
Architectonics of Thinking: The Conception of Human
Brain Organization as Multiprocessing System
Valery Shyrochin and Vadym Mukhin
National Technical University of Ukraine “Kiev Polytechnic Institute”
03056 Kiev, Ukraine
Abstract. This paper is devoted to the development of hypothesis about human
brain “cartation”, i.e. spatially distributed structure of human brain systems for
cogitative activities maintenance, containing neural parts with various degree of
rigidity and different functional tasks (cartoids), which was suggested by
Institute of Brain of the Russian Academy of Sciences (St.-Petersburg) under
supervision of acad. N. Bekhtereva.
In the paper is suggested the conception of the structurally-logic organization of
thinking processes, which defines the main attitudes between the emotional-
strong-willed (unconscious) and the intellectual-ethical (conscious) components
(cartoids-processors) of thinking for the situation analysis and for the choice of
actions ways by the person during decisions making and realization. The
conception is based on the architectonics of the artificial intellect of the future
generations for creation of the emotionally and morally-oriented knowledge
bases and supercomputers, capable to realize all the processes of the productive
creative thinking.
1 Introduction
Nowadays, the important scientific problem is the development of computer systems
with the artificial intellect, which facilities are more and more closer to the human
abilities to think productive. [1] The artificial intellect systems should in the shortest
terms make, instead of the person, the decision, which are, for example, by validity
and speed parameters, better than decisions, that are making by the person. Due to
wide-spread using of the computer systems and the global and corporate networks,
consisting from the personal and professional computers, the interest to the playing,
planning and other systems for decisions making, has essentially increased. [2],[3]
The meta-mechanisms, that simulating the functions of human intellect, are the base
components of the intellectual software, allowing automate the cogitative activities
not only for the ordinary computer users, but also for the programmers.
Thus, the actual problem is researching of the architectonics (meta-models and
neural processors) of human thinking, which will allow to design the structurally-
logic organization of artificial neural intellect, which is capable to realize both
conscious formal-logic, and unconscious emotional-intuitive mechanisms of the
creative thinking and the informal decisions making by person. [1]
Shyrochin V. and Mukhin V. (2007).
Architectonics of Thinking: The Conception of Human Brain Organization as Multiprocessing System.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks and Intelligent Information Processing, pages 21-29
DOI: 10.5220/0001640600210029
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 The Architectonics of Common Bus-based Images Processing
with Neural Networks
The important factor of human’s reactions is the verbal expression of the person’s
attitude to a perceived image on the basis of perceived before actions ways and of the
management skills (articulation) of the speech mechanism for the ideas expression.
The attitude to Wi-concept can be reflected in speech, i.e. can be determined the word
or the semantically connected chain of words that are formed by a neural-stack of a
actions ways window (articulation windows). The corresponded neural networks with
their final neurons are directly connected to reflex arches of the speech mechanism
muscles management: a mouth, tongue, throats and breath which realize "knitting" of
sound speech images structures, which probably reflecting the real World and
allowing coordinate the actions of the people’s groups and collectives. The general
structure of effectors networks connections of neural-stacks for various windows of
the neural-screen of human brain bark is shown on Fig. 1.
Using the effectors networks of brain organization as example there is an
opportunity precisely to show differences of databases, for example, for recognition
visual both sound images, and bases of knowledge which collect in the actions ways
window for realization of corresponding skills and actions algorithms, including the
ways and algorithms of a “convincing articulation” which can be perceived as logic
thinking.
In databases for recognition of visual or sound images are accumulated and
"passively" stored the big enough volumes of "etalon" images, including phonetic
sound and sign visual images of words and word-combinations which provide
recognition with the general perception only as: "has understood" or "has learned", so
it is possible to generate corresponding, associated with this concept, actions.
To understand are means to save up some set of "reference" sound or visual images
which will allow for neural-stacks to distinguish images similar to them and to
generate corresponding signals Wi-"known", which can have both verbal and
emotional form: “has understood!”
To know are means to save up some set of ways for "correct" articulation which
will allow to connect "logically" and "convincingly" to express in the sounded speech
images some concepts and their correct or desirable attitudes to concrete discussed
problem area.
The skills of "convincing" speech are got during all human life and, first of all,
during dialogue, education and training on more than fifteen-year of base and high
educational schools and universities speech trainings and competitions. Knowledge
allow to generate the "adequate", clear for surrounding humans reaction as
corresponding actions, which special case is the statement. [4], [5]
In the knowledge bases of Wi-concepts contact to the "etalon" images of the
actions ways (in speech or impellent forms) to maintain the actions efficiency
according to the existing rules and/or existing laws in mutual relations of the person
with other people and an environment.
The basic knowledge of the person as syntax-logic images conjunctions of
"correct" articulation are collected in neural-stacks of actions ways (skills) window in
frontal areas of an impellent zone of the right and left hemisphere of human brain
bark, which are directly connected by descending nervous ways to the speech
22

mechanism (a mouth, a throat, tongue and lips), and also with average, oblong and a
spinal cord, and through them with bodies and muscles of all body of the person.
Many "sharp" direct reactions of articulation or action ways on to certain images and
concepts are not realized by the person or because of absence of subconscious
emotional (power) support, or are blocked by conscious and overconscious strong-
willed efforts of moral-ethical behaviour skills.
The skill to think “in itself” in the form of internal speech actually is the habitual
blocking of the articulations separate phases, for example, breath and lips moving, at
undistinguished for itself realization of "convincing" articulation skills, although
sometimes in deep meditations a certain mutter or even silent speech nevertheless
sounds.
The neural-stacks of action ways window, which is subdivided into a window of an
articulation, a window of coordination and a window of movement management, as it
is shown on a Fig. 1, together with neural-stacks tactile window in the central area of
a brain include up to 50-60 % of all neurons of brain bark that is the confirmation of
importance of the movement (ways of actions) for all representatives of the biological
World. Distinctive feature and a trouble of the human is filling of the neural-stacks of
action (movement) ways window with "etalon" syntax-logic articulation images
conjunction instead of coordination or movement skills, that sometimes even is
dangerous during enforced studying of the foreign languages on the average or old
human age. There are known the cases of the full loss of the coordination in space
skills after the hard work in the foreign language environment of the man with bad
language background.
Sensitive-moving nerves of perepherial (somatics and vegetatives) nerves system
Visual window
Neural – stack of sound window
NEURAL-SCREEN
NEURAL -SCREEN
Sensitive window
Window of action ways
Soun
d
w
i
n
d
ow
Plainly-drawing
images
Sign
images
Spatial
images
Musical
images
Verbal
images
Movement
management
window
Coordination
window
Articulation
window
Intonation
images
Neural – stack of visual window
Wi - concepts, situations
Wi - signs, formulas
Wi - evaluations, miracle
Wi - concepts, words
Wi - intonation (threat)
Wi - emotion, harmony
Таctile
images
Taste
images
Olfactory
images
Neural-stack of action ways windows Neural-stack of sensitive window
Wi - sensations
Wi - understandings,
spectrums of taste
and smell
Wi - pains, sufferings
Zi - articulation, semantics-
logical conjucntions of
words (minds)
Zi - emotions, fears
Zi – coordination
Z
i – movement mana
g
ement
Reflex arches
Reflex arches
Neural-PROM
and neural-ROM
of average and
oblong cord
Dreams
images
Hand – written
speech
Ganglias
and spinal
cord
Sensing
images
CBIT
CBVI
CBIT
CBIT
CBIT
CBIT
CBIT
Pu
bli
c an
d
inner speech,
minds
Descending
pyramidal
nervous
ways
Ascending pyramidal
nervous ways
CBIT – Common Bus of Images Traces; CBVI – Common Bus of Visual Images
Fig. 1. The general structure of effectors networks connections of neural-stacks for various
windows of the neural-screen of human brain bark.
23

In general, the output signals Zi of the allocated layers of actions ways window of
neural networks are the control signals which on descending pyramidal nervous ways
are transferred in peripheral nervous system for realization of the actions connected to
fixed concept and corresponding visual or other image. But the intellect of the person
is in fact that before to start to operate he should think, accept and to explain for
surrounding human his decision.
Frequently the decision is accepted by the person only intuitively, i.e. by transfer
Wi from neural networks outputs from the one window on the receptors layers inputs
of other windows, and the actions ways windows with output control signals Zi of
neural-stack, which “go through itself”, i.e. on descending and ascending nervous
ways with blocking in a spinal cord, allow at a level of body sensations images "to
evaluate" an opportunity of accepted decision realization. And only after that the
correctly or incorrectly choose words conjunctions during an external or internal
articulation (meditations) allow to prove formally the decision and to sound it in
speech for coordination of collective actions. [6]
3 The General Scheme of Decision Making in Intellectual Neural
Networks
The general circuit of conclusions for any intellectual neural network includes some
stages of transformations: image recognition; concept; the estimation of situation; the
choice of action way; decision making; action way realization. [7]
The conclusions scheme in emotionally-oriented intellectual neural networks
includes also an additional blocking-inducing chain of emotional reactions and
adjusting influences on realization of habitual or unusual actions ways, which is based
on known for neural networks concept and includes: the concept; emotional reaction
(fears, curiosity, cares); the choice of the natural or got actions skills; the forcible-
adjusting influence on decision-making (passion, famine, cold) – control and
realization of actions skills.
In the intellectual emotional-oriented human neural networks the conclusions
scheme includes also the parallel chain of verbal support for the "deep" conscious
analysis of a situation and a logic substantiation of the decision making, that is
sharply necessary at coordination of collective actions, but not always used in the real
life as it is shown on Fig. 2.
Each stages in the conclusions scheme is a signaling of Wi-concepts from outputs
of last layer of neurons of neural networks of the one windows and neural-stacks on
inputs neural networks of other windows with the subsequent processing of the
concept and concomitant factors (other types of images) in the effectors layers and
the formation of the new Wi-concept-sensations and Zi-control-ways of the actions.
Quite often the humans use Wi-emotions without the analysis of concepts or Wi-
word without formation of corresponding concepts, that practically excludes an
opportunity of decision-making and results in the impulsive inadequate actions or in
the infinite and pointless conversations.
Basically the conclusions scheme in an ordinary life frequently does without a
verbal support, and the advancing of subconscious emotions even is appreciable in
comparison with overconscious intuitive estimation of current situation and the more
24

so with its conscious analysis on the basis of the all logic known to the person or even
on the ethics which replace logic in many cases and, in particular, because of its
absence.
Verbal support essentially slows down the process of conscious decision-making,
because the speech images of words and phrases are compared to many images types
of corresponding concepts and their relations in neural-stacks of various windows of
the neural-screen and for the first hand with speech images in a neural-stack of a
sound window and speech images of a neural-stack of actions ways window for
articulation, where the bases of the person knowledge as corresponding types of
“ready conclusions” fragments of the speech images about "correct" or "wrong"
decisions in certain situations are collected, which are perceived during all life and
labour activity of the human as a result of dialogue, education, training and self-
training. It is should be noticed, that first two chains of the conclusions scheme,
realized by subconsciousness and overconsciousness are peculiar to all representatives
of the biological world.
The special problem is the conceptual (substantial) analysis of neural networks
functions for overconscious estimations of situation, based on the "glorified" intuition.
In abilities of an intuitive prediction the certain role is played the factors of spatial
transformations of visual images in some allocated layers-processors of human brain
and using of the other types of “etalon” visual images and associated with them in
neural-stacks of all windows of the neural-screen.
The recognition of the most important concepts and problems in overconsciously
changing pictures and the whole scripts of situations by the random or directed
choosing of the comprehensible actions ways variants provide the especially
successful decisions generation, which intuitively result to completely surprising
Emotion
Evaluation of
situation(intuition)
Concept
Actions ways
realization
Moral – ethics
principles and
do
g
mas
The natural
and got actions
skills
Decision
Making
Formal
substantiation of
action ways
Inducing factors:
passion, famine,
cold
Choice of action
ways
(intuitive logics)
Analysis of
situation (logics
or ethics)
Constraining
and inducing
fears and cares
Recognition of
speech sound
and others Sp/
Sg images
Recognition of
spatial visual
and others VsI
images
Recognition of
intonation
sound and
other EsI
CONSCIOUSNESS
OVERCONSCIOUSNESS
SUBCONSCIOUSNESS
Word
Intuitive and conscious evaluations:
Must
Bad
Good
Good
Very much
necessar
y
Terribly
Control
Will
Impossible
Time to act
Fig. 2. The general scheme of conclusions in the emotional-oriented neural networks o
f
human brain.
25

unexpressed, but to desirable results. Such "wonderful" prediction and corresponding
rare, but successful concurrences of circumstances, really take place and are
considered by many humans as the Miracle.
The human brain as neural networks super-parallel and highly reliable intellectual
and emotionally – oriented supercomputer is the perfect creation of the Nature, but its
logic organization and architecture can be realized not only on neurons, but also on
some other elements or technological base in near and even the foreseeable Future.
4 The Role of Fuzzy Intuitive Estimations and Fears in Decision
Making Process
The spectrum of the overconsciousness intuitive estimations-understandings of a
situation by the person is insignificant. The negative intuitive estimations-
understandings of current situation like “something is bad”, “poorly”, “very bad” and
“is awful”, through the mechanism of the Will and the subsystem of the Passion-
Prana (Prana means the life power), as shown on United Seven-Components Model of
Human Intellect (USCMHI), induce the alarm and Emotional Rise of Reserve Forces
(ERRF), which provide through Neural Humoral System (NHS) inflow of forces for
overcoming difficulties, problems or sufferings, and in case of powerlessness due to
expected ("it is "very bad" and "is awful") cause so-called “black fear”. The positive
intuitive estimations-understandings of a situation, for example: “let it be”, “not
poorly”, “there are no problems”, “it is good-normally”, “very well”, “perfectly”, also
cause sometimes even the greater ERRF on the same Ring of Decision-Making
(RDM): Will – Emotions (pleasure) – NHS.
The dynamical changes at the repeated independent decision of practical problems
in the RDM are storing the skills of the intellect for "good" decisions acceptance on
the concrete situations and thus its adaptation in the real world is provided. The
conscious speech substantiation or the explanatory of the accepted decisions
frequently appears difficultly formalized for the person or not explained at all, that
results to misunderstanding or to mistrust on the people. The intellectual and neural-
physical opportunities of the person adaptation to real environment conditions are
extremely high. Undoubtedly, that the main role during adaptation plays not only the
consciousness, but also overconsciousness and subconsciousness of the person and
corresponding mechanisms and skills of situational management (See Fig. 2).
The development of the human intellect is provided due to the mechanism of self-
training and accumulation of knowledge, skills of decision-making in contours of the
mental overconsciousness (less often conscious) situational management by iterative
overconsciousness (intuitive), subconscious (sensual) and conscious (formal) analysis
of mental images of a subject and the actions ways, and the expected results with the
subsequent formation of the overconsciousness intuitive (less often conscious logic)
estimations-understandings of achievement degree level of conscious or
overconscious goals.
26
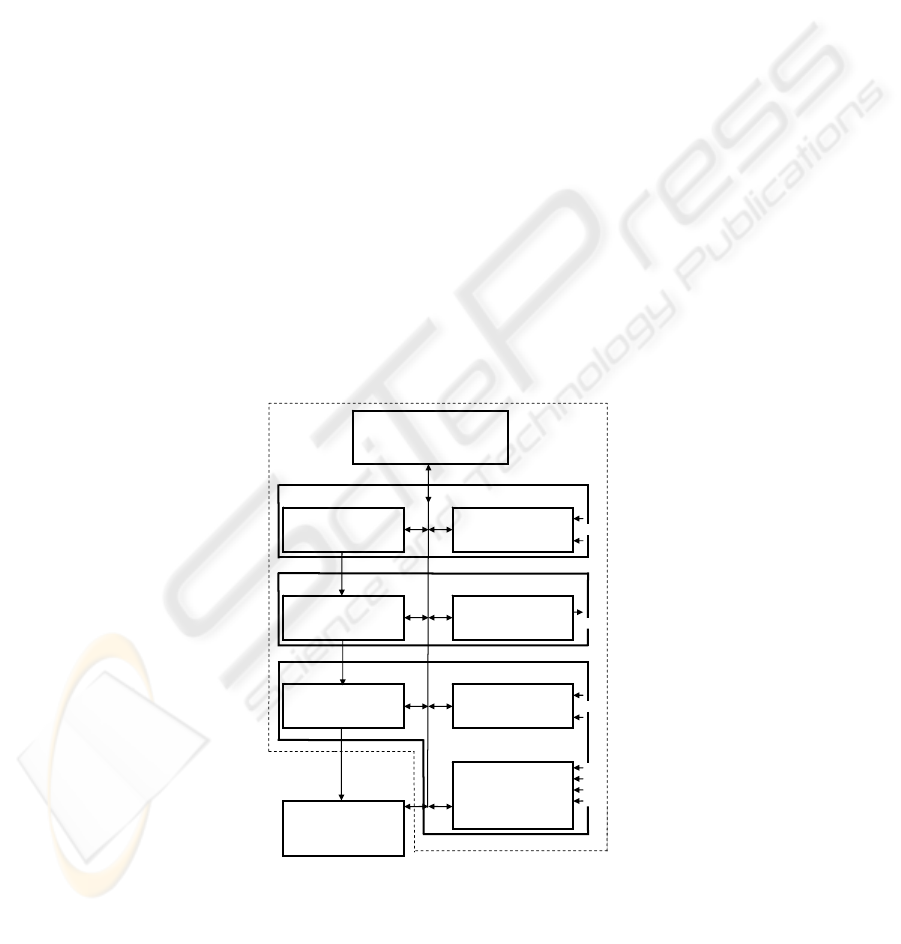
5 The Structure of Processor-ware of Supercomputer of Human
Brain
The uniform form for representation of the all traces of the objects for supervision
images as traces of the structures of adjustments-associations of the neural networks,
formed in neural-stacks of all windows of the neural-screen, plays the main role in the
organization of coordinated work of overconsciousness, consciousnesses and
subconsciousness and of their uniform interface as the Common Bus of Images
Traces (CBIT). The beginning and the end of CBIT are in an impellent window of the
human brain neural-screen, where as result of decision-making cycles the concrete
decision on a concrete situation (See earlier Fig. 1 and Fig. 2) is realized.
CBIT is combine of the stacks of the all neural-screen windows with impellent
window and its neural-stack, that is actively working in the decision-making Contour
and includes: descending pyramidal ways – a spinal cord and ganglies – ascending
pyramidal ways – the window and neural-stack of sensations and again an impellent
window and its neural-stacks, and in some cases also visual and sound windows and
their neural-stacks for the fast or direct (long) multi stages images recognition,
conclusion and decision-making. The base structure of processor hardware for
emotionally-oriented supercomputer of the future generations, capable to realize the
basic functions of overconsciousnesses, consciousnesses and subconsciousness of the
person on USCMHI, is shown on Fig. 3.
As it was shown before, the primary emotionally-oriented subsystem of
overconscious-subconscious situational management can provide the continuation of
human kind and the other representatives of the bio-World even in the most severe
conditions of surrounding nature. Thus two base subsystems for decision-making are
Multilevel and multilayered memory
of all neural-screen windows and of
the other structures of brain
(NEURAL-STACKS)
NEURAL-SCREEN
of human brain
Traces of the decision
Traces of prompting
The processor of spatial
processing and fast visions
classification
(Video V-processor)
The processor of the fast
decisions analysis and of
"wonderful" inspirations
(Fuzzy F-processor)
VISUAL WINDOW
Traces of situation
OVERCONSCIOUSNESS
Sight
IT
CB
The processor of "knitting" and
conclusion of speech sound
images and speech design
(Speech S-processor)
The processor of the semantic
analysis and formal
substantiation of decisions
(Linguistic L-processor)
ARTICULATION WINDOW
Prompting
CONSCIOUSNESS
Speech
The processor of the fast speech
and other sound images analysis
(Audio A-processor)
The processor of emotional
adjustment and fast realization
of actions ways
(Emotional E-processor)
SOUND WINDOW
Solution
SUBCONSCIOUSNESS
Sound
IT
CB
The processor of fast processing
of olfactory, flavouring and
sensitive images and other
sensations from the human body
and his inner organs
(Tactile T-processor)
System of coordination and
management of elementary
actions and life-support
(HardWare of intellect)
(BIO - ROBOT
)
SENSITIVE WINDOW
Performance
Skills
Touch
Taste
Smell
Sensations
Fig. 3. The base structure of processor-ware of the emotionally and morally-oriented
supercomputer of human brain.
27

involved: the overconsciousness, working with the induced visions of perceived
images-excitations and with the packed traces of visions as adjustments-associations
of the neural networks, and also the subconsciousness, operating with sound,
olfactory and sensational images, that induced and packed in parameters of neural-
stacks.
The important factor in conclusions of human and in the all decision-making
Contour is the visions of action subject, scripts of a concrete situation and expected
result. Such visions should be reflected on the neural-screen during all the time of the
operative processing of the speech and other images, which are formed and
transferred on CBIT. Therefore, obvious is the special role of visual support for the
working of the all subsystems of human intellect – overconsciousness,
consciousnesses and even subconsciousness, so the special Common Bus for visual
subject and sign images (CBSI), which directly connects the processor of spatial
images processing (Video V-processor) by overconsciousness with the basic
processors (neural-stacks) of the brain base subsystems is obviously necessary.
The consciousness is formed only after when the person seizes speech, i.e. the
specific sound signals, which fragments (words) and their various elements
(statement) have the certain conditional messages, accepted in some environment – in
the society and reflected in the dictionaries. Such elements of speech (language of
dialogue) by the messages spectrum should differ essentially from estimations-
understandings of overconsciousness.
The consciousness of the person-expert can scan the all windows of the
neural-screen and to generate the mental speech image, that is marking basing on the
words and statements the specific features of certain image projections of observable
object, that is provided the allocation of the information and its probable further
registration. That is why in some believes, that “the first was a word”. It is true, but
only for the human consciousness formation.
6 Conclusions
In the paper is suggested the base biological model of thinking: “any image – action”,
and also the internal articulation (idea) or the external articulation (speech) are
considered as the actions ways, that naturally depend on the collective actions
synchronization. Although there is the "latent" system organization of cartoids
connections in receptor and effector layers of human brain, we suggest the system-
technical model of the functional-oriented neural processors and of the neural
coprocessors interactions organization for processing of the various type of the
images and of the images traces from the knowledge bases stacks. These elements are
the base for the multilevel associations of the images and their processing methods as
system-psychological software, which realize all the processes of cognitive,
confidential, creative cogitative and creative activities of the person (for more detail
see [1]).
The advantage of the suggested structures is their flexibility and feature to create
the diversified contours for the mental images processing, that provides the various
decisions making depending on certain situation. The thinking and feeling robots will
be highly survivable and adaptive. The specific of the suggested structures is the
28

complexity of the artificial intellect subsystems integration in the real practice,
because it requires the significant material and human resources. However, the
effective realization of the intellectual systems is impossible without the concrete
concepts of the architectonics of thinking.
References
1. Shyrochin, V.P.: Architectonics of Thinking and Neural Intellect. Kiev, Junior (2004) 558
p. (in Russian)
2. Luger, G.F.: Artificial Intelligence. Structures and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving.
Addison Wesley (2002) 864 p.
3. Anderson, J.R.: The Architecture of Cognition. Cambridge University Press (2003) 406 p.
4. Barr, A., Feigenbaum, E.: Handbook of Artificial Intellegence. Los Altos, CA, William
Kaufman (2001) 564 p.
5. Bekhtereva, N.P.: Magic of Brain and Labyrinthes of Life. Saint-Petersburg, “Notabene”
(1999) 302 p. (in Russian)
6. Jeannerod, M.: The Cognitive Neuroscience of Action. Oxford, Backwell (1997)
7. Winograd, T., Flores, F.: Understanding Computers and Cognition. Norwood, N.J., Ablex,
(1996)
29
