev-
eral sets of fuzzy rules are used for estimating intent
based on physiological signals.
In this work we are interested in computing a
value of possibility of the interest of a person to inter-
act with the robot. This value is computed using only
visual information, but the modularity of the system
makes easy the posterior incorporation of other types
of input data as sound or laser range finder. The inter-
est is computed according to the position of the person
and its degree of attention. In a first step, people de-
tection and tracking problems are solved by a stereo-
scopic system. The use of stereo vision brings sev-
eral advantages when developing human-robot appli-
cations. On the one hand, the information regarding
disparities becomes more invariable to illumination
changes than the images provided by a single camera,
being a very advantageous factor for the background
estimation (Darrell et al., 2001). Furthermore, the
possibility to know the distance to the person could
be of great assistance for the tracking as well as for a
better analysis of their gestures.
Once the surrounding people is spotted, we pro-
pose a new method for estimating the interest of the
detected people in interacting with the robot by means
of computer vision and fuzzy logic. The person’s at-
tention is detected by the analysis of the pose of his
head. To detect the head pose we have employed a
view based approach using Support Vector Machines
(SVM) (Cristianini and Shawe-Taylor, 2000) that let
us classify the head pose in real time.
The approach presented in this work is not only
valid for robotic applications. It can also be employed
in intelligent systems that use stereoscopic devices.
For example, it can be applied in intelligent spaces
where one or several intelligent devices wish to inter-
act with people according the interest shown by each
person.
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows. Section 2 gives an general overview of the
hardware and software system, describing the method
employed for the detection and tracking of people in
the surroundings of the robot. In Section 3 it is ex-
plained the SVM based approach to estimate the head
pose and the fuzzy system for estimating the interest
of people. In Section 4 it is shown the experimenta-
tion carried out, and finally, Section 5 outlines some
conclusions and future works.
2 PEOPLE DETECTION AND
TRACKING
The hardware system is comprised by a laptop to pro-
cess the information, a stereoscopic system with a
binocular camera (PtGrey, 2005) and a Nomad 200
mobile robot (see Fig. 1).
Figure 1: Robot with stereo vision system.
The ability of detecting and tracking people is fun-
damental in robotic systems when it is desirable to
achieve a natural human-robot interaction. They are
achieved in our architecture by combining stereo vi-
sion and color using plan-view maps. Following, the
process for people detection and tracking is explained
in a summarized way. The readers more interested
in this process are referred to (Mu
˜
noz-Salinas et al.,
2006).
Our robot has a stereo camera that is mounted
on a pan-tilt unit (PTU). The stereo camera captures
two images from slightly different positions (cali-
brated stereo pair) that are transferred to the com-
puter to calculate a disparity image containing the
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
182

points matched in both images. Knowing the intrin-
sic parameters of the stereo camera it is possible to
reconstruct the three-dimensional position p
cam
of a
matched pixel (u, v). Then, the points captured are
translated to a “robot” reference system, placed at
the center of the robot at ground level in the direc-
tion of the heading of the robot. Generally, the num-
ber of points captured by our stereo system is very
high. In order to perform a reduction of the amount
of information, the points captured by the camera are
orthogonally projected into a 2D plan-view map O
named occupancy map (Harville, 2004; Haritaoglu
et al., 2002; Hayashi et al., 2004).
The next step in our processing, is to identify the
different objects present in O that could correspond to
human beings (human-like objects). For that purpose,
O is processed with a closing operator in order to link
possible discontinuities in the objects caused by the
errors in the stereo calculation. Then, objects are de-
tected as groups of connected cells. Those objects
whose area are similar to the area of a human being
and whose sum of cells (occupancy level of the ob-
ject) is above a threshold θ
occ
are considered human-
like objects. This test is performed in a flexible way
so that it is possible to deal with the stereo errors and
partial occlusions. However, the human-like objects
detected might not belong to real people but to ele-
ments of the environment. The approach employed
in this work to detect a person consists in detecting if
any of the human-like objects found in O show a face
in the camera image.
Face detection is a process that can be time con-
suming if applied on the entire image, thus, it is only
applied on regions of the camera image where the
head of each object should be (head region). As the
human head has a typical average width and height,
the system analyzes first if the upper part of a human-
like object has similar dimensions. If the object does
not pass this test, the face detector is not applied to
it. This test is performed in a flexible manner so
that it can handle stereo errors and people with dif-
ferent morphological characteristics can pass it. If the
human-like object passes this test, the corresponding
region in the image is analyzed to detect if it con-
tains a face. The face detector employed is based on
the face detector of Viola and Jones (Viola and Jones,
2001) which was later improved by Lienhart (Lienhart
and Maydt, 2002). We have employed the OpenCv’s
Library (Intel, 2005) implementation that is trained to
detect frontal human faces and works on gray level
images.
Once a face has been detected on a human-like
object, a color model of the person torso is created
(Comaniciu et al., 2000). The idea is to assist the
tracking process by capturing information about the
color of the clothes of the user so that the robot can
distinguish him/her from other people in the environ-
ment. Therefore, pixels around what it should be the
chest of the person are used. The position of the chest
in the camera image is estimated as 40 cm below the
top of the head region. The size of the region used to
create the color model depends on the distance of the
person from the camera. When the object is far from
the camera the region used is smaller to avoid includ-
ing pixels from the background and it becomes bigger
when the object is near to the camera.
Tracking consists in detecting in subsequent
frames the human-like object that corresponds to the
person being tracked. The Kuhn’s well-known Hun-
garian Method for solving optimal assignment prob-
lems (Kuhn, 1955) is employed for that purpose.
Two pieces of information are combined (position and
color) to assign a value to each human-like object in-
dicating its likelihood to be the person being tracked.
On one hand, a prediction of the future position of the
person being tracked is calculated using the Kalman
filter. The nearer a human-like object is from the
position estimated for the person being tracked, the
higher likelihood it will have to be him/her. On the
other hand, color information is employed to achieve
a more robust tracking. The more similar the color
of a human-like object is to the clothes’ color of the
person being tracked, the higher likelihood it will
have to be him/her. Both likelihood are combined
so that when the person being tracked is near oth-
ers, color information can help to distinguish him/her.
The human-like object with highest likelihood is con-
sidered to be the person being tracked if its likelihood
value exceeds a certain threshold. In that case, the
Kalman filter is updated with the new observations
and also the color model of the person is updated so
that it can adapt to the illumination changes that take
place.
When the position of the person being tracked
is located, the system determines the location of his
head in the camera image. In this work, the head is
modeled as an ellipse whose size in the camera image
is determined according to the distance of the person
to the camera. Firstly, the system calculates an initial
estimation of the head position in the camera image
based on stereo information. Then, the initial position
is refined by a local search process. For that purpose,
the gradient around the ellipse perimeter is examined
in order to determine the likelihood of a position using
the Birchfield’s method (Birchfield, 1998). The posi-
tion with higher likelihood is considered the person’s
head position.
A FUZZY SYSTEM FOR INTEREST VISUAL DETECTION BASED ON SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
183

VL L M H VH
1
0 1
Interest
Left Center
1
0 deg 90 deg 180 deg
Right
Angle
1
Low Medium High
0m 1.5m 2.5m 8m
Distance
Low HighMedium
0 1
1
Attention
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 2: Fuzzy sets of the linguistic variables: (a) Distance (b) Angle (c) Attention (d) Interest.
3 INTEREST DETECTION
In the previous section, we have described as the robot
is able to detect and track them the persons in its
vicinity by using the stereo system. This section ex-
plains our approach for estimating the interest of the
detected people in interacting with the robot by means
of fuzzy logic. The approach presented in this work
is based on stereo vision but the system can be eas-
ily expanded to merge other sources of information.
The advantages of using fuzzy logic are mainly three.
Firstly, the robot has to deal with information from
the stereo system that is affected by uncertainty and
vagueness. Fuzzy logic is a good tool to manage
these factors using linguistic variables. Secondly, the
human knowledge can be usually expressed as rules.
Fuzzy logic allows to establish relationships among
the variables of a problem through fuzzy rules pro-
viding an inference mechanism. Finally, there are
methods in fuzzy logic to fuse the results from several
fuzzy rules in order to achieve a final overall result.
Therefore, the system designed in this work, based
exclusively in stereo information, can be integrated
with other fuzzy systems using other types of infor-
mation as source sound localization, gesture analysis
or speech recognition systems.
In this work, the determination of the degree of
interest of a person is based on its position and its de-
gree of attention. The position of a person is analyzed
using both its distance to the center of the robot and its
angle in respect to the heading direction of the robot.
The first feature is measured by the linguistic variable
Distance and the second one by the linguistic variable
Angle. These linguistic variables have three possible
values each of them, that are shown in Fig. 2. The
meaning of these two variables is the following: if the
person is detected near to the robot and more or less
centered with respect to it, then we consider that the
person is more interested in establishing interaction
with the robot than when the person is far or at the left
or right side of the robot. Nevertheless, the position
of the person is not enough to determine his interest
in interacting with the robot. Thus, the third feature
shown in this paper is the person’s attention detected
by the analysis of the pose of his head. To detect the
head pose we have employed a view based approach
using SVM that is explained in the next section.
3.1 Estimating Face Attention using
SVM
One of the most prominent cues to detect if a person is
paying attention to the system is the orientation of his
face, i.e., a higher degree of attention can be assumed
when a person is looking at the system than when it
is backwards. This section describes our approach for
face attention estimation.
We have divided head poses in three main cat-
egories: “A” that comprehends all the frontal faces
(faces looking directly at the camera), “B” that com-
prehends all the slightly sided faces (faces looking to
some point slightly above, below or aside from the
camera) and “C” that comprehends all the other faces
(side faces, faces looking at some point in the ceiling
or ground, backward heads). Figure 3 shows exam-
ples of each one of the categories employed.
Figure 3: Head Pose Estimation: Classes A, B and C.
We have created a head pose database comprised
by a total of 4000 samples equally distributed among
the three classes. The database contain images of 21
different people (men and women), of different races,
with different hair cuts and some of them wearing
glasses. The database samples were manually clas-
sified into categories “A”, “B” or “C” according to
where people were looking at. All the images are
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
184

gray-scale and 48x40 sized.
Since the information contained in the patterns
is redundant, we have applied Principal Component
Analysis (PCA) to reduce the data dimensionality.
PCA (Henry and Dunteman, 1989) is a technique
widely employed for dimensionality reduction able to
retain those characteristics of the data set that con-
tribute most to its variance, by keeping lower-order
principal components and ignoring higher-order ones.
Such low-order components often contain the “most
important” aspects of the data. The more high-order
characteristics we remove, the faster the process of
training and estimation. However, it is important
to use a number of characteristics that allow us to
achieve good results without affecting our need to
have real time results. We made some tests with dif-
ferent number of characteristics and we determined
that 50 characteristics allowed a good trade-off be-
tween classification accuracy and computing time.
The training process has been carried out using
SVM. For that purpose, we have employed the libsvm
library (free software available in Internet (Chang and
Lin, 2006)). For more information about SVM, the
interest reader is referred to (Cristianini and Shawe-
Taylor, 2000). To certificate that results were satisfac-
tory before applying the model we trained the SVM
with 85% of the data set and kept the remainder 15%
to test the model generated. The result on the test set
was of 93.14% of accuracy.
Our system estimates the attention of each de-
tected person in real time despite of his/her move-
ments. For that purpose, the head location in the cam-
era image of each person is determined using the tech-
niques described in Sect. 2. The head region of each
person is resized to 48x40 pixels and then, the first 50
principal components are extracted and passed to the
SVM classifier.
SVM estimates the head pose in one of the three
categories previously indicated. However, the classi-
fier output is an instantaneous value that does not take
into account past observations. In order to consider
past observations, we define the variable HP
(t)
as:
HP
(t)
= αHP
(t−1)
+ (1 − α)SvmOut
t
(1)
where SvmOut
t
is defined on the basis of the classifier
output as:
SV MOut
t
=
1 if current output of SVM = “A”;
0.5 if current output of SVM = “B”;
0 if current output of SVM = “C”.
In Eq. 1, α is a weighting factor that ponders the
influence of past observations. In this work we set
α = 0.3 that is sufficient to avoid abrupt variations
and isolated pose estimation errors.
To deal with the uncertainty and vagueness in this
process we use a linguistic variable called “Attention”
and divide it into “High”, “Medium” and “Low” val-
ues (see Fig. 2). This variable will take as input values
the measures of face attention estimation considered
by HP (Eq. 1). In figure 2 it is possible to see the
labels for the variable “Attention”.
3.2 Fuzzy System for Interest
Estimation
Once the three linguistic variables have been defined,
the rules base that integrates them are explained in
this section. The idea that governs the definition of
the rules base is dominated by the value of the vari-
able Attention. If the attention has an high value the
possibility of interest is also high depending on the
distance and the angle of the person to the robot. If
the attention is medium then the possibility of interest
has to be decrease but like in the former case depend-
ing on the distance and angle. Finally if the attention
is low, it means that the person is not looking at all to
the area where the robot is located and the possibility
of interest is defined as low or very low depending on
the other variables. The rules for the case in which
Attention is High are shown by Table 1. The other
cases are expressed in a similar way using the appro-
priate rules. The output linguistic variable is Interest
that has the five possible values shown by Figure 2(d).
Table 1: Rules in the case of high Attention.
IF THEN
Attention Distance Angle Interest
High Low Left High
High Low Center Very High
High Low Right High
High Medium Left Medium
High Medium Center High
High Medium Right Medium
High High Left Low
High High Center Medium
High High Right Low
Finally to compute the value of possible interest, a
fuzzy inference process is carried out using the opera-
tor minimum as implication operator. Then the output
fuzzy sets are aggregated and the overall output is ob-
tained. The overall output fuzzy set can be understood
as a possibility distribution of the interest of the per-
son in the [0, 1] interval. Therefore values near to 1
mean a high level of interest and vice versa.
A FUZZY SYSTEM FOR INTEREST VISUAL DETECTION BASED ON SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
185

Figure 4: Interest according distance and attention. Frames in each row (a, b and c), (d, e and f ) and (g, h and i) show the
person at different distances while frames in each column (a, d and g), (b, e and h) and (c, f and i) show the person with
different attention.
4 EXPERIMENTATION
A broader experimentation has been done to validate
our system. All of these experimentations results
were very satisfactory in respect to interest estimation
using our system. Because of space reasons we opted
to describe in detail only one of the experimentations.
To perform the stereo process we have used images of
size 320x240 and sub-pixel interpolation to enhance
the precision in the stereo calculation. The operation
frequency of our system is about 30 Hz without con-
sidering the time required for stereo computation.
Regarding the interest estimation, we have
checked that the interest degree assigned to each
tracked person increases and decreases dynamically
accordingly to the behavior of the person in relation
to the robot. To test it, one person has been recorded
moving in front of the robot in a manner that it was
possible to have frames of the person in all the situ-
ations regarding “Attention” and “Distance”. Frames
from this video can be seen in Fig. 4. In this figure,
frames a, b, and c show the person close to the robot
(”Low Distance”) and looking in different ways. In-
terest is higher when when person looks towards the
robot. In frames d, e and f it is possible to observe
the same situation but at a higher distance (”Medium
Distance”). Therefore the final interest value com-
puted is slightly lower. In frames g, h and i we have
the same person in the same situations (in respect to
where he is looking at) but at even a higher distance
from the robot. Therefore the final interest value com-
puted is even lower. It is also possible to observe that
when the person is looking approximately the same
way (in frames a, d, g person is showing low atten-
tion, in frames b, e, h person is showing medium at-
tention and in frames c, f , i he is showing high atten-
tion) interest varies usually according distance. The
closer to the robot the higher the interest.
As it was expected, the higher value of interest
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
186
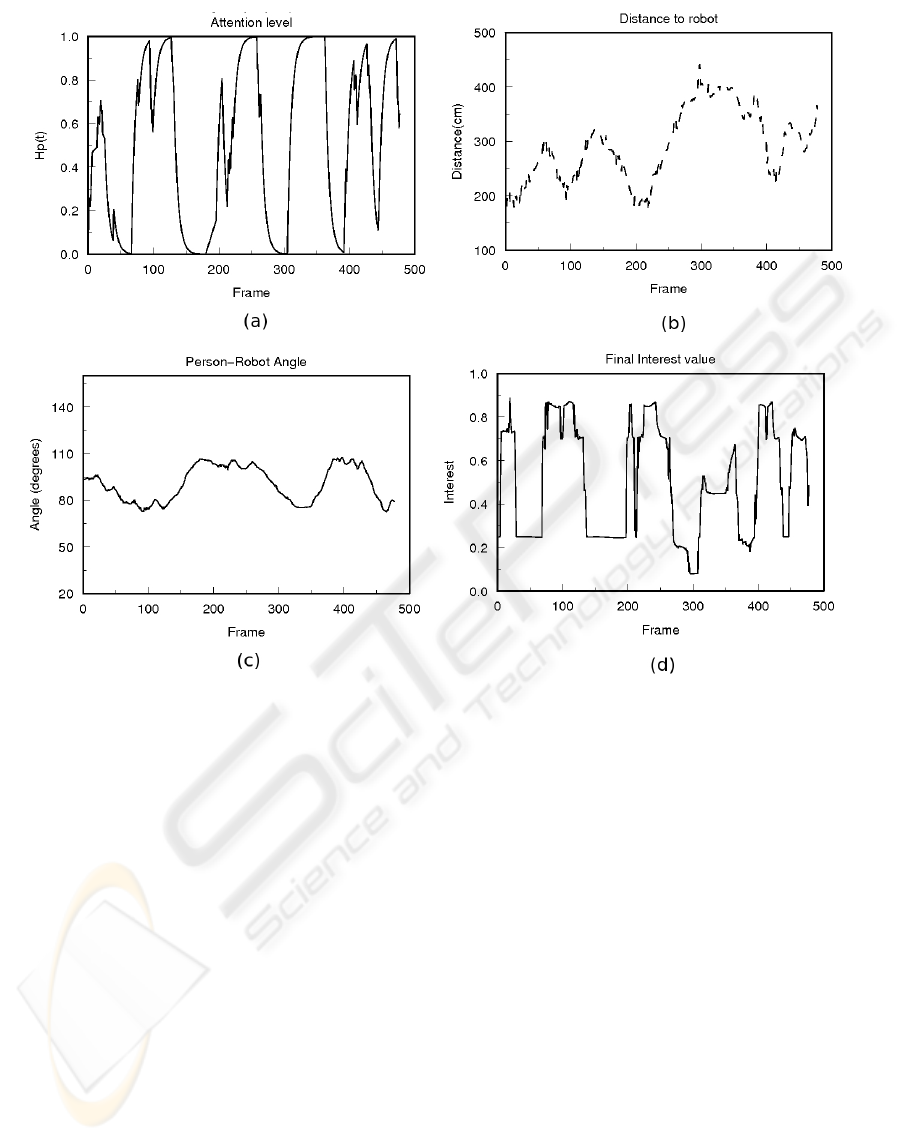
Figure 5: Graphs that show the variation of variables “Attention” (a), “Distance” (b), “Angle” (c) and “Interest” (d) during the
video referred in Section 4.
is achieved in frame c, because the person is look-
ing directly at the robot and it is very close to it. On
the other hand, in frame g the person is not paying
any attention to the robot, moving at a distance far-
away from it. Therefore the lowest interest value is
achieved in this frame.
It is also possible to observe in the graphs showed
in Fig. 5 the variation of variables “Attention”, “Dis-
tance” and “Angle” in Fig. 5.a, Fig. 5.b and Fig. 5.c
respectively during the whole video. The forth graph
Fig. 5.d is the interest computed also for the whole
video. It is also possible to observe in these graphs
the relationship among the interest computed and the
other variables.
In order to better understand the per-
formance of the system, several videos
are available in the following web site
http://decsai.ugr.es/∼ruipaul/interest.htm.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we have shown a system for detecting,
tracking and estimating the interest of the people in
the surroundings of a mobile robot, using stereo vi-
sion, head pose estimation by SVM and fuzzy logic.
As a first step, the method for people detection and
tracking has been briefly shown. While a person is
being tracked, the fuzzy system computes a level of
possibility about the interest that this person has in
interacting with the robot. This possibility value is
based on the position of the person in relation with
the robot, as well as on an estimation of the atten-
tion that the person pays to the robot. To examine the
attention that a person pays to the robot we analyze
in real time the head pose of the person. This analy-
sis is solved by a view based approach using Support
Vector Machines. Thanks to SVM head pose can be
detected achieving a great percentage of success that
A FUZZY SYSTEM FOR INTEREST VISUAL DETECTION BASED ON SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
187

is no dependent of the morphological features of the
heads. The experimentation shows that the system is
able to detect the persons present in its vicinity, track
their motions and give a value of possible interest on
the interaction of the persons with the robot.
The proposed method can be easily updated in
future works to analyze other types of input data as
sounds or laser range finder. Also, the degree of in-
terest will be useful to plan the actions of the robot
towards the persons in order to allow a more natural
human-robot interaction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the Span-
ish MEC project TIN2006-05565 and Andalusian Re-
gional Government project TIC1670.
REFERENCES
Aguirre, E. and Gonz
´
alez, A. (2000). Fuzzy behaviors for
mobile robot navigation: Design, coordination and fu-
sion. International Journal of Approximate Reason-
ing, 25:255–289.
Bennewitz, M., Faber, F., Joho, D., Schreiber, M., and
Behnke, S. (2005). Integrating vision and speech
for conversations with multiple persons. In IROS’05:
Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent
Robots and Systems, pages 2523 – 2528.
Bien, Z. and Song, W. (2003). Blend of soft computing
techniques for effective human-machine interaction
in service robotic systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,
134(1):5–25.
Birchfield, S. (1998). Elliptical Head Tracking Using Inten-
sity Gradients and Color Histograms. In IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 232–237.
Chang, C. and Lin, C. (2006). Libsvm.
a library for support vector machines.
http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/libsvm/.
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., and Meer, P. (2000). Real-Time
Tracking of Non-Rigid Objects using Mean Shift. In
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, volume 2, pages 142–149.
Cristianini, N. and Shawe-Taylor, J. (2000). An Introduction
To Support Vector Machines (and other Kernel Based
Methods). Cambridge University Press.
Darrell, T., Demirdjian, D., Checka, N., and Felzenszwalb,
P. (2001). Plan-view trajectory estimation with dense
stereo background models. In Eighth IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2001),
volume 2, pages 628 – 635.
Fritsch, J., Kleinehagenbrock, M., Lang, S., Pl
¨
otz, T., Fink,
G. A., and Sagerer, G. (2003). Multi-modal anchor-
ing for human-robot interaction. Robotics and Au-
tonomous Systems, 43(2-3):133–147.
Ghidary, S. S., Nakata, Y., Saito, H., Hattori, M., and
Takamori, T. (2002). Multi-modal interaction of hu-
man and home robot in the context of room map gen-
eration. Autonomous Robots, 13(2):169–184.
Haritaoglu, I., Beymer, D., and Flickner, M. (2002). Ghost
3d: detecting body posture and parts using stereo. In
Workshop on Motion and Video Computing, pages 175
– 180.
Harville, M. (2004). Stereo person tracking with adaptive
plan-view templates of height and occupancy statis-
tics. Image and Vision Computing, 2:127–142.
Hayashi, K., Hashimoto, M., Sumi, K., and Sasakawa, K.
(2004). Multiple-person tracker with a fixed slanting
stereo camera. In 6th IEEE International Conference
on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pages
681–686.
Henry, G. and Dunteman (1989). Principal Components
Analysis. SAGE Publications.
Intel (2005). OpenCV: Open source Computer Vision li-
brary.
Kuhn, H. W. (1955). The hungarian method for the assign-
ment problem. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly,
2:83–97.
Kulic, D. and Croft, E. (2003). Estimating intent for hu-
man robot interaction. In International Conference on
Advanced Robotics, pages 810–815.
Lienhart, R. and Maydt, J. (2002). An Extended Set of
Haar-Like Features for rapid Object detection. In
IEEE Conf. on Image Processing, pages 900–903.
Mu
˜
noz-Salinas, R., Aguirre, E., and Garc
´
ıa-Silvente, M.
(2006). People detection and tracking using stereo vi-
sion and color. To appear in Image and Vision Com-
puting. Available online at www.sciencedirect.com.
PtGrey (2005). Bumblebee. Binocu-
lar stereo vision camera system.
http://www.ptgrey.com/products/bumblebee/index.html.
Saffiotti, A. (1997). The uses of fuzzy logic in autonomous
robot navigation. Soft Computing, 1:180–197.
Snidaro, L., Micheloni, C., and Chiavedale, C. (2005).
Video security for ambient intelligence. IEEE Trans-
actions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part A,
35:133 – 144.
Song, W., Kim, D., Kim, J., and Bien, Z. (2001). Visual
servoing for a user’s mouth with effective intention
reading in a wheelchair-based robotic arm. In ICRA,
pages 3662–3667.
Viola, P. and Jones, M. (2001). Rapid object detection using
a boosted cascade of simple features. In IEEE Conf.
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
511–518.
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
188
